|
Ankylosaurini
Ankylosaurinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurid dinosaurs, existing from the Early Cretaceous about 105 million years ago until the end of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 mya. Many genera are included in the clade, such as ''Ankylosaurus'', ''Pinacosaurus'', ''Euoplocephalus'', and ''Saichania''. Features Ankylosaurines are defined as being closer relatives to ''Ankylosaurus'' than to ''Shamosaurus''. Diagnostic features of ankylosaurines include the nuchal shelf that obscures the occiput in dorsal view, and the quadrate condyle which is obscured lightly by the quadratojugal boss. Phylogeny The following cladogram is based on the 50% majority rule phylogenetic analysis In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... of Arbour & Currie (2015): References Ankylosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurus
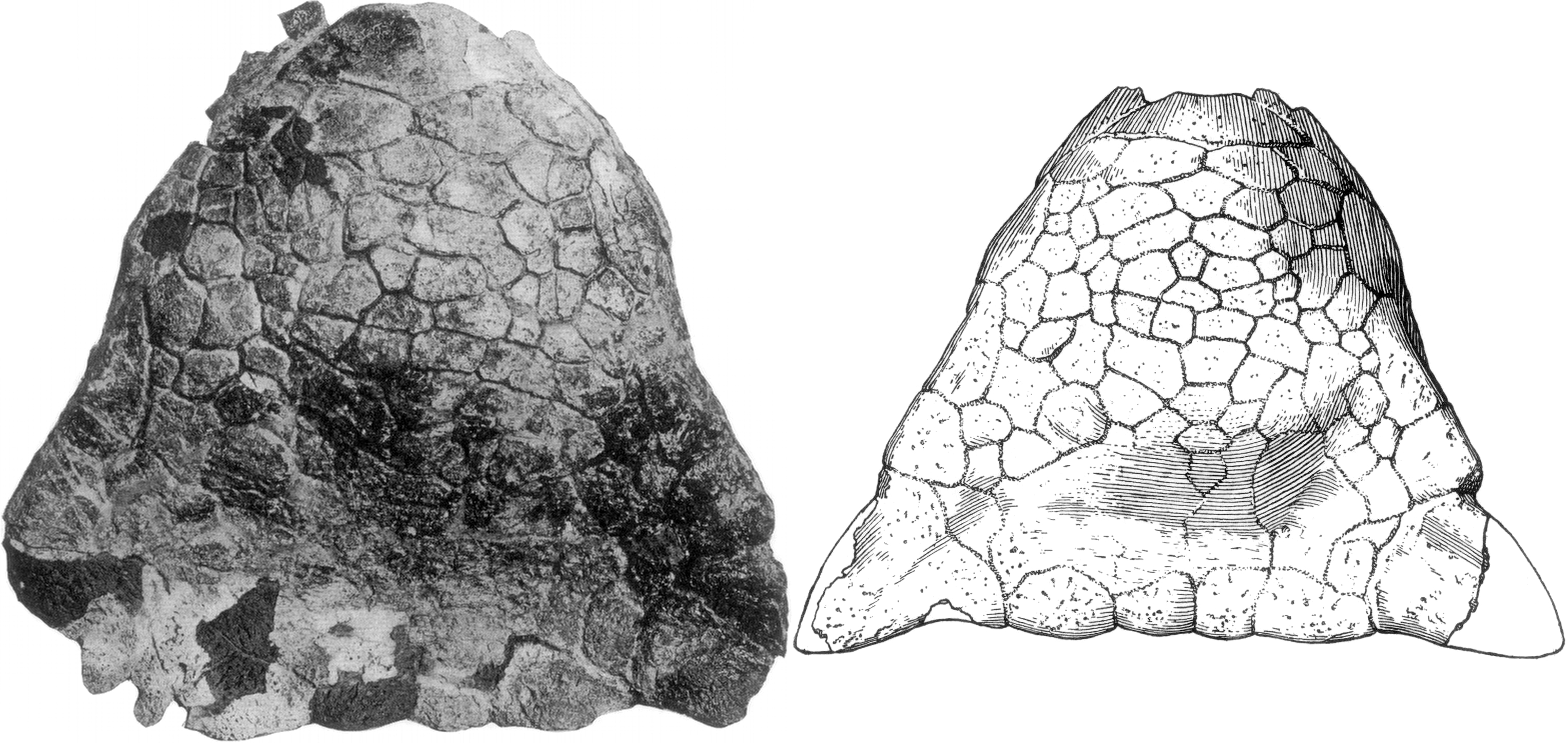
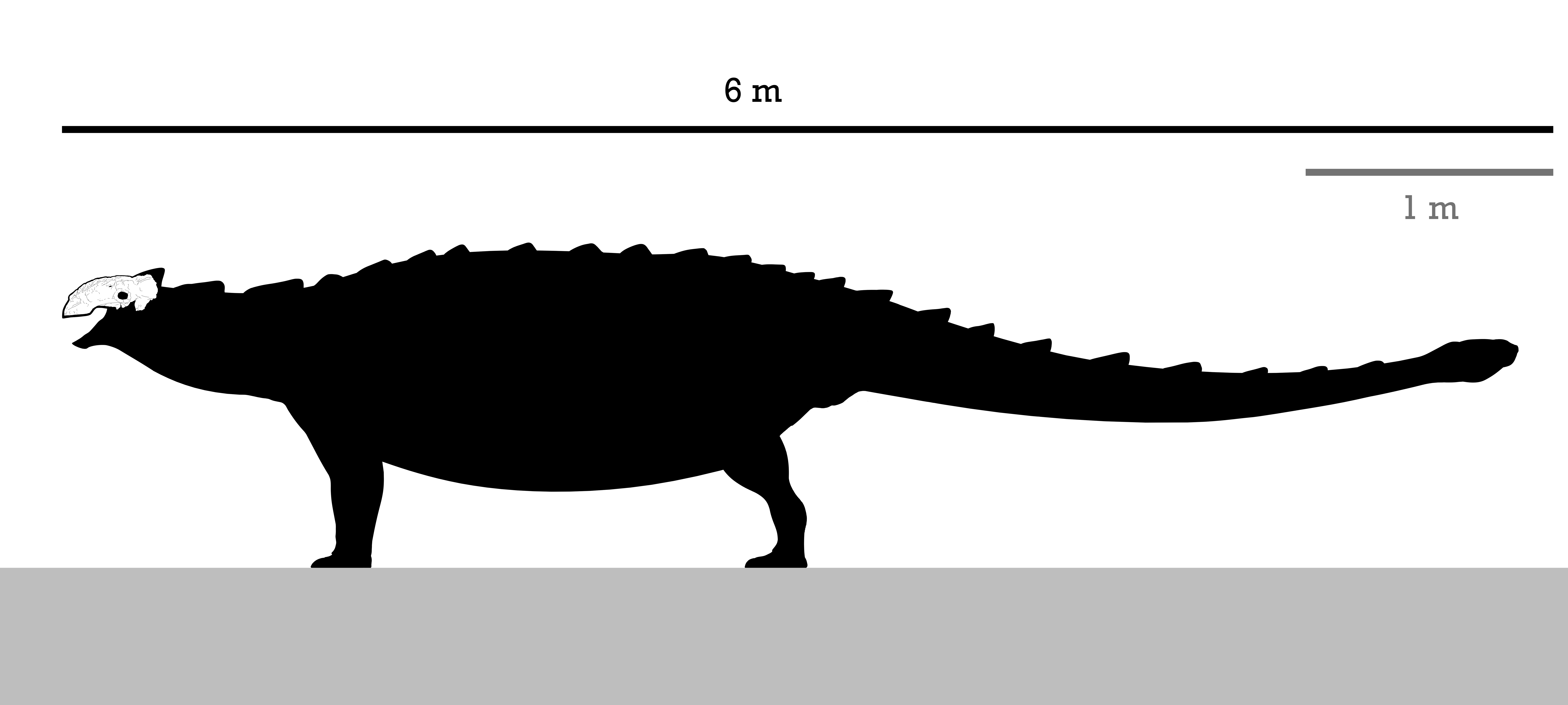
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest-known ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was quadrupedal, with a broad, robust body. It had a wide, low skull, with two horns pointing backward from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
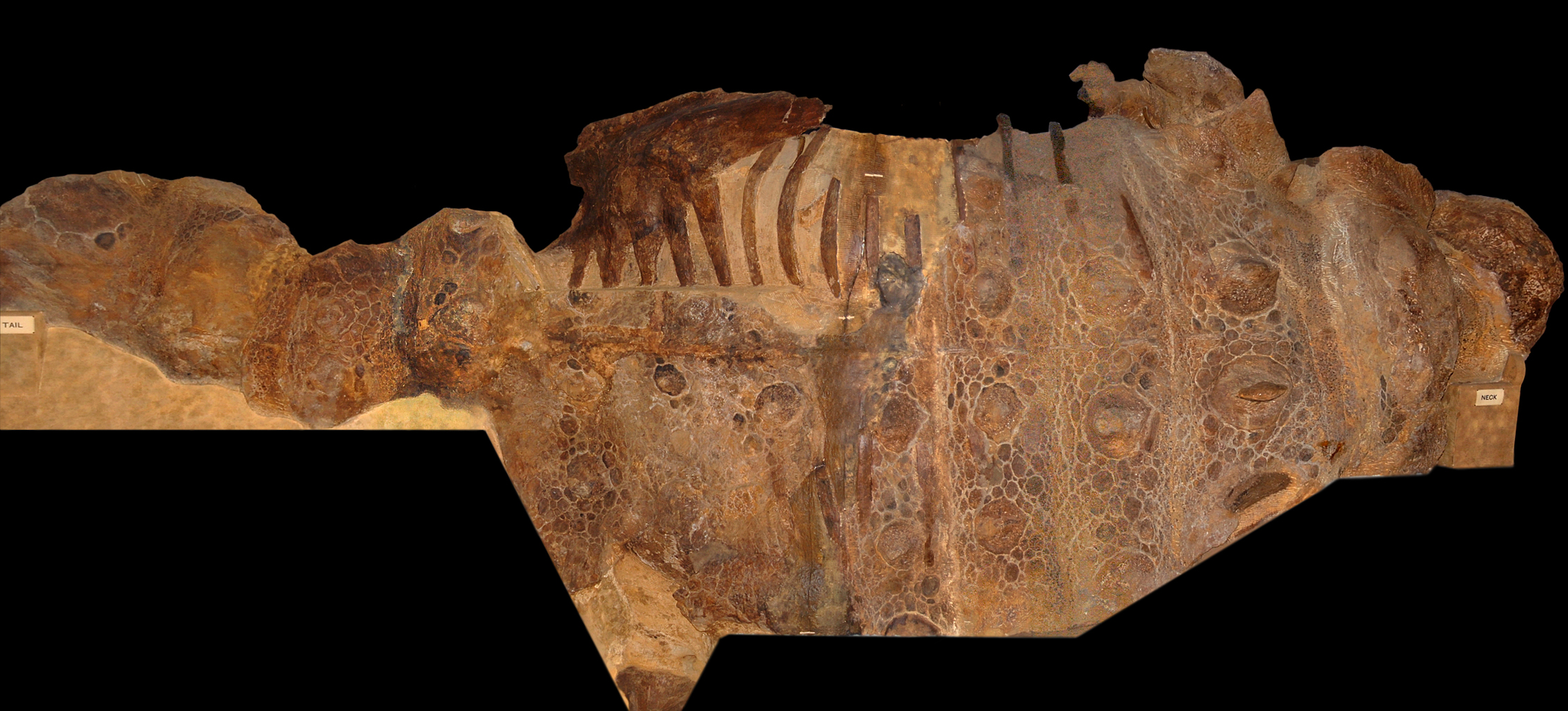
Zuul
''Zuul'' is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurine dinosaur from the Campanian Judith River Formation of Montana. The type species is ''Zuul crurivastator''. It is known from a complete skull and tail, which represents the first ankylosaurin known from a complete skull and tail club, as well as the most complete ankylosaurid specimen thus far recovered from North America. The specimen also preserved ''in situ'' osteoderms, keratin, and skin remains. Discovery and naming In 2014, Theropoda Expeditions LLC was excavating a possible ''Gorgosaurus'' specimen near Havre, Montana. On 16 May, a skid-steer loader removing a -high overburden unexpectedly hit upon an ankylosaurian tail club. An almost complete ankylosaur skeleton proved to be present. As it had not been eroded on the surface, it was in pristine condition. It was found overturned, with the stomach facing upwards. The skeleton was largely articulated, but the skull and some neck vertebrae were separated from the main tors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolosaurus Thronus
''Scolosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation and upper levels of the Oldman Formation in the Late Cretaceous (latest middle Campanian stage, about 76.5 Ma ago) of Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, ''S. cutleri'' and ''S. thronus''. The type species, ''S. cutleri'', measured up to in length and in body mass. Discovery ''Scolosaurus'' was named by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás in 1928, based on holotype NHMUK R.5161, a nearly complete specimen that preserves the entire skeleton except for the distal end of the tail, the right forelimb, the right hindlimb, and the skull. The rare preservation of osteoderms and skin impression are also present. The fossil skeleton was discovered by William Edmund Cutler, an independent fossil collector in 1914 at Quarry 80 of the Deadlodge Canyon locality. It was collected from the bottom of the Dinosaur Park Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolosaurus
''Scolosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation and upper levels of the Oldman Formation in the Late Cretaceous (latest middle Campanian stage, about 76.5 Ma ago) of Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, ''S. cutleri'' and ''S. thronus''. The type species, ''S. cutleri'', measured up to in length and in body mass. Discovery ''Scolosaurus'' was named by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás in 1928 in paleontology, 1928, based on holotype Natural History Museum, London, NHMUK R.5161, a nearly complete specimen that preserves the entire skeleton except for the distal end of the tail, the right forelimb, the right hindlimb, and the skull. The rare preservation of osteoderms and skin impression are also present. The fossil skeleton was discovered by William Edmund Cutler, an independent fossil collector in 1914 at Quarry 80 of the Deadlodge Canyon locality. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziapelta
''Ziapelta'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid. Its fossils have been found in the Hunter Wash and De-na-zin members of the Kirtland Formation of Upper Cretaceous (Campanian) New Mexico. It was named in 2014, in a research paper led by ankylosaur researcher Victoria Arbour. There is a single species in the genus, ''Ziapelta sanjuanensis.'' The genus is named after the Zia sun symbol, a stylized sun with four groups of rays, having religious significance to the Zia people of New Mexico, and the iconic symbol on the state flag of New Mexico, and ''pelta'' (Latin), a small shield, in reference to the osteoderms found on