|
Materials Testing Reactor
The Materials Testing Reactor (MTR) was an early nuclear reactor specifically designed to facilitate the conception and design of future reactors. It produced much of the foundational irradiation data that underlies the nuclear power industry. It operated in Idaho at the National Reactor Testing Station from 1952 to 1970. Design and administrative history The design evolution for MTR began in 1944 at Clinton Laboratories (now Oak Ridge National Laboratory), originally for the production of fission products. The concept evolved from a 50-kW homogeneous reactor to a heavy-water-cooled and moderated core, and then again at the suggestion of Eugene Wigner to a 30 MW light-water-cooled and moderated core. A full-scale mock-up of the reactor at Oak Ridge was built to verify the design, but the Atomic Energy Commission announced on December 27, 1947 that all reactor development would be centralized at the Argonne National Laboratory (ANL). A directive was issued to ANL to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materials Testing Reactor
A materials test reactor (MTR) is a high power research nuclear reactor. Examples Materials testing reactors include: * The Materials Testing Reactor (MTR), an early reactor that operated in Idaho from 1952-1970. *Dounreay Materials Testing Reactor, a Dido class reactor in the United Kingdom. *ETRR-2, at the Nuclear Research Center in Inshas, Egypt. * Jules Horowitz Reactor, under construction at the Cadarache nuclear facility in southern France. *Research reactor in Petten, the Netherlands. * PINSTECH National Laboratory (PNL) in Pakistan. *Reactor Technology Complex of the Idaho National Laboratory in Idaho, United States. * RV-1 nuclear reactor in Venezuelan Institute for Scientific Research, Venezuela *SAFARI-1, outside of Pretoria, South Africa, also used to produce medical isotopes. See also *List of nuclear reactors A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Chopper
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, and each has a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, they are both referred to as nucleons. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks. The chemical properties of an atom are mostly determined by the configuration of electrons that orbit the atom's heavy nucleus. The electron configuration is determined by the charge of the nucleus, which is determined by the number of protons, or atomic number. The number of neutrons is the neutron number. Neutrons do not affect the electron configuration, but the sum of atomic and neutron numbers is the mass of the nucleus. Atoms of a chemical eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
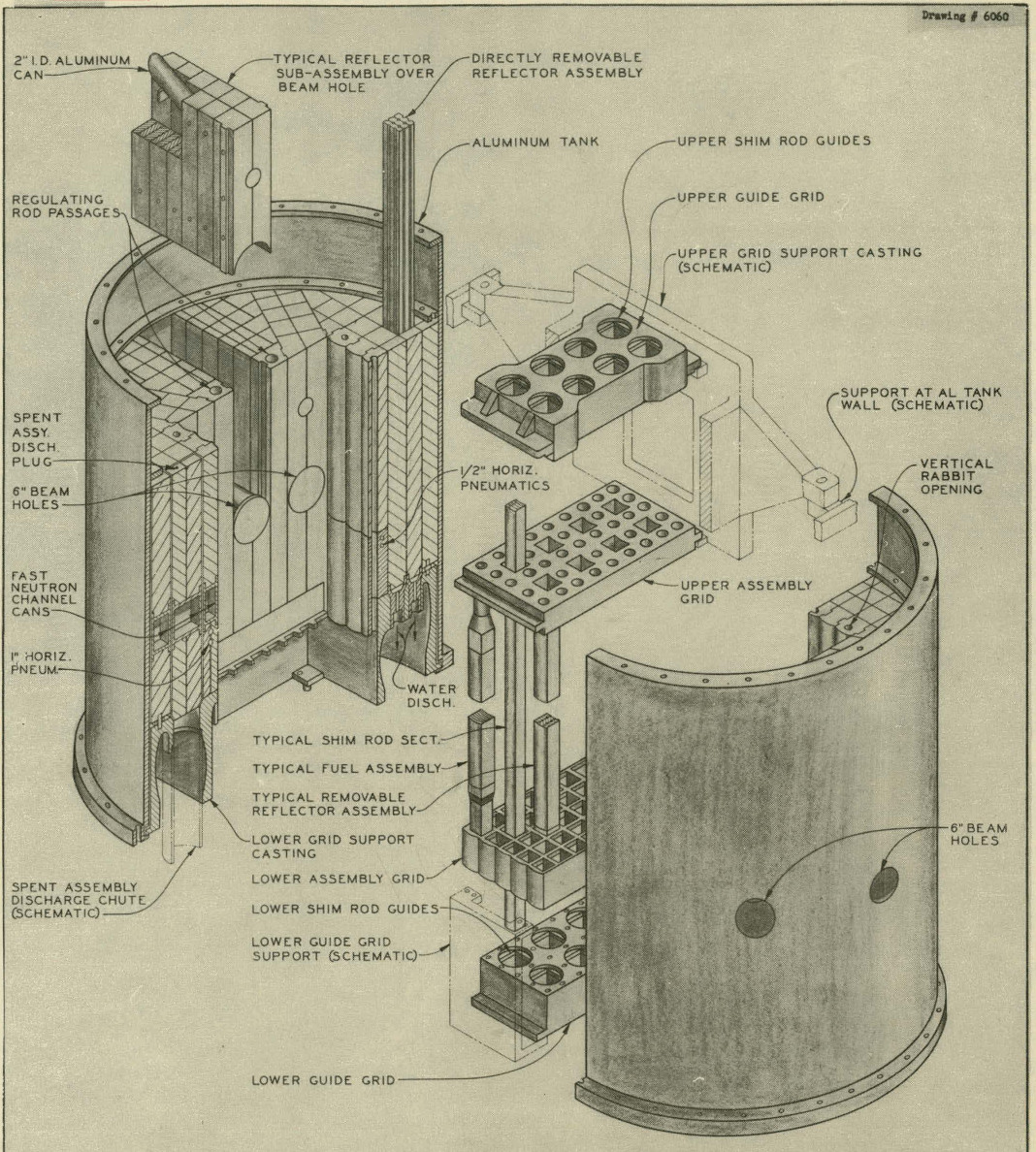
Materials Testing Reactor Experimental Facilities
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geological origin or biological function. Materials science is the study of materials, their properties and their applications. Raw materials can be processed in different ways to influence their properties, by purification, shaping or the introduction of other materials. New materials can be produced from raw materials by synthesis. In industry, materials are inputs to manufacturing processes to produce products or more complex materials. Historical elements Materials chart the history of humanity. The system of the three prehistoric ages (Stone Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age) were succeeded by historical ages: steel age in the 19th century, polymer age in the middle of the following century (plastic age) and silicon age in the second half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon-41
Argon (18Ar) has 26 known isotopes, from 29Ar to 54Ar and 1 isomer (32mAr), of which three are stable (36Ar, 38Ar, and 40Ar). On the Earth, 40Ar makes up 99.6% of natural argon. The longest-lived radioactive isotopes are 39Ar with a half-life of 268 years, 42Ar with a half-life of 32.9 years, and 37Ar with a half-life of 35.04 days. All other isotopes have half-lives of less than two hours, and most less than one minute. The least stable is 29Ar with a half-life of approximately seconds. The naturally occurring 40K, with a half-life of 1.248 years, decays to stable 40Ar by electron capture (10.72%) and by positron emission (0.001%), and also transforms to stable 40Ca via beta decay (89.28%). These properties and ratios are used to determine the age of rocks through potassium–argon dating. Despite the trapping of 40Ar in many rocks, it can be released by melting, grinding, and diffusion. Almost all of the argon in the Earth's atmosphere is the product of 40K decay, since 99. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curie (unit)
The curie (symbol Ci) is a non- SI unit of radioactivity originally defined in 1910. According to a notice in '' Nature'' at the time, it was to be named in honour of Pierre Curie, but was considered at least by some to be in honour of Marie Curie as well, and is in later literature considered to be named for both. It was originally defined as "the quantity or mass of radium emanation in equilibrium with one gram of radium (element)", but is currently defined as 1 Ci = decays per second after more accurate measurements of the activity of Ra (which has a specific activity of ). In 1975 the General Conference on Weights and Measures gave the becquerel (Bq), defined as one nuclear decay per second, official status as the SI unit of activity. Therefore: : 1 Ci = = 37 GBq and : 1 Bq ≅ ≅ 27 pCi While its continued use is discouraged by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and other bodies, the curie is still widely used throughout government, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Activation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emitting gamma rays, or particles such as beta particles, alpha particles, fission products, and neutrons (in nuclear fission). Thus, the process of neutron capture, even after any intermediate decay, often results in the formation of an unstable activation product. Such radioactive nuclei can exhibit half-lives ranging from small fractions of a second to many years. Neutron activation is the only common way that a stable material can be induced into becoming intrinsically radioactive. All naturally occurring materials, including air, water, and soil, can be induced (activated) by neutron capture into some amount of radioactivity in varying degrees, as a result of the production of neutron-rich radioisotopes. Some atoms require more than one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Shield
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Exposure can be from a source of radiation external to the human body or due to internal irradiation caused by the ingestion of radioactive contamination. Ionizing radiation is widely used in industry and medicine, and can present a significant health hazard by causing microscopic damage to living tissue. There are two main categories of ionizing radiation health effects. At high exposures, it can cause "tissue" effects, also called "deterministic" effects due to the certainty of them happening, conventionally indicated by the unit gray and resulting in acute radiation syndrome. For low level exposures there can be statistically elevated risks of radiation-induced cancer, called "stochastic effects" due to the uncertainty of them happening, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a weak conductor of heat and electricity. Types and varieties Natural graphite The principal types of natural graphite, each occurring in different types of ore deposits, are * Crystalline small flakes of graphite (or flake graphite) occurs as isolated, flat, plate-like particles with hexagonal edges if unbroken. When broken the edges can be irregular or angular; * Amorphous graphite: very fine flake graphite is sometimes called amorphous; * Lump graphite (or vein graphite) occurs in fissure veins or fractures and appears as massive platy intergrowths of fibrous or acicular cry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |