Ethnic Groups In The Philippines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The
/ref> Japanese Filipinos, and many more. Aside from migrant groups which speak their own languages, most Filipinos speak languages classified under the Austronesian language family, including the various Negrito peoples of the archipelago, which are genetically and phenotypically distinct from the other ethnic groups of the Philippines. While these groups have maintained a culture and identity distinct from neighboring ethnic groups, they have long adapted their neighbors' Austronesian languages. Traditionally subcategorized geographically as the Ati people of Visayas and Mindanao, and the Aeta of Luzon, the Negrito population was estimated at 31,000 as of 2004.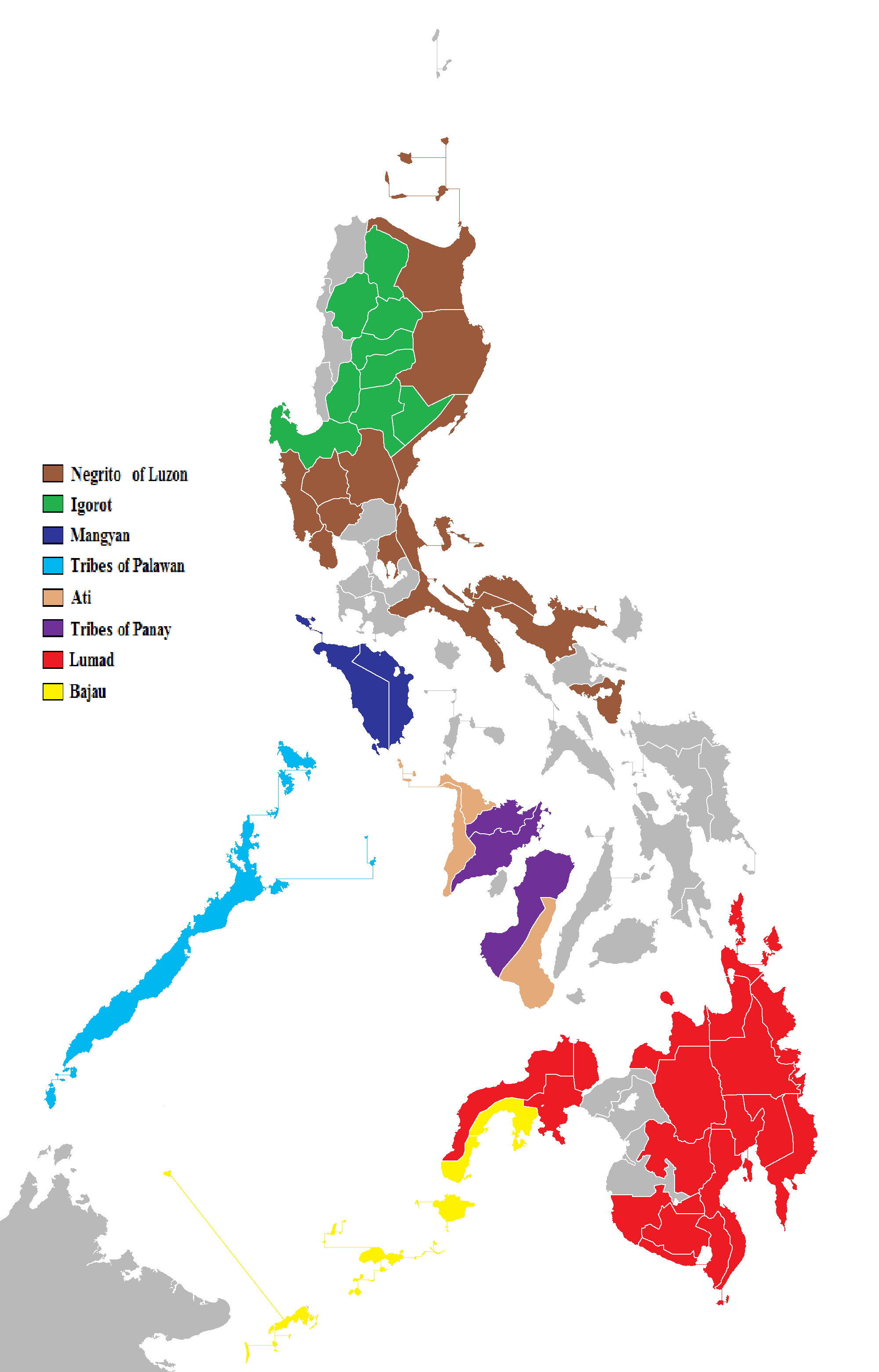
 The most widely accepted theory, however, is the "Out-of-Taiwan" model which follows the Austronesian expansion during the
The most widely accepted theory, however, is the "Out-of-Taiwan" model which follows the Austronesian expansion during the  Prehistoric Tabon Man, found in Palawan in 1962 was, until 2007, the oldest human remains discovered by anthropologists in the Philippines. Archaeological evidence indicates similarities with two early human fossils found in Indonesia and China, called the Java Man and Peking Man. In 2007, a single metatarsal from an earlier fossil was discovered in Callao Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan. That earlier fossil was named as
Prehistoric Tabon Man, found in Palawan in 1962 was, until 2007, the oldest human remains discovered by anthropologists in the Philippines. Archaeological evidence indicates similarities with two early human fossils found in Indonesia and China, called the Java Man and Peking Man. In 2007, a single metatarsal from an earlier fossil was discovered in Callao Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan. That earlier fossil was named as
 There are more than 100 highland, lowland, and coastland tribal groups in the Philippines. These include:
There are more than 100 highland, lowland, and coastland tribal groups in the Philippines. These include:
 Mangyan is the generic name for the eight indigenous groups found on the island of Mindoro, southwest of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, each with its own tribal name, language, and customs. They occupy nearly the whole of the interior of the island of Mindoro. The total population may be around 280,000, but official statistics are difficult to determine under the conditions of remote areas, reclusive tribal groups and some having little if any outside world contact.
Mangyan is the generic name for the eight indigenous groups found on the island of Mindoro, southwest of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, each with its own tribal name, language, and customs. They occupy nearly the whole of the interior of the island of Mindoro. The total population may be around 280,000, but official statistics are difficult to determine under the conditions of remote areas, reclusive tribal groups and some having little if any outside world contact.
 The Negrito are several Australo-Melanesian groups who inhabit isolated parts of
The Negrito are several Australo-Melanesian groups who inhabit isolated parts of 
 Lowland Christianized groups of the Visayas archipelago. The Visayans are a metaethnicity race native to the whole Visayas, to the southernmost islands of
Lowland Christianized groups of the Visayas archipelago. The Visayans are a metaethnicity race native to the whole Visayas, to the southernmost islands of
 The
The
– , - ! scope="row" , Mestizo de Español (Spanish Mestizo) , , These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the Spanish and
, These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the Spanish and
– , - ! scope="row" , Mestizo de Sangley (Chinese Mestizo) , , These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the '' Sangley'' (Chinese) and sometimes Japanese migrants who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era. Most were of Hokkien Chinese ancestry with a few being of
, These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the '' Sangley'' (Chinese) and sometimes Japanese migrants who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era. Most were of Hokkien Chinese ancestry with a few being of  , These are mixed descendants of the above ''Mestizo de Español'' with the ''Mestizo de Sangley'' settlers, or vice versa, who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era. Most would now have native ancestry, along with usually Hokkien Chinese ancestry or sometimes Cantonese/Taishanese or Japanese ancestry and with Spanish or Hispanic ancestry.
,
,
, These are mixed descendants of the above ''Mestizo de Español'' with the ''Mestizo de Sangley'' settlers, or vice versa, who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era. Most would now have native ancestry, along with usually Hokkien Chinese ancestry or sometimes Cantonese/Taishanese or Japanese ancestry and with Spanish or Hispanic ancestry.
,
,
– , - ! scope="row" , Indian Filipino / Mestizo de Bombay (Indian Mestizo) , , Philippines has been part of Indianized kingdoms from the 7th century Srivijaya and earlier era. Indian culture, language, scripture, food, belief, arts, martial arts, epics have had profound impact on pre-Spanish Philippines which is still visible. They have contributed to the unique cultural blend in the Philippines. One source estimated the size of the Indian community in the Philippines in 2008 at 150,000 persons. Most Indians in the Philippines belong to either Sindhi or
, Philippines has been part of Indianized kingdoms from the 7th century Srivijaya and earlier era. Indian culture, language, scripture, food, belief, arts, martial arts, epics have had profound impact on pre-Spanish Philippines which is still visible. They have contributed to the unique cultural blend in the Philippines. One source estimated the size of the Indian community in the Philippines in 2008 at 150,000 persons. Most Indians in the Philippines belong to either Sindhi or
– , - ! scope="row" , Sangil/Sangirese , , The Sangil people (also called Sangir, Sangu, Marore, Sangirezen, or Talaoerezen) are originally from the Sangihe and Talaud Islands (now part of
, The Sangil people (also called Sangir, Sangu, Marore, Sangirezen, or Talaoerezen) are originally from the Sangihe and Talaud Islands (now part of
– , - ! scope="row" , Jewish Filipino , , , Filipino Jews numbered at the most 500 people. Other estimates range between 100 and 18,500 people (0.000001% and 0.005% of the country's total population). ,
, , Filipino Jews numbered at the most 500 people. Other estimates range between 100 and 18,500 people (0.000001% and 0.005% of the country's total population). ,
– , - ! scope="row" , American Filipino / Filipino Americans , , American (''Amerikano/Kano'') settlement in the Philippines began during the
, American (''Amerikano/Kano'') settlement in the Philippines began during the
– , - ! scope="row" , Filipinos with Arab Ancestry , ,
,
–
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
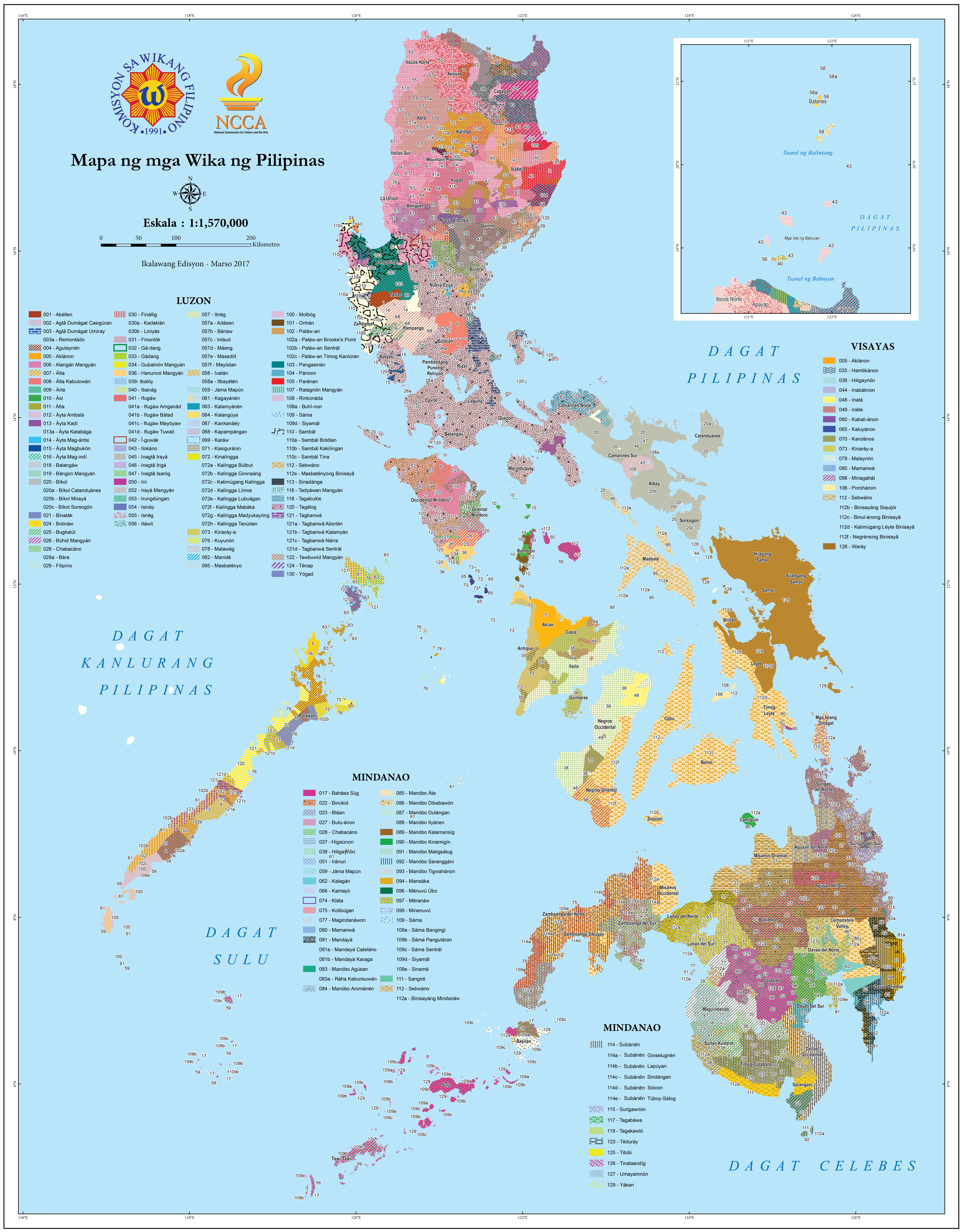
is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous People groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither indigenous nor moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
The Muslim-majority ethnic groups ethnolinguistic groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan are collectively referred to as the Moro people, a broad category which includes some indigenous people groups and some non-indigenous people groups. With a population of over 5 million people, they comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people. The Spanish called them Moros after the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct o ...
, despite no resemblance or cultural ties to them apart from their religion.
About 142 of the Philippines' Indigenous People groups are not classified as Moro peoples. Some of these people groups are commonly grouped together due to their strong association with a shared geographic area, although these broad categorizations are not always welcomed by the ethnic groups themselves.National Statistics Office. “Statistics on Filipino Children.” Journal of Philippine Statistics, vol. 59, no. 4, 2008, p. 119. For example, the indigenous peoples of the Cordillera Mountain Range in northern Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, ...
are often referred to using the exonym "Igorot people," or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples
The indigenous peoples of the Cordillera Mountain Range of northern Luzon, Philippines are often referred to using the exonym Igorot people, or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples. There are nine main ethnolinguistic groups whose domains ar ...
. Meanwhile, the non-Moro peoples of Mindanao are collectively referred to as the Lumad, a collective autonym conceived in 1986 as a way to distinguish them from their neighboring indigenous Moro and Visayan neighbors.
About 86 to 87 percent of the Philippine population belong to the 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither indigenous nor Moro. These groups are sometimes collectively referred to as "Lowland Christianized groups," to distinguish them from the other ethnolinguistic groups. The most populous of these groups, with populations exceeding a million individuals, are the Ilocano, the Pangasinense, the Kapampangan, the Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
, the Bicolano
Bikol or Bicol usually refers to:
*Bicol Region, the administrative region in the Philippines
Bikol or Bicol may also refer to:
Languages and people
*Bikol languages, the languages spoken in the Bicol region in the Philippines
**Albay Bikol lang ...
, and the Visayans (including the Cebuano, the Boholano, the Hiligaynon/Ilonggo, and the Waray Waray may refer to:
* Waray people of the Philippines
* Waray language, the fifth most spoken native language of the Philippines, spoken by the Waray people
* Waray literature
* Warray language
Warray (Waray) was an Australian language spoken ...
). Many of these groups converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, particularly both the native and migrant lowland-coastal groups, and adopted foreign elements of culture throughout the country's history.
Due to the past history of the Philippines since the Spanish colonial era, there are also some historical migrant heritage groups such as the Chinese Filipinos and Spanish Filipinos, both of whom intermixed with the above lowland Austronesian-speaking ethnic groups, which produced Filipino Mestizos
In the Philippines, Filipino Mestizo ( es, mestizo (masculine) / mestiza (feminine); Filipino/ tl, Mestiso (masculine) / Mestisa (feminine)) or colloquially ''Tisoy'', is a name used to refer to people of mixed native Filipino and any foreign ...
. These groups also comprise and contribute a considerable proportion of the country's population, especially its bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. Th ...
, and economy and were integral to the establishment of the country, from the rise of Filipino nationalism by the '' Ilustrado'' intelligentsia to the Philippine Revolution. Other peoples of migrant and/or mixed descent include those such as, American Filipinos, Indian Filipinos,With a sample population of 105 Filipinos, the company of ''Applied Biosystems'', analysed the Y-DNA of average Filipinos and it is discovered that about 0.95% of the samples have the Y-DNA Haplotype "H1a", which is most common in South Asia and had spread to the Philippines via precolonial Indian missionaries who spread Hinduism./ref> Japanese Filipinos, and many more. Aside from migrant groups which speak their own languages, most Filipinos speak languages classified under the Austronesian language family, including the various Negrito peoples of the archipelago, which are genetically and phenotypically distinct from the other ethnic groups of the Philippines. While these groups have maintained a culture and identity distinct from neighboring ethnic groups, they have long adapted their neighbors' Austronesian languages. Traditionally subcategorized geographically as the Ati people of Visayas and Mindanao, and the Aeta of Luzon, the Negrito population was estimated at 31,000 as of 2004.


Origins
There are several opposing theories regarding the origins of ancient Filipinos, starting with the " Waves of Migration" hypothesis of H. Otley Beyer in 1948, which claimed that Filipinos were "Indonesians" and "Malays" who migrated to the islands. This is completely rejected by modern anthropologists and is not supported by any evidence, but the hypothesis is still widely taught in Filipino elementary and public schools resulting in the widespread misconception by Filipinos that they are "Malays
Malays may refer to:
* Malay race, a racial category encompassing peoples of Southeast Asia and sometimes the Pacific Islands
** Overseas Malays, people of Malay race ancestry living outside Malay archipelago home areas
** Cape Malays, a communit ...
".
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
in a series of maritime migrations originating from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
that spread to the islands of the Indo-Pacific; ultimately reaching as far as New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
, Easter Island, and Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
. Austronesians themselves originated from the Neolithic rice-cultivating pre-Austronesian civilizations of the Yangtze River delta in coastal southeastern China pre-dating the conquest of those regions by the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
. This includes civilizations like the Liangzhu culture, Hemudu culture, and the Majiabang culture. It connects speakers of the Austronesian languages in a common linguistic and genetic lineage, including the Taiwanese indigenous peoples, Islander Southeast Asians, Chams, Islander Melanesians, Micronesians, Polynesians, and the Malagasy people. Aside from language and genetics, they also share common cultural markers like multihull and outrigger boats, tattooing, rice cultivation, wetland agriculture, teeth blackening, jade carving, betel nut chewing, ancestor worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune o ...
, and the same domesticated plants and animals (including dogs, pigs, chickens, yams, bananas, sugarcane, and coconuts).
 Prehistoric Tabon Man, found in Palawan in 1962 was, until 2007, the oldest human remains discovered by anthropologists in the Philippines. Archaeological evidence indicates similarities with two early human fossils found in Indonesia and China, called the Java Man and Peking Man. In 2007, a single metatarsal from an earlier fossil was discovered in Callao Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan. That earlier fossil was named as
Prehistoric Tabon Man, found in Palawan in 1962 was, until 2007, the oldest human remains discovered by anthropologists in the Philippines. Archaeological evidence indicates similarities with two early human fossils found in Indonesia and China, called the Java Man and Peking Man. In 2007, a single metatarsal from an earlier fossil was discovered in Callao Cave, Peñablanca, Cagayan. That earlier fossil was named as Callao Man
''Homo luzonensis'', also locally called "Ubag" after a mythical caveman, is an extinct, possibly pygmy, species of archaic human from the Late Pleistocene of Luzon, the Philippines. Their remains, teeth and phalanges, are known only from Calla ...
.
The Negritos arrived about 30,000 years ago and occupied several scattered areas throughout the islands. Recent archaeological evidence described by Peter Bellwood claimed that the ancestors of Filipinos, Malaysians, and Indonesians first crossed the Taiwan Strait during the Prehistoric period. These early mariners are thought to be the Austronesian people. They used boats to cross the oceans, and settled into many regions of Southeast Asia, the Polynesian Islands, and Madagascar.
Two early East Asian waves ( Austroasiatic and possible Austric) were detected, one most strongly evidenced among the Manobo people who live in inland Mindanao, and the other in the Sama-Bajau and related people of the Sulu archipelago, Zamboanga Peninsula, and Palawan. The admixture found in the Sama people indicates a relationship with the Lua
Lua or LUA may refer to:
Science and technology
* Lua (programming language)
* Latvia University of Agriculture
* Last universal ancestor, in evolution
Ethnicity and language
* Lua people, of Laos
* Lawa people, of Thailand sometimes referred t ...
and Mlabri people of mainland Southeast Asia, and reflects a similar genetic signal found in western Indonesia. These happened sometime after 15,000 years ago and 12,000 years ago respectively, around the time the last glacial period was coming to an end.
The first Austronesians reached the Philippines at around 2200 BC, settling the Batanes Islands and northern Luzon. From there, they rapidly spread downwards to the rest of the islands of the Philippines and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, as well as voyaging further east to reach the Northern Mariana Islands by around 1500 BC. They assimilated the older Negrito groups which arrived during the Paleolithic, resulting in the modern Filipino ethnic groups
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island gr ...
which all display various ratios of genetic admixture between Austronesian and Negrito groups. By the 14th century, the Malayo-Polynesian ethnolinguistic groups had dominated and displaced the Negrito population in most areas. Traders from southern China, Japan, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
and Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, also contributed to the ethnic, and cultural development of the islands. Papuan ancestry was also detected among the ethnic Blaan and Sangir people of Mindanao, suggesting that there was westward expansion of peoples from Papua New Guinea into the Philippines. The integration of Southeast Asia into Indian Ocean trading networks around 2,000 years ago also shows some impact, with South Asian genetic signals present within some Sama-Bajau communities.
By the 16th century, Spanish colonization brought new groups of people to the Philippines mainly Spaniards and Mexicans. Many settled in the Philippines, and intermarried with the indigenous population. This gave rise to the Filipino mestizo or individuals of mixed Austronesian and Hispanic descent. There was migration of a military nature from Latin-America (Mexico and Peru) to the Philippines, composed of varying races (Amerindian, Mestizo and Criollo) as described by Stephanie J. Mawson in her book "Convicts or Conquistadores? Spanish Soldiers in the Seventeenth-Century Pacific". Also, in her dissertation paper called, ‘Between Loyalty and Disobedience: The Limits of Spanish Domination in the Seventeenth Century Pacific’, she recorded an accumulated number of 15,600 soldier-settlers sent to the Philippines from Latin-America during the 1600s. In contrast, there were only 600 Spaniards who immigrated from Europe, in which timeframe, the total population of the Philippines was only about 667,612. Another 35,000 Mexican immigrants arrived in the 1700s and they were part of a Philippine population of 1.2 Million, forming about 2.91% of the population. Old Spanish censuses state that as much as 33.5% or one third of the population of the main island of Luzon had full or partial Hispanic or Latino (Mestizo and Native-American) descent.
The current modern-day Chinese Filipinos are mostly the descendants of immigrants from Southern Fujian in China from the 20th century and late 19th century, possibly numbering around 2 million, although there are an estimated 27 percent of Filipinos who have partial Chinese ancestry, stemming from precolonial and colonial Chinese ( Sangley) migrants from the past centuries especially during the Spanish Colonial Era. Intermarriage between the groups is evident in the major cities and urban areas, and spans back to Spanish colonial times, where a colonial middle-class group known as the Mestizo de Sangley ( Chinese mestizos) descend from. Its descendants during the late 19th century produced a major part of the '' ilustrado'' intelligentsia of the late Spanish Colonial Philippines, that were very influential with the creation of Filipino nationalism and the sparking of the Philippine Revolution.
There are also Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Ja ...
, which include escaped Christians (Kirishitan) who fled the persecutions of Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu which the Spanish empire in the Philippines had offered asylum from to form part of the Japanese settlement in the Philippines
Japanese settlement in the Philippines or Japanese Filipino, refers to one of the largest branches of Japanese diaspora having historical contact with and having established themselves in what is now the Philippines. This also refers to Filipino ci ...
. In the 16th and 17th centuries, thousands of Japanese people traders also migrated to the Philippines and assimilated into the local population.
The Philippines was a former American colony and during the American colonial era, there were over 800,000 Americans who were born in the Philippines. , there were 220,000 to 600,000 American citizens living in the country. There are also 250,000 Amerasians scattered across the cities of Angeles City, Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
, and Olongapo.
Practicing forensic anthropology, while exhuming cranial bones in several Philippine cemeteries, researcher Matthew C. Go estimated that 7% of the mean amount, among the samples exhumed, have attribution to European descent. Research work published in the Journal of Forensic Anthropology, collating contemporary Anthropological data show that the percentage of Filipino bodies who were sampled from the University of the Philippines, that is phenotypically classified as Asian ( East, South and Southeast Asian) is 72.7%, Hispanic (Spanish-Amerindian Mestizo, Latin American, and/or Spanish-Malay Mestizo) is at 12.7%, Indigenous American ( Native American) at 7.3%, African at 4.5%, and European at 2.7%.
Genetics
The results of a massive DNA study conducted by the National Geographic's, "The Genographic Project", based on genetic testings of 80,000 Filipino people by the National Geographic in 2008–2009, found that the average Filipino's genes are around 53% Southeast Asia and Oceania, 36% East Asian, 5% Southern European, 3% South Asian and 2% Native American.Native ethnolinguistic groups
Small indigenous ethnic communities remain marginalized, and often poorer than the rest of society.Moro ethnolinguistic groups
The collective term Moro people or Bangsamoro people refers to the, at least 13, islamicized ethnolinguistic groups ofMindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
, Sulu and Palawan. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non- Christian majority population in the country, and comprise about 5% of the total Philippine population, or 5 million people. Most Moros are followers of Sunni Islam of the Shafi'i madh'hab. The Muslim Moros originally had a few independent states such as the Maguindanao Sultanate, the Lanao Sultanates, and the Sulu Sultanate. The Sultanate of Sulu once exercised sovereignty over the present day provinces of Basilan, Palawan, Sulu, Tawi-Tawi, the eastern part of the Malaysian state of Sabah
Sabah () is a state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indonesia to the south. The Federal Territory ...
(formerly North Borneo) and North Kalimantan in Indonesia.
Non-Moro indigenous people groups
 There are more than 100 highland, lowland, and coastland tribal groups in the Philippines. These include:
There are more than 100 highland, lowland, and coastland tribal groups in the Philippines. These include:
Igorot
The Igorots/Cordillerans live in the highlands ofLuzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, ...
. They are primarily located in the Cordillera Administrative Region, Caraballo Mountains, and Sierra Madre.
Mangyan
 Mangyan is the generic name for the eight indigenous groups found on the island of Mindoro, southwest of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, each with its own tribal name, language, and customs. They occupy nearly the whole of the interior of the island of Mindoro. The total population may be around 280,000, but official statistics are difficult to determine under the conditions of remote areas, reclusive tribal groups and some having little if any outside world contact.
Mangyan is the generic name for the eight indigenous groups found on the island of Mindoro, southwest of the island of Luzon in the Philippines, each with its own tribal name, language, and customs. They occupy nearly the whole of the interior of the island of Mindoro. The total population may be around 280,000, but official statistics are difficult to determine under the conditions of remote areas, reclusive tribal groups and some having little if any outside world contact.
Tribal Palaweño
The indigenous peoples of Palawan are a diverse group of both indigenous tribes and lowland groups that historically migrated to the island of Palawan and its outlying islands. These ethnolinguistic groups are widely distributed to the long strip of mainland island literally traversingLuzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, ...
, Visayas and Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
. Listed below are specifically the tribal groups of Palawan, as opposed to its urban lowland groups that historically settled its cities and towns.
Palawan is home to many indigenous peoples whose origins date back thousands of centuries. Pre-historic discoveries reveal how abundant cultural life in Palawan survived before foreign occupiers and colonizers reached the Philippine archipelago. Today, Palawan is making its best to preserve and conserve the richness of its cultural groups. The provincial government strives to support the groups of indigenous peoples of Palawan.
Suludnon
They are highland Visayan peoples, related to the lowland Kinaray-a, Aklanon, and Hiligaynon of Panay Island, Visayas.Negrito
 The Negrito are several Australo-Melanesian groups who inhabit isolated parts of
The Negrito are several Australo-Melanesian groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
.Snow, Philip. ''The Star Raft: China's Encounter With Africa.'' Cornell Univ. Press, 1989 () They all live in remote areas throughout the islands in the Philippines.

Lumad
The Lumad are the un- Islamized and un- Christianized (or only recently Christianized) indigenousAustronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, M ...
peoples of Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
. They include several ethnolinguistic groups such as the Manobo, the Tasaday, the Mamanwa, the Mandaya, the B'laan, the T'boli, and the Kalagan. They primarily inhabit the eastern parts of Mindanao such as the Caraga, and Davao Regions.
Other ethnolinguistic groups
About 86 to 87 percent of the Philippine population belong to the ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither indigenous nor moro. These groups are sometimes collectively referred to as "Lowland Christianized groups," to distinguish them from indigenous ("upland") groups and moro peoples.Groups in mainland Luzon
Lowland Christianized groups of the island ofLuzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, ...
.
Groups in the Mimaropa Region
Lowland Christianized groups of the region of Mimaropa, consisting of the islands or provinces of Mindoro, Marinduque, Romblon, Palawan, and other surrounding islands.Groups in the Visayas
 Lowland Christianized groups of the Visayas archipelago. The Visayans are a metaethnicity race native to the whole Visayas, to the southernmost islands of
Lowland Christianized groups of the Visayas archipelago. The Visayans are a metaethnicity race native to the whole Visayas, to the southernmost islands of Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, ...
and the northern and eastern coastal parts of Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
. They are speakers of one or more Visayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, Hiligaynon and Waray-Waray. Other groups speak smaller languages such as Aklanon, Boholano, Butuanon, Capiznon
Capiznon or Capiceño () is an Austronesian regional language spoken in Western Visayas in the Philippines. Capiznon is concentrated in the province of Capiz in the northeast of Panay Island. It is a member of the Bisayan language family and th ...
, Eskaya
The Eskaya, less commonly known as the Visayan-Eskaya, is the collective name for the members of a cultural minority found in Bohol, Philippines, which is distinguished by its cultural heritage, particularly its literature, language, dress an ...
, Kinaray-a, Masbateño, Porohanon, Romblomanon, and Surigaonon. If speakers of the Visayan languages are to be grouped together, they would comprise the largest ethnic group in the nation, numbering at around 33 million as of 2010.
Groups in Mindanao
Lowland Christianized groups of the island ofMindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
.
Immigrants & mixed peoples
 The
The Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
consists of a wide number of settlers that form part of the national population. They historically immigrated or descended from various countries or lands throughout the history of the Philippines, from as early as the precolonial period, the Spanish colonial period
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, the American colonial period, Japanese occupation, and modern era. Historically in the context of modern countries, they most notably came from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
, China, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, Japan, and India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
. Much of these immigrant peoples throughout the centuries eventually integrated or assimilated into the country's population, producing new groups of intermixed people that many identify as part of their Filipino identity.
Across the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
for the past centuries especially since the Spanish Colonial Era, the main historical migrant heritage groups are also the Chinese Filipinos and Spanish Filipinos who in Spanish Colonial Times later intermixed with the above lowland native Filipino ethnic groups, which produced the '' Mestizo de Sangley'' ( Chinese Mestizo) and '' Mestizo de Español'' ( Spanish Mestizo) respectively. There was also the rarer mix of ''Tornatrás'' during the Spanish Colonial Era, who were either the mix of both the Spanish and Chinese ( Sangley) in Spanish Colonial Philippines or the mix of the Chinese mestizo and Spanish mestizo, resulting in carrying all three ancestries from Spanish, Chinese, and Native Filipino ancestry. Historically though, it was the '' Mestizo de Sangley'' ( Chinese Mestizo) that numbered the most among '' mestizos'', though the '' Mestizos de Español
Español may refer to:
*from or pertaining to Spain
* Spanish language
* Spanish people
*Djudeo-Espanyol or Judaeo-Spanish, a language spoken by Jews
*Argant, an ancient variety of red wine grape alternatively named Espagnol
* RCD Espanyol
* Club ...
'' ( Spanish Mestizos) carried more social prestige due to the colonial caste system hierarchy that usually elevated Spanish blood and christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, cont ...
to the peak, hence many Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or oth ...
today associate the term "''mestizo''" with Spanish mestizos, while most descendants of the '' Mestizo de Sangley'' ( Chinese Mestizo), despite assuming many of the important roles in the economic, social, and political life of the nation, also later readily assimilated into the fabric of Philippine society or sometimes falsely claim Spanish descent due to this situation.
Historical foreign migrants and intermixed peoples
These groups are the historical foreign migrant peoples and the intermixed peoples they produced with native groups, especially the native urban lowland peoples of the Philippines. Those listed below are those groups in modern times that still have some number of Filipinos claiming identity with such background. }) with a Japanese school, a Shinto shrine and a diplomatic mission from Japan. The place that used to be "''Little Tokyo''" in Davao was Mintal. Many have roots from eitherOkinawa
is a prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 km2 (880 sq mi).
Naha is the capital and largest city ...
( Ryukyu) or Mainland Japan. When World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
broke out, many were killed or expelled because of their unwilling or willing fifth column collaboration with the Japanese Imperial Army (mostly as translator). This led to many Japanese mestizos who tended to deny their Japanese heritage and changed their family names in order to avoid discrimination. Eventually, many either intermarried and assimilated into the Filipino populace, such as those in Davao who intermarried with the Bagobo
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopte ...
, and those in Baguio with the Igorot. Many eventually completely lost their Japanese identity while others have immigrated to the US or "returned" to Japan, the homeland of their forebears. Most Japanese Filipinos in the modern times (colloquially called ''Japino'') are now fresh new immigrants from Japanese businessmen who went with female OFW entertainers in Japan. The Filipina mothers usually return to the Philippines with their children along with them. Other Japanese who stayed in the country initially came to the Philippines to learn English or set up businesses. These days, most Japanese Filipinos can be found around Davao or Baguio
Baguio ( ,
), officially the City of Baguio ( ilo, Siudad ti Baguio; fil, Lungsod ng Baguio), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Cordillera Administrative Region, Philippines. It is known as the "Summer Capital of the Philippines ...
or Iloilo or Cebu, with only a few around Metro Manila
Metropolitan Manila (often shortened as Metro Manila; fil, Kalakhang Maynila), officially the National Capital Region (NCR; fil, link=no, Pambansang Punong Rehiyon), is the capital region, seat of government and one of three List of metrop ...
, though historically there were many around Manila, such as Plaza Dilao in Paco, Manila.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , Mestizo de Español (Spanish Mestizo) ,
 , These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the Spanish and
, These are mixed descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the Spanish and Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
settlers who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era. Most were of either Spanish ancestry or Amerindian-Spanish ancestry (The term 'Mestizo' originated in Latin America). The first groups of Hispanics sailed in 1565 with Miguel López de Legazpi from New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
, in what is now Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal ...
state, Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
to colonize the Philippines. In addition to this, select cities such as Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
, Vigan, Bauang, Naga, Iriga, Iloílo
Iloilo City, officially the City of Iloilo ( hil, Siyudad/Dakbanwa sang Iloilo; fil, Lungsod ng Iloilo), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Western Visayas region of the Philippines on the island of Panay. It is the capital city of th ...
, Bacólod, Cebú
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 167 ...
and Zamboanga, which were home to military fortifications or commercial ports during the Spanish era, also hold sizable ''mestizo'' communities.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , Mestizo de Sangley (Chinese Mestizo) ,
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
or Taishanese
Taishanese (), alternatively romanized in Cantonese as Toishanese or Toisanese, in local dialect as Hoisanese or Hoisan-wa, is a dialect of Yue Chinese native to Taishan, Guangdong. Although it is related to Cantonese, Taishanese has little ...
or sometimes Japanese ancestry. ''Sangley'' is a Hokkien word from sng-lí ��理meaning "business."
,
, –
, -
! scope="row" , Tornatrás (Spanish-Chinese Mestizo)
, – , - ! scope="row" , Indian Filipino / Mestizo de Bombay (Indian Mestizo) ,
 , Philippines has been part of Indianized kingdoms from the 7th century Srivijaya and earlier era. Indian culture, language, scripture, food, belief, arts, martial arts, epics have had profound impact on pre-Spanish Philippines which is still visible. They have contributed to the unique cultural blend in the Philippines. One source estimated the size of the Indian community in the Philippines in 2008 at 150,000 persons. Most Indians in the Philippines belong to either Sindhi or
, Philippines has been part of Indianized kingdoms from the 7th century Srivijaya and earlier era. Indian culture, language, scripture, food, belief, arts, martial arts, epics have had profound impact on pre-Spanish Philippines which is still visible. They have contributed to the unique cultural blend in the Philippines. One source estimated the size of the Indian community in the Philippines in 2008 at 150,000 persons. Most Indians in the Philippines belong to either Sindhi or Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
ethnic groups, and are largely businessmen and traders. A smaller population of Indians belonging to the Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
ethnic group form part of the clergy of Roman Catholic dioceses in the country. Besides age old indianized influences from indianized history of precolonial states inherited from neighboring Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, Indian Filipinos (''Bumbay'') or ''Mestizo de'' ''Bombay'' are the mixed colonial descendants of the native peoples of the Philippines with the Indian or ''Bumbay'' migrants from Bombay (now Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
, Maharashtra) ''or Sepoy'' soldiers from Madras (now Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil languag ...
) who settled in the Spanish East Indies (Philippines) during the Spanish Era, especially during the British occupation of Manila in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
. Many settled in what is Cainta, in what was then the Province of Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
(currently part of Rizal Province). As of 2006, between 70 and 75 percent of Indians in the Philippines lived in Metro Manila, with the largest community outside of Manila being in Isabela province. The region in and around Cainta still has many Sepoy descendants. However, Indian business people started to arrive in larger numbers in The Philippines during the American colonial period (1898–1930s) – especially during the 1930s and 1940s, when many Indians and Indian Filipinos lived in Filipino provinces, including Davao. The longest serving Mayor of Manila, Ramon Bagatsing, was of Indian-Punjabi descent, having moved to Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
from Fabrica, Negros Occidental before the second world war. A second surge of Indian businessmen, especially Sindhis arrived in Philippines during the 1947 India-Pakistan partition. In the present day, most of the Indians and Indian Filipinos in the Philippines are Sindhi and Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
as well as a large Tamil population. Many are fluent in Filipino(Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
) and English as well as local languages of the provinces and islands. Many are prosperous middle class with their main occupations in clothing sales and marketing. Sikhs are involved largely in finance, money lending (locally called ''Five – six'' ), sales
Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods sold in a given targeted time period. The delivery of a service for a cost is also considered a sale.
The seller, or the provider of the goods or services, completes a sale in ...
and marketing.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , Sangil/Sangirese ,
 , The Sangil people (also called Sangir, Sangu, Marore, Sangirezen, or Talaoerezen) are originally from the Sangihe and Talaud Islands (now part of
, The Sangil people (also called Sangir, Sangu, Marore, Sangirezen, or Talaoerezen) are originally from the Sangihe and Talaud Islands (now part of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
) and parts of Davao Occidental
Davao Occidental ( Cebuano: ''Kasadpang Dabaw''; Filipino: ''Kanlurang Davao''), officially the Province of Davao Occidental, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is the municipality of Malita. ...
(particularly in the Sarangani Islands), Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Sultan Kudarat, South Cotabato, and North Cotabato. Their populations (much like the Sama-Bajau) were separated when borders were drawn between the Philippines and Indonesia during the colonial era. The Sangil people are traditionally animistic, much like other Lumad peoples. During the colonial era, the Sangil (who usually call themselves "Sangir") in the Sangihe Islands mostly converted to Protestant Christianity due to proximity and contact with the Christian Minahasa people of Sulawesi. In the Philippines, most Sangil converted to Islam due to the influence of the neighboring Sultanate of Maguindanao. However, elements of animistic rituals still remain. The Indonesian and Filipino groups still maintain ties and both Manado Malay and Cebuano are spoken in both Indonesian Sangir and Filipino Sangil, in addition to the Sangirese language. The exact population of Sangil people in the Philippines is unknown, but is estimated to be around 10,000 people.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , Jewish Filipino ,
 , , Filipino Jews numbered at the most 500 people. Other estimates range between 100 and 18,500 people (0.000001% and 0.005% of the country's total population). ,
, , Filipino Jews numbered at the most 500 people. Other estimates range between 100 and 18,500 people (0.000001% and 0.005% of the country's total population). , Metro Manila
Metropolitan Manila (often shortened as Metro Manila; fil, Kalakhang Maynila), officially the National Capital Region (NCR; fil, link=no, Pambansang Punong Rehiyon), is the capital region, seat of government and one of three List of metrop ...
has the largest Jewish community in the Philippines, which consists of roughly seventy families. The country's only synagogue, Beth Yaacov, is located in Makati, as is the Chabad House. There are, of course, other Jews elsewhere in the country, like the Bagelboys of Subic and Angeles City but these are obviously fewer and almost all transients, either diplomats or business envoys, and their existence is almost totally unknown in mainstream society. There are a few Israelis
Israelis ( he, יִשְׂרָאֵלִים, translit=Yīśrāʾēlīm; ar, الإسرائيليين, translit=al-ʾIsrāʾīliyyin) are the citizens and nationals of the State of Israel. The country's populace is composed primarily of Jew ...
in Manila working at call centers and a few other executives. There are also a number of converts to Judaism.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , American Filipino / Filipino Americans ,
 , American (''Amerikano/Kano'') settlement in the Philippines began during the
, American (''Amerikano/Kano'') settlement in the Philippines began during the Spanish colonial period
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, when Americans came to the islands primarily to conduct business and trade. They owned many businesses in the sugar industry. There was not much American inflow to the Philippines until after the Philippine–American War. After the USA won the war and colonized the Philippines, thousands of Americans settled there temporarily or permanently. Most were either members of the U.S. military or Christian missionaries. After independence in 1946, many Americans chose to remain in the Philippines while maintaining relations with relatives in the US. Most of them were professionals, but missionaries continued to settle the country. In 2015, the U.S. State Department estimated that there were more than 220,000 U.S. citizens living in the Philippines, with a significant mixed population of Amerasian
An Amerasian may refer to a person born in Asia to an Asian mother and a U.S. military father. Other terms used include War babies or G.I. babies. There are also those who may have mothers in the U.S. military or have Amerasian ancestry through the ...
s and descendants from the colonial era as well. Since 1898, when the United States annexed the Philippines from Spain, there were as many as 21 U.S. bases and 100,000 U.S. military personnel stationed there. The bases closed in 1992 leaving behind thousands of Amerasian children. There are an estimated 52,000 Amerasians in the Philippines, but an academic research paper presented in the U.S. (in 2012) by an Angeles, Pampanga, Philippines Amerasian college research study unit suggests that the number could be a lot more, possibly reaching 250,000 this is also partially due to the fact that almost all Amerasian intermarried with other Amerasian and Filipino natives. This group also includes Filipino American (Fil-Am), and sometimes Filipino Canadian, returnee migrants from the United States and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
.
,
, – , - ! scope="row" , Filipinos with Arab Ancestry ,
 ,
, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
(''Arabo'') traders first visited the Philippines during the precolonial era. They sailed through Southeast Asia, including the Philippines, for trade and commerce on their way to trade with China, just like Persian and Indian traders. These early Arab traders followed the pre-Islamic religions of Arabian Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, Paganism and Sabeanism. After the advent of Islam, in 1380, Karim ul’ Makhdum, the first Islamic missionary to reach the Sulu Archipelago, brought Islam to what is now the Philippines, first arriving in Jolo. Subsequent visits of Arab Muslim missionaries strengthened the Islamic faith in the Philippines, concentrating in the south and reaching as far north as Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital city, capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is Cities of the Philippines#Independent cities, highly urbanize ...
. Starting with the conquest of Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
by the Portuguese and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
by the Dutch, the Philippines began to receive a number of Malaysian-Arab refugees including several Malaysian princes and displaced court advisors. Soon, vast sultanates were established overlapping the existing indigenous Filipino barangay (village) governing system and Indianized royalty. The two largest were the Sultanate of Maguindanao, which loosely governed most of southern Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of t ...
and the Sultanate of Sulu, which included Basilan, Jolo, and parts of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java Isl ...
. Several other smaller but famous sultanates were also established such as the sultanates of Lanao in Mindanao, which was later conquered by the Spanish in the 16th century. The ties between the sultanates in Mindanao remained economically and culturally close to Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
, and Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
until the end of the 19th century when the sultanates were weakened by the Spanish and later the American military during the Spanish and American colonial period. Today, there are numerous Arab-descended Filipino families, especially royal or noble Muslim families in Mindanao. In modern times, there has also been immigration from Arab countries in the middleeast, especially those recently devastated by war in the recent decades like Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and Syria.
,
, –
Recent modern immigrants and expatriates
These migrant groups are relatively recent immigrants and expatriate groups that mostly immigrated in the modern era, specifically around the 20th century especially from post- WW2 Philippine independence to the present era. Recent modern immigrants, expatriates, foreign students, foreign citizens with work permits and resident aliens are all included. Common reasons for modern immigration into the Philippines include employment, education, tourism, marriage migration counter flow from returning overseas Filipino workers and emigrants, etc. According to a 2013 country migration report, the recent most notable nationalities of foreign aliens with work permits includeKoreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
, Chinese, Japanese, Americans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Amer ...
,Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and British (either British citizen or British National (Overseas) – from British Hong Kong). Most of these foreign aliens with work permits are based in the National Capital Region (Metro Manila), followed by Calabarzon (Southern Tagalog), and Central Visayas, representing the more developed regions of the country. Most of them are employed in the manufacturing sector, although they tend to be involved in other sectors as well. The majority work in administrative, executive and managerial positions. The top three nationalities of registered aliens are Chinese (59,000), Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
(39,000) and Americans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Amer ...
(26,000). According to the 2010 Cen