|
Anguidae
Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group includes the slowworms, glass lizards, and alligator lizards, among others. The family is divided into two subfamilies (Anguinae and Gerrhonotinae), and contains about 87 species in 8 genera. Morphology and reproduction Anguids have hard osteoderms beneath their scales giving them an armored appearance. Many of the species have reduced or absent limbs, giving them a snake-like appearance, while others are fully limbed. Body type varies among species, with sizes ranging from 10 cm to 1.5 m. The group includes oviparous and viviparous species, both of which can be observed in a single genus at times. Feeding and habitat These lizards are known carnivorous or insectivorous foragers, feeding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptosaurinae
Glyptosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of anguid lizards that lived in the Northern Hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous and the Paleogene. Description Glyptosaurines are known primarily from their osteoderms, scale-like pieces of bone that are embedded in the skin and cover much of their bodies. The shape and extent of the osteoderms in glyptosaurines are similar to those seen in an unrelated group of lizards called Monstersauria, which includes the living Gila monster and beaded lizard. The osteoderms of glyptosaurines are unusually complex, consisting of four distinct layers of bony tissue. These tissues may have derived from both the dermis (the lower layer of the skin) and the epidermis (the outer layer of the skin) during their development in the embryo. The tissue forming the outermost layer of glyptosaurine osteoderms is similar to tooth enamel and has even been given its own name, osteodermine. Glyptosaurines have been split into the subgroups Melanosaurini and Glyptos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviparity
Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the mother. The term 'viviparity' and its adjective form 'viviparous' derive from the Latin ''vivus'' meaning "living" and ''pario'' meaning "give birth to". Reproductive mode Five modes of reproduction have been differentiated in animals based on relations between zygote and parents. The five include two nonviviparous modes: ovuliparity, with external fertilisation, and oviparity, with internal fertilisation. In the latter, the female lays zygotes as eggs with a large vitellus, yolk; this occurs in all birds, most reptiles, and some fishes. These modes are distinguished from viviparity, which covers all the modes that result in live birth: *Histotrophic viviparity: the zygotes develop in the female's oviducts, but find their nutrients b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerrhonotus
''Gerrhonotus'' is a genus of anguid lizards that are commonly referred to as alligator lizards, due to a vague resemblance to an alligator. Along with glass lizards (''Ophisaurus'') and many other lizards, alligator lizards have the ability to regrow their tail. Species and subspecies There are nine recognized species in the genus ''Gerrhonotus''. One species has recognized subspecies."''Gerrhonotus'' ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org. *''Gerrhonotus farri'' – Farr's alligator lizardBeolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Gerrhonotus farri'', p. 88; ''G. liocephalus loweryi'', p. 161; ''G. lugoi'', p. 162). *''Gerrhonotus infernalis'' – Texas alligator lizard *''Gerrhonotus lazcanoi'' *''Gerrhonotus liocephalus'' – smooth-headed alligator lizard, Texas alligator lizard, Wiegmann's alligator lizard **''Gerrhonotus liocephalus austrinus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
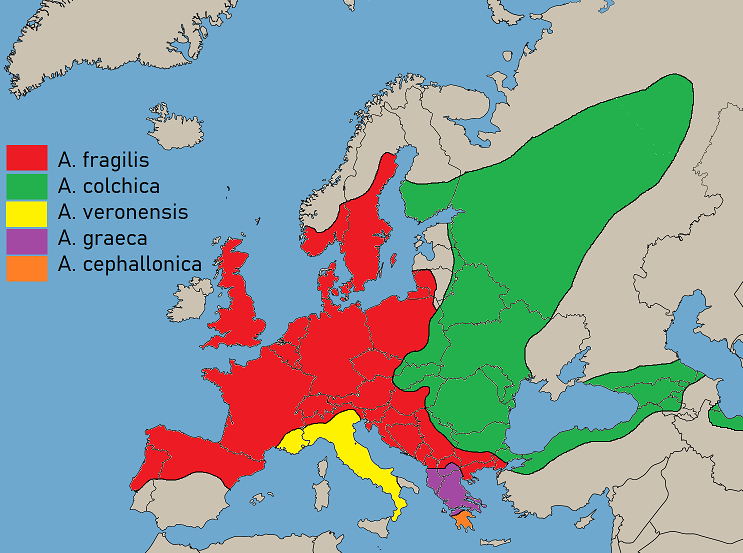
Anguis Fragilis
The slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple and hazelworm. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake (although the slowworm's eyes are functional). Slow worms are semifossorial (burrowing) lizards, spending much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth with scales that do not overlap one another. Like many other lizards, they autotomize, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, they are common in gardens and allotments, and can be encouraged to enter and help remove pest insects by placing black plastic or providing places to shelter such as piles of logs, corrugated iron sheets or under tiles. On warm days, one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopasia
''Dopasia'' is a genus of lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus contains seven species, which are native to Asia. They are most closely related to the North American ''Ophisaurus'', and are sometimes considered part of that genus. Species The following species are recognized as being valid. *'' Dopasia buettikoferi'' – Buettikofer's glass lizard *'' Dopasia gracilis'' – Burmese glass lizard, Asian glass lizard, Indian glass snake *'' Dopasia hainanensis'' – Hainan glass lizard *'' Dopasia harti'' – Hart's glass lizard *'' Dopasia ludovici'' – Ludovic's glass lizard *'' Dopasia sokolovi'' – Sokolov's glass lizard *'' Dopasia wegneri'' – Wegner's glass lizard ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ... in parenth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odaxosaurus
''Odaxosaurus'' is an extinct genus of anguid lizards that existed in western North America from the Late Cretaceous to the Paleocene. Fossils of the type species ''Odaxosaurus piger'' and the species ''O. priscus'' are widespread throughout Late Cretaceous formations in the western United States and Canada. First described in 1928 from the Lance Formation in Wyoming, ''O. piger'' has since been found in the Hell Creek Formation in Wyoming and Montana, the Frenchman and Scollard formations in Alberta, and the Aguja Formation in Texas. It was one of the few species of lizards to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which is estimated to have killed off 83% of all lizard species. The second species, ''O. priscus'', was named in 1996 from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta and has since been found in the Kaiparowits Formation in southern Utah. Remains of an anguid from the Kirtland Formation The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic column wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguidae Phylogeny PDF
Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group includes the slowworms, glass lizards, and alligator lizards, among others. The family is divided into two subfamilies (Anguinae and Gerrhonotinae), and contains about 87 species in 8 genera. Morphology and reproduction Anguids have hard osteoderms beneath their scales giving them an armored appearance. Many of the species have reduced or absent limbs, giving them a snake-like appearance, while others are fully limbed. Body type varies among species, with sizes ranging from 10 cm to 1.5 m. The group includes oviparous and viviparous species, both of which can be observed in a single genus at times. Feeding and habitat These lizards are known carnivorous or insectivorous foragers, feeding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguis
SlowwormsThe "slow-" in slowworm is distinct from the English adjective ''slow'' ("not fast"); the word comes from Old English ''slāwyrm'', where ''slā-'' means "slowworm" and ''wyrm'' means "serpent, reptile". () (also called blindworms and hazelworms) are a small genus (''Anguis'') of snake-like legless lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus has several living species, including the common slowworm, the eastern slowworm, the Greek slowworm, the Peloponnese slowworm, and the Italian slowworm (''Anguis veronensis''). There are also known fossil species. Description Slowworms are typically grey-brown, with the females having a coppery sheen and two lateral black stripes, and the males displaying electric blue spots, particularly in the breeding season. They give birth to live young, which are about long at birth and generally have golden stripes. Slowworms are slow-moving and can be easily caught, which has given rise to the folk etymology that the "slow" in slowworm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophisaurus
''Ophisaurus'' (from the Greek 'snake-lizard') is a genus of superficially snake-like lizards in the family Anguidae. Known as joint snakes, glass snakes, or glass lizards, they are so-named because their tails are easily broken; like many lizards, they have the ability to deter predation by dropping off part of the tail, which can break into several pieces, like glass. The tail remains mobile, distracting the predator, while the lizard becomes motionless, allowing eventual escape. This serious loss of body mass requires a considerable effort to replace, and can take years to do so. Despite this ability, the new tail is usually smaller than the original. Although most species have no legs, their head shapes, movable eyelids, and external ear openings identify them as lizards. A few species have very small, stub-like legs near their rear vents. These are vestigial organs, meaning they once served an evolved purpose but are no longer used. They reach lengths of up to , but about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |