|
Antifuse
An antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path (typically when the current through the path exceeds a specified limit), an antifuse starts with a high resistance, and programming it converts it into a permanent electrically conductive path (typically when the voltage across the antifuse exceeds a certain level). This technology has many applications. Christmas tree lights Antifuses are best known for their use in mini-light (or miniature) style low-voltage Christmas tree lights. Ordinarily (for operation from mains voltages), the lamps are wired in series. (The larger, traditional, C7 and C9 style lights are wired in parallel and are rated to operate directly at mains voltage.) Because the series string would be rendered inoperable by a single lamp failing, each bulb has an antifuse installed within it. When the bulb blows, the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Read-only Memory
A programmable read-only memory (PROM) is a form of digital memory where the contents can be changed once after manufacture of the device. The data is then permanent and cannot be changed. It is one type of read-only memory (ROM). PROMs are used in digital electronic devices to store permanent data, usually low level programs such as firmware or microcode. The key difference from a standard ROM is that the data is written into a ROM during manufacture, while with a PROM the data is programmed into them after manufacture. Thus, ROMs tend to be used only for large production runs with well-verified data. PROMs may be used where the volume required does not make a factory-programmed ROM economical, or during development of a system that may ultimately be converted to ROMs in a mass produced version. PROMs are manufactured blank and, depending on the technology, can be programmed at wafer, final test, or in system. Blank PROM chips are programmed by plugging them into a device call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function. Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike for microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device. PLDs can broadly be categorised into, in increasing order of complexity, Simple Programmable Logic Devices (SPLDs), comprising programmable array logic, programmable logic array and generic array logic; Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). History In 1969, Motorola offered the XC157, a mask-programmed gate array with 12 gates and 30 uncommitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zener Diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached. Zener diodes are manufactured with a great variety of Zener voltages and some are even variable. Some Zener diodes have a sharp, highly doped p–n junction with a low Zener voltage, in which case the reverse conduction occurs due to electron quantum tunnelling in the short space between p and n regions − this is known as the Zener effect, after Clarence Zener. Diodes with a higher Zener voltage have a more gradual junction and their mode of operation also involves avalanche breakdown. Both breakdown types are present in Zener diodes with the Zener effect predominating at lower voltages and avalanche breakdown at higher voltages. They are used to generate low-power stabilized supply rails from a higher voltage and to provide reference voltages for circuits, especially stabilized powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, and must be replaced or rewired, depending on its type. Fuses have been used as essential safety devices from the early days of electrical engineering. Today there are thousands of different fuse designs which have specific current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity, and response times, depending on the application. The time and current operating characteristics of fuses are chosen to provide adequate protection without needless interruption. Wiring regulations usually define a maximum fuse current rating for particular circuits. Short circuits, overloading, mismatched loads, or device failure are the prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Light
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution became ubiquitous in developed countries in the 20th century, lights for urban streets followed, or sometimes led. Many lamps have light-sensitive photocells that activate the lamp automatically when needed, at times when there is little-to-no ambient light, such as at dusk, dawn, or at the onset of dark weather conditions. This function in older lighting systems could be performed with the aid of a solar dial. Many street light systems are being connected underground instead of wiring from one utility post to another. Street lights are an important source of public security lighting intended to reduce crime. History Preindustrial era Early lamps were used by Greek and Roman civilizations, where light primarily served the purpose of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-intensity Discharge Lamp
High-intensity discharge lamps (HID lamps) are a type of electrical gas-discharge lamp which produces light by means of an electric arc between tungsten electrodes housed inside a translucent or transparent fused quartz or fused alumina arc tube. This tube is filled with noble gas and often also contains suitable metal or metal salts. The noble gas enables the arc's initial strike. Once the arc is started, it heats and evaporates the metallic admixture. Its presence in the arc plasma greatly increases the intensity of visible light produced by the arc for a given power input, as the metals have many emission spectral lines in the visible part of the spectrum. High-intensity discharge lamps are a type of arc lamp. Brand new high-intensity discharge lamps make more visible light per unit of electric power consumed than fluorescent and incandescent lamps, since a greater proportion of their radiation is visible light in contrast to infrared. However, the lumen output of HID lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed-signal Circuit
A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die."ESS Mixed Signal Circuits" Their usage has grown dramatically with the increased use of , , portable electronics, and automobiles with electronics and digital sensors. Overview Integrated circuits (IC ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
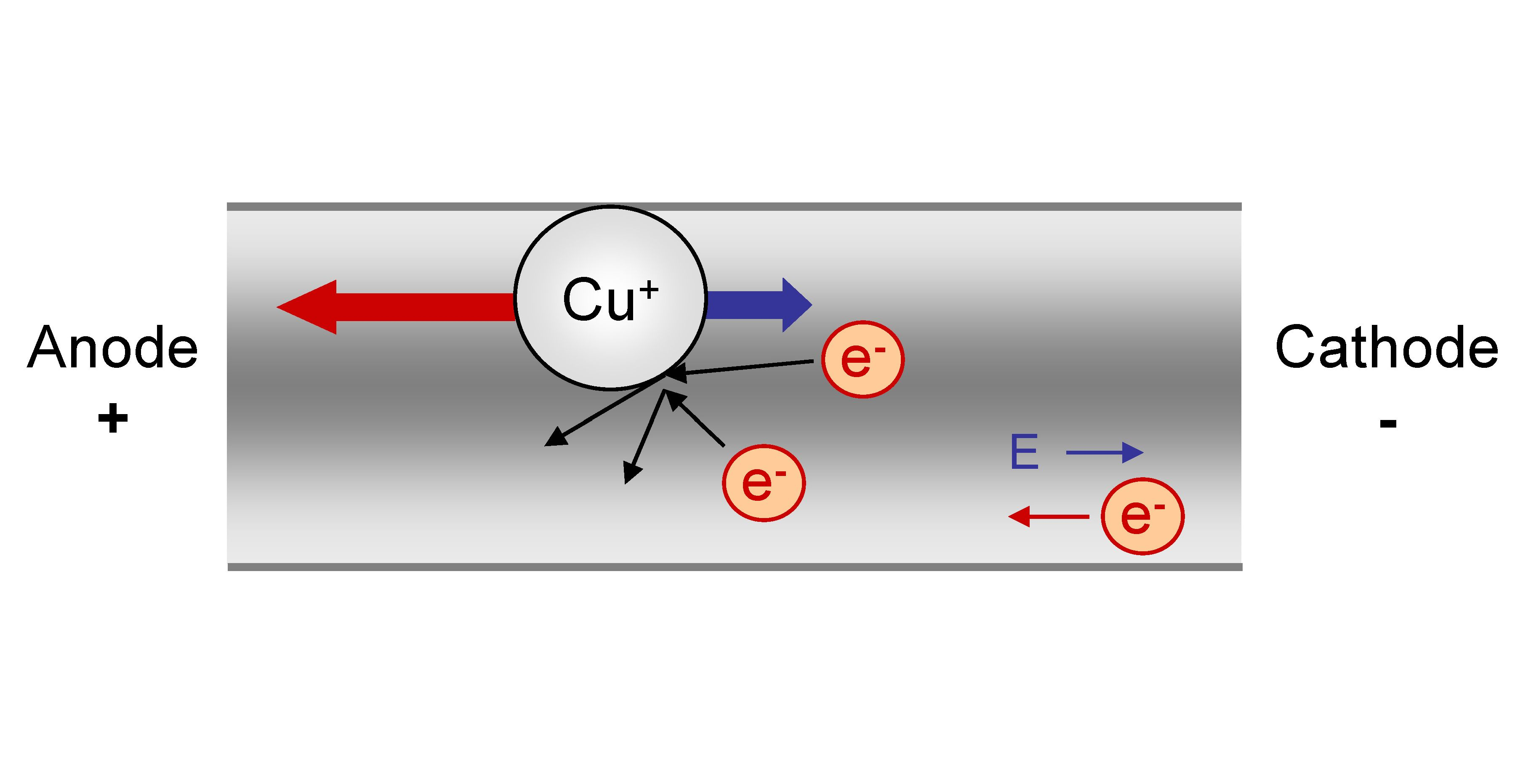
Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in microelectronics and related structures. As the structure size in electronics such as integrated circuits (ICs) decreases, the practical significance of this effect increases. History The phenomenon of electromigration has been known for over 100 years, having been discovered by the French scientist Gerardin. The topic first became of practical interest during the late 1960s when packaged ICs first appeared. The earliest commercially available ICs failed in a mere three weeks of use from runaway electromigration, which led to a major industry effort to correct this problem. The first observation of electromigration in thin films was made by I. Blech.I. Blech: ''Electromigration in Thin Aluminum Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry. Polysilicon is produced from metallurgical grade silicon by a chemical purification process, called the Siemens process. This process involves distillation of volatile silicon compounds, and their decomposition into silicon at high temperatures. An emerging, alternative process of refinement uses a fluidized bed reactor. The photovoltaic industry also produces upgraded metallurgical-grade silicon (UMG-Si), using metallurgical instead of chemical purification processes. When produced for the electronics industry, polysilicon contains impurity levels of less than one part per billion (ppb), while polycrystalline solar grade silicon (SoG-Si) is generally less pure. A few companies from China, Germany, Japan, Korea and the United States, such as GCL-Poly, Wacker Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is also often used to refer to the thermal energy contained in a system as a component of its internal energy and that is reflected in the temperature of the system. For both uses of the term, heat is a form of energy. An example of formal vs. informal usage may be obtained from the right-hand photo, in which the metal bar is "conducting heat" from its hot end to its cold end, but if the metal bar is considered a thermodynamic system, then the energy flowing within the metal bar is called internal energy, not heat. The hot metal bar is also transferring heat to its surroundings, a correct statement for both the strict and loose meanings of ''heat''. Another example of informal usage is the term '' heat content'', used despite the fact that p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |