|
Parallel Lives
The ''Parallel Lives'' ( grc-gre, Βίοι Παράλληλοι, ''Bíoi Parállēloi''; la, Vītae Parallēlae) is a series of 48 biographies of famous men written by the Greco-Roman philosopher, historian, and Apollonian priest Plutarch, probably at the beginning of the second century. It is also known as ''Plutarch's Lives'' (, ''Ploútarchou Bíoi''; ); ''Parallels'' (, ''Parállēla''; ); the ''Comparative Lives'' (, ''Sygkritikoí Bíoi''; ); the ''Lives of Illustrious Men'' (); and the ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'' (, ''Bioi Rhōmaiōn kai Hellēnōn''; or ). The lives are arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings. The surviving ''Parallel Lives'' comprises 23 pairs of biographies, each pair consisting of one Greek and one Roman of similar destiny, such as Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar, or Demosthenes and Cicero. It is a work of considerable importance, not only as a source of information about the individuals described, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeronea
Chaeronea ( English: or ; el, Χαιρώνεια , ) is a village and a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece, located about 35 kilometers east of Delphi. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Livadeia, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 111.445 km2, the community is 26.995 km2. Population 1,382 (2011). It is located near Mount Thourion in the Kifisós river valley, NW of Thebes. History First settled in the Prehistoric period at the site now known as Magoula Balomenou (Μαγούλα Μπαλωμένου), its older name was Arne, and it was originally on the shore of Lake Copais (later drained). Chaeronea was subject to Orchomenus which was, beginning in 600 BC, a member of the Boeotian League. In the late 5th century BC, Chaironeia belonged to one of the 11 Boeotian districts along with Acraephnium and Copia. Chaeronea's importance lay in its strategic position near the head of the defile wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
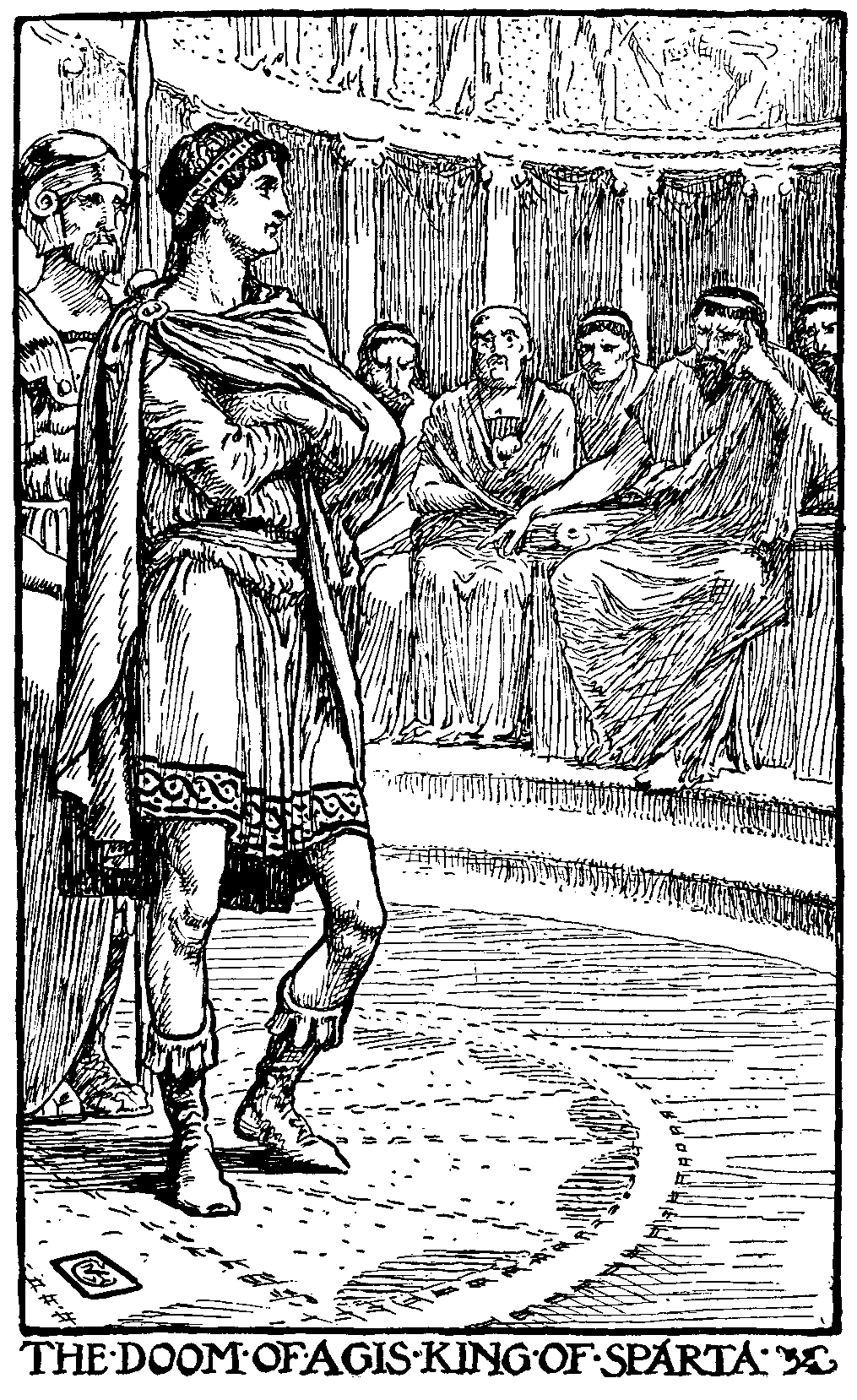
Agis IV
Agis IV ( grc-gre, Ἄγις; c. 265 BC – 241 BC), the elder son of Eudamidas II, was the 25th king of the Eurypontid dynasty of Sparta. Posterity has reckoned him an idealistic but impractical monarch. Family background and accession Agis was the son of Eudamidas II () and grandson of Archidamus IV (), who belonged to the Eurypontid dynasty, one of the two royal families of Sparta (the other being the Agiads). The reign of Agis marks a re-emergence of the Eurypontids, who had disappeared from the records since the defeat of Archidamus IV against Demetrios Polyorketes in 294. His father is indeed the most obscure of all the Spartan kings, perhaps due to a mental or physical disability. Eudamidas II's dates of reign are therefore very conjectural. The traditional year of his death is c.245, but he may have died earlier (up to 263), in which case a regent was appointed during Agis' minority, as he was born c.265. The most likely candidate is his uncle Agesilaus, who play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones (calendar), nones, and ides (calendar), ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's Egyptian calendar, former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the Byzantine Empire, later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numa Pompilius
Numa Pompilius (; 753–672 BC; reigned 715–672 BC) was the legendary second king of Rome, succeeding Romulus Romulus () was the legendary foundation of Rome, founder and King of Rome, first king of Ancient Rome, Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus ... after a one-year interregnum. He was of Sabine origin, and many of Rome's most important religious and political institutions are attributed to him, such as the Roman calendar, Vestal Virgins, the cult of Mars, the cult of Jupiter, the cult of Romulus, and the office of ''pontifex maximus''. Genealogy According to Plutarch, Numa was the youngest of Pomponius's four sons, born on the day of Rome's founding (traditionally, 21 April 753 BC). He lived a severe life of discipline and banished all luxury from his home. Titus Tatius, king of the Sabines and a colleague of Romulus, gave in marriage his only daughter, Tatia (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Sources
A tertiary source is an index or textual consolidation of already published primary and secondary sourcesPrimary, secondary and tertiary sources. ". University Libraries, University of Maryland. Retrieve 07/26/2013 that does not provide additional interpretations or analysis of the sources.Tertiary sources . James Cook University. Some tertiary sources can be used as an aid to find key (seminal) sources, key terms, general [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Source
In scholarship, a secondary sourcePrimary, secondary and tertiary sources . University Libraries, University of Maryland.Secondary sources ". James Cook University. is a or recording that relates or discusses information originally presented elsewhere. A secondary source contrasts with a , which is an original source of the information being discussed; a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work * Leiden Conventions The Leiden Conventions or Leiden system is an established set of rules, symbols, and brackets used to indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the Numantine War in Spain. He oversaw the final defeat and destruction of the city of Carthage. He was a prominent patron of writers and philosophers, the most famous of whom was the Greek historian Polybius. In politics, he opposed the populist reform program of his murdered brother-in-law, Tiberius Gracchus. Family Scipio Aemilianus was the second son of Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus, the commander of the Romans' victorious campaign in the Third Macedonian War, and his first wife, Papiria Masonis. Scipio was adopted by his first cousin, Publius Cornelius Scipio, the eldest son of his aunt Aemilia Tertia and her husband Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, the acclaimed commander who won the decisive battle of the Second Pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–183 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the best military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning “the African,” but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochos III during the Roman–Seleucid War. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epaminondas
Epaminondas (; grc-gre, Ἐπαμεινώνδας; 419/411–362 BC) was a Greek general of Thebes and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent position in Greek politics called the Theban Hegemony. In the process, he broke Spartan military power with his victory at Leuctra and liberated the Messenian helots, a group of Peloponnesian Greeks who had been enslaved under Spartan rule for some 230 years after being defeated in the Messenian War ending in 600 BC. Epaminondas reshaped the political map of Greece, fragmented old alliances, created new ones, and supervised the construction of entire cities. He was also militarily influential and invented and implemented several major battlefield tactics. Xenophon, the historian and contemporary, is the main source for Epaminondas' military prowess, and Xenophon describes his admiration for him in his major work '' Hellenica'' (book VII, ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the " Bard of Avon" (or simply "the Bard"). His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. He remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18, he married Anne Hathaway, with whom he had three children: Susanna, and twins Hamnet and Judith. Sometime between 1585 and 1592, he began a successful career in London as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |