|
Newar Caste System
Newar caste system is the system by which Newārs, the historical inhabitants of Kathmandu Valley, are divided into groups on the basis of Vedic varna model and divided according to their hereditary occupations. First introduced at the time of the Licchavis (A.D. 300 – c. 879), the Newar caste system assumed its present shape during the medieval Malla period (A.D. 1201–1769). The Newar caste structure resembles more closely to North India and Madheshis than that of the Khas 'Parbatiyas' in that all four Varna (Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra) and untouchables are represented. The social structure of Newars is unique as it is the last remaining example of a pre-Islamic North Indic civilisation in which Buddhist elements enjoy equal status with the Brahmanic elements. History of assimilation According to various historical sources, even though the presence of ''varna'' and caste had been a known element in the social structure of the Kathmandu Valley since the Lic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
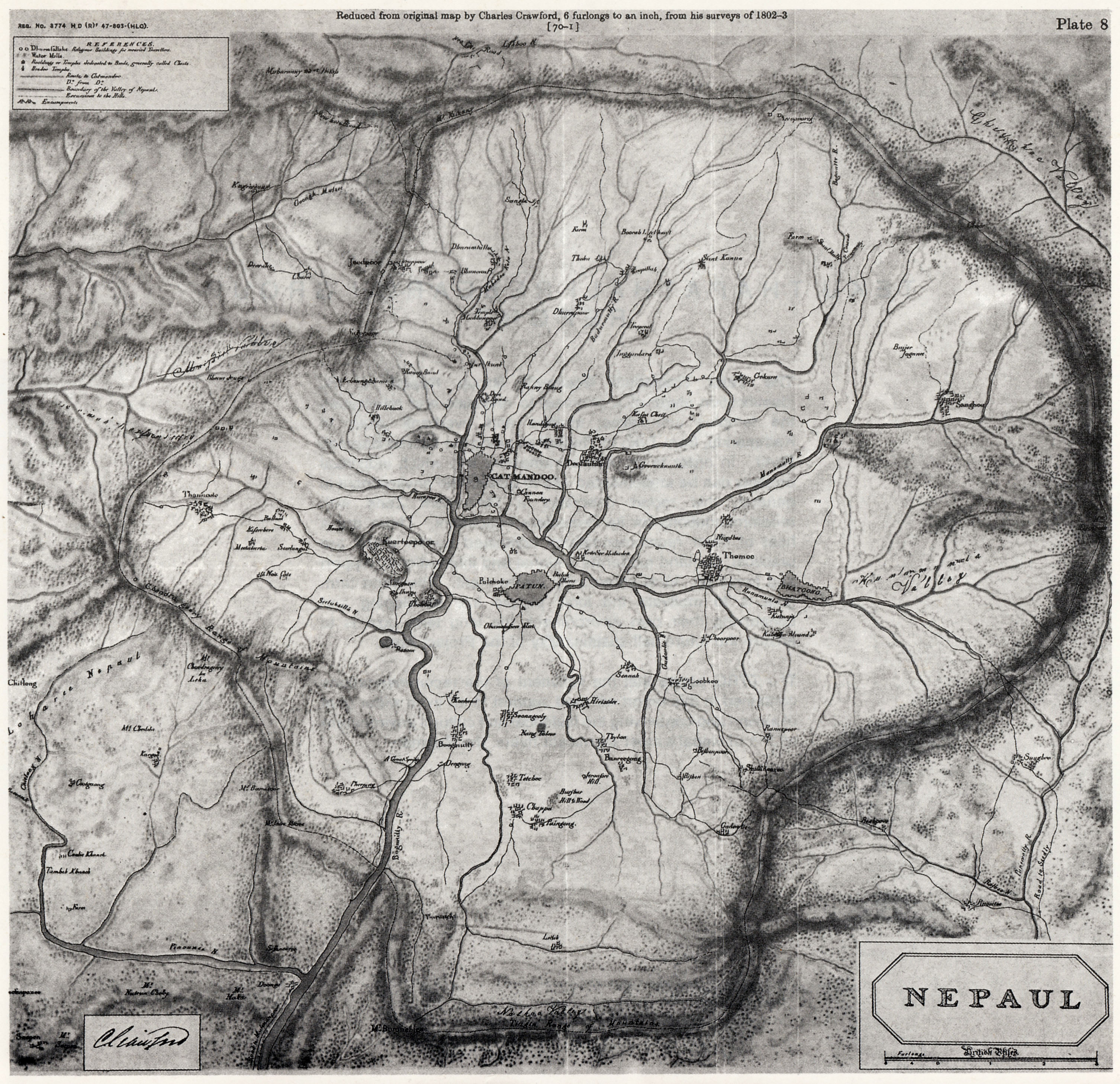
Nepaul Valley Map 1802
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanyakubja Brahmins
Kanyakubja Brahmins are a Brahmin community mainly found in northern India. They are classified as one of the Pancha Gauda Brahmin communities native to the north of the Vindhyas. Kanyakubja Brahmins are also considered most Martial of all Brahmins and Were mostly powerful landlords during British colonial period in the Awadh Region. Sub-groups of this community include the Saryupareen Brahmins,Jujhautiya Brahmins and the Bhumihar Bhumihars, also called Babhan, are a Hindu caste mainly found in Bihar (including the Mithila region), the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, the Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh, and Nepal. The Bhumihars claim Brahmin stat ...People of India Uttar Pradesh Volume XLII Part Two edited by A Hasan & J C Das pages 718 to 724 Manohar Publications References Brahmin communities of Uttar Pradesh Brahmin communities of Bihar Brahmin communities of Madhya Pradesh Brahmin communities of West Bengal Brahmin communities of Assa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajracharya
A vajrācārya (vajra + acharya, Tib. རྡོ་རྗེ་སློབ་དཔོན་, ''dorje lopön'', Wyl. ''rdo rje slob dpon,'' Jp. “kongō ajari” 金剛阿闍梨) is a Vajrayana Buddhist master, guru or priest. It is a general term for a tantric master in Vajrayana Buddhist traditions, including Tibetan Buddhism, Shingon, Bhutanese Buddhism, Newar Buddhism. Tibetan Buddhism In Tibetan Buddhism, Dorje Lopön is a title given to high-level religious leaders who preside over tantric rituals and initiations. Dorje is the Tibetan equivalent of the Sanskrit vajra and therefore the term appears frequently in Tibetan Buddhist terminology relating to Vajrayana. A Dorje Lopön is usually well educated and trained in tantric practice, and is therefore a well respected figure. They might be the heads of monasteries or spiritual communities. Newar Buddhism Bajracharyas are a married priestly class among the Newar communities of Nepal. They are knowledgeable in Newa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Caste System
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic example of classification of castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, especially the Mughal Empire and the British Raj. It is today the basis of affirmative action programmes in India as enforced through its constitution. The caste system consists of two different concepts, ''varna'' and '' jati'', which may be regarded as different levels of analysis of this system. Based on DNA analysis, endogamous i.e. non-intermarrying Jatis originated during the Gupta Empire. Our modern understanding of caste as an institution in India has been influenced by the collapse of the Mughal era and the rise of the British colonial government in India. The collapse of the Mughal era saw the rise of powerful men who associated themselves with kings, priests and ascetics, affirming the regal and martial form of the caste ideal, and it also res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajkarnikar
Rajkarnikar (Devanagari: राजकर्णिकार) are a newar clan of confectioners and sweet makers situated in Kathmandu Valley, in Nepal. Etymology and origin The name "Rajkarnikar" means state official. Rajkarnikars in Nepal are found mostly in Yen or Kathmandu Valley, over the regions of Kathmandu, Bhaktapur and Lalitpur (Patan in Nepali; Yela in Newari ); In 2011, their population was 83,000. Around 60,000 still reside in rural areas, and around 20,000 in urban areas. They speak Nepalbhasa. The ethologist and anthropologist, Brian Houghton Hodgson, during his posting in Nepal, Hodgson became proficient in Nepali and Newari. They are part of Newar clans and descendants of Kirat People. Traditional Occupation Halwais are sweet makers by tradition. They take on many responsibilities that are considered religiously important. Traditional sweets prepared include Jeri, Swari, and Haluwa. Rajkarnikars are Newar and have their own caste system. The caste-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapali (Newar Caste)
Kapali is one of the Caste of Newar community in Nepal. It is an ancient caste of Nepal. Kapali caste are found in various parts of Nepal. Newar Kapalis predominantly used to possess high tantric power. The Newar people are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal. Description Generally, Kapalis of Shiva Gotra are widely found in Nepal. They follow mixed Hinduism as well as Buddhism. They mostly follow Hinduism and consider Shiva as the supreme body whereas Guru Gorakhnath is considered as the supreme deity for their welfare. Kapali are taken as kid of Lord Shiva. Although, in different time period, Kapali have developed their own Tantric system. Kapali plays Myali ( a musical instrument like Flute made up of animal bone) which has the immense power to call God in the stone idol. The musical instrument is also capable to make the rainfall from the sky as per Sadhak's power. Kapalis had served as nurse, doctor or delivery person during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundhi
Sundhi also known as Sodhi or Sundi or Sudi or Sudhi or Shoundika, is an Indian caste whose traditional occupation has been brewing of alcoholic drinks. According to Suratha Kumar Malik, Sundhi castes belong to the Dalit community, who are hooch traders and do small businesses. The Sundhis are included in the Other Backward Class category in the states of Bihar, Jharkhand and Odisha; and in the Scheduled Caste category in West Bengal, where they are also known as Shunri Shunris are a Bengali Hindu caste whose traditional occupation is the distillation and selling of country wine. History In the census of 2001, the Shunris numbered 317,543 in West Bengal, consisting of 1.7% of the total Scheduled caste popul ... (except Saha).Singh, K. S. (1992). People of India: The scheduled castes. India: Anthropological Survey of India. p. 1244 References Indian castes Brewing and distilling castes Social groups of Bihar Social groups of Jharkhand Social groups of Odisha S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnata Dynasty
Karnata was a southern kingdom, mentioned in the great epic Mahabharata, This kingdom gave the name to the South Indian state Karnataka. The Karnata Kingdom forms the total portion of ancient Karnataka state of India. References in Mahabharata Sahadeva's Military Campaign to the South of India *Mahabharata, Book 2, Chapter 30 Sahadeva conquered the town of Sanjayanti and the country of the Pashandas and the Karanatakas by means of his messengers alone, and made all of them pay tributes to him. The hero brought under his subjection and exacted tributes from the Paundrayas and the Dravidas along with the Udrakeralas and the Andhras and the Talavanas, the Kalingas and the Ushtrakarnikas, and also the delightful city of Atavi and that of the Yavanas. Nakula's Military Campaign to the West of India *Mahabharata, Book 2, Chapter 32 Nakula subjugated the whole of the desert country and the region known as Sairishaka full of plenty, as also that other one called Mahetta. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shresthas
The Śreṣṭha ( ne, श्रेष्ठ) or () is the second largest Newar caste group, occupying around 21% of overall Newar population, or about 1.1% of Nepal’s total population. It is believed that the word ''Srēṣṭha'' is derived from the Newar word ''Śeśyah'', which itself is derivation of a Sanskrit word ''Sista'' meaning 'noble', although literal meaning of the word also translated to 'best or important.' "Shrestha" itself was later adopted as the specific family surname by members of this high-caste Hindu group, although there are over 50 other recognized surnames of Srēṣṭhas. Despite their numerically low national population, their high-status and socio-economic capital puts Śreṣṭhas amongst the most socio-economically privileged and politically over-represented segments of Nepali population. Prior to Nepal’s unification, Srēṣṭha was a collective high-status title given to those Hindu clans referred to as 'Bhāro' (from ''bhārdār''/noble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja Kannauj is an ancient city. It is said that the Kanyakubja Brahmins who included Shandilya (teacher of Rishi Bharadwaja) were held one of the three prominent families originally from Kannauj. In Classical India, it served as the center of imperial Indian dynasties. The earliest of these was the Maukhari dynasty, and later, Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana dynasty.Tripathi, ''History of Kanauj'', p. 192 The city later came under the Gahadavala dynasty, and under the rule of Govindachandra, the city reached "unprecedented glory". Kannauj was also the main place of war in the Tripartite struggle between the Gurjara-Pratihara, the Palas and the Rashtra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