all ankylosaurids. The specific name is in reference to San Juan County and the San Juan basin, where the fossils were found. Multiple specimens have been described to date, though the fossils are mostly from the front part of the animal. The adult length of ''Ziapelta'' is estimated at between and long, depending on whether the holotype was full-grown. It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saichania
''Saichania'' (Mongolian meaning "beautiful one") is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Mongolia and China. The first fossils of ''Saichania'' were found in the early 1970s in Mongolia. In 1977 the type species ''Saichania chulsanensis'' was named. The description of this species has been based on limited fossil material; especially the rear of the animal is not well known. ''Saichania'' was more robustly built than other members of the Ankylosauridae, measuring in length and in body mass. Neck vertebrae, shoulder girdle, ribs and breast bones were fused or firmly connected. Its body was flat and low-slung, standing on four short legs. The forelimbs were very powerful. The head was protected by bulbous armour tiles. It could defend itself against predators like '' Tarbosaurus'' with a tail-club. On the torso keeled osteoderms were present. ''Saichania'' bit off plants in its desert habitat with a horny beak and processed them in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyoplosaurus
''Dyoplosaurus'' (meaning “double-armoured lizard”) is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from Alberta that lived during the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian, ~76.5–75 Ma) in what is now the Dinosaur Park Formation. ''Dyoplosaurus'' represents a close relative of ''Scolosaurus'' and ''Anodontosaurus'', two ankylosaurids known from the Horseshoe Canyon and Dinosaur Park Formation. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen was obtained in 1919 from the bottom ten metres of the Dinosaur Park Formation by Levi Sternberg, near what is now the Red Deer River in Alberta, Canada. The holotype specimen, ROM 784, consists of a partial skull roof, mandible fragments with teeth, osteoderms, skin impressions, articulated post-thoracic vertebrae, partial thoracic ribs, a partial ilium, both ischia, tail club, associated radius, metacarpal, femur, tibia, fibula, and pes. The holotype is currently housed at the Royal Ontario Museum. Two specimens were referred to ''Dyoplosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacosaurus
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China. The first remains of the genus were found in 1923, and the type species ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' was named in 1933. ''Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus'' named in 1999, is a second possibly valid species differing from the type species in details of the skull armour. Of ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' many skeletons have been found, more than of any other ankylosaur. These predominantly consist of juveniles that perhaps lived in herds roaming the desert landscape of their habitat. ''Pinacosaurus'' was a medium-sized ankylosaurine, about five metres long and weighed up to two tonnes. Its body was flat and low-slung but not as heavily built as in some other members of the Ankylosaurinae. The head was protected by bone tiles, hence its name. Each nostril was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platypelta
''Platypelta'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation (early Late Campanian stage, about 77.5-76.5 Ma ago) of southern Alberta, Canada. The type species is ''Platypelta coombsi''. Discovery and naming In 1914, Barnum Brown and Peter Kaisen, working for the American Museum of Natural History, in Alberta at the Sand Creek near the Red Deer River, eight miles southeast of Steveville, excavated an ankylosaur skeleton, specimen AMNH 5337. In 1971, it was referred to ''Euoplocephalus tutus'' by Walter Preston Coombs. In 2001 however, Paul Penkalski concluded that this skeleton was nearly identical to another exemplar, AMNH 5403, and that both likely represented a separate taxon.Penkalski, P., 2001, "Variation in specimens referred to ''Euoplocephalus tutus''", pp 261-298 in: Carpenter, K. (ed.): ''The Armored Dinosaurs'' Bloomington (Indiana University Press) In 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarchia
''Tarchia'' (meaning "brainy one") is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Discovery and naming In 1970, a Polish-Mongolian expedition discovered an ankylosaurian skull near Khulsan. In 1977, Teresa Maryańska named and described the type species ''Tarchia kielanae''. The generic name is derived from Mongolian тархи (''tarkhi'', "brain") and Latin ''~ia'', in reference to a brain size presumed larger than that of the related form '' Saichania''. The specific name honours Professor Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, the leader of the expedition. The holotype, ZPal MgD-I/111, was discovered in the Upper Cretaceous (possibly Campanian-Maastrichtian) Barun Goyot Formation (previously known as the 'Lower Nemegt Beds') of the Nemegt Basin of Mongolia. It consists of a skull roof, braincase and rear skull elements. Maryańska referred three additional specimens: ZPAL MgDI/43, a large postcranial skeleton containing three "free" tail vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsagantegia
''Tsagantegia'' (; meaning Tsagan Teg) is a genus of medium-sized ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, ''T. longicranialis''. The specimen consists of a very partial individual, comprising the skull and lacking postcranial remains. Since it only preserves the skull, ''Tsagantegia'' is mainly characterized by its elongated snout and the flattened facial osteoderms, greatly differing from other ankylosaurs. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen, MPC 700/17, is a virtually complete skull that was recovered from the locality Tsagan-Teg (or "White Mountain") of the Bayan Shireh Formation in the southeastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia. It was formally described in 1993 by the Russian paleontologist Tatyana Alekseyevna Tumanova. The generic name, ''Tsagantegia'', is in reference to Tsagan Teg, the locality of its discovery, and the specific name, ''longicranialis'', is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talarurus
''Talarurus'' ( ; meaning "basket tail" or "wicker tail") is a genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 96 million to 89 million years ago. The first remains of ''Talarurus'' were discovered in 1948 and later described by the Russian paleontologist Evgeny Maleev with the type species ''T. plicatospineus''. It is known from multiple yet sparse specimens, making it one of the most well known ankylosaurines, along with ''Pinacosaurus''. Elements from the specimens consists of various bones from the body; five skulls have been discovered and assigned to the genus, although the first two were very fragmented. It was a medium-sized, heavily built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to long and weighed about , nearly a ton. Like other ankylosaurs it had heavy armour and a club on its tail, limiting its speed. ''Talarurus'' is classified as a member of the Ankylosauria, in the Ankylosaurinae, a group of derived a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |