|
Zygomaturus
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 and C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, during the regional Waitean faunal stage. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became extinct curing the latter half of the Late Pleistocene, with typical estimates being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
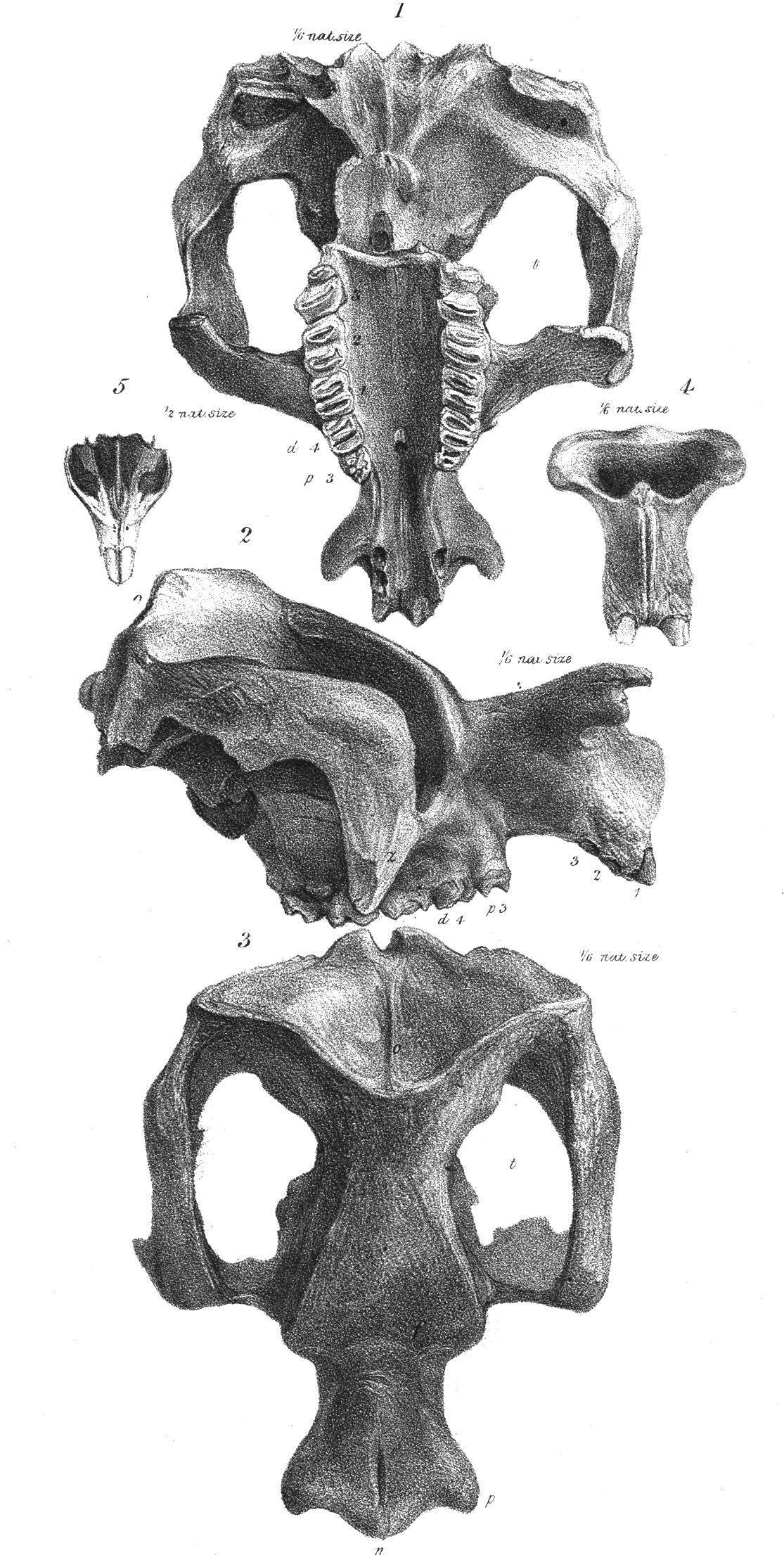
Zygomaturus Skull
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 carbon fixation, C3 and C4 carbon fixation, C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of Browsing (herbivory), browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, during the regional Waitean faunal stage. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became extinct curing the latter hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaturus BW
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 and C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, during the regional Waitean faunal stage. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became extinct curing the latter half of the Late Pleistocene, with typical estimates being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaturus Trilobus Jaw
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 and C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, during the regional Waitean faunal stage. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became extinct curing the latter half of the Late Pleistocene, with typical estimates being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diprotodontidae
The Diprotodontidae are an extinct family of large herbivorous marsupials, endemic to Australia and New Guinea during the Oligocene through Pleistocene periods from 28.4 million to 40,000 years ago. The family consisted of large quadrupedal terrestrial browsers, notably including the largest marsupial that ever lived, the rhino-sized ''Diprotodon''. The group first appeared during the Late Oligocene, with representatives that were mostly sheep-sized, and substantially diversified beginning during the Late Miocene, reaching an apex of diversity during the Pliocene with seven genera, likely due to the increase of open forested landscapes. The last known members of the group including ''Diprotodon'' and '' Zygomaturus'' from mainland Australia, and ''Hulitherium ''Hulitherium tomasetti'' (meaning "Huli beast", after the Huli people) is an extinct zygomaturine marsupial from New Guinea during the Pleistocene. The species name honours Berard Tomasetti, a Catholic priest in Papu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neohelos
''Neohelos'' is an extinct diprotodontid marsupial, that lived from the early to middle-Miocene. There are four species assigned to this genus, ''Neohelos tirarensis'', the type species, ''N. stirtoni'', ''N. solus'' and ''N. davidridei''. ''N. davidridei'' is the most derived species of the genus, and its premolar morphology shows that it is structurally and ancestor of the genus ''Kolopsis''. All four species are from the Bullock Creek in the Northern Territory and Riversleigh of Australia. Description ''Neohelos'' is known from many specimens, assigned to all the species. ''N. tirarensis'' includes a partial skull, premaxillas, maxillas, teeth, and dentarys; ''N. solus'' is known from a maxilla and dentary; ''N. davidridei'' includes teeth and a maxilla fragment; and ''N. stirtoni'' is known from a mostly complete skull, a maxilla and a dentary. Distinguishing characteristics A revision of ''Neohelos'' found a set of features in all the species that are absent in all oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hulitherium
''Hulitherium tomasetti'' (meaning "Huli beast", after the Huli people) is an extinct zygomaturine marsupial from New Guinea during the Pleistocene. The species name honours Berard Tomasetti, a Catholic priest in Papua New Guinea, who brought the fossils to the attention of experts. Discovery While excavating a bank to widen the Pureni Mission airstrip in Wabag, New Guinea, to comply with new regulations, the Huli workers unearthed fossils in 1967. They reportedly were frightened by their discovery as bones in their culture are associated with the ancestors, so the material was somewhat damaged by their inquisitive prodding until they were brought to the attention of Father Bernard Tomasetti, who recognized the significance. Geologists Paul Williams and Michael Plane subsequently headed field expeditions in the area beginning in 1969 in search of more remains. Among the material was the partial skeleton of a diprotodontid, catalogue number CPC 25718, comprising: a well-pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne Museum
The Melbourne Museum is a natural and cultural history museum located in the Carlton Gardens, Melbourne, Carlton Gardens in Melbourne, Australia. Located adjacent to the Royal Exhibition Building, the museum was opened in 2000 as a project of the Government of Victoria, on behalf of Museums Victoria which administers the venue. The museum won Best Tourist Attraction at the Australian Tourism Awards in 2011. In addition to its galleries, the museum features spaces such as ''Curious?'', which is a place to meet staff and find answers relating to the collections, research, and behind-the-scenes work of Museums Victoria; as well as a cafe and a gift shop. The back-of-house area houses some of the Victoria's State Collections, which holds over 17 million items, including objects relating to Indigenous Australian and Pacific Islander cultures, geology, historical studies, palaeontology, technology and society, and zoology, as well as a library collection that holds 18th and 19th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willandra Lakes Region
The Willandra Lakes Region is a World Heritage Site in the Far West region of New South Wales, Australia. The Willandra Lakes Region is the traditional meeting place of the Muthi Muthi, Ngiyampaa and Barkinji Aboriginal tribes. The area was inscribed on the World Heritage List at the 5th Session of the World Heritage Committee in 1981. The Region contains important natural and cultural features including exceptional examples of past human civilization including the world's oldest cremation site. A small section of the region is protected by the Mungo National Park. The World Heritage status of the region was created and negotiated in 1981. The site was gazetted on the Australian National Heritage List on 21 May 2007 under the . The region is also listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register. History Willandra Lakes has formed over the last 2 million years. The ancient shorelines are stratified into three major layers of sediments that were deposited at different st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Mammals Of Australia
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Genus Extinctions
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Marsupials
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Vombatiforms
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



