Plasticizer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its


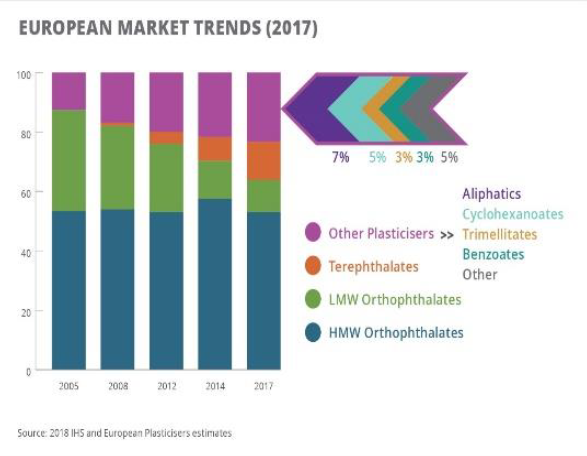 Plasticizers for polymers are either liquids with low volatility or solids. According to 2017 data, the total global market for plasticizers was 7.5 million metric tonnes. In North America the 2017 volume was ~1.01 million metric tonnes and in Europe the figure was 1.35 million metric tonnes, split between various end-use applications with a chemical type trend moving to higher molecular weight (HMW) orthophthalates and alternative types following regulatory issues concerning lower molecular weight (LMW) orthophthalates.
Almost 90% of polymer plasticizers, most commonly phthalate
Plasticizers for polymers are either liquids with low volatility or solids. According to 2017 data, the total global market for plasticizers was 7.5 million metric tonnes. In North America the 2017 volume was ~1.01 million metric tonnes and in Europe the figure was 1.35 million metric tonnes, split between various end-use applications with a chemical type trend moving to higher molecular weight (HMW) orthophthalates and alternative types following regulatory issues concerning lower molecular weight (LMW) orthophthalates.
Almost 90% of polymer plasticizers, most commonly phthalate


2,2,2-trinitroethyl 2-nitroxyethyl ether and a method of preparation - US Patent 4745208
/ref>
Plasticisers Information CentreDIDP
DINPDBPBBP
DEHP
Risk Assessment Reports by the European Chemicals Bureau (ECB). {{Authority control Cement Concrete Concrete admixtures
viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, and/or to decrease friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding (motion), sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative la ...
during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticizers are commonly added to polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s such as plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
s and rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, a ...
, either to facilitate the handling of the raw material during fabrication, or to meet the demands of the end product's application. For example, plasticizers are commonly added to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which otherwise is hard and brittle, to make it soft and pliable; which makes it suitable for products such as shower curtains
A shower is a place in which a person bathes under a spray of typically warm or hot water. Indoors, there is a drain in the floor. Most showers have temperature, spray pressure and adjustable showerhead nozzle. The simplest showers have a ...
, vinyl flooring, clothing, bags, flexible plastic tubing, and electric wire insulation/coating.
Plasticizers are also often added to concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most ...
formulations to make them more workable and fluid for pouring, thus allowing the water contents to be reduced. Similarly, they are often added to clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
s, stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
, solid rocket fuel, and other pastes prior to molding and forming. For these applications, plasticizers largely overlap with dispersants.
For polymers


 Plasticizers for polymers are either liquids with low volatility or solids. According to 2017 data, the total global market for plasticizers was 7.5 million metric tonnes. In North America the 2017 volume was ~1.01 million metric tonnes and in Europe the figure was 1.35 million metric tonnes, split between various end-use applications with a chemical type trend moving to higher molecular weight (HMW) orthophthalates and alternative types following regulatory issues concerning lower molecular weight (LMW) orthophthalates.
Almost 90% of polymer plasticizers, most commonly phthalate
Plasticizers for polymers are either liquids with low volatility or solids. According to 2017 data, the total global market for plasticizers was 7.5 million metric tonnes. In North America the 2017 volume was ~1.01 million metric tonnes and in Europe the figure was 1.35 million metric tonnes, split between various end-use applications with a chemical type trend moving to higher molecular weight (HMW) orthophthalates and alternative types following regulatory issues concerning lower molecular weight (LMW) orthophthalates.
Almost 90% of polymer plasticizers, most commonly phthalate ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s, are used in PVC, giving this material improved flexibility and durability. The majority is used in films and cables.
Mechanism of action
It was commonly thought that plasticizers work by embedding themselves between the chains ofpolymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s, spacing them apart (increasing the "free volume"), or swelling them and thus significantly lowering the glass transition temperature for the plastic and making it softer; however it was later shown that the free volume explanation could not account for all of the effects of plasticization. The classical picture on the mobility of polymer chain is more complex in the presence of plasticizer than that drawn by Fox&Flory for simple polymer chain. The molecules of plasticizer take control over mobility of the chain, and polymer chain does not show an increase of the free volume around polymer ends; in the case that the plasticizer/ water creates hydrogen bonds with hydrophilic parts of polymer, the associated free volume can be decreased.
For plastics such as PVC, the more plasticizer added, the lower their cold flex temperature will be. Plastic items containing plasticizers can exhibit improved flexibility and durability. Plasticizers can become available for exposure due to migration and abrasion of the plastic since they are not bound to the polymer matrix. The " new car smell" is often attributed to plasticizers or their degradation products. However, multiple studies on the makeup of the smell do not find phthalates in appreciable amounts, likely due to their extremely low volatility and vapor pressure.
The effect of plasticizers on elastic modulus is dependent on both temperature and plasticizer concentration. Below a certain concentration, referred to as the crossover concentration, a plasticizer can increase the modulus of a material. The material's glass transition temperature will decrease however, at all concentrations. In addition to a crossover concentration a crossover temperature exists. Below the crossover temperature the plasticizer will also increase the modulus.

Selection
Over the last 60 years more than 30,000 different substances have been evaluated for their suitability as polymer plasticizers. Of these, only a small number – approximately 50 – are today in commercial use.Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
plasticizers are selected based upon cost-performance evaluation. The rubber compounder must evaluate ester plasticizers for compatibility, processibility, permanence and other performance properties. The wide variety of ester chemistries that are in production include sebacates, adipates, terephthalates, dibenzoates, glutarate
Glutaric acid is the organic compound with the formula C3H6(COOH)2 . Although the related "linear" dicarboxylic acids adipic and succinic acids are water-soluble only to a few percent at room temperature, the water-solubility of glutaric acid is ...
s, phthalates, azelates, and other specialty blends. This broad product line provides an array of performance benefits required for the many elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic ...
applications such as tubing and hose products, flooring, wall-coverings, seals and gaskets, belts, wire and cable, and print rolls.
Low to high polarity esters provide utility in a wide range of elastomers including nitrile, polychloroprene, EPDM, chlorinated polyethylene, and epichlorohydrin. Plasticizer-elastomer interaction is governed by many factors such as solubility parameter, molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
, and chemical structure. Compatibility and performance attributes are key factors in developing a rubber formulation for a particular application.
Plasticizers used in PVC and other plastics are often based on ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s of polycarboxylic acids with linear or branched aliphatic alcohols of moderate chain length. These compounds are selected on the basis of many critieria including low toxicity, compatibility with the host material, nonvolatility, and expense. Phthalate esters of straight-chain and branched-chain alkyl alcohols meet these specifications and are common plasticizers. Ortho-phthalate esters have traditionally been the most dominant plasticizers, but regulatory concerns have led to the move away from classified substances to non-classified which includes high molecular weight ortho-phthalates and other plasticisers, especially in Europe.
Antiplasticizers
Antiplasticizers are polymer additives that have effect opposite to those of plasticizers. They increase the modulus while decreasing the glass transition temperature.Safety and toxicity
Substantial concerns have been expressed over the safety of some polymer plasticizers, especially because some low molecular weight ortho-phthalates have been classified as potentialendocrine disruptor
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause ...
s with some developmental toxicity reported.
Common polymer plasticizers
Ortho phthalates
* Phthalate-based plasticizers are used in situations where good resistance to water and oils is required. Some common phthalate plasticizers are: *Low Molecular Weight Ortho Phthalates ** Dimethyl phthalate (DMP), used in fragrances, as an insect repellent, and in several industrial processes as a solvent/carrier ** Diethyl phthalate (DEP), used in fragrances as a carrier and extender/fixative ** Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) ** Di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP), used for cellulose plastics, food wraps, adhesives, perfumes, and cosmetics - about a third of nail polishes, glosses, enamels, and hardeners contain it, together with someshampoo
Shampoo () is a hair care product, typically in the form of a viscous liquid, that is used for cleaning hair. Less commonly, shampoo is available in solid bar format. Shampoo is used by applying it to wet hair, massaging the product into th ...
s, sunscreens, skin emollients, and insect repellents
** Butyl benzyl phthalate (benzyl butyl phthalate, BBzP) is found in vinyl tiles, traffic cones, food conveyor belts, artificial leather, and plastic foams
**Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, diethylhexyl phthalate, diisooctyl phthalate, DEHP; incorrectly — dioctyl phthalate, DIOP) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2C8H17)2. DEHP is the most common member of the cl ...
(DEHP) also commonly known as (dioctyl phthalate, DOP or diethylhexyl phthalate), historically used in flooring materials, medical devices, myriad consumer products, and high explosives, such as Semtex. DEHP was the most common plasticizer for decades and still holds that title globally even as it has largely been replaced now with higher molecular weight phthalates and alternatives in the US and Europe
*High Molecular Weight Ortho Phthalates
** Diisononyl phthalate (DINP), used in flooring materials, found in garden hoses, shoes, toys, and building materials
** Bis(2-propylheptyl) phthalate (DPHP), used in cables, wires and roofing materials
** Diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP), used for insulation of wires and cables, car undercoating, shoes, carpets, pool liners
** Diisoundecyl phthalate (DIUP), used for insulation of wires and cables, car undercoating, shoes, carpets, pool liners. Good high temperature and outdoor weathering performance
** Ditridecyl phthalate (DTDP) is the highest molecular weight phthalate plasticizer, providing greater performance at high temperature. It is the preferred plasticizer for automotive cable and wire application.
Terephthalates
*Terephthalates are isomeric with ortho phthalates but have proven to have cleaner toxicological results due to their inability to form stable monoesters during hydrolysis and metabolic breakdown. ** Bis(2-ethylhexyl)terephthalate (DEHT, Dioctyl terephthalate, DOTP) (Eastman Chemical Company Trademark: Eastman 168™), used as a replacement for DEHP and DINP **Diisopentyl terephthalate (DiPT)(Evonik Industries Trademark: ELATUR® DPT), used as a replacement for DBP and DiBP **Dibutyl terephthalate (DBT)(Eastman Chemical Trademark: Eastman Effusion™), used as a replacement for DBP and DiBPTrimellitates
*Trimellitate
Trimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СООН)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, trimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2, ...
s are used in automobile interiors and other applications where resistance to high temperature is required. They have extremely low volatility.
**Tri-(2-ethylhexyl)trimellitate
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
(TEHTM) (TOTM, Trioctyl Trimellitate plasticizer)
**Tri-(isononyl)trimellitate
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
(TINTM)
**Tri-(isodecyl)trimellitate
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
(TIDTM)
**Tri-(isotridecyl)trimellitate
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cy ...
(TITDTM)
Adipates & Sebacates
* Adipate-based plasticizers are used for low-temperature or resistance toultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
light. An example is:
**Bis(2-ethylhexyl)adipate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate or DEHA is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CO2C8H17)2. It is the diester of 2-ethylhexanol and adipic acid. It is a colorless oily liquid.
DEHA is sometimes called "dioctyl adipate", incorrectly. Another na ...
(DEHA, dioctyl adipate plasticizer)
* Sebacate- based plasticizers provide excellent compatibility with a range of plastic materials and synthetic rubbers (specifically nitrile rubber and neoprene), superior properties at low temperatures, and good oil resistivity. Some examples are:
** Dibutyl sebacate (DBS)
**Di-(2-ethylhexyl)sebacate
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
, Di-octyl Sebacate (or DOS plasticizer)
Organophosphates
* Organophosphates include the following: ** Tricresyl phosphate (TCP) **2-ethylhexyldiphenyl phosphate **Tri-2-ethylhexyl phosphateOther
* 1,2-Cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid diisononyl ester (BASF Trademark: Hexamoll DINCH) *Bis(2-ethylhexyl) cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylate (Hanwha Trademark: Eco-DEHCH) *Alkyl sulphonic acid phenyl ester (ASE). (Lanxess Chemical Trademark: Mesamoll) *Triethylene glycol di-2ethylhexanoate (Eastman Chemical Trademark: Eastman TEG-EH) Bio-based plasticizers have been investigated, such asglycerol triacetate
Triacetin, is the organic compound with the formula . It is classified as a triglyceride, i.e., the triester of glycerol. It is a colorless, viscous, and odorless liquid with a high boiling point and a low melting point. It has a mild, sweet tast ...
(Triacetin) and acetyltributylcitrate
Acetyltributylcitrate is an organic compound that is used as a plasticizer. As such, it is a potential replacement of DEHP and DINP. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is found in nail polish and other cosmetics. It is ...
. They are used in niche applications. Epoxidized soybean oil is used broadly as a secondary plasticizer in many vinyl applications.
*Note: Bisphenol A, or BPA, is not a plasticizer, although it is often wrongly described as one.
Plasticizers for inorganic materials
Concrete
In theconcrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most ...
technology, plasticizers and superplasticizers are also called high range water reducers. When added to concrete mixtures, they confer a number of properties including improved workability and strength. The strength of concrete is inversely proportional to the amount of water added, i.e., the water-cement (w/c) ratio. In order to produce stronger concrete, less water is added (without "starving" the mix), which makes the concrete mixture less workable and difficult to mix, necessitating the use of plasticizers, water reducers, superplasticizers, fluidizer or dispersants.
Plasticizers are also often used when pozzolanic ash
Pozzolana or pozzuolana ( , ), also known as pozzolanic ash ( la, pulvis puteolanus), is a natural siliceous or siliceous- aluminous material which reacts with calcium hydroxide in the presence of water at room temperature (cf. pozzolanic reaction ...
is added to concrete to improve strength. This method of mix proportioning is especially popular when producing high-strength concrete and fiber-reinforced concrete.
Adding 1-2% plasticizer per unit weight of cement is usually sufficient. Adding an excessive amount of plasticizer will result in excessive segregation of concrete and is not advisable. Depending on the particular chemical used, use of too much plasticizer may result in a retarding effect.
Plasticizers are commonly manufactured from lignosulfonates, a by-product from the paper industry. Superplasticizers have generally been manufactured from sulfonated Aromatic sulfonation is an organic reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an arene is replaced by a sulfonic acid functional group in an electrophilic aromatic substitution. Aryl sulfonic acids are used as detergents, dye, and drugs.
Stoichiomet ...
naphthalene condensate or sulfonated melamine formaldehyde, although newer products based on polycarboxylic ethers are now available. Traditional lignosulfonate-based plasticisers, naphthalene and melamine sulfonate-based superplasticisers disperse the flocculated cement particles through a mechanism of electrostatic repulsion (see colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others exten ...
). In normal plasticisers, the active substances are adsorbed on to the cement particles, giving them a negative charge, which leads to repulsion between particles. Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity ...
, naphthalene, and melamine sulfonate superplasticisers are organic polymers. The long molecules wrap themselves around the cement particles, giving them a highly negative charge so that they repel each other.
Polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer (PCE) or just polycarboxylate (PC), work differently from sulfonate-based superplasticizers, giving cement dispersion by steric stabilisation. This form of dispersion is more powerful in its effect and gives improved workability retention to the cementitious mix.
Stucco
Plasticizers can be added to wallboardstucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
mixtures to improve workability. In order to reduce the energy consumed drying wallboard, less water is added, which makes the gypsum mixture very unworkable and difficult to mix, necessitating the use of plasticizers, water reducers, or dispersants. Some studies also show that too much lignosulfonate dispersant could result in a set-retarding effect. Data showed that amorphous crystal formations occurred that detracted from the mechanical needle-like crystal interaction in the core, preventing a stronger core. The sugars, chelating agents in lignosulfonates such as aldonic acids and extractive compounds are mainly responsible for set retardation. These low range water reducing dispersants are commonly manufactured from lignosulfonates, a by-product from the paper industry.
High range superplasticizers (dispersants) have generally been manufactured from sulfonated Aromatic sulfonation is an organic reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an arene is replaced by a sulfonic acid functional group in an electrophilic aromatic substitution. Aryl sulfonic acids are used as detergents, dye, and drugs.
Stoichiomet ...
naphthalene condensate, although polycarboxylic ethers represent more modern alternatives. Both of these high range water reducers are used at 1/2 to 1/3 of the lignosulfonate types.
Traditional lignosulfonate and naphthalene sulfonate-based plasticisers disperse the flocculated gypsum particles through a mechanism of electrostatic repulsion (see Colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others exten ...
). In normal plasticisers, the active substances are adsorbed on to the gypsum particles, giving them a negative charge, which leads to repulsion between particles. Lignin and naphthalene sulfonate plasticizers are organic polymers. The long molecules wrap themselves around the gypsum particles, giving them a highly negative charge so that they repel each other.
Energetic materials
Energetic material Energetic materials are a class of material with high amount of stored chemical energy that can be released.
Typical classes of energetic materials are e.g. explosives, pyrotechnic compositions, propellants (e.g. smokeless gunpowders and rocket f ...
pyrotechnic compositions, especially solid rocket propellants and smokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared to ...
s for guns, often employ plasticizers to improve physical properties of the propellant binder or of the overall propellant, to provide a secondary fuel, and ideally, to improve specific energy yield (e.g. specific impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is ...
, energy yield per gram of propellant, or similar indices) of the propellant. An energetic plasticizer improves the physical properties of an energetic material while also increasing its specific energy yield. Energetic plasticizers are usually preferred to non-energetic plasticizers, especially for solid rocket propellants. Energetic plasticizers reduce the required mass of propellant, enabling a rocket vehicle to carry more payload or reach higher velocities than would otherwise be the case. However, safety or cost considerations may demand that non-energetic plasticizers be used, even in rocket propellants. The solid rocket propellant used to fuel the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
solid rocket booster employs HTPB, a synthetic rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About 32-million metric tons of rubbers are produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubbe ...
, as a non-energetic secondary fuel.
Plasticizers for energetic materials
Here are some energetic plasticizers used in rocket propellants andsmokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared to ...
s:
* Nitroglycerine (NG, aka "nitro", glyceryl trinitrate)
* Butanetriol trinitrate (BTTN)
* Dinitrotoluene (DNT)
* Trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN, aka Metriol trinitrate, METN)
* Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN, less commonly DEGN)
* Triethylene glycol dinitrate (TEGDN, less commonly TEGN)
* Bis(2,2-dinitropropyl)formal (BDNPF)
* Bis(2,2-dinitropropyl)acetal (BDNPA)
*2,2,2-Trinitroethyl 2-nitroxyethyl ether
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline ...
(TNEN)
Due to the secondary alcohol groups, NG and BTTN have relatively low thermal stability. TMETN, DEGDN, BDNPF, and BDNPA have relatively low energies. NG and DEGDN have relatively high vapor pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phase ...
./ref>
See also
* Conservation and restoration of plastic objectsReferences
External links
Plasticisers Information Centre
DINP
DEHP
Risk Assessment Reports by the European Chemicals Bureau (ECB). {{Authority control Cement Concrete Concrete admixtures