|
Bornavirus
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fatal neurologic disease of mammals restricted to central Europe; and proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) in birds. Bornaviruses may cause encephalitis in mammals like horses or sheep. The family includes 11 species assigned to three genera. History Borna disease was first identified in 1926 and its genome was isolated in 1990. The ICTV proposed the creation in 1996 of the family ''Bornaviridae'' along with the genus ''Bornaviru''s (today ''Orthobornavirus''). The viral family is named after the city of Borna in Saxony, Germany, which is where many animals were lost to the sporadic encephalopathy caused by the viral disease. Structure Orthobornavirions are enveloped, with spherical geometries and helical capsids. The diameter is ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Disease Virus
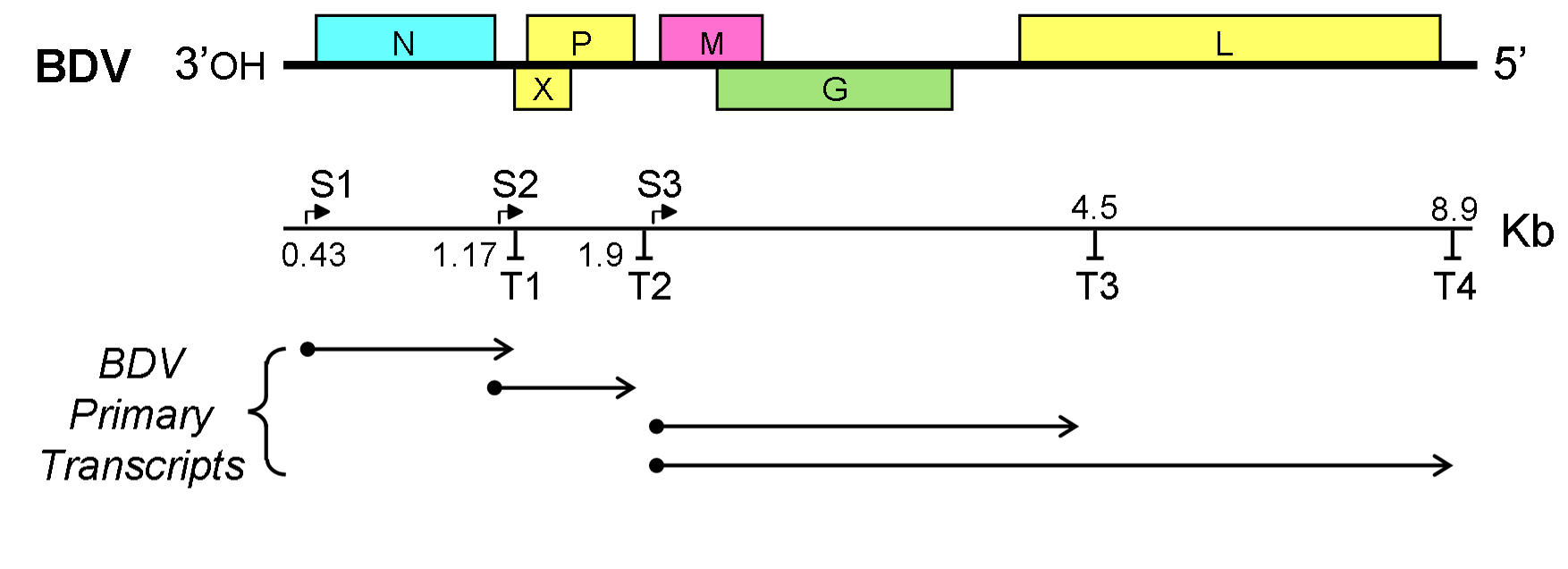
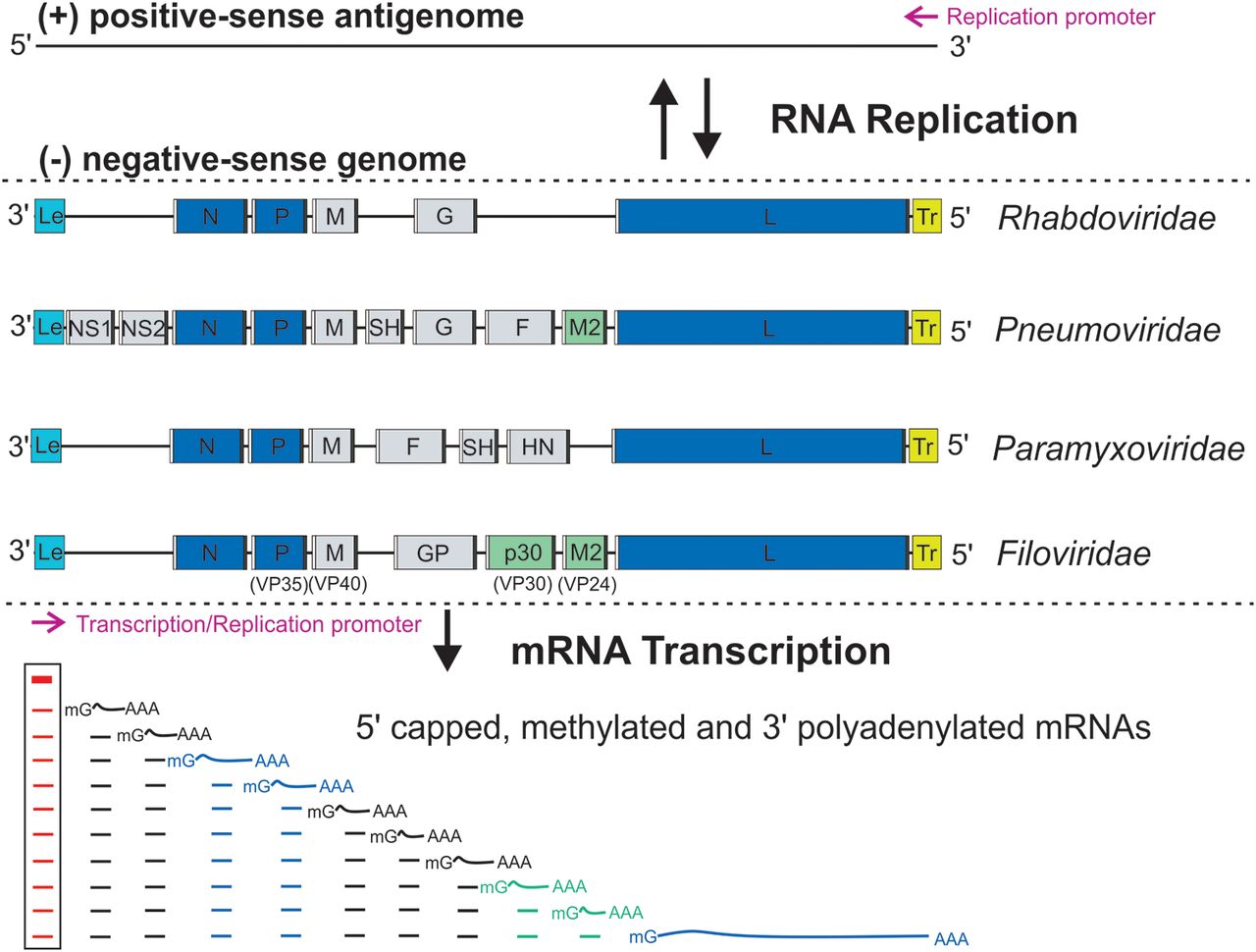
The Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 (BoDV-1 and BoDV-2) are members of the species ''Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus'' and cause Borna disease in mammals. Virology Genome BoDV-1/2 have the smallest genome (8.9 kilobases) of any ''Mononegavirales'' member and are unique within that order in their ability to replicate within the host cell nucleus. BoDV-1 was isolated from a diseased horse in the 1970s, but the virus particles were difficult to characterise. Nonetheless, the virus' genome has been characterised. It is a linear negative-sense single stranded RNA virus in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Several of the proteins encoded by the BoDV-1 genome have been characterised. The G glycoprotein is important for viral entry into the host cell. It has been suggested that the p10, or X, protein plays a role in viral RNA synthesis or ribonucleoprotein transport. The P40 nucleoprotein from BoDV-1 is multi-helical in structure and can be divided into two subdomains, each of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornaviridae
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fatal neurologic disease of mammals restricted to central Europe; and proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) in birds. Bornaviruses may cause encephalitis in mammals like horses or sheep. The family includes 11 species assigned to three genera. History Borna disease was first identified in 1926 and its genome was isolated in 1990. The ICTV proposed the creation in 1996 of the family ''Bornaviridae'' along with the genus ''Bornaviru''s (today ''Orthobornavirus''). The viral family is named after the city of Borna in Saxony, Germany, which is where many animals were lost to the sporadic encephalopathy caused by the viral disease. Structure Orthobornavirions are enveloped, with spherical geometries and helical capsids. The diameter is ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variegated Squirrel
The variegated squirrel (''Sciurus variegatoides'') is a tree squirrel in the genus ''Sciurus'' found in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, southern Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. Fifteen subspecies are recognised. It is a common squirrel and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it a "least-concern species". Variegated squirrels kept as pets in Germany have been implicated in the transmission of a bornavirus to humans from which three people have died. Description The variegated squirrel is a medium-sized squirrel; the head-and-body length is about with a tail of much the same length. It weighs about . The several subspecies differ in appearance and there is often a considerable variation between the appearances of individuals in the same population. The dorsal colouration varies between dark brown to yellowish grey. The neck tends to be darker than other parts and there is often a paler patch behind the ears. The underparts are usually som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borna Disease
Borna disease, also known as sad horse disease, is an infectious neurological syndrome of warm-blooded animals, caused by Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 (BoDV-1/2). BoDV-1/2 are neurotropic viruses of the species ''Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus,'' and members of the ''Bornaviridae'' family within the ''Mononegavirales'' order. Borna disease is a severe neurological illness that predominantly affects horses and sheep, but it has been observed in a wide range of mammals. The disease is characterised by ataxia and abnormal depressive behaviour, frequently culminating in death. There have been rare cases of human fatalities associated with encephalitis caused by Borna disease virus infection. Additionally, correlative evidence exists linking BoDV-1/2 infection with neuropsychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorder in humans. History Borna disease was first described in 1885, when all horses belonging to a cavalry regiment stationed near the city of Borna in Saxony, Germany, died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononegavirales
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. All of these viruses cause significant disease in humans. Many other important pathogens of nonhuman animals and plants are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus families: '' Artoviridae'', ''Bornaviridae'', ''Filoviridae'', ''Lispiviridae'', ''Mymonaviridae'', ''Nyamiviridae'', ''Paramyxoviridae'', ''Pneumoviridae'', ''Rhabdoviridae'', '' Sunviridae'', and ''Xinmoviridae''. Use of term The order ''Mononegavirales'' (pronounced: ) According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Mononegavirales'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, and never abbreviated. The names of the order's physical members ("mononegaviruses" or "mononegavirads") are to be writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proventricular Dilatation Disease
Proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) is an incurable probably viral disease of psittacine birds. It was first recognized and described in 1978 by Dr. Hannis L. Stoddard. Since the first reported cases were involving species of macaw, the condition was termed macaw wasting syndrome. Clinical signs The clinical presentation of this disease varies with the individual as well as in severity of those symptoms. Often the symptoms include a gastrointestinal component, but many times birds with this disease will present with neurologic signs as well, or in lieu of digestive anomalies. Gastrointestinal signs may include: Regurgitation, crop impaction, poor appetite, weight loss, or passage of undigested food in the feces.Harrison, and Lightfoot. 2006 ''Clinical Avian Medicine''. Spix Publishing, Palm Beach, Florida. Neurologic symptoms may include: Weakness, ataxia, paresis, proprioceptive deficits, head tremors, and rarely seizures. Muscle wasting and a generalized poor body condition is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seroprevalence
Seroprevalence is the number of persons in a population who test positive for a specific disease based on serology (blood serum) specimens; often presented as a percent of the total specimens tested or as a proportion per 100,000 persons tested. As positively identifying the occurrence of disease is usually based upon the presence of Antibody, antibodies for that disease (especially with viral infections such as herpes simplex, HIV, and SARS-CoV-2), this number is not significant if the Sensitivity and specificity, specificity of the antibody is low. References External links HIV Portland Glossary definition of seroprevalence Epidemiology Serology {{med-diagnostic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treeshrew
The treeshrews (or tree shrews or banxrings) are small mammals native to the tropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. They make up the entire order Scandentia, which split into two families: the Tupaiidae (19 species, "ordinary" treeshrews), and the Ptilocercidae (one species, the pen-tailed treeshrew). Though called 'treeshrews', and despite having previously been classified in Insectivora, they are not true shrews, and not all species live in trees. They are omnivores; among other things, treeshrews eat fruit. Treeshrews have a higher brain to body mass ratio than any other mammal, including humans, but high ratios are not uncommon for animals weighing less than . Among orders of mammals, treeshrews are closely related to primates, and have been used as an alternative to primates in experimental studies of myopia, psychosocial stress, and hepatitis. Name The name '' Tupaia'' is derived from ''tupai'', the Indonesian word for squirrel, and was provided by Sir Stamfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhesus Macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or grey in colour, it is in length with a tail and weighs . It is native to South, Central, and Southeast Asia and has the widest geographic range of all non-human primates, occupying a great diversity of altitudes and a great variety of habitats, from grasslands to arid and forested areas, but also close to human settlements. Feral colonies are found in the United States, thought to be either released by humans or escapees after hurricanes destroyed zoo and wildlife park facilities. The rhesus macaque is diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrial. It is mostly herbivorous, mainly eating fruit, but will also consume seeds, roots, buds, bark, and cereals. Studies show almost 100 different plant species in its diet. Rhesus macaques are gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callosciurinae
The Callosciurinae are an Asiatic subfamily of squirrels containing over 60 species (mostly found in South East Asia) named after the genus ''Callosciurus'', which means "beautiful squirrels". Classification *Family SciuridaeThorington, R. W. Jr. and R. S. Hoffman. 2005. Family Sciuridae. pp. 754–818 ''in'' Mammal Species of the World a Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. D. E. Wilson and D. M. Reeder eds. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. **Subfamily Callosciurinae ***Tribe Callosciurini ****''Callosciurus'' - Beautiful squirrels (15 species) ****'' Dremomys'' - Red-cheeked squirrels or Asian montane squirrels (six species) ****''Exilisciurus'' - Asian pygmy squirrels (three species) ****'' Glyphotes'' - sculptor squirrel ****'' Hyosciurus'' - Long-nosed squirrels (two species) ****''Lariscus'' - Striped ground squirrels (four species) ****'' Menetes'' - Berdmore's ground squirrel or Indochinese ground squirrel ****'' Nannosciurus'' - Black-eared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciurinae
Sciurinae is a subfamily of squirrels (in the family Sciuridae), uniting the flying squirrels with certain related tree squirrels. Older sources place the flying squirrels in a separate subfamily (Pteromyinae) and unite all remaining sciurids into the subfamily Sciurinae, but this has been strongly refuted by genetic studies. Classification Subfamily SciurinaeThorington, R. W. and R. S. Hoffmann. 2005. Family Sciuridae. pp 754–818 in Mammal Species of the World A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. walker's mammals of the world 5th edition Volume 1 *Tribe Sciurini **Genus ''Microsciurus'' – American dwarf squirrels ***Central American dwarf squirrel, ''M. alfari'' ***Amazon dwarf squirrel, ''M. flaviventer'' ***Western dwarf squirrel, ''M. mimulus'' ***Santander dwarf squirrel, ''M. santanderensis'' **Genus '' Rheithrosciurus'' *** Tufted ground squirrel, ''R. macrotis'' **Genus ''Sciurus'' ***Subgenus ''Sciurus'' ****Allen's squirrel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_by_Davidraju_img7.jpg)