|
Baguette Cut
A diamond cut is a style or design guide used when shaping a diamond for polishing such as the Brilliant (diamond cut), brilliant cut. Cut does not refer to shape (pear, oval), but the symmetry, proportioning and polish of a diamond. The cut of a diamond greatly affects a diamond's brilliance; this means if it is cut poorly, it will be less luminous. In order to best use a diamond gemstone's material properties of diamond, material properties, a number of different diamond cuts have been developed. A diamond cut constitutes a more or less symmetrical arrangement of facets, which together modify the shape and appearance of a diamond crystal. Diamond cutting, Diamond cutters must consider several factors, such as the shape and size of the crystal, when choosing a cut. The practical history of diamond cuts can be traced back to the Middle Ages, while their theoretical basis was not developed until the turn of the 20th century. Design, creation and innovation continue to the present d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard conditions for temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Of Ghor
Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad ibn Sam ( fa, معز الدین محمد بن سام), also Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri ( fa, معز الدین محمد غوری) (1144 – March 15, 1206), commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor, also Ghūr, or Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri, was a ruler from the Ghurid dynasty based in what is today Afghanistan who ruled from 1173 CE to 1206 CE. He extended the Ghurid dominions eastwards and laid the foundation of Islamic rule in the Indian Subcontinent, which lasted after him for nearly half a millennium. During his joint reign with his brother Ghiyasuddin Ghori (r. c. 1163–1203), the Ghurids reached the epogee of their territorial expansion. During his early military career as a prince and governor of the southern tract of the Ghurid Empire, Muhammad subjugated the Oghuz tribe after multiple raids and captured Ghazna where he was crowned by his brother Ghiyasuddin Ghori, who was ruling from his capital Firozkoh since 1163. Muhammad of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,Statistics Belgium; ''Loop van de bevolking per gemeente'' (Excel file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, . Retrieved 1 November 2017. it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of around 1,200,000 people, it is the second-largest metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaif
Scaif is a polishing wheel infused with a mixture of olive oil and diamond dust used in the diamond cutting industry. It was invented in 1456 by Lodewyk van Bercken. With the scaif, it became possible to polish all the facets of the diamond symmetrically at angles that reflected the light best. This invention revolutionized the diamond cutting industry and correspondingly, much increased the popularity of diamonds. The scaif consists of a hard disk, parallel to the floor. The disk looks like and is rotated in the same way as a potter's wheel. On the top surface a film of olive oil and diamond dust is placed. Surrounding the disk is a circular frame to catch the oil that is spun off as the disk is rotated. Hovering just above the surface of the disk is a mechanical arm to hold the diamond. It can be finely adjusted, to move the diamond into the exact position needed for polishing the facets. As the facets are polished more diamond dust is produced, replenishing the supply. Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the country by population. The area of the whole city amounts to more than 13,840 hectares (138.4 km2; 53.44 sq miles), including 1,075 hectares off the coast, at Zeebrugge (from , meaning 'Bruges by the Sea'). The historic city centre is a prominent World Heritage Site of UNESCO. It is oval in shape and about 430 hectares in size. The city's total population is 117,073 (1 January 2008),Statistics Belgium; ''Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008'' (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. "''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France, and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings", irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval duchy of Brabant and the medieval county of Loon, where the modern national identity and culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "Vlamingen" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both the peoples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodewyk Van Berken
Lodewyk van Bercken (also known in French as ''Louis de Berquem'') was a mid- to late-15th century Flemish jeweller and diamond cutter, renowned in the industry for inventing the scaif. The device revolutionized the diamond cutting industry and contributed to increased popularity of diamonds. Van Bercken was born in Bruges. He is credited with inventing the scaif, a polishing wheel infused with a mixture of olive oil and diamond dust. With the scaif, it became possible to polish all the facets of the diamond symmetrically at angles that best reflected the light. Charles the Bold Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy became the patron of van Bercken and in the 1470s commissioned him to cut a 137 carat (27.4 g) stone that later became known as the Florentine Diamond. Van Bercken experimented with three diamonds belonging to Charles the Bold. One stone was the Beau Sancy, another became the property of Pope Sixtus V, and the third was given by Charles to Louis XI. Later Charles the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
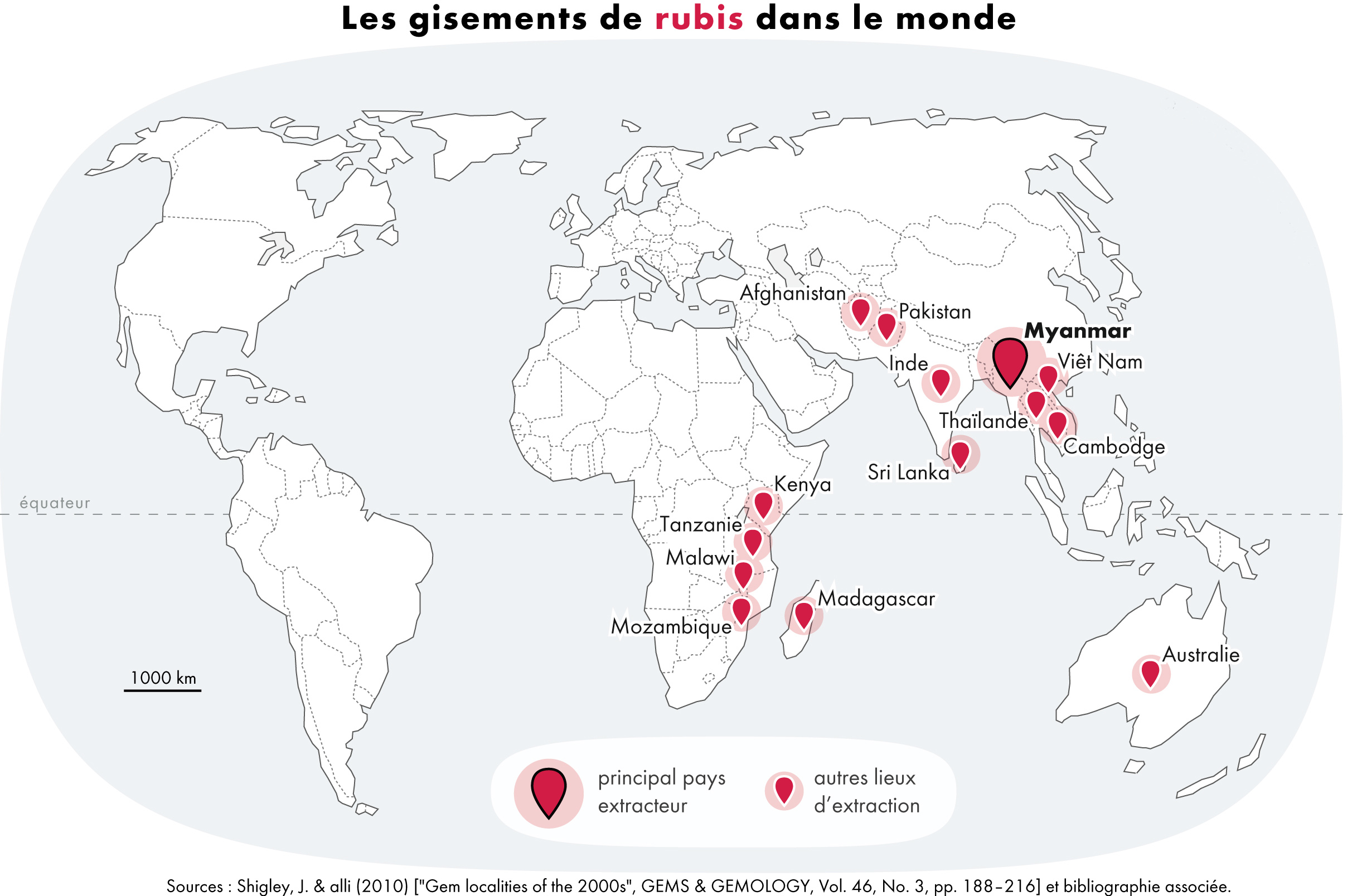
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamantine Lustre
Lustre (British English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhibit unus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culet
{{inline, date=November 2022 In gemology, a culet is a flat face on the bottom of a gemstone. During the 14th century, after the adoption of the table cut, a further facet was added to the bottom of the cut parallel to the surface of the table. The term used for these bottom facets derives from the Latin word for bottom, ''culus''. The culet is added largely to protect the integrity of the gemstone. On a diamond, the cleavage plane runs parallel to the octahedral faces, and so any damage to the tip of the diamond could cause a split up the entire length of the pavilion. With other gemstones that are not subject to cleavage, the culet is added to protect the fragility of the pointed tip. The culet has remained optional on many diamond cuts up to the present day, and was omitted from Marcel Tolkowsky's original designs for the round brilliant A brilliant is a diamond or other gemstone cut in a particular form with numerous facets so as to have exceptional brilliance. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)