|
Arylsulfatase
Arylsulfatase (EC 3.1.6.1, sulfatase, nitrocatechol sulfatase, phenolsulfatase, phenylsulfatase, ''p''-nitrophenyl sulfatase, arylsulfohydrolase, 4-methylumbelliferyl sulfatase, estrogen sulfatase) is a type of sulfatase enzyme with systematic name ''aryl-sulfate sulfohydrolase''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : an aryl sulfate + H2O \rightleftharpoons a phenol + sulfate Types include: *Arylsulfatase A (also known as "cerebroside-sulfatase") *Arylsulfatase B (also known as "''N''-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase") *Steroid sulfatase (formerly known as "arylsulfatase C") * ARSC2 * ARSD *ARSE *ARSF * ARSG * ARSH * ARSI * ARSJ * ARSK See also * Aryl In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used ... References Hydrolases EC 3.1.6 {{biochem-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylsulfatase B
Arylsulfatase B (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, chondroitinsulfatase, chondroitinase, acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase, N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate sulfohydrolase, ) is an enzyme associated with mucopolysaccharidosis VI (Maroteaux–Lamy syndrome). Arylsulfatase B is among a group of arylsulfatase enzymes present in the lysosomes of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys of animals. The purpose of the enzyme is to hydrolyze sulfates in the body. ARSB does this by breaking down glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), which are large sugar molecules in the body. ARSB targets two GAGs in particular: dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate.U.S. National Library of Medicine"ARSB" Genetics Home Resource, 7 November 2010, Retrieved 22 November 2010 Over 130 mutations to ARSB have been found, each leading to a deficiency in the body. In most cases, the mutation occurs on a single nucleotide in the sequence. An arylsulfatase B deficiency can lead to an accumulation of GAGs in lysosomes, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylsulfatase A
Arylsulfatase A (or cerebroside-sulfatase) is an enzyme that breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. In humans, arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ''ARSA'' gene. Pathology A deficiency is associated with metachromatic leukodystrophy, an autosomal recessive In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ... disease. Biochemistry Enzyme regulation Arylsulfatase A is inhibited by phosphate, which forms a covalent bond with the active site 3-oxoalanine. ; References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Arylsulfatase A Deficiency - Metachromatic Leukodystrophy OMIM entries on ARSA Deficiency * * * {{hydrolase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
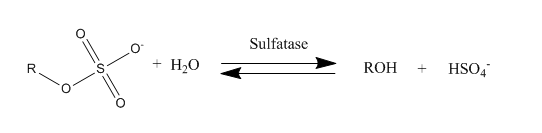
Sulfatase
Sulfatases are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates. Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with sulfotransferases, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters. Occurrence and importance Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. Steroid sulfatase is distributed in a wide range of tissues throughout the body, enabling sulfated steroids synthesized in the adrenals and gonads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Sulfatase
Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.2), formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the ''STS'' gene. Reactions This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the following chemical reaction : 3β-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one 3-sulfate + H2O \rightleftharpoons 3β-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one + sulfate Also acts on some related steryl sulfates. Function The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the conversion of sulfated steroid precursors to the free steroid. This includes DHEA sulfate, estrone sulfate, pregnenolone sulfate, and cholesterol sulfate, all to their unconjugated forms (DHEA, estrone, pregnenolone, and cholesterol, respectively). The encoded protein is found in the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is present as a homodimer. Clinical significance A congenital deficiency in the enzyme is associated with X-linked ichthyosis, a scaly-skin disease affecting roughly 1 in every 2,000 to 6,000 mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylsulfatase E
Arylsulfatase E, also known as ARSE, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ARSE'' gene. Function Arylsulfatase E is a member of the arylsulfatase subfamily of sulfatase enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. It is glycosylated postranslationally and localized to the golgi apparatus The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ins .... Sulfatases are essential for the correct composition of bone and cartilage matrix. Clinical significance Deficiencies in ARSE are associated with X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata, a disease characterized by abnormalities in cartilage and bone development. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARSD (arylsulfatase)
ARSD or ArsD may refer to: *ARS-D, the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia *ArsD, a trans-acting repressor of the arsRDABC operon that confers resistance to arsenicals and antimonials in ''Escherichia coli''; see Ars operon *ARSD, the United States Navy hull classification symbol for "salvage lifting vessel"; see also Rescue and salvage ship *ARSD, a type of arylsulfatase *ARSD, the New York Stock Exchange symbol for the Arabian American Development Company *Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College , mottoeng = May our learning be endowed with radiance , established = , type = Government , chairperson = Pawan Jaggi , principal = Gyantosh Kumar Jha , students ..., formerly Sanatan Dharma College, a co-educational constituent college of the University of Delhi in India *The American Roller Skating Derby, a professional roller derby league in the United States {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon. A simple aryl group is phenyl (), a group derived from benzene. Examples of other aryl groups consist of: * The tolyl group () which is derived from toluene (methylbenzene) * The xylyl group (), which is derived from xylene (dimethylbenzene) * The naphthyl group (), which is derived from naphthalene Arylation is the process in which an aryl group is attached to a substituent. It is typically achieved by cross-coupling reactions. Nomenclature The most basic aryl group is phenyl, which is made up of a benzene ring with one hydrogen atom substituted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARSK
Arsk ( rus, Арск, p=ˈarsk; tt-Cyrl, Арча, ''Arça'') is a town and the administrative center of Arsky District in the Tatarstan, Russia, located on the Kazanka River, from the republic's capital of Kazan. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 18,114. Etymology The Tatar name of the town () can be translated as " Udmurt's" or "Udmurtian". History It was founded at the end of the 14th century''Inhabited Localities of the Republic of Tatarstan'', p. 63 by Volga Bulgarians. It was the seat of Archa Darugha (a type of subdivision) during the Khanate of Kazan period. Even though the town was located in the area mostly populated by Tatars, the larger part of the ''darughas population was Udmurt. It is possible that earlier population of this area was also Finnic, who later assimilated with the Tatars. Arsk was one of the strongest forts in the khanate. In 1506, it was the site of the Battles of Arsk Field, in which Tatar forces were defeated by the Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)