|
Al-Hamadani
Badi' al-Zamān al-Hamadāni or al-Hamadhāni ( ar, بديع الزمان الهمذاني التغلبي; 969–1007) was a medieval Arab man of letters born in Hamadan, Iran. He is best known for his work the ''Maqamat Badi' az-Zaman al-Hamadhani'', a collection of 52 episodic stories of a rogue, Abu al-Fath al-Iskandari, as recounted by a narrator, 'Isa b. Hisham. His Arabic name translates into "The Wonder of the Age". Life Very little is known about Al-Hamadani’s early life and primary sources are very limited. The main biographical account comes from the Persian scholar, ath-Thalibi, and most later biographies are derived from that. According to al-Hamadani’s own account, he was of Arabic descent and his family had some education, but scholars have disputed these bare facts. He was probably born and educated in Hamadan, Iran. More is known about Al-Hamadani’s adult life. In 380/990, al-Hamadhani, then aged 22, left his native city and began travelling to the vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmed Ibn Faris
Abū al-Ḥusayn Aḥmad ibn Fāris ibn Zakariyyā ibn Muḥammad ibn Ḥabīb al-Rāzī ( ar, أبو الحسين أحمد بن فارس بن زكريا بن محمد بن حبيب الرازي, died Ray, Iran 395/1004) was a Persians, Persian linguist, scribe, scholar, philologist and lexicographer, As well as bearing the epithet ''al-Rāzī'' ('meaning 'from Ray'), ibn Fāris was also known variously by the epithets al-Shāfiʿī, al-Mālikī, al-lughawī ('the linguist'), al-naḥwī ('the grammarian'), al-Qazwīnī ('from Qazvin') and (possibly inaccurately) al-Zahrāwī ('from al-Zahrāʾ').H. Fleisch, 'Ibn Fāris', in ''Encyclopædia of Islam'', ed. by P. J. Bearman and others, 2nd edn, 12 vols (Leiden: Brill, 1960–2005), . He is noted for compiling two of the early dictionaries to organise words alphabetically rather than according to the word's rhyming pattern. He was primarily associated with Ray.Хрестоматия по исламу / Сост. и отв. ред. С ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamadan
Hamadan () or Hamedan ( fa, همدان, ''Hamedān'') (Old Persian: Haŋgmetana, Ecbatana) is the capital city of Hamadan Province of Iran. At the 2019 census, its population was 783,300 in 230,775 families. The majority of people living in Hamadan identify as ethnic Persians. Hamedan is believed to be among the oldest Iranian cities. It is possible that it was occupied by the Assyrians in 1100 BCE; the Ancient Greek historian, Herodotus, states that it was the capital of the Medes, around 700 BCE. Hamedan has a green mountainous area in the foothills of the 3,574-meter Alvand Mountain, in the midwest part of Iran. The city is 1,850 meters above sea level. The highly cultural nature of this old city and its historic sites attract tourists during the summer to this city, located approximately southwest of Tehran. The major sights of this city are the Ganj Nameh inscription, the Avicenna monument and the Baba Taher monument. The main language in the city is Persian. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Ahmad Al-Khwarizmi
Muḥammad ibn al-ʿAbbās Abū Bakr al-Khwārazmī, better simply known as Abu Bakr al-Khwarazmi was a 10th-century Iranian peoples, Iranian poet and secretary, who throughout his long career served in the court of the Hamdanids, Samanids, Saffarids and Buyids. He is best known as the author of the early encyclopedia ''Mafātīḥ al-ʿulūm'' (“Key to the Sciences”) in the Arabic language. Life Al-Khwarazmi is a somewhat obscure figure. He was born in 935 in Khwarazm, the birthplace of his father. His mother was a native of Amol in Tabaristan. He periodically refers to himself as al-Khwarazmi or al-Tabari, while other sources refer to him as al-Tabarkhazmi or al-Tabarkhazi. Al-Khwarizmi may have been a nephew of al-Tabari, the prominent Persian historian. For a time, al-Khwarizmi worked as a clerk in the Samanid Empire, Samanid court at Bukhara in Transoxiana, Transoxania, where he acquired his nickname, “al-Katib’’ which literally means “the secretary” or “the scr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maqamat Badi' Az-Zaman Al-Hamadhani
''Maqamat Badi' al-Zaman al-Hamadhani'' (Arabic: مقامات بديع الزمان الهمذاني), are an Arabic collection of stories from the 9th century, written by Badi' al-Zaman al-Hamadani. Of the 400 episodic stories, roughly 52 have survived. Description The work consists of a series of anecdotes of social satire written and the narrative concerns the travels of a middle-aged man as he uses his charm and eloquence to swindle his way across the Arabic world. The work is characterized by the alternation of rhymed prose (sajʿ) and poetry. They are narrated from the point of view of a fictitious character, 'very likely a traveling merchant who has money and time', ʿĪsā ibn Hishām, about the adventures of an eloquent beggar named Abū al-Fatḥ al-Iskandarī'. The Maqamat are also known for their intertextuality and narrative construction. According to Ailin Qian, The core of the Hamadhānian ''maqāmah'' is dialogue, and al-Hamadhānī, by using techniques such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaranj
Zaranj or Zarang ( Persian/Pashto/ bal, زرنج) is a city in southwestern Afghanistan, near the border with Iran, which has a population of 160,902 people as of 2015. It is the capital of Nimruz Province and is linked by highways with Lashkargah and Kandahar to the east, Farah to the north and the Iranian city of Zabol to the west. Zaranj is a major border crossing between Afghanistan and Iran, which is of significant importance to the trade-route between Central Asia and South Asia with the Middle East. The history of Zaranj dates back over 2500 years and Ya'qub ibn al-Layth al-Saffar, founder of the Saffarid dynasty, was born in this old civilization. History Modern Zaranj bears the name of an ancient city whose name is also attested in Old Persian as ''Zranka''. In Greek, this word became Drangiana. Other historical names for Zaranj include Zirra, Zarangia, Zarani etc. Ultimately, the word Zaranj is derived from the ancient Old Persian word ''zaranka'' ("waterland"). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffarid Dynasty
The Saffarid dynasty ( fa, صفاریان, safaryan) was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1003. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conquest, the Saffarid dynasty was part of the Iranian Intermezzo. The dynasty's founder was Ya'qub bin Laith as-Saffar, who was born in 840 in a small town called Karnin (Qarnin), which was located east of Zaranj and west of Bost, in what is now Afghanistan. A native of Sistan and a local ''ayyār'', Ya'qub worked as a coppersmith (''ṣaffār'') before becoming a warlord. He seized control of the Sistan region and began conquering most of Iran and Afghanistan, as well as parts of Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The Saffarids used their capital Zaranj as a base for an aggressive expansion eastward and westward. They first invaded the areas south of the Hindu Kush, and then overthrew the Tahirid dynasty, annex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalaf Ibn Ahmad
Abu Ahmad Wali 'l-Dawla Khalaf ibn Ahmad (November 937 – March 1009) was the Saffarid amir of Sistan from 963 until 1002. Although he was renowned in the eastern Islamic world as a scholar, his reign was characterized by violence and instability, and Saffarid rule over Sistan came to an end with his deposition. Early life Khalaf was born in the middle of November 937 to Abu Ja'far Ahmad and Banu, a granddaughter of the second Saffarid amir, Amr ibn al-Layth. Little is known about the first twenty-six years of his life; presumably much of it was spent learning. From 957 or 958 at the latest he was recognized as heir to the throne and his name was included on his father's coins. Succession to the Amirate At the end of March 963 Abu Ja'far Ahmad was murdered in Zarang. At the time of the assassination, Khalaf had been outside the capital. When he heard about his father's death, he rode for the town of Bust, whose governor immediately pledged his support. Soon afterward he led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd Kōh'') in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road between the Middle East, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west. Herat dates back to Avestan times and was traditionally known for its wine. The city has a number of historic sites, including the Herat Citadel and the Musalla Complex. During the Middle Ages Herat became one of the important cities of Khorasan, as it was known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan''. After the conquest of Tamerlane, the city became an important center of intellectual and artistic life in the Islamic world. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier is suggested to be an Iranian word, from the Pahlavi root of ''vičir'', which originally had the meaning of a ''decree'', ''mandate'', and ''command'', but later as its use in Dinkard also suggests, came to mean ''judge'' or ''magistrate''. Arthur Jeffery considers the word to be a "good Iranian" word, as has a well-established root in Avestan language. The Pahlavi ''vi� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu'l-Hasan Isfaraini
Abu'l-Hasan Ali ibn Fadl ibn Ahmad Isfarayini ( fa, ابوالحسن علی بن فضل بن احمد اسفراینی, died 1013/14), commonly known as Abu'l-Hasan Isfarayini (), was a Persian ''vizier'' of the Ghaznavid sultan Mahmud of Ghazni () from 998 to 1010. Biography Isfarayini was most likely from the town of Isfarayin in the northwestern part of Khurasan. Not much is known about his early life; he began his career as a Samanid secretary (''dabir'') under the Turkic slave-general Fa'iq. During this period the Samanid dynasty was in heavy decline and was struggling for holding control over Khurasan and Transoxiana from several ambitious military leaders who had rebelled against their authority, the most dangerous ones being Fa'iq and the Simjurid Abu 'Ali Simjuri. The Ghaznavid prince and Samanid general Sebüktigin, however, managed to defeat the rebels, but soon took control over Khurasan, while the remains of the Samanid dynasty in Bukhara was conquered by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
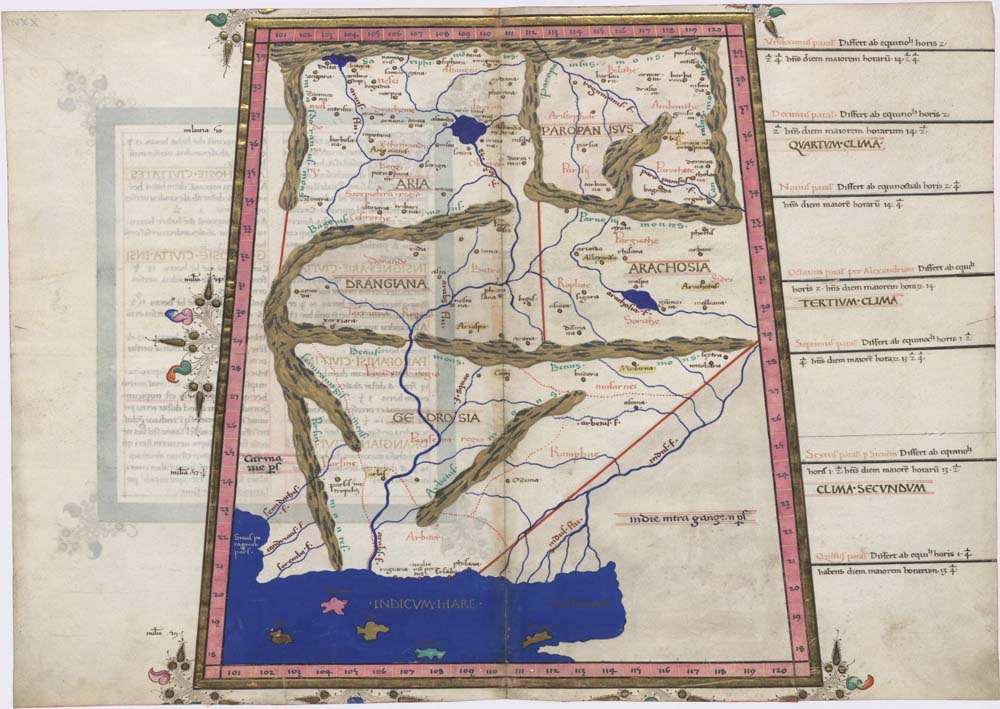
Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( Nimruz, Helmand, Kandahar). Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between the two countries. Etymology Sistan derives its name from ''Sakastan'' ("the land of the Saka"). The Sakas were a Scythian tribe which from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century migrated to the Iranian Plateau and Indus valley, where they carved a kingdom known as the Indo-Scythian Kingdom. In the Bundahishn, a Zoroastrian scripture written in Pahlavi, the province is called "Seyansih". After the Arab conquest of Iran, the province became known as Sijistan/Sistan. The more ancient Old Persian name of the region - prior to Saka dominanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |