|
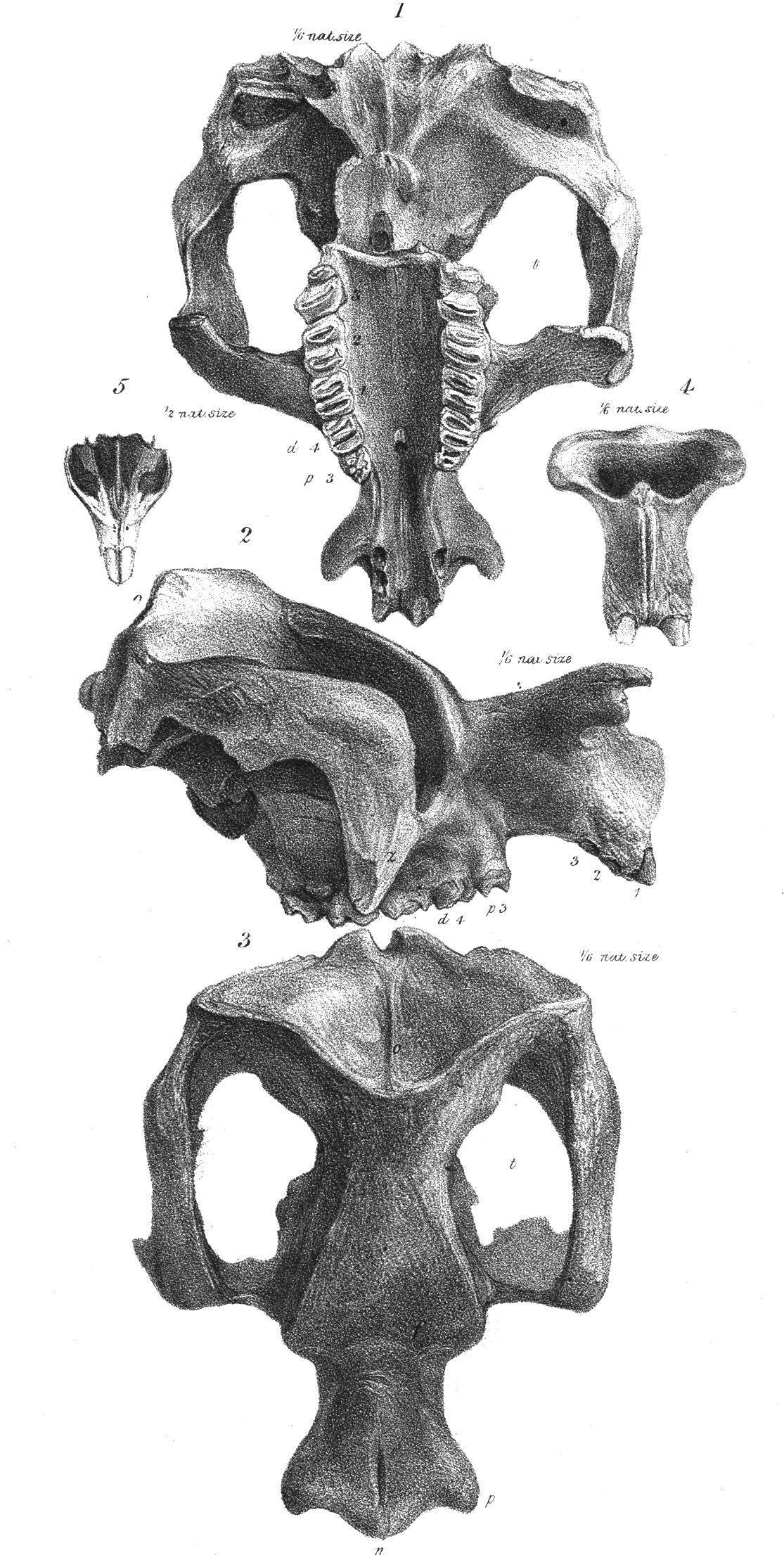
Neohelos
''Neohelos'' is an extinct diprotodontid marsupial, that lived from the early to middle-Miocene. There are four species assigned to this genus, ''Neohelos tirarensis'', the type species, ''N. stirtoni'', ''N. solus'' and ''N. davidridei''. ''N. davidridei'' is the most derived species of the genus, and its premolar morphology shows that it is structurally and ancestor of the genus ''Kolopsis''. All four species are from the Bullock Creek in the Northern Territory and Riversleigh of Australia. Description ''Neohelos'' is known from many specimens, assigned to all the species. ''N. tirarensis'' includes a partial skull, premaxillas, maxillas, teeth, and dentarys; ''N. solus'' is known from a maxilla and dentary; ''N. davidridei'' includes teeth and a maxilla fragment; and ''N. stirtoni'' is known from a mostly complete skull, a maxilla and a dentary. Distinguishing characteristics A revision of ''Neohelos'' found a set of features in all the species that are absent in all oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neohelos Solus Holotype
''Neohelos'' is an extinct diprotodontid marsupial, that lived from the early to middle-Miocene. There are four species assigned to this genus, ''Neohelos tirarensis'', the type species, ''N. stirtoni'', ''N. solus'' and ''N. davidridei''. ''N. davidridei'' is the most derived species of the genus, and its premolar morphology shows that it is structurally and ancestor of the genus ''Kolopsis''. All four species are from the Bullock Creek in the Northern Territory and Riversleigh of Australia. Description ''Neohelos'' is known from many specimens, assigned to all the species. ''N. tirarensis'' includes a partial skull, premaxillas, maxillas, teeth, and dentarys; ''N. solus'' is known from a maxilla and dentary; ''N. davidridei'' includes teeth and a maxilla fragment; and ''N. stirtoni'' is known from a mostly complete skull, a maxilla and a dentary. Distinguishing characteristics A revision of ''Neohelos'' found a set of features in all the species that are absent in all oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaturinae
The Zygomaturinae are an extinct subfamily of marsupials. The phylogeny and taxonomy of this clade is poorly understood and problematic. Zygomaturines are currently thought to be a subfamily within Diprotodontidae The Diprotodontidae are an extinct family of large herbivorous marsupials, endemic to Australia and New Guinea during the Oligocene through Pleistocene periods from 28.4 million to 40,000 years ago. The family consisted of large quadrupedal te ..., rather than a distinct family. References * Prehistoric Mammals of Australia and New Guinea: One Hundred Million Years of Evolution by John A. Long, Michael Archer, Timothy Flannery, and Suzanne Hand (page 91) Prehistoric vombatiforms Chattian first appearances {{paleo-marsupial-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diprotodontoidea
The Vombatiformes are one of the three suborders of the large marsupial order Diprotodontia. Seven of the nine known families within this suborder are extinct; only the families Phascolarctidae, with the koala, and Vombatidae, with three extant species of wombat, survive. Among the extinct families are the Diprotodontidae, which includes the rhinoceros sized ''Diprotodon'', believed to be the largest marsupials ever, as well as the "marsupial lions" Thylacoleonidae and "marsupial tapirs" Palorchestidae. "Vombatiformes" is neo-Latin for "wombat-shaped things", and took its name from its type family. The suborder Vombatiformes, with its closely related members and their compact body form, contrasts with the other two diprotodont suborders, the Macropodiformes: kangaroos, wallabies, and the quokka; and the Phalangeriformes: possums, including the gliders such as the wrist-winged gliders. The koala and wombats are believed by many biologists to share a common ancestor and to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaturus
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 and C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, during the regional Waitean faunal stage. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became extinct curing the latter half of the Late Pleistocene, with typical estimates being a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullock Creek (Northern Territory)
The Bullock Creek Fossil site is one of three known vertebrate fossil sites in the Northern Territory of Australia, along with the Alcoota Fossil Beds and the Kangaroo Well site on Deep Well Station. It is located about south-southeast of Darwin, on Camfield Station in the locality of Victoria River. The Bullock Creek Fossil Site is part of the Camfield Fossil Beds which outcrop in a narrow belt about 50 km long. The Bullock Creek local fauna are approximately dated to the mid Miocene (about 12 million years ago). The Camfield Fossil Beds which contain the Bullock Creek local fauna consist of light coloured calcareous sandstone, siltstone and limestone. Ferruginous mottling is found at the base and chalcedonic silification at the top. The presentation of fossils at the site ranges from poorly sorted fragmentary lags to associations with partial skeletons which includes complete crania (skulls) with intact delicate structures. The Bullock Creek Fossil Site is of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Fossil Mammal Sites (Riversleigh)
Riversleigh World Heritage Area is Australia's most famous fossil location, recognised for the series of well preserved fossils deposited from the Late Oligocene to more recent geological periods. The fossiliferous limestone system is located near the Gregory River in the north-west of Queensland, an environment that was once a very wet rainforest that became more arid as the Gondwanan land masses separated and the Australian continent moved north. The approximately area has fossil remains of ancient mammals, birds, and reptiles of the Oligocene and Miocene ages, many of which were discovered and are only known from the Riversleigh area; the species that have occurred there are known as the Riversleigh fauna. The fossils at Riversleigh are unusual because they are found in soft freshwater limestone which has not been compacted. This means the animal remains retain their three-dimensional structure, rather than being partially crushed like in most fossil sites. The area is loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk ( ALP) , legislature = Parliament of Queensland , judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene
The Middle Miocene is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Langhian and Serravallian stages. The Middle Miocene is preceded by the Early Miocene. The sub-epoch lasted from 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma to 11.608 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). During this period, a sharp drop in global temperatures took place. This event is known as the Middle Miocene Climate Transition. For the purpose of establishing European Land Mammal Ages The European Land Mammal Mega Zones (abbreviation: ELMMZ, more commonly known as European land mammal ages or ELMA) are zones in rock layers that have a specific assemblage of fossils (biozones) based on occurrences of fossil assemblages of Europe ... this sub-epoch is equivalent to the Astaracian age. External links GeoWhen Database - Middle Miocene .02 02 * * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene Epoch made up of two stages: the Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was preceded by the Oligocene epoch. As the climate started to get cooler, the landscape started to change. New mammals evolved to replace the extinct animals of the Oligocene epoch. The first members of the hyena and weasel family started to evolve to replace the extinct ''Hyaenodon'', entelodonts and bear-dogs. The chalicotheres survived the Oligocene epoch. A new genus of entelodont called ''Daeodon'' evolved in order to adapt to the new habitats and hunt the new prey animals of the Early Miocene epoch; it quickly became the top predator of North America. But it became extinct due to competition from '' Amphicyon'', a newcomer from Eurasia. ''Amphicyon'' bested ''Daeodon'' because the bear-dog Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |