|
Abjadi Order
The Abjad numerals, also called Hisab al-Jummal ( ar, حِسَاب ٱلْجُمَّل, ), are a decimal alphabetic numeral system/alphanumeric code, in which the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet are assigned numerical values. They have been used in the Arabic-speaking world since before the eighth century when positional Arabic numerals were adopted. In modern Arabic, the word ' () means ' ' in general. In the Abjad system, the first letter of the Arabic alphabet, ʾalif, is used to represent 1; the second letter, bāʾ, 2, up to 9. Letters then represent the first nine intervals of 10s and those of the 100s: yāʾ for 10, kāf for 20, qāf for 100, ending with 1000. The word '' ʾabjad'' () itself derives from the first four letters (A-B-J-D) of the Semitic alphabet, including the Aramaic alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, and other scripts for Semitic languages. These older alphabets contained only 22 letters, stopping at taw, numerically equivalent to 400. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabetic Numeral System
An alphabetic numeral system is a type of numeral system. Developed in classical antiquity, it flourished during the early Middle Ages. In alphabetic numeral systems, numbers are written using the Grapheme, characters of an alphabet, syllabary, or another writing system. Unlike Acrophony, acrophonic numeral systems, where a numeral is represented by the first letter of the lexical name of the numeral, alphabetic numeral systems can arbitrarily assign letters to numerical values. Some systems, including the Arabic, Georgian numerals, Georgian and Hebrew numerals, Hebrew systems, use an already established alphabetical order. Alphabetic numeral systems originated with Greek numerals around 600 BC and became largely extinct by the 16th century. After the development of Positional notation, positional numeral systems like Hindu–Arabic numerals, the use of alphabetic numeral systems dwindled to predominantly ordered lists, pagination, religious functions, and divinatory magic. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ṯāʾ
() is one of the six letters the Arabic alphabet added to the twenty-two from the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ). In Modern Standard Arabic it represents the voiceless dental fricative , also found in English as the " th" in words such as "thank" and "thin". In Persian, Urdu Urdu (;"Urdu" '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allah
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", and is linguistically related to the Aramaic words Elah and Syriac (ʼAlāhā) and the Hebrew word '' El'' ('' Elohim'') for God. The feminine form of Allah is thought to be the word Allat. The word ''Allah'' has been used by Arabic people of different religions since pre-Islamic times. The pre-Islamic Arabs worshipped a supreme deity whom they called Allah, alongside other lesser deities. Muhammad used the word ''Allah'' to indicate the Islamic conception of God. ''Allah'' has been used as a term for God by Muslims (both Arab and non-Arab) and even Arab Christians after the term " al- ilāh" and "Allah" were used interchangeably in Classical Arabic by the majority of Arabs who had become Muslims. It is also often, albeit not exclusiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basmala
The ''Basmala'' ( ar, بَسْمَلَة, ; also known by its incipit ; , "In the name of Allah"), or Tasmiyyah (Arabic: ), is the titular name of the Islamic phrase "In the name of God, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful" (Arabic: , ). It is one of the most important phrases in Islam and is used by Muslims mostly before starting "good deeds" (for instance, during daily prayer) as well as beginning of most daily actions. It is used in over half of the constitutions of countries where Islam is the official religion or more than half of the population follows Islam, usually the first phrase in the preamble, including those of Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Brunei, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Maldives, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia and the United Arab Emirates. It is the phrase recited before each chapter (''surah'') of the Qur'anexcept for the ninth.See, however, the discussion of the eighth and ninth ''sura''s at Al-Anfal (the eighth ''sura''). Muslim disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline (list)
An outline, also called a hierarchical outline, is a list arranged to show hierarchical relationships and is a type of tree structure. An outline is used to present the main points (in sentences) or topics (terms) of a given subject. Each item in an outline may be divided into additional sub-items. If an organizational level in an outline is to be sub-divided, it shall have at least two subcategories, as advised by major style manuals in current use. An outline may be used as a drafting tool of a document, or as a summary of the content of a document or of the knowledge in an entire field. It is not to be confused with the general context of the term "outline", which a summary or overview of a subject, presented verbally or written in prose (for example, ''The Outline of History'' is not an outline of the type presented below). The outlines described in this article are lists, and come in several varieties. A sentence outline is a tool for composing a document, such as an essay, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu–Arabic Numeral System
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system or Indo-Arabic numeral system Audun HolmeGeometry: Our Cultural Heritage 2000 (also called the Hindu numeral system or Arabic numeral system) is a positional decimal numeral system, and is the most common system for the symbolic representation of numbers in the world. It was invented between the 1st and 4th centuries by Indian mathematicians. The system was adopted in Arabic mathematics by the 9th century. It became more widely known through the writings of the Persian mathematician Al-Khwārizmī: "Historians have speculated on al-Khwarizmi's native language. Since he was born in a former Persian province, he may have spoken the Persian language. It is also possible that he spoke Khwarezmian, a language of the region that is now extinct." (''On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals'', ) and Arab mathematician Al-Kindi (''On the Use of the Hindu Numerals'', ). The system had spread to medieval Europe by the High Middle Ages. The system is base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Alphabet
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan (Dari Persian) since the 7th century after the Muslim conquest of Persia. The Persian dialect spoken in Tajikistan (Tajiki Persian) is written in the Tajik alphabet, a modified version of the Cyrillic alphabet which has been in use since the Soviet era. The Persian alphabet is directly derived and developed from the Arabic alphabet. After the Muslim conquest of Persia and the fall of the Sasanian Empire in the 7th century, Arabic became the language of government and especially religion in Persia for two centuries. The replacement of the Pahlavi scripts with the Persian alphabet to write the Persian language was done by the Saffarid dynasty and Samanid dynasty in 9th-century Greater Khorasan. The script is mostly but not exclusively right-to-left; mathematical expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
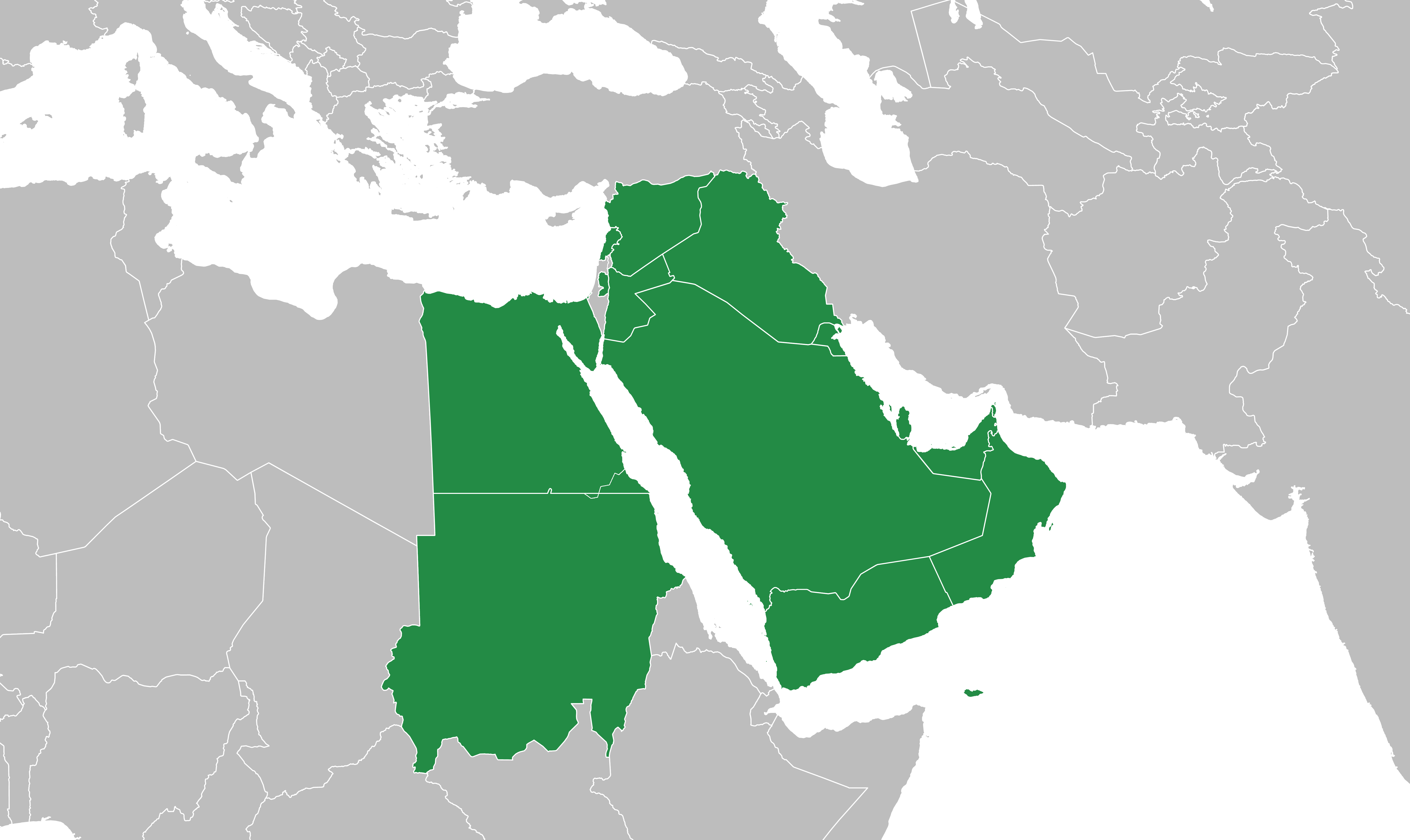
Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to ''Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part (Cyrenaica) being linked more to Egypt and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, Libya, Mauritania (also considered part of West Africa), Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the disputed territory of Western Sahara (controlled mostly by Morocco and partly by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic) and the Spanish cities Ceuta and Melilla.Article 143. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people. Through the 18th and 19th centuries, English sources often referred to the region as the Barbary Coast or the Barbary States, a term derived from the demonym of the Berbers. Sometimes, the region is referred to as the Land of the Atlas, referring to the Atlas Mountains, which are located within it. The Maghreb is usually defined as encompassing much of the northern part of Africa, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shin (letter)
Shin (also spelled Šin (') or Sheen) is the twenty-first letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Shin , Hebrew Shin , Aramaic Shin , Syriac Shin ܫ, and Arabic Shin (in abjadi order, 13th in modern order). Its sound value is a voiceless sibilant, or . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Sigma () (which in turn gave Latin and Cyrillic С), and the letter '' Sha'' in the Glagolitic and Cyrillic scripts (, ). The South Arabian and Ethiopian letter ''Śawt'' is also cognate. Origins The Proto-Sinaitic glyph, according to William Albright, was based on a "tooth" and with the phonemic value š "corresponds etymologically (in part, at least) to original Semitic ''ṯ'' (th), which was pronounced ''s'' in South Canaanite". The Phoenician letter expressed the continuants of two Proto-Semitic phonemes, and may have been based on a pictogram of a tooth (in modern Hebrew ''shen''). The Encyclopaedia Judaica, 1972, records that it originally represented a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samekh
Samekh (Phoenician ''sāmek'' ; Hebrew ''samekh'' , Syriac ''semkaṯ'') is the fifteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including the Hebrew alphabet. Samekh represents a voiceless alveolar fricative . Unlike most Semitic consonants, the pronunciation of remains constant between vowels and before voiced consonants. In the Hebrew language, the samekh generally shares a similar pronunciation as the left-dotted shin. The numerical value of samekh is 60. History The Phoenician letter may continue a glyph from the Middle Bronze Age alphabets, either based on a hieroglyph for a tent peg or support, possibly the ''djed'' "pillar" hieroglyph (c.f. Hebrew root סמך s-m-kh 'support', סֶמֶךְ semekh 'support, rest', סוֹמֵךְ somekh 'support peg, post', סוֹמְכָה somkha 'armrest', סָמוֹכָה smokha 'stake, support', indirectly '' s'mikhah'' ; Aramaic סַמְכָא samkha 'socket, base', סְמַךְ smakh 'support, help'; Syriac ܣܡܟܐ semkha 'support') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopsephy
Isopsephy (; ''isos'' meaning "equal" and ''psephos'' meaning "pebble") or isopsephism is the practice of adding up the number values of the letters in a word to form a single number. The total number is then used as a metaphorical bridge to other words evaluating the equal number, which satisfies ''isos'' or "equal" in the term. The early Greeks used pebbles arranged in patterns to learn arithmetic and geometry, which corresponds to ''psephos'' or "pebble" and "counting" in the term. Isopsephy is related to gematria: the same practice using the Hebrew alphabet. It is also related to the ancient number systems of many other peoples (for the Arabic alphabet version, see Abjad numerals). A gematria of Latin script languages was also popular in Europe from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance, and its legacy remains in code-breaking, numerology, and Masonic symbolism today (see arithmancy). History Until Arabic numerals were adopted and adapted from Indian numerals in the 8th and 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |