|
Zuara
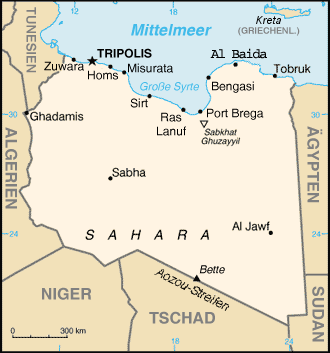
Zuwarah, or Zuwara or Zwara ( Berber language: At Willul or Zwara, ) is a coastal Berber-speaking city in Libya. Zuwara or At Willul is famous for its beaches and seafood. It is situated west of Tripoli and from the Tunisian border. It is the capital of the Nuqat al Khams district. Its population speaks Zuwara Berber, a Zenati Berber language. Zuwarah consists of 49 districts. History The settlement was first mentioned by the traveller Abdallah al-Tijani in the years 1306-1309 as ''Zwara al-saghirah'' ("Little Zwarah"). In the Catalan Atlas (1375) it was called as Punta dar Zoyara. The town is mentioned by Leo Africanus in the 16th century. It later served as the western outpost of Italian Libya (1912–43), being the terminus of the now-defunct Italian Libya Railway from Tripoli to the east. Its artificial harbour shelters a motorized fishing fleet. Cereals, dates, and esparto grass (used to make cordage, shoes, and paper) are local products. It was in 1973 in Zuwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuwara Berber
Zuwara Berber or Twillult language (also: ''Zuara'', ''Zwara'', (Berber name: Twillult, ⵝⵡⵉⵍⵍⵓⵍⵝ) is a Berber dialect, one of the Berber Zenati languages. It is spoken in Zuwara city, located on the coast of western Tripolitania in northwestern Libya. Several works of Terence Mitchell, most notably ''Zuaran Berber (Libya): Grammar and texts'', provide an overview of the language's grammar along with a set of texts, based mainly on the speech of his consultant Ramadan Azzabi. Some articles on this subject were also published by Luigi Serra. The speakers refer to their specific variety of the language as ''twillult'' /t.ˈwil.lult/ ‘the language of Willul’, and the word "Mazigh" /ˈma.ziʁ/ may refer both to the wider Amazigh language or to any Amazigh person.Gussenhoven, C. (2018). Zwara (Zuwārah) Berber. ''Journal of the International Phonetic Association'', ''48''(3), 371-387. URL : http://gep.ruhosting.nl/carlos/zwara_zuwarah_berber.pdf Although rare fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Libya Railways
Italian Libya Railways was a group of small railways built in the Italian colony of Libya between the two World Wars. History The Kingdom of Italy built in Italian Libya nearly 400 km of railways with gauge. Projects The Italian authorities decided to give priority to the construction of roads in Libya when Benito Mussolini took control of the Italian colonies. After 1926 no more railways were made in Libya, but during World War II the need of railways transport to the front during the war in the frontier with British Egypt changed this approach. In spring 1941 the Italian government started the construction of a new railway between Tripoli and Benghazi, but by the end of 1942 all was stopped because of the Italian defeat in north Africa: only 18 km were done in Cirenaica. In the same period was started the enlargement of the "Tripoli-Zuara" until the border with Tunisia (and also these works was blocked by the Italian defeat at El Alamein in November 1942). Additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esparto
Esparto, halfah grass, or esparto grass is a fiber produced from two species of perennial grasses of north Africa, Spain and Portugal. It is used for crafts, such as cords, basketry, and espadrilles. ''Stipa tenacissima'' and ''Lygeum spartum'' are the species used to produce esparto. ''Stipa tenacissima'' (''Macrochloa tenacissima'') produces the better and stronger esparto. It is endemic to the Western Mediterranean (growing in Portugal, Spain, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya). The Spanish name for the plant is "atocha"; a pre-Roman word. "Esparto" or σπάρτο in Greek may refer to any woven products of sedge or broom, including cords and ropes. This species grows forming a steppic landscape - esparto grasslands - which covers large parts of Spain and Algeria. History Esparto leaves have been used for millennia. The oldest baskets of esparto, dating back 7,000 years, were found in a cave in southern Spain (Cueva de los Murciélagos, Albuñol, Granada). This colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dania Ben Sassi
Dania Ben Sassi, Tamazight: Danya At Sasi, Arabic: دانيا بن ساسي (born 1998) is a Libyan Amazigh singer whose music went viral during the First Libyan Civil War, due to the fact her music praises Amazigh resistance and are sung in Tamazight. Early life Dania Ben Sassi was born in Belgrade in Serbia in 1998, to a Libyan father from Zuwarah and a Serbian mother. Her father had been forced into exile in Serbia, after fleeing the Gaddafi regime due to his activism for Libyan Berber rights. She is fluent in Serbian and Libyan Tamazight and can write Tifinagh. She studied Economics at the University of Belgrade. Musical career Ben Sassi's music is inspired by the Amazighs , image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 ... of Libya and their resistance to cultural assimilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Libya ...
This is a list of the 100 largest populated places in Libya. Some places in the list could be considered suburbs or neighborhoods of some large cities in the list, so this list is not definitive. ''Source:Amraja M. el Khajkhaj, "Noumou al Mudon as Sagheera fi Libia", Dar as Saqia, Benghazi-2008, pp. 118-123.'' See also * Transliteration of Libyan placenames *List of metropolitan areas in Africa *List of largest cities in the Arab world References External links * {{List of cities in the Middle East Libya, List of cities in Libya Cities A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 Libyan Local Elections
Local elections were held in Zuwarah in 2011 and in several other municipalities in Libya during 2012. Zuwarah Zuwarah residents elected their local council in 2011, following the 2011 Libyan Civil War. Benghazi Municipal elections were held in Benghazi on 19 May. More than 200,000 people registered to vote in Benghazi, and 414 candidates stood for election for the 41 free seats in the 44-member City Council. These are the first elections of their kind in Benghazi since the 1960s. Given the large number of candidates, there has been not very much time for them to campaign and present their views to the people of the 11 Districts of Benghazi. According to the head of Benghazi's electoral commission, Suleiman Zubi, a total of 138,312 people voted in the election, with turnout between 64% and 69%. Despite 22 female candidates standing for election, only one female, Najat Rashid Mansur Al-Kikhia, was elected to the council. Al-Kikhia did however receive the most votes of any individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Libyan Rebel Coastal Offensive
The 2011 Libyan rebel coastal offensive was a major rebel offensive of the Libyan Civil War. It was mounted by anti-Gaddafi forces with the intention of cutting off the supply route from Tunisia for pro-Gaddafi loyalist forces in Tripoli. Background The offensive was launched by opposition forces based in the Nafusa Mountains who had managed to make a breakthrough in loyalist lines around the mountains just a few days before. Loyalists and rebels had been fighting for the mountain chain for over five months, often in back-and-forth battles. However, due to an intense NATO bombing campaign of loyalist forces, pro-Gaddafi troops had to pull back from the mountains. This gave a chance for the rebels to go on the offensive toward the coast west of Tripoli. Offensive The offensive started on 13 August 2011 with rebels advancing toward the oil refinery town of Zawiya supported by NATO air-strikes. The town revolted against Gaddafi governmental control in late February but the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumayl, Libya
Jumayl (Al Jamīl, El Gemil and Aljmail) ( ar, الجميل ''Favor'') is a town in central Nuqat al Khams District of western Libya. It is located about southwest of the port of Zuwara Zuwarah, or Zuwara or Zwara (Berber language: At Willul or Zwara, ) is a coastal Berber-speaking city in Libya. Zuwara or At Willul is famous for its beaches and seafood. It is situated west of Tripoli and from the Tunisian border. It is the .... , Jumayl had an estimated population of 102,000. World Gazetteer Notes External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libyan Army (1951-2011)
The Libyan Army ( ar, الجيش الليبي) is the brand for a number of separate military forces in Libya, which are under the command of the internationally recognised Government of National Accord (GNA). Since December 2015 the groups of the Libyan Army has been nominally subordinated to the internationally recognised Government of National Accord (GNA) based in Tripoli. Due to the instability in the country in 2011 civil war and the outbreak of a new conflict in 2014, the Libyan ground forces remain structurally divided, with components constituting the Tobruk-based Libyan National Army (LNA) under the command of Khalifa Haftar. The forces loyal to the GNA have been fighting against various other factions in Libya, including the Islamic State. Some efforts have been made to create a truly national army, but most of the forces under the Tripoli government's command consist of various militia groups, such as the Tripoli Protection Force, and local factions from citie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |