Isozyme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
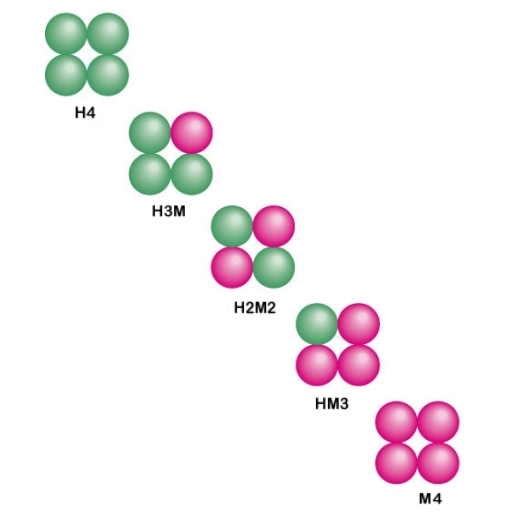
 1.) The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer made of two different sub-units, the H-form and the M-form. These combine in different combinations depending on the tissue:
2.) Isoenzymes of creatine phosphokinase: Creatine kinase (CK) or creatine phosphokinase (CPK) catalyses the interconversion of phospho creatine to creatine .
CPK exists in 3 isoenzymes. Each isoenzymes is a dimer of 2 subunits M (muscle), B (brain) or both
3.) Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase: Six isoenzymes have been identified. The enzyme is a monomer, the isoenzymes are due to the differences in the carbohydrate content (sialic acid residues). The most important ALP isoenzymes are α1-ALP, α2-heat labile ALP, α2-heat stable ALP, pre-β ALP and γ-ALP. Increase in α2-heat labile ALP suggests hepatitis whereas pre-β ALP indicates bone diseases.
1.) The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer made of two different sub-units, the H-form and the M-form. These combine in different combinations depending on the tissue:
2.) Isoenzymes of creatine phosphokinase: Creatine kinase (CK) or creatine phosphokinase (CPK) catalyses the interconversion of phospho creatine to creatine .
CPK exists in 3 isoenzymes. Each isoenzymes is a dimer of 2 subunits M (muscle), B (brain) or both
3.) Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase: Six isoenzymes have been identified. The enzyme is a monomer, the isoenzymes are due to the differences in the carbohydrate content (sialic acid residues). The most important ALP isoenzymes are α1-ALP, α2-heat labile ALP, α2-heat stable ALP, pre-β ALP and γ-ALP. Increase in α2-heat labile ALP suggests hepatitis whereas pre-β ALP indicates bone diseases.
Allozyme Electrophoresis Techniques
– a complete guide to starch gel electrophoresis
Development of new isozyme specific therapeutics
– Fatty Acid Dioxygenases and Eicosanoid Hormones (Estonia) Enzymes Biochemistry
biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology ...
, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. different ''K''M values), or are regulated differently. They permit the fine-tuning of metabolism to meet the particular needs of a given tissue or developmental stage.
In many cases, isozymes are encoded by homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
genes that have diverged over time. Strictly speaking, enzymes with different amino acid sequences that catalyse the same reaction are isozymes if encoded by different genes, or allozymes if encoded by different allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s of the same gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
; the two terms are often used interchangeably.
Introduction
Isozymes were first described by R. L. Hunter and Clement Markert (1957) who defined them as ''different variants of the same enzyme having identical functions and present in the same individual''. This definition encompasses (1) enzyme variants that are the product of different genes and thus represent differentloci
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** '' Locus Award ...
(described as ''isozymes'') and (2) enzymes that are the product of different alleles of the same gene (described as ''allozymes'').
Isozymes are usually the result of gene duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene ...
, but can also arise from polyploidisation or nucleic acid hybridization. Over evolutionary time, if the function of the new variant remains ''identical'' to the original, then it is likely that one or the other will be lost as mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s accumulate, resulting in a pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are ...
. However, if the mutations do not immediately prevent the enzyme from functioning, but instead modify either its function, or its pattern of expression, then the two variants may both be favoured by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
and become specialised to different functions. For example, they may be expressed at different stages of development or in different tissues.
Allozymes may result from point mutations or from insertion-deletion ( indel) events that affect the coding sequence of the gene. As with any other new mutations, there are three things that may happen to a new allozyme:
* It is most likely that the new allele will be non-functional—in which case it will probably result in low fitness and be removed from the population by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
.
* Alternatively, if the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
residue that is changed is in a relatively unimportant part of the enzyme (e.g., a long way from the active site), then the mutation may be selectively neutral and subject to genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
.
* In rare cases, the mutation may result in an enzyme that is more efficient, or one that can catalyse a slightly different chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and break ...
, in which case the mutation may cause an increase in fitness, and be favoured by natural selection.
Examples
An example of an isozyme isglucokinase
Glucokinase () is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role ...
, a variant of hexokinase which is not inhibited by glucose 6-phosphate. Its different regulatory features and lower affinity for glucose (compared to other hexokinases), allow it to serve different functions in cells of specific organs, such as control of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
release by the beta cells of the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
, or initiation of glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
synthesis by liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
cells. Both these processes must only occur when glucose is abundant.

 1.) The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer made of two different sub-units, the H-form and the M-form. These combine in different combinations depending on the tissue:
2.) Isoenzymes of creatine phosphokinase: Creatine kinase (CK) or creatine phosphokinase (CPK) catalyses the interconversion of phospho creatine to creatine .
CPK exists in 3 isoenzymes. Each isoenzymes is a dimer of 2 subunits M (muscle), B (brain) or both
3.) Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase: Six isoenzymes have been identified. The enzyme is a monomer, the isoenzymes are due to the differences in the carbohydrate content (sialic acid residues). The most important ALP isoenzymes are α1-ALP, α2-heat labile ALP, α2-heat stable ALP, pre-β ALP and γ-ALP. Increase in α2-heat labile ALP suggests hepatitis whereas pre-β ALP indicates bone diseases.
1.) The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer made of two different sub-units, the H-form and the M-form. These combine in different combinations depending on the tissue:
2.) Isoenzymes of creatine phosphokinase: Creatine kinase (CK) or creatine phosphokinase (CPK) catalyses the interconversion of phospho creatine to creatine .
CPK exists in 3 isoenzymes. Each isoenzymes is a dimer of 2 subunits M (muscle), B (brain) or both
3.) Isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase: Six isoenzymes have been identified. The enzyme is a monomer, the isoenzymes are due to the differences in the carbohydrate content (sialic acid residues). The most important ALP isoenzymes are α1-ALP, α2-heat labile ALP, α2-heat stable ALP, pre-β ALP and γ-ALP. Increase in α2-heat labile ALP suggests hepatitis whereas pre-β ALP indicates bone diseases.
Distinguishing isozymes
Isozymes (and allozymes) are variants of the same enzyme. Unless they are identical in their biochemical properties, for example their substrates and enzyme kinetics, they may be distinguished by abiochemical assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a ...
. However, such differences are usually subtle, particularly between ''allozymes'' which are often neutral variants. This subtlety is to be expected, because two enzymes that differ significantly in their function are unlikely to have been identified as ''isozymes''.
While isozymes may be almost identical in function, they may differ in other ways. In particular, amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
substitutions that change the electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respecti ...
of the enzyme are simple to identify by gel electrophoresis, and this forms the basis for the use of isozymes as molecular markers. To identify isozymes, a crude protein extract is made by grinding animal or plant tissue with an extraction buffer, and the components of extract are separated according to their charge by gel electrophoresis. Historically, this has usually been done using gels made from potato starch, but acrylamide gels provide better resolution.
All the proteins from the tissue are present in the gel, so that individual enzymes must be identified using an assay that links their function to a staining reaction. For example, detection can be based on the localised precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
of soluble indicator dyes such as tetrazolium salts
The formazans are compounds of the general formula -N=N-C(R')=N-NH-R" formally derivatives of formazan 2NN=CHN=NH unknown in free form.
Formazan dyes are artificial chromogenic products obtained by reduction of tetrazolium salts by dehydrogenase ...
which become insoluble when they are reduced by cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the orde ...
such as NAD or NADP, which generated in zones of enzyme activity. This assay method requires that the enzymes are still functional after separation (native gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF ...
), and provides the greatest challenge to using isozymes as a laboratory technique.
Isoenzymes differ in kinetics (they have different ''K''M and Vmax values).
Isozymes and allozymes as molecular markers
Population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and pop ...
is essentially a study of the causes and effects of genetic variation within and between populations, and in the past, isozymes have been amongst the most widely used molecular markers for this purpose. Although they have now been largely superseded by more informative DNA-based approaches (such as direct DNA sequencing, single nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellites), they are still among the quickest and cheapest marker systems to develop, and remain () an excellent choice for projects that only need to identify low levels of genetic variation, e.g. quantifying mating systems.
Other major examples
*Thecytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compo ...
isozymes play important roles in metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
and steroidogenesis.
*The multiple forms of phosphodiesterase also play major roles in various biological processes. Although more than one form of these enzymes have been found in individual cells, these isoforms of the enzyme are unequally distributed in the various cells of an organism. From the clinical standpoint they have been found to be selectively activated and inhibited, an observation which has led to their use in therapy.
References
* * {{cite journal , last1 = Weiss , first1 = B. , last2 = Hait , first2 = W.N. , year = 1977 , title = Selective cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents , journal = Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. , volume = 17 , pages = 441–477 , doi=10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.002301 , pmid = 17360 * Wendel, JF, and NF Weeden. 1990. "Visualisation and interpretation of plant isozymes." pp. 5–45 in D. E. Soltis and P. S. Soltis, eds. ''Isozymes in plant biology.'' Chapman and Hall, London. * Weeden, NF, and JF Wendel. 1990. "Genetics of plant isozymes". pp. 46–72 in D. E. Soltis and P. S. Soltis, eds. ''Isozymes in plant biology.'' Chapman and Hall, London * Crawford, DJ. 1989. "Enzyme electrophoresis and plant systematics". pp. 146–164 in D. E. Soltis and P. S. Soltis, eds. ''Isozymes in plant biology.'' Dioscorides, Portland, Oregon. *Hamrick, JL, and MJW Godt. 1990. "Allozyme diversity in plant species". pp. 43–63 in A. H. D. Brown, M. T. Clegg, A. L. Kahler and B. S. Weir, eds. ''Plant Population Genetics, Breeding, and Genetic Resources.'' Sinauer, Sunderland *Biochemistry by jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer (Intro taken from this textbook) ;SpecificExternal links
Allozyme Electrophoresis Techniques
– a complete guide to starch gel electrophoresis
Development of new isozyme specific therapeutics
– Fatty Acid Dioxygenases and Eicosanoid Hormones (Estonia) Enzymes Biochemistry