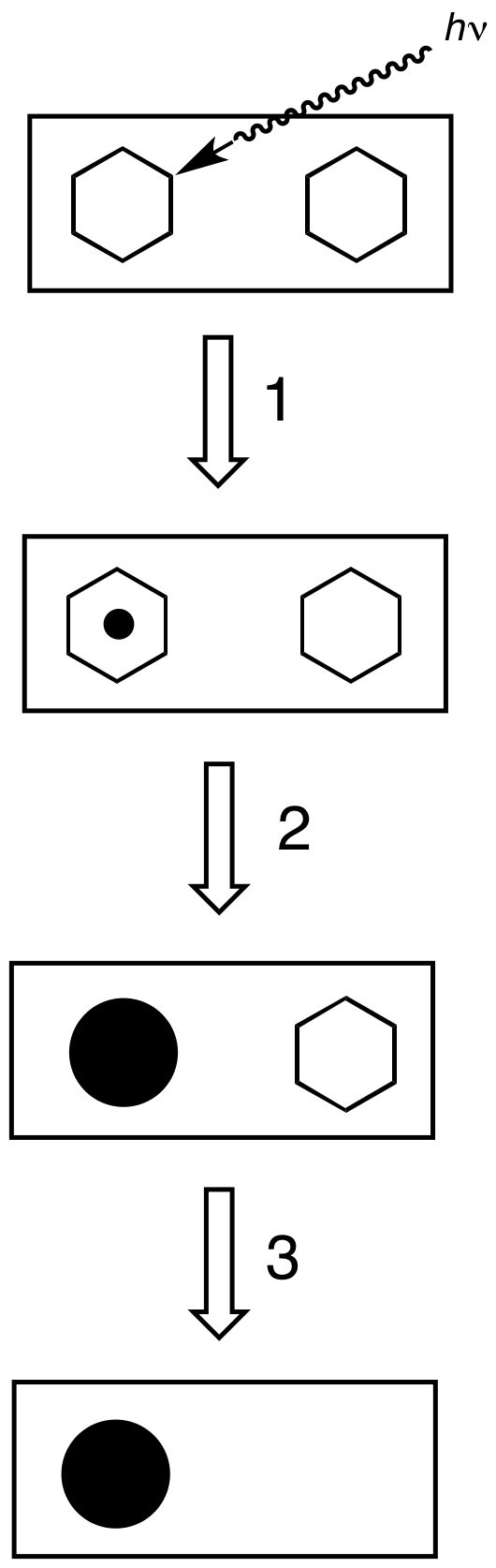
|
Ammonium Hydrosulfide
Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . Composition It is the salt derived from the ammonium cation and the hydrosulfide anion. The salt exists as colourless, water-soluble, micaceous crystals. On Earth the compound is encountered mainly as a solution, not as the solid, but ice is believed to be a substantial component of the cloud decks of the gas-giant planets Jupiter and Saturn, with sulfur produced by its photolysis responsible for the color of some of those planets' clouds. It can be generated by mixing hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. Preparation Solutions of ammonium hydrosulfide can be prepared by passing hydrogen sulfide gas through concentrated ammonia solution. According to a detailed 1895 report, hydrogen sulfide reacts with concentrated aqueous ammonia solution at room temperature to give . When this species is cooled to 0 °C and treated with additional hydrogen sulfide, one obtains . An ice-cold solution of this substance kept a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, Combustibility and flammability, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of Carbohydrate, sugars by yeasts or via Petrochemistry, petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds, and as a Alcohol fuel, fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Compounds
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Handbook Of Chemistry And Physics
The ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently () in its 103rd edition, published in 2022. It is sometimes nicknamed the "Rubber Bible" or the "Rubber Book", as CRC originally stood for "Chemical Rubber Company". As late as the 1962–1963 edition (3604 pages) the ''Handbook'' contained myriad information for every branch of science and engineering. Sections in that edition include: Mathematics, Properties and Physical Constants, Chemical Tables, Properties of Matter, Heat, Hygrometric and Barometric Tables, Sound, Quantities and Units, and Miscellaneous. Earlier editions included sections such as "Antidotes of Poisons", "Rules for Naming Organic Compounds", "Surface Tension of Fused Salts", "Percent Composition of Anti-Freeze Solutions", "Spark-gap Voltages", "Greek Alphabet", "Musical Scales", "Pigments and Dyes", "Comparison of Tons and Pounds", "Twist Drill and St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds. DNCB is produced commercially by the nitration of ''p''-nitrochlorobenzene with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids. Other methods afford the compound less efficiently include the chlorination of dinitrobenzene, nitration of o-nitrochlorobenzene and the dinitration of chlorobenzene. Uses By virtue of the two nitro groups, the chloride is susceptible to nucleophilic substitution. In this way, the compound is a precursor to many other compounds. Laboratory use DNCB is used as a substrate in GST enzyme activity assays. The molecule is conjugated to a single molecule of reduced glutathione which then absorbs at 340 nm. Affinity of CDNB for each class of GST varies and so it is not a good measure of activity for some forms (e.g. GSTT and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patina
Patina ( or ) is a thin layer that variously forms on the surface of copper, brass, bronze and similar metals and metal alloys (tarnish produced by oxidation or other chemical processes) or certain stones and wooden furniture (sheen produced by age, wear, and polishing), or any similar acquired change of a surface through age and exposure. Additionally, the term is used to describe the aging of high-quality leather. The patinas on leather goods are unique to the type of leather, frequency of use, and exposure. Patinas can provide a protective covering to materials that would otherwise be damaged by corrosion or weathering. They may also be aesthetically appealing. Usage On metal, patina is a coating of various chemical compounds such as oxides, carbonates, sulfides, or sulfates formed on the surface during exposure to atmospheric elements (oxygen, rain, acid rain, carbon dioxide, sulfur-bearing compounds). In common parlance, weathering rust on steel is often mistakenly refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Developing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All photographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Sulfide008
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stink Bomb
A stink bomb, sometimes called a stinkpot, is a device designed to create an unpleasant smell. They range in effectiveness from being used as simple pranks to military grade malodorants or riot control chemical agents. History A stink bomb that could be launched with arrows was invented by Leonardo da Vinci. The 1972 U.S. presidential campaign of Edmund Muskie was disrupted at least four times in Florida in 1972 with the use of stink bombs during the Florida presidential primary. Stink bombs were set off at campaign picnics in Miami and Tampa, at the Muskie campaign headquarters in Tampa and at offices in Tampa where the campaign's telephone bank was located. The stink bomb plantings served to disrupt the picnics and campaign operations, and was deemed by the U.S. Select Committee on Presidential Campaign Activities of the U.S. Senate to have "disrupted, confused, and unnecessarily interfered with a campaign for the office of the Presidency". In 2004, it was reported that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |