|
Aspartokinase
Aspartate kinase or aspartokinase (AK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of the amino acid aspartate. This reaction is the first step in the biosynthesis of three other amino acids: methionine, lysine, and threonine, known as the "aspartate family". Aspartokinases are present only in microorganisms and plants, but not in animals, which must obtain aspartate-family amino acids from their diet. Consequently, methionine, lysine and threonine are essential amino acids in animals. Nomenclature The generic abbreviation for aspartokinases is AK. However, the nomenclature for aspartokinase genes and proteins varies considerable among species. The main aspatokinases are ''lysC'' (''Bacillus subtilis'', ''Escherichia coli'' and many other bacteria), ''ask'' (''Mycobacterium bovis'', ''Thermus thermophilus''), ''AK1''–''AK3'' (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), ''FUB3'' (''Fusarium'' and ''Gibberella'') and ''HOM3'' (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''). Additionally, ''apk'' is a synonym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LysC
LysC is a prokaryotic aspartokinase involved in the biosynthesis of the amino acid lysine. It is found in a variety of bacteria, including ''Bacillus subtilis'', ''Escherichia coli'' and ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''. It is notable for containing a riboswitch, a structure in its messenger RNA that prevents its translation when bound to lysine. Such lysine riboswitch thus acts as a mechanism of negative feedback Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by .... References {{reflist Bacterial enzymes EC 2.7.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibition
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isozyme
In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different ''K''M values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage. In many cases, isozymes are encoded by homologous genes that have diverged over time. Strictly speaking, enzymes with different amino acid sequences that catalyse the same reaction are isozymes if encoded by different genes, or allozymes if encoded by different alleles of the same gene; the two terms are often used interchangeably. Introduction Isozymes were first described by R. L. Hunter and Clement Markert (1957) who defined them as ''different variants of the same enzyme having identical functions and present in the same individual''. This definition encompasses (1) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Regulation
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site. The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site'' or ''regulatory site''. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change and/or a change in protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as ''allosteric activators'', whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called ''allosteric inhibitors''. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such as feedback from downstream products or feedforward from upstream substrates. Long-range allostery is especially important in cell signaling. Allosteric regulation is also particularly important in the cell's ability to adjust enzyme activity. The term ''allostery'' comes from the Ancient Greek ''allos'' (), "other", and ''stereos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
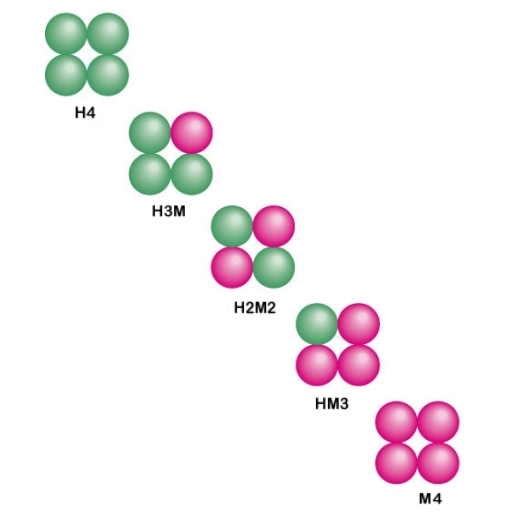
Morpheein
Morpheeins are proteins that can form two or more different homo-oligomers (morpheein forms), but must come apart and change shape to convert between forms. The alternate shape may reassemble to a different oligomer. The shape of the subunit dictates which oligomer is formed. Each oligomer has a finite number of subunits (stoichiometry). Morpheeins can interconvert between forms under physiological conditions and can exist as an equilibrium of different oligomers. These oligomers are physiologically relevant and are not misfolded protein; this distinguishes morpheeins from prions and amyloid. The different oligomers have distinct functionality. Interconversion of morpheein forms can be a structural basis for allosteric regulation, an idea noted many years ago, and later revived. A mutation that shifts the normal equilibrium of morpheein forms can serve as the basis for a conformational disease. Features of morpheeins can be exploited for drug discovery. The dice image (F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacteria, bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 micrometre, μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their Homology (biology), homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley body, Berkeley bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibberella
''Gibberella'' is a genus of fungi in the family Nectriaceae. In 1926, Japanese scientists observed that rice plants infected with ''Gibberella'' had abnormally long stems (" foolish seedling disease"). A substance, gibberellin, was derived from this fungus. Gibberellin is a plant hormone that promotes cell elongation, flower formation, and seedling growth. Species *'' Gibberella acerina'' *'' Gibberella acervalis'' *'' Gibberella acuminata'' *''Gibberella africana'' *''Gibberella agglomerata'' *'' Gibberella atrofuliginea'' *''Gibberella atrorufa'' *''Gibberella australis'' *'' Gibberella avenacea'' *'' Gibberella baccata'' *''Gibberella bambusae'' *''Gibberella bolusiellae'' *''Gibberella bresadolae'' *''Gibberella briosiana'' *''Gibberella butleri'' *''Gibberella buxi'' *''Gibberella cantareirensis'' *''Gibberella cicatrisata'' *''Gibberella circinata'' *''Gibberella coffeae'' *''Gibberella coronicola'' *'' Gibberella creberrima'' *''Gibberella culmicola'' *''Gibberella c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusarium
''Fusarium'' is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these ''Fusarium'' species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless (some existing on the skin as commensal members of the skin flora), some ''Fusarium'' species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals. The name of ''Fusarium'' comes from Latin ''fusus'', meaning a spindle. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the genus is complex. A number of different schemes have been used, and up to 1,000 species have been identified at times, with approaches varying between wide and narrow concepts of speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |