|
Benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate
Trimesic acid, also known as benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CO2H)3. It is one of three isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid. A colorless solid, trimesic acid has some commercial value as a precursor to some plasticizer A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture. Plasticizer ...s. Trimesic acid can be combined with ''para''-hydroxypyridine to make a water-based gel, stable up to 95 °C. Trimesic acid crystallizes from water to form a hydrogen-bonded hydrated network with wide unidimensional empty channels. See also * Trimellitic acid (1,2,4-benzenetricarboxylic acid) * Hemimellitic acid (1,2,3-benzenetricarboxylic acid) References Benzoic acids Tricarboxylic acids Carboxylic acid-based porous polymer monomers {{OrganicAcid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It launched a British division in the 1950s. Academic Press was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier said in 2000 it would buy Harcourt, a deal completed the next year, after a regulatory review. Thus, Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ... Well-known products include the '' Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzenetricarboxylic Acid
Benzenetricarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenetricarboxylic acid comes in three isomers: All isomers share the molecular weight 210.14 g/mol and the chemical formula A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as pare ... C9H6O6. {{chemistry index Benzoic acids Tricarboxylic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture. Plasticizers are commonly added to polymers and plastics such as PVC, either to facilitate the handling of the raw material during fabrication, or to meet the demands of the end product's application. Plasticizers are especially key to the usability of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), the third most widely used plastic. In the absence of plasticizers, PVC is hard and brittle; with plasticizers, it is suitable for products such as vinyl siding, roofing, vinyl flooring, rain gutters, plumbing, and electric wire insulation/coating. Plasticizers are also often added to concrete formulations to make them more workable and fluid for pouring, thus allowing the water contents to be reduced. Similarly, they are often added to clays, stucco, solid rocket fuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Pyridone
4-Pyridone is an organic compound with the formula . It is a colorless solid. Preparation 4-Pyridone, and its derivatives, are prepared from 4-pyrone and amines in protic solvents. : Tautomerism 4-Pyridone exists a keto-enol tautomerism with its enol tautomer 4-hydroxypyridine. In solution, the keto tautomer is favoured, and the enol tautomer only becomes important in very dilute solutions or solutions of non-polar solvents. However, the enol tautomer is dominant in the gas phase. Derivatives Fluridone is an aquatic herbicide Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ... that contains a 4-pyridone subunit. : See also * 2-Pyridone * 4-Piperidone * Dehydroacetic acid References {{DEFAULTSORT:Pyridone, 4- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
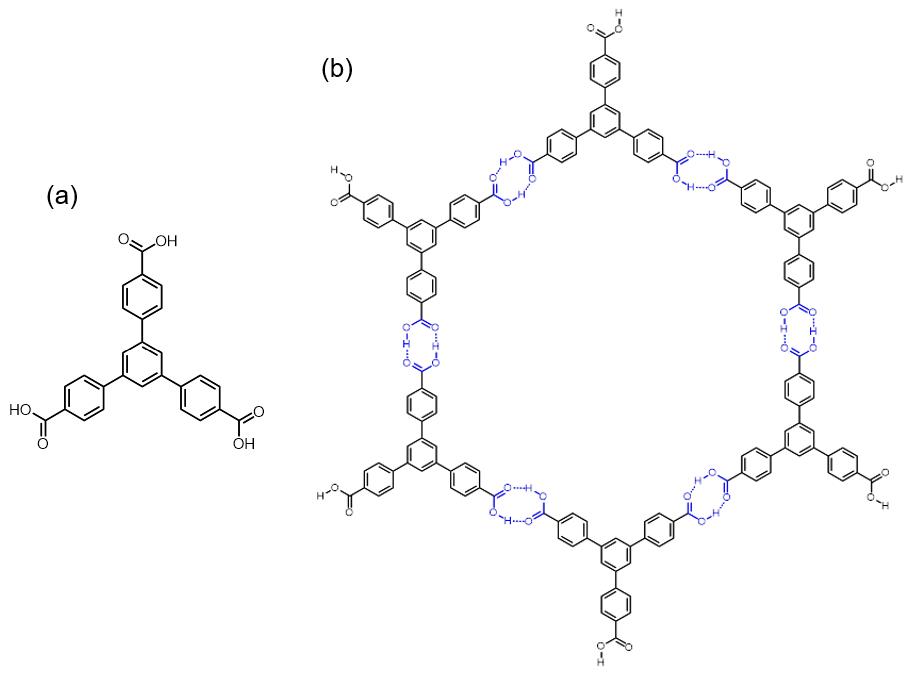
Hydrogen-bonded Organic Framework
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) are a class of porous polymers formed by hydrogen bonds among molecular monomer units to afford porosity and structural flexibility. There are diverse hydrogen bonding pair choices that could be used in HOFs construction, including identical or nonidentical hydrogen bonding donors and acceptors. For organic groups acting as hydrogen bonding units, species like carboxylic acid, amide, 2,4-diaminotriazine, and imidazole, etc., are commonly used for the formation of hydrogen bonding interaction. Compared with other organic frameworks, like Covalent organic framework, COF and Metal–organic framework, MOF, the binding force of HOFs is relatively weaker, and the activation of HOFs is more difficult than other frameworks, while the reversibility of hydrogen bonds guarantees a high crystallinity of the materials. Though the stability and pore size expansion of HOFs has potential problems, HOFs still show strong potential for applications in differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |