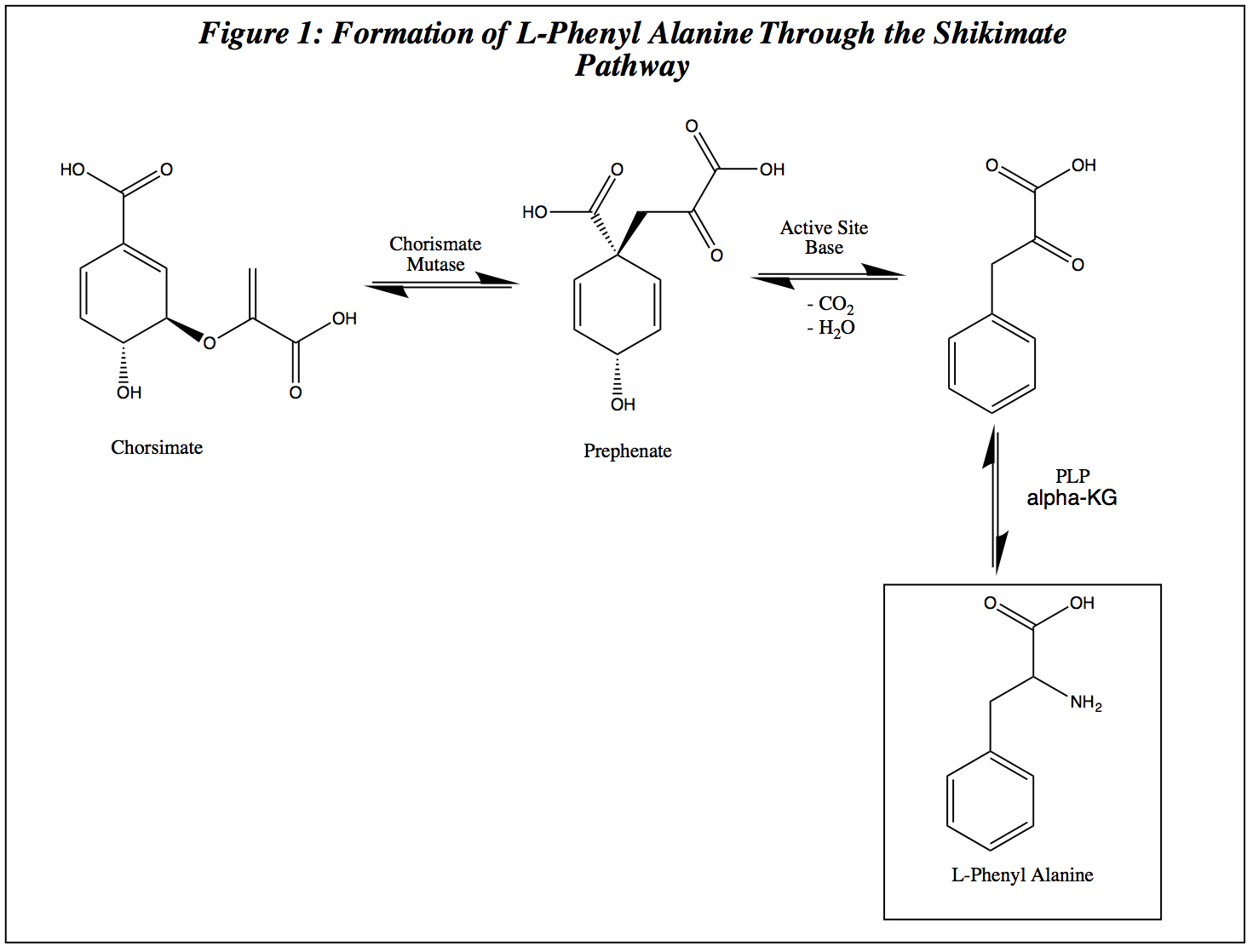
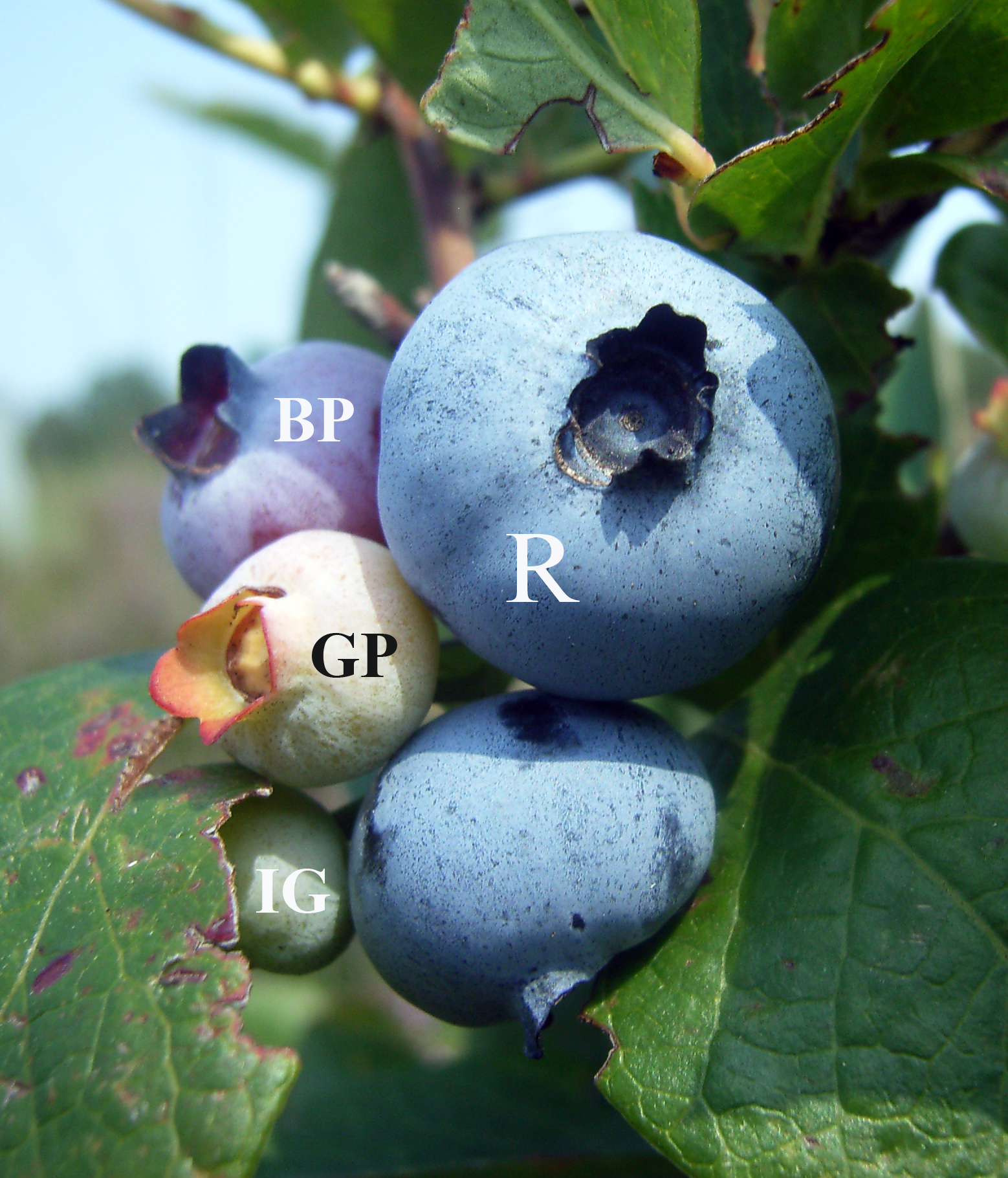
|
Anthocyanidin
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through purple, blue, and bluish green as a function of pH. Anthocyanidins are an important subclass of the polymethine dyes and flavonoids. The flavylium cation is a chromenylium cation with a phenyl group substituted in position 2; and chromenylium (also called benzopyrylium) is a bicyclic version of pyrylium. The positive charge can move around the molecule. At least 31 monomeric anthocyanidins have been properly identified in living organisms, mostly as the core components of anthocyanins. The latter are responsible for the red, purple, blue, or black color of many fruits (like grapes and blueberries), flowers (like roses), leaves (like purple cabbage), and even tubers (like radishes and purple yams). They are also found in some ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanin
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "''Die Farben der Blüthen''". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins. Anthocyanins belong to a parent class of molecules called flavonoids synthesized via the phenylpropanoid pathway. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Anthocyanins are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars. They are odorless and moderately astringent. Although approved as food and beverage colorant in the European Union, anthocyanins are not appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanidin
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator. List of cyanidin derivatives * Antirrhinin (cyanidin-3-rutinoside or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion * Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in red onion * Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromone, chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelargonidin
Pelargonidin is an anthocyanidin, a type of plant pigment producing a characteristic orange color used in food and industrial dyes. Natural occurrences Presence in flowers Pelargonidin can be found in red geraniums (Geraniaceae). It is the predominant pigment causing the red coloration in the spathes of '' Philodendron'' (Araceae). The orange-coloured flowers of blue pimpernel (''Anagallis monelli'', Myrsinaceae) have a higher concentration of pelargonidin pigment. Red and Pink Roses (Rosa) obtain their color from this phytochemical. Presence in food Pelargonidin can be found in berries such as ripe raspberries and strawberries, as well as blueberries, blackberries, cranberries but also in saskatoon berries and chokeberries. It is also found in plums and pomegranate The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall. The pomegranate was originally described through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delphinidin
Delphinidin (also delphinidine) is an anthocyanidin, a primary plant pigment, and also an antioxidant. Delphinidin gives blue hues to flowers in the genera ''Viola'' and ''Delphinium''. It also gives the blue-red color of the grape that produces Cabernet Sauvignon, and can be found in cranberries and Concord grapes as well as pomegranates, and bilberries. Delphinidin, like nearly all other anthocyanidins, is pH-sensitive, i.e. a natural pH indicator, and changes from blue in basic solution to red in acidic solution. Glycosides Several glycosides derived from delphinidin are known: * Myrtillin (delphinidin-3-''O''-glucoside) and tulipanin (delphinidin-3-''O''-rutinoside) can be found in blackcurrant pomace. * Violdelphin (delphinidin 3-rutinoside-7-''O''-(6-''O''-(4-(6-''O''-(4-hydroxybenzoyl)-β-D-glucosyl)oxybenzoyl)-β-D-glucoside) is responsible for the purplish-blue flower color of ''Aconitum chinense''. * Nasunin (delphinidin-3-(''p''-coumaroylrutinoside)-5-gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Deoxyanthocyanidin
The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides (3-deoxyanthocyanins or 3-DA) are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol. 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are yellow anthocyanidins that can be found primarily in ferns and mosses (Timberlake and Bridle, 1975, 1980), in ''Sorghum bicolor'' and in purple corn (Nakatani et al., 1979) (maíz morado). 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are reported to be stable to color loss due to change in pH. Synthetic 3-deoxyanthocyanidins with a carboxylate group at carbon 4 show unusually stable colorant properties at pH 7. In ''Sorghum'', the ''SbF3'H2'' gene, encoding a flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, seems to be expressed in pathogen-specific 3-deoxyanthocyanidin phytoalexins synthesis, for example in ''Sorghum-Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peonidin
Peonidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin derived from Cyanidin, and a primary plant pigment. Peonidin gives purplish-red hues to flowers such as the peony The peony or paeony is a flowering plant in the genus ''Paeonia'' , the only genus in the family Paeoniaceae . Peonies are native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. Scientists differ on the number of species that can be distinguished, ..., from which it takes its name, and roses. It is also present in some blue flowers, such as the morning glory. Like most anthocyanidins, it is pH sensitive, and changes from red to blue as pH rises because anthocyanidins are highly conjugated chromophores. When the pH is changed, the extent of the conjugation (of the double bonds) is altered, which alters the wavelength of light energy absorbed by the molecule. (Natural anthocyanidins are most stable in a very low pH environment; at pH 8.0, most become colorless.) At pH 2.0, peonidin is cherry red; at 3.0 a strong yellowis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymethine
Polymethines are compounds made up from an ''odd'' number of methine groups (CH) bound together by alternating single and double bonds.Kachovski and Dekhtyar, ''Dyes and Pigments'', 22 (1983) 83-97. Compounds made up from an ''even'' number of methine groups are known as polyenes. Polymethine dyes Cyanines are synthetic dyes belonging to polymethine group. Anthocyanidins are natural plant pigments belonging to the group of the polymethine dyes. Polymethines are fluorescent dyes that may be attached to nucleic acid probes for different uses, ''e.g.'', to accurately count reticulocyte Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mat ...s. References Alkenes {{alkene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurantinidin
Aurantinidin is a water-soluble, red plant dye. It is a member of the class of compounds known as anthocyanidins and is a hydroxy derivative of pelargonidin. Aurantinidin has been reported to occur in '' Impatiens aurantiaca'' (Balsaminaceae), and also in cultivars from genus ''Alstroemeria ''Alstroemeria'' (), commonly called the Peruvian lily or lily of the Incas, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Alstroemeriaceae. They are all native to South America, although some have become naturalized in the United States, Mexi ...''.''FLAVONOIDS: Chemistry, biochemistry and applications'' by Oyvind M. Andersen and Kenneth R.Markham References {{Anthocyanins Natural dyes Anthocyanidins Pyrogallols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus '' Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteolinidin
Luteolinidin is a member of the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins. It is a cation with ill-defined anions. This orange species that can be found in ''Sorghum bicolor''. Luteolinidin was shown to inhibit CD38 with relatively high potency compared with previously used inhibitors Glycosides Luteolinidin 5-''O''-β-D- -''O''-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2-''O''-acetylglucopyranoside(a 3-deoxyanthocyanidin laminaribioside) can be found in the fern ''Parablechnum novae-zelandiae ''Parablechnum novae-zelandiae'', synonym ''Blechnum novae-zelandiae'', commonly known as palm-leaf fern or kiokio, is a species of fern found in New Zealand. It can often be found growing in clay Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soi ...'' (syn. ''Blechnum novae-zelandiae''). See also * List of compounds with carbon number 15 References {{anthocyanins Anthocyanidins Sorghum">Anthocyanidins.html" ;"title="--> {{anthocyanins Anthocyanidins">--> {{anthocyanins Anthocyanidins Sorghum Catechols Resorcinol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malvidin
Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, the 3',5'-methoxy derivative of delphinidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature. Natural occurrences Malvidin is responsible for the blue color found in petals of the '' Primula'' plants of the ''polyanthus'' group. Blue flowers of the blue pimpernel (''Anagallis monelli'') have also a higher concentration of malvidin. It is responsible primarily for the color of red wine, ''Vitis vinifera'' being one of its sources. It is also present in other berries, such as blueberries ('' Vaccinium corymbosum'') or the saskatoon berries ('' Amelanchier alnifolia''). Chemistry Slightly acidic and neutral solutions of malvidin are characteristically of a red color, while basic solutions of malvidin yield a blue color. The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid. Use as a marker in archaeology The breakdown of malvidin releases syringic acid Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |