Cyanidin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyanidin is a natural
 L-phenylalanine then undergoes an elimination of the primary amine with
L-phenylalanine then undergoes an elimination of the primary amine with  Naringenin is then converted to cyanidin through several oxidizing and reducing steps. First naringenin is reacted with two equivalents of oxygen, ''alpha''-Ketogluteratic acid, and flavanone 3-hydroxylase to form
Naringenin is then converted to cyanidin through several oxidizing and reducing steps. First naringenin is reacted with two equivalents of oxygen, ''alpha''-Ketogluteratic acid, and flavanone 3-hydroxylase to form 
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. T ...
. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through ...
(glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycoside ...
version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
, bilberry
Bilberries (), or sometimes European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus ''Vaccinium'' (family Ericaceae), bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is '' Vaccinium myrtill ...
, blackberry
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by many species in the genus ''Rubus'' in the family Rosaceae, hybrids among these species within the subgenus ''Rubus'', and hybrids between the subgenera ''Rubus'' and ''Idaeobatus''. The taxonomy ...
, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry
''Aronia'' is a genus of deciduous shrubs, the chokeberries, in the family Rosaceae native to eastern North America and most commonly found in wet woods and swamps. The genus Aronia is considered to have 3 species. The most common and wide ...
, cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
, elderberry
''Sambucus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Adoxaceae. The various species are commonly called elder or elderberry. The genus was formerly placed in the honeysuckle family, Caprifoliaceae, but was reclassified as Adoxaceae due to ge ...
, hawthorn
Hawthorn or Hawthorns may refer to:
Plants
* '' Crataegus'' (hawthorn), a large genus of shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae
* ''Rhaphiolepis'' (hawthorn), a genus of about 15 species of evergreen shrubs and small trees in the family Rosace ...
, loganberry
The loganberry (''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') is a hybrid of the North American blackberry (''Rubus ursinus'') and the European raspberry ('' Rubus idaeus'').
The plant and the fruit resemble the blackberry more than the raspberry, but the fru ...
, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
s and plums, and in red cabbage
The red cabbage (purple-leaved varieties of ''Brassica oleracea'' Capitata Group) is a kind of cabbage, also known as Blaukraut after preparation. Its leaves are colored dark red/purple. However, the plant changes its color according to the pH ...
and red onion
Red onions (also known as purple or blue onions in some mainland European countries, though not the UK) are cultivars of the onion ('' Allium cepa''), and have purplish-red skin and white flesh tinged with red. They are most commonly used in c ...
. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH < 3, violet at pH 7-8, and blue at pH > 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6 or Sirt6) is a stress responsive protein deacetylase and mono-ADP ribosyltransferase enzyme encoded by the SIRT6 gene. In laboratory research, SIRT6 appears to function in multiple molecular pathways related to aging, including ...
(SIRT6) activator.
List of cyanidin derivatives
*Antirrhinin
Antirrhinin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-rutinoside of cyanidin.
Occurrence
It can be found in ''Antirrhinum majus'' (common snapdragon).
It can be found in blackcurrant, açaí, black raspberry, litchi pericarp and common fig
The fig is ...
(cyanidin-3-rutinoside
Rutinose is the disaccharide also known as 6-''O''-α-L- rhamnosyl-D-glucose (C12H22O10) that is present in some flavonoid glycosides. It is prepared from rutin by hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of wa ...
or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry
Black raspberry is a common name for three species of the genus ''Rubus'':
*''Rubus leucodermis
''Rubus leucodermis'', also called whitebark raspberry or blackcap raspberry, is a species of ''Rubus'' native to western North America.
Descripti ...
* Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry
Black raspberry is a common name for three species of the genus ''Rubus'':
*''Rubus leucodermis
''Rubus leucodermis'', also called whitebark raspberry or blackcap raspberry, is a species of ''Rubus'' native to western North America.
Descripti ...
* Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion
Red onions (also known as purple or blue onions in some mainland European countries, though not the UK) are cultivars of the onion ('' Allium cepa''), and have purplish-red skin and white flesh tinged with red. They are most commonly used in c ...
* Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in red onion
* Chrysanthemin
Chrysanthemin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of cyanidin.
Natural occurrences
Chrysanthemin can be found in the roselle plant (''Hibiscus sabdariffa'', Malvaceae), different Japanese angiosperms, '' Rhaponticum'' (Asteraceae), The fr ...
(cyanidin-3-''O''-glucoside), found in blackcurrant pomace
* Ideain
Ideain, the cyanidin 3-O-galactoside, is an anthocyanin, a type of plant pigment.
Natural occurrences
Ideain is the main anthocyanin in red-skinned or red-fleshed (for example Weirouge) apple varieties. It is also found in Chinese hawthorn frui ...
(cyanidin 3-O-galactoside), found in ''Vaccinium'' species
* Cyanin (cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside
Cyanidin-3,5-''O''-diglucoside, also known as cyanin, is an anthocyanin. It is the 3,5-''O''-diglucoside of cyanidin.
Natural occurrences
Cyanin can be found in species of the genus '' Rhaponticum'' (Asteraceae).
In food
Cyanin can be found ...
), found in red wine
Biosynthesis
Cyanidin can be synthesized in berry plants through theshikimate pathway
The shikimate pathway (shikimic acid pathway) is a seven-step metabolic pathway used by bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, some protozoans, and plants for the biosynthesis of folates and aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine) ...
and polyketide synthase
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynth ...
(PKS) III. The shikimate pathway is a biosynthetic pathways that uses the starting materials Phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) and Erythrose 4-phosphate
Erythrose 4-phosphate is a phosphate of the simple sugar erythrose. It is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway and the Calvin cycle.
In addition, it serves as a precursor in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids tyrosine, pheny ...
to form shikimic acid
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower ''shik ...
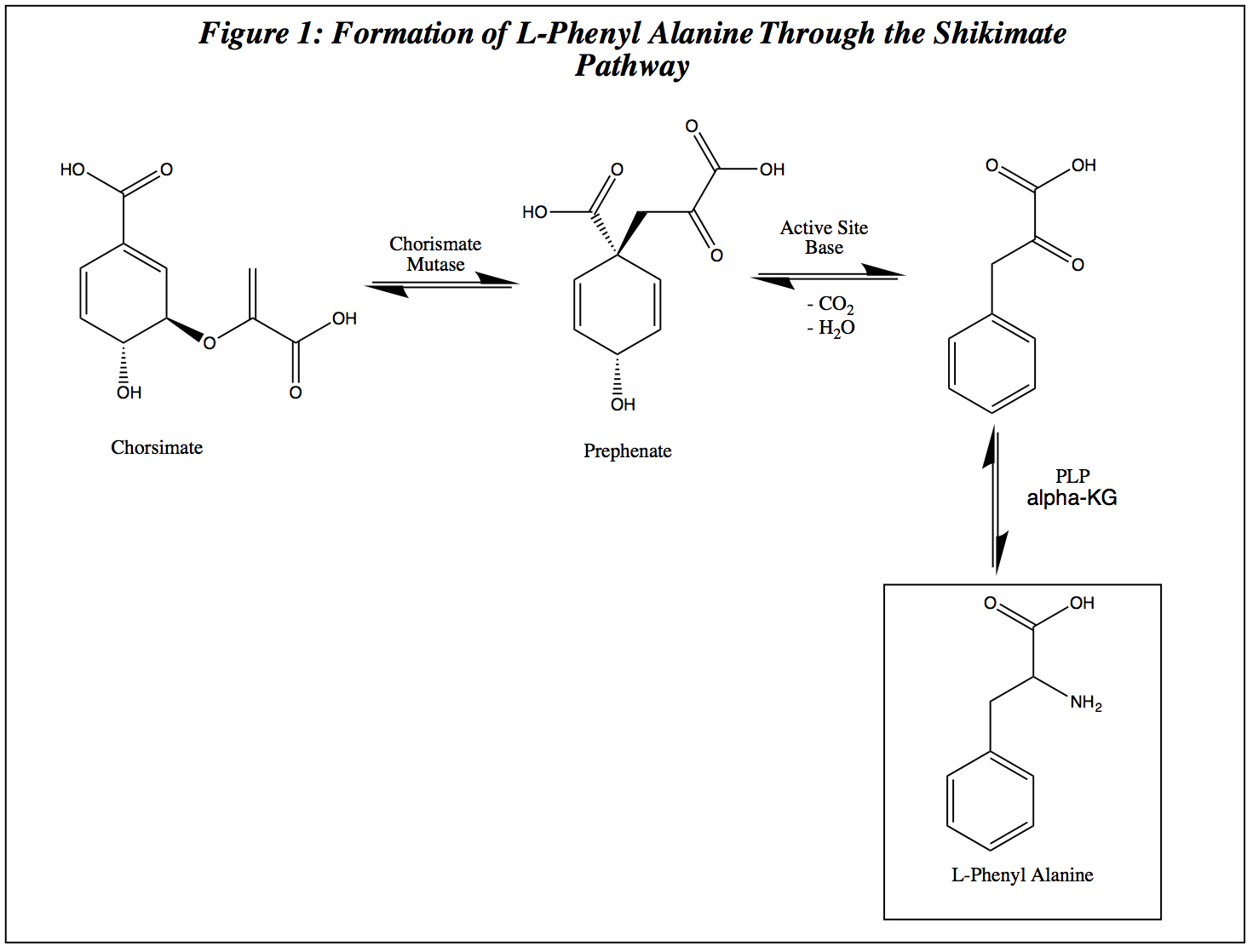
, which then further reacts to form specific aromatic amino acids. L- phenylalanine, which is necessary in the production of cyanidin, is synthesized through the shikimate pathway.
In the synthesis of L-phenylalanine, chorismate
Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. It is a precursor for:
* The aromatic amino acids phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine
* Indole, indole ...
undergoes a Claisen rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a ,3sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, ...
by a Chorismate mutase enzyme to form prephenate
Prephenic acid, commonly also known by its ion, anionic form prephenate, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, as well as of a large number of secondary metabolites of the Shikimic acid, sh ...
. Prephenate undergoes dehydration, decarboxylation, and transamination with Pyridoxal phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent a ...
(PLP) and alpha-Ketoglutaric acid to form L-phenylalanine (figure 1).
 L-phenylalanine then undergoes an elimination of the primary amine with
L-phenylalanine then undergoes an elimination of the primary amine with Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
The enzyme phenylalanine ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.24) catalyzes the conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and ''trans''-cinnamic acid.:
:L-phenylalanine = ''trans''-cinnamate + NH3
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) is the first and committed ...
(PAL) to form cinnamate. Through an oxidation with molecular oxygen and NADPH, a hydroxyl group is added to the para position of the aromatic ring. The compound then reacts with Coenzyme A (CoA), CoA ligase, and ATP to attach CoA to the carboxylic acid group. The compound reacts with naringenin
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs.
Structure
Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydro ...
- chalcone synthase and three malonyl CoA molecules to add six carbon atoms and three more keto groups ring through PKS III. Aureusidin synthase
Aureusidin synthase (, ''AmAS1'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''2',4,4',6'-tetrahydroxychalcone 4'-O-beta-D-glucoside:oxygen oxidoreductase''.
Aureusidin synthase has two main enzymatic tasks: hydroxylation at the 3-position on the B-ring ...
catalyses the aromatization and cyclization of the newly added carbonyl groups and facilitates the release of CoA. The compound then spontaneously cyclizes to form naringenin
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs.
Structure
Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydro ...
(figure 2).
 Naringenin is then converted to cyanidin through several oxidizing and reducing steps. First naringenin is reacted with two equivalents of oxygen, ''alpha''-Ketogluteratic acid, and flavanone 3-hydroxylase to form
Naringenin is then converted to cyanidin through several oxidizing and reducing steps. First naringenin is reacted with two equivalents of oxygen, ''alpha''-Ketogluteratic acid, and flavanone 3-hydroxylase to form dihydrokaempferol
Aromadendrin (aromodendrin or dihydrokaempferol) is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in the wood of ''Pinus sibirica''.
Metabolism
The enzyme dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase uses ''cis''-3,4-leucopelargonidin and NADP+ to pro ...
. The compound then reacts with NADPH and dihydroflavinol 4-reductase to form leucopelargonidin
Leucopelargonidin is a colorless chemical compound related to leucoanthocyanins. It can be found in ''Albizia lebbeck'' (East Indian walnut), in the fruit of ''Anacardium occidentale'' (Cashew), in the fruit of ''Areca catechu'' (Areca nut), in th ...
, which is further oxidized with oxygen, ''alpha''-Ketogluteratic acid, and anthocyanidin synthase. This compound spontaneously loses a water molecule and a hydroxide ion to form cyanidinDewick, P. M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd: United Kingdom 2009; pp 137-186 (figure 3).

Activation
Among manyanthocyanidin
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through ...
s studied, cyanidin most potently stimulated activity of the sirtuin 6
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6 or Sirt6) is a stress responsive protein deacetylase and mono-ADP ribosyltransferase enzyme encoded by the SIRT6 gene. In laboratory research, SIRT6 appears to function in multiple molecular pathways related to aging, including ...
enzyme.
References
{{Anthocyanidins Anthocyanidins