|
Brianite
Brianite is a phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Na2CaMg(PO4)2. It was first identified in an iron meteorite. This mineral is named after Brian Harold Mason (1917–2009), a pioneer in meteoritics. It was first reported from the Dayton meteorite in Montgomery County, Ohio in 1966. It occurs in phosphate nodules within the meteorite. Associated minerals include: panethite, whitlockite, albite, enstatite, schreibersite, kamacite, taenite, graphite, sphalerite and troilite. See also * Glossary of meteoritics This is a glossary of terms used in meteoritics, the science of meteorites. # * 2 Pallas – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the CR meteorites. * 4 Vesta – second-largest asteroid in the asteroid b ... References Phosphate minerals Meteorite minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 {{Phosphate-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panethite
Panethite, chemical formula , is a rare phosphate mineral that was only found in one meteorite on Earth. It was originally found in the Dayton meteorite in Ohio. It is classified as H-M symbol (2/m) with space group of ''P''21/n. It is amber in color. It was named in the honor of Friedrich Adolf Paneth (1887–1958), a German chemist who made many contributions toward the discovery of the origin of the universe, and especially studies of meteorites. Structure Using X-ray diffraction, the unit cell and the space group parameters were determined. The strongest lines of the X-ray were 5.10(6), 3.236(5), 3.007(10), 2.749, 2.710(7) (American Mineralogist, 509). But the error of the cell lengths were relatively high due to twinning and some disorder in the grains examined. Panethite has a monoclinic crystal system with a0=10.18 ±0.01Å, b0=14.90 ±0.02Å, c0=25.87 ±0.03Å and β =91.1˚, and its space group P21/n. Within the error that accompanied the microprobe analysis, the X-ray d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Harold Mason
Brian Harold Mason (18 April 1917 – 3 December 2009) was a New Zealand geochemist and mineralogist who was one of the pioneers in the study of meteorites. He played a leading part in understanding the nature of the Solar System through his studies of meteorites and lunar rocks. He also examined and classified thousands of meteorites collected from Antarctica. Life Mason was born in Port Chalmers, Dunedin, in 1917 and was brought up in Christchurch, New Zealand. He was educated at Christchurch Boys' High School and studied geology and chemistry at Canterbury University College, graduating MSc with first-class honours in 1939. In November he left for Norway to work towards a doctorate, arriving in January 1940, but along with a colleague who held a British passport fled to Sweden in May following Operation Weserübung, the German invasion of Norway. In 1943, he completed a PhD in geochemistry at the University of Stockholm under Victor Goldschmidt and left the country for Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Mineral
Phosphate minerals contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate (PO43−) anion along sometimes with arsenate (AsO43−) and vanadate (VO43−) substitutions, and chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions that also fit into the crystal structure. The phosphate class of minerals is a large and diverse group, however, only a few species are relatively common. Applications Phosphate rock has high concentration of phosphate minerals, most commonly of the apatite group. It is the major resource mined to produce phosphate fertilizers for the agriculture sector. Phosphate is also used in animal feed supplements, food preservatives, anti-corrosion agents, cosmetics, fungicides, ceramics, water treatment and metallurgy. The largest use of minerals mined for their phosphate content is the production of fertilizer. Phosphate minerals are often used for control of rust and prevention of corrosion on ferrous materials applied with electrochemical conversion co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schreibersite
Schreibersite is generally a rare iron nickel phosphide mineral, , though common in iron-nickel meteorites. It has been found on Disko Island in Greenland and Illinois. Another name used for the mineral is rhabdite. It forms tetragonal crystals with perfect 001 cleavage. Its color ranges from bronze to brass yellow to silver white. It has a density of 7.5 and a hardness of 6.5 – 7. It is opaque with a metallic luster and a dark gray streak. It was named after the Austrian scientist Carl Franz Anton Ritter von Schreibers (1775–1852), who was one of the first to describe it from iron meteorites.Schreibersite Webmineral Schreibersite is reported from the Magura Meteorite, Arva-(present name – Orava), Slovak Republic; the |
Meteorite Minerals
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples " bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater. Meteorites that are recovered after being observed as they transit the atmosphere and impact the Earth are called meteorite falls. All others are known as meteorite finds. Meteorites have traditionally been divided into three broad categories: stony meteorites that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Minerals
Phosphate minerals contain the tetrahedrally coordinated phosphate (PO43−) anion along sometimes with arsenate (AsO43−) and vanadate (VO43−) substitutions, and chloride (Cl−), fluoride (F−), and hydroxide (OH−) anions that also fit into the crystal structure. The phosphate class of minerals is a large and diverse group, however, only a few species are relatively common. Applications Phosphate rock has high concentration of phosphate minerals, most commonly of the apatite group. It is the major resource mined to produce phosphate fertilizers for the agriculture sector. Phosphate is also used in animal feed supplements, food preservatives, anti-corrosion agents, cosmetics, fungicides, ceramics, water treatment and metallurgy. The largest use of minerals mined for their phosphate content is the production of fertilizer. Phosphate minerals are often used for control of rust and prevention of corrosion on ferrous materials applied with electrochemical conversion co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Meteoritics
This is a glossary of terms used in meteoritics, the science of meteorites. # * 2 Pallas – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the CR meteorites. * 4 Vesta – second-largest asteroid in the asteroid belt and likely source of the HED meteorites. * 221 Eos – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the CO meteorites. * 289 Nenetta – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the angrites. * 3103 Eger – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the aubrites. * 3819 Robinson – an asteroid from the asteroid belt and one of the likely parent bodies of the angrites. * IA meteorite – an iron meteorite group now part of the IAB group/complex. * IAB meteorite – an iron meteorite and primitive achondrite of the IAB group/complex. * IB meteorite – an iron meteorite group now part of the IAB group/complex. * IC meteorite – an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troilite
Troilite is a rare iron sulfide mineral with the simple formula of FeS. It is the iron-rich endmember of the pyrrhotite group. Pyrrhotite has the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2) which is iron deficient. As troilite lacks the iron deficiency which gives pyrrhotite its characteristic magnetism, troilite is non-magnetic. Troilite can be found as a native mineral on Earth but is more abundant in meteorites, in particular, those originating from the Moon and Mars. It is among the minerals found in samples of the meteorite that struck Russia in Chelyabinsk on February 15th, 2013. Uniform presence of troilite on the Moon and possibly on Mars has been confirmed by the Apollo, Viking and Phobos space probes. The relative intensities of isotopes of sulfur are rather constant in meteorites as compared to the Earth minerals, and therefore troilite from Canyon Diablo meteorite is chosen as the international sulfur isotope ratio standard, the Canyon Diablo Troilite (CDT). Structure Troilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
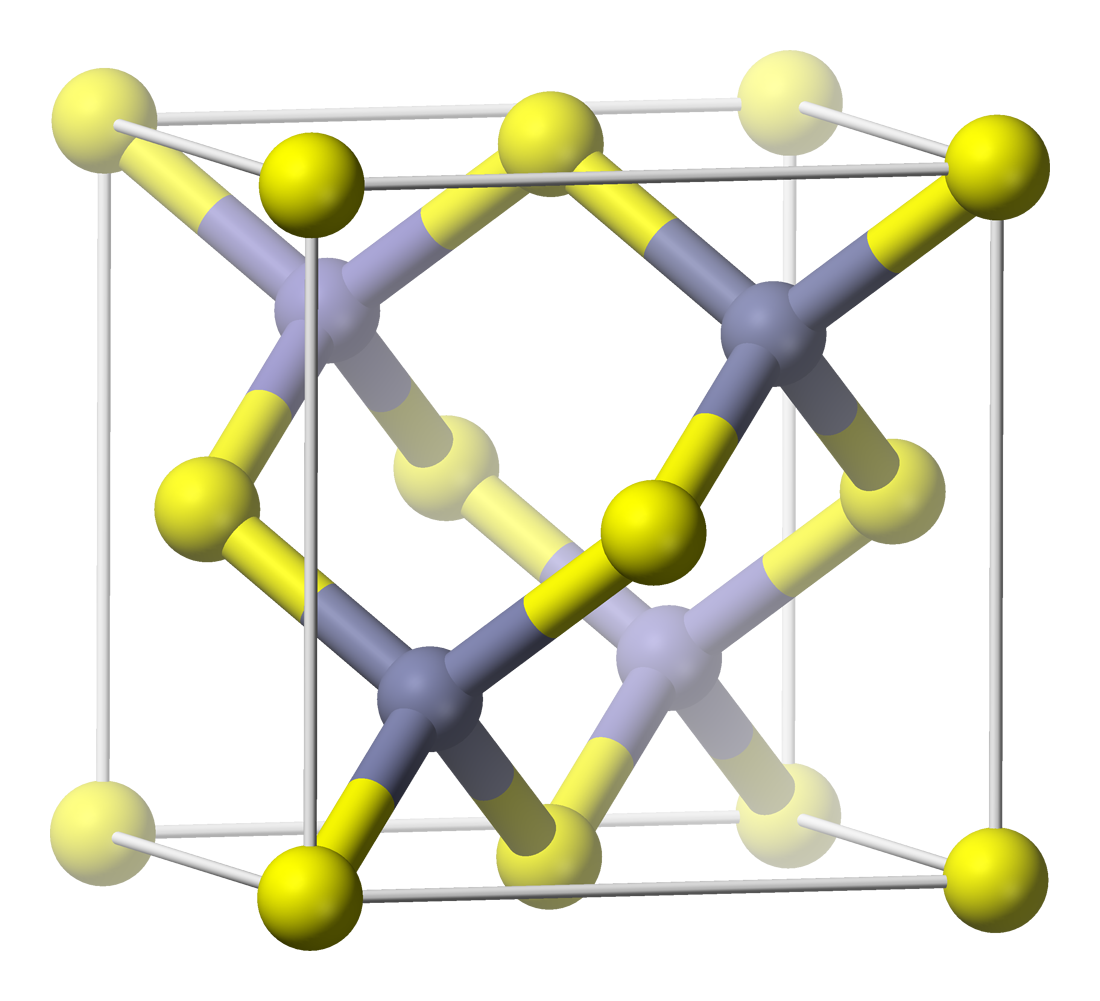
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a weak conductor of heat and electricity. Types and varieties Natural graphite The principal types of natural graphite, each occurring in different types of ore deposits, are * Crystalline small flakes of graphite (or flake graphite) occurs as isolated, flat, plate-like particles with hexagonal edges if unbroken. When broken the edges can be irregular or angular; * Amorphous graphite: very fine flake graphite is sometimes called amorphous; * Lump graphite (or vein graphite) occurs in fissure veins or fractures and appears as massive platy intergrowths of fibrous or acicular crystalline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taenite
Taenite is a mineral found naturally on Earth mostly in iron meteorites. It is an alloy of iron and nickel, with a chemical formula of and nickel proportions of 20% up to 65%. The name is derived from the Greek ταινία for "band, ribbon". Taenite is a major constituent of iron meteorites. In octahedrites it is found in bands interleaving with kamacite forming Widmanstätten patterns, whereas in ataxites it is the dominant constituent. In octahedrites a fine intermixture with kamacite can occur, which is called plessite. Taenite is one of four known Fe-Ni meteorite minerals: The others are kamacite, tetrataenite, and antitaenite. Properties It is opaque with a metallic grayish to white color. The structure is isometric-hexoctahedral ( cubic). Its density is around 8 g/cm3 and hardness is 5 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale. Taenite is magnetic, in contrast to antitaenite. The structure is isometric-hexoctahedral ( cubic). The crystal lattice has the c≈a= 3.582±0.002 Å ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamacite
Kamacite is an alloy of iron and nickel, which is found on Earth only in meteorites. According to the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) it is considered a proper nickel-rich variety of the mineral native iron. The proportion iron:nickel is between 90%:10% and 95%:5%; small quantities of other elements, such as cobalt or carbon may also be present. The mineral has a metallic luster, is gray and has no clear cleavage although its crystal structure is isometric-hexoctahedral. Its density is about 8 g/cm3 and its hardness is 4 on the Mohs scale. It is also sometimes called balkeneisen. The name was coined in 1861 and is derived from the Greek root ''καμακ-'' "kamak" or ''κάμαξ'' "kamaks", meaning vine-pole. It is a major constituent of iron meteorites (octahedrite and hexahedrite types). In the octahedrites it is found in bands interleaving with taenite forming Widmanstätten patterns. In hexahedrites, fine parallel lines called Neumann lines are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |