|
Archbishopric Of Vienne
The Archbishopric of Vienne, named after its episcopal seat in Vienne in the Isère département of southern France, was a metropolitan Roman Catholic archdiocese. It is now part of the Archdiocese of Lyon. History The legend according to which Crescens, the first Bishop of Vienne, is identical with the Crescens of Saint Paul's Second Letter to Timothy, iv, 20 certainly postdates the letter of Pope Zosimus to the Church of Arles (417) and the letter of the bishops of Gaul in 451; because, although both these documents allude to the claims to glory which Arles owes to St. Trophimus, neither of them mentions Crescens. Archbishop Ado of Vienne (860–875) set afoot this legend of the Apostolic origin of the See of Vienne and put down St. Zachary, St. Martin and St. Verus, later successors of Crescens, as belonging to the Apostolic period. This legend was confirmed by the ''Recueil des privilèges de l'Eglise de Viene'', which, however, was not compiled under the supervision o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienne, Isère
Vienne (; frp, Vièna) is a town in southeastern France, located south of Lyon, at the confluence of the Gère and the Rhône. It is the fourth largest-commune in the Isère department, of which it is a subprefecture alongside La Tour-du-Pin. Vienne was a major centre of the Roman Empire under the Latin name ''Vienna''. Before the arrival of the Roman armies, Vienne was the capital of the Allobroges, a Gallic people. Transformed into a Roman colony in 47 BC under Julius Caesar, Vienne became a major urban centre, ideally located along the Rhône, then a major axis of communication. Emperor Augustus banished Herod the Great's son, the ethnarch Herod Archelaus to Vienne in 6 AD. The town became a Roman provincial capital and remains of Roman constructions are widespread across modern Vienne. It was also an important early bishopric in Christian Gaul. Its most famous bishop was Avitus of Vienne. At the Council of Vienne, which was convened there in October 1311, Pope Clement V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Arles (314)
Arles (ancient Arelate) in the south of Roman Gaul (modern France) hosted several councils or synods referred to as ''Concilium Arelatense'' in the history of the early Christian church. Council of Arles in 314 The first council of Arles"Arles, Synod of" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 597. took place a year after the Edict of Milan, in which Christianity became a legal religion. This council was the first called by Constantine and is the forerunner of the First Council of Nicaea. Augustine of Hippo called it an Ecumenical Council. It had the following outcomes: * Conscientious objectors would be excommunicated.Nonviolence: Twenty-Five Lessons from the History of a Dangerous Idea, Mark Kurlanski, 2006 * Easter should be held on the same day throughout the world, rather than being set by each local church. * Donatism was condemned as a heresy and Donatus Magnus was excommunicated. This had begun as an appeal by the Donatists to Constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Valence
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Valence (–Die–Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux) (Latin: ''Dioecesis Valentinensis (–Diensis–Sancti Pauli Tricastinorum)''; French: ''Diocèse de Valence (–Die–Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux'') is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Roman Catholic Church in southern France. The contemporary diocese is co-extensive with the department of Drôme. The Cathedral of Valence was originally dedicated to Saints Cornelius and Cyprianus (Bishops of Rome and of Carthage, both mid-third century martyrs), but in 1095, during his visit to France to rouse up the aristocracy for a Crusade to liberate the Holy Land, Pope Urban II rededicated the cathedral to Saint Apollinaris, one of Valence's sixth century bishops. The Cathedral had fourteen Canons, including a Dean, a Provost, the Archdeacon, a Theologian, and the Abbot of S. Felix. In the Great Western Schism (1378–1417), the Bishops of Valence-et-Die were all appointed by and were loyal to the Popes of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Grenoble
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Grenoble–Vienne-les-Allobroges (Latin: ''Diocesis Gratianopolitana–Viennensis Allobrogum''; French: ''Diocèse de Grenoble–Vienne-les-Allobroges'') is a diocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in south-eastern France. The diocese, erected in the 4th century as the Diocese of Grenoble, comprises the department of Isère and the former canton of Villeurbanne (Rhône), in the Region of Rhône-Alpes. In 2006, the name was changed from the diocese of Grenoble to the diocese of Grenoble–Vienne. The current bishop is J ean-Marc Eychenne, appointed on September 14, 2022. Before the French Revolution it was a suffragan diocese of the Archbishopric of Vienne and included the deanery or see at Savoy, which in 1779, was made a bishopric in its own right, with the episcopal seat at Chambéry. By the Concordat of 1801, the bishop of Grenoble was made a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Lyon. Thirteen archipresbyterates of the former Archd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Callixtus II
Pope Callixtus II or Callistus II ( – 13 December 1124), born Guy of Burgundy, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 February 1119 to his death in 1124. His pontificate was shaped by the Investiture Controversy, which he was able to settle through the Concordat of Worms in 1122. As son of Count William I of Burgundy, Guy was a member of and connected to the highest nobility in Europe. He became archbishop of Vienne and served as papal legate to France. He attended the Lateran Synod of 1112. He was elected pope at Cluny in 1119. The following year, prompted by attacks on Jews, he issued the bull '' Sicut Judaeis'' which forbade Christians, on pain of excommunication, from forcing Jews to convert, from harming them, from taking their property, from disturbing the celebration of their festivals, and from interfering with their cemeteries. In March 1123, Calixtus II convened the First Lateran Council which passed several disciplinary decrees, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitten
, neighboring_municipalities= Ayent, Conthey, Grimisuat, Grône, Les Agettes, Nax, Nendaz, Saint-Léonard, Salins, Savièse, Vernamiège, Vex , twintowns = Sion (; german: Sitten ; it, Seduno; la, Sedunum) is a Swiss town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Valais and of the district of Sion. it had a population of (known as ''Sédunois(es)''). On 17 January 1968, the former municipality of Bramois merged into the municipality of Sion.Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz accessed 9 February 2013 On 1 January 2013, the former municipality of Salins merged into the municipality of Sio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Dora Baltea, and at the junction of the Great and Little St Bernard Pass routes. History Aosta was settled in proto-historic times and later became a centre of the Salassi, many of whom were killed or sold into slavery by the Romans in 25 BC. The campaign was led by Terentius Varro, who then founded the Roman colony of ''Augusta Praetoria Salassorum'', housing 3,000 retired veterans. After 11 BC Aosta became the capital of the Alpes Graies ("Grey Alps") province of the Empire. Its position at the confluence of two rivers, at the end of the Great and the Little St Bernard Pass, gave it considerable military importance, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesiastical Province
An ecclesiastical province is one of the basic forms of jurisdiction Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels. Jur ... in Christianity, Christian Churches with traditional hierarchical structure, including Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity. In general, an ecclesiastical province consists of several diocese, dioceses (or eparchy, eparchies), one of them being the archdiocese (or archeparchy), headed by a metropolitan bishop or archbishop who has ecclesiastical jurisdiction over all other bishops of the province. In the Greco-Roman world, ''ecclesia'' ( grc, ἐκκλησία; la, ecclesia) was used to refer to a lawful assembly, or a called legislative body. As early as Pythagoras, the word took on the additional meaning of a community with shared beliefs. This is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
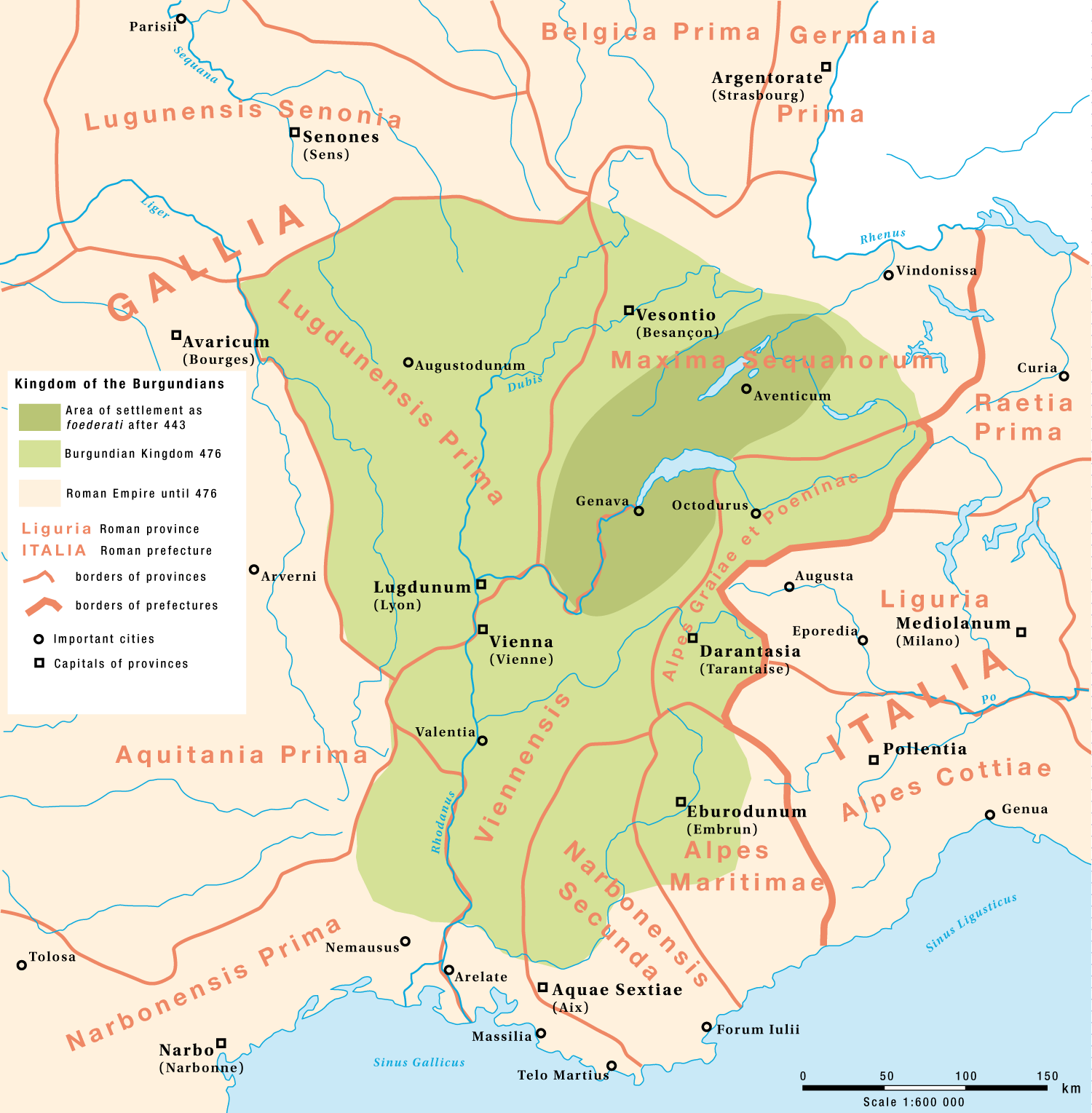
Kingdom Of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and Lyon. As a political entity, Burgundy existed in a number of forms with different boundaries, notably, when it was divided into Upper and Lower Burgundy and Provence. Two of the entities, the first around the 6th century and the second around the 11th century, were called the Kingdom of Burgundy. At other times were the Kingdom of Provence, the Duchy of Burgundy and the County of Burgundy. Kingdom of the Burgundians (411–534) Burgundy is named after a Germanic tribe of Burgundians who originated in mainland Scandinavia, then settled on the island of Bornholm, whose name in Old Norse was ''Burgundarholmr'' ("Island of the Burgundians"). From there they migrated south through Germanic lands into Roman Gaul and settled in the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenoble
lat, Gratianopolis , commune status = Prefecture and commune , image = Panorama grenoble.png , image size = , caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint-André, jardin de ville, banks of the Isère , arrondissement = Grenoble , canton = Grenoble-1, 2, 3 and 4 , INSEE = 38185 , postal code = 38000, 38100 , mayor = Éric Piolle , term = 2020–2026 , party = EELV , image flag = Flag of Grenoble.svg , image coat of arms = Coat of Arms of Grenoble.svg , intercommunality = Grenoble-Alpes Métropole , coordinates = , elevation min m = 212 , elevation m = 398 , elevation max m = 500 , area km2 = 18.13 , population = , population date = , population footnotes = , urban pop = 451096 , urban area km2 = 358.1 , u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Canton of Geneva, Republic and Canton of Geneva. The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva (the city and its closest Swiss suburbs and exurbs) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud and in the French Departments of France, departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area as officially defined by Eurostat, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence, Drôme
Valence (, ; oc, Valença ) is a commune in southeastern France, the prefecture of the Drôme department and within the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region. It is situated on the left bank of the Rhône, about south of Lyon, along the railway line that runs from Paris to Marseille. It is the eighth-largest city in the region by its population and has 64,726 registered inhabitants in 2018 (132,556 inhabitants in the urban area (''unité urbaine''). The city is divided into four cantons. Its inhabitants are called ''Valentinois''. Located in the heart of the Rhone corridor, Valence is often referred to as "the door to the South of France", the local saying ''à Valence le Midi commence'' ("at Valence the Midi begins") pays tribute to the city's southern culture. Between Vercors and Provence, its geographical location attracts many tourists. Axes of transport and communications are the A7 and A49 autoroutes, the RN7, Paris/Marseille TGV line, as well as the Rhône. In addition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |