|
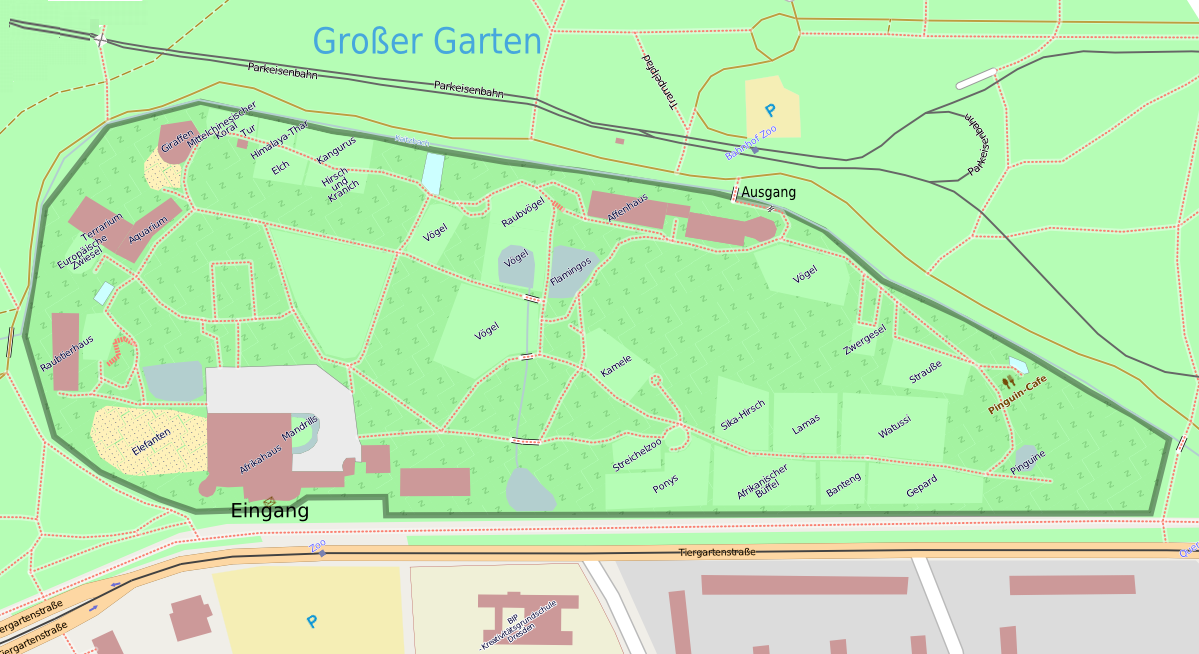
Zoo Dresden
Dresden Zoo or Zoo Dresden, is a zoo situated in the city of Dresden, Germany. It was opened in 1861, making it Germany's fourth oldest zoo. It was originally designed by Peter Joseph Lenné. The zoo is located on the southern edge of the Großer Garten (Great Garden), a large city centre park. The zoo houses about 3000 animals of almost 400 species, especially Asian animals. It is a member of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA) and the European Association of Zoos and Aquaria (EAZA). The zoo is served on its southern side by tram lines 9 and 13 of the Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe, the local municipal transport company. On its northern side is the Zoo station of the Dresdner Parkeisenbahn, a minimum gauge railway through the Großer Garten that is largely operated by children. In Literature At the end of the short story "Tobermory" (1909) by Saki Hector Hugh Munro (18 December 1870 – 14 November 1916), better known by the pen name Saki and also frequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne), and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the foreland of the Ore Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe
Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe AG (DVB) is the municipal transport company of the city of Dresden in Germany. It is a member of the Verkehrsverbund Oberelbe transport association that manages a common public transport structure for Dresden and its surrounding areas. The DVB operates the Dresden tram network comprising 12 tram lines, with a total line length of approximately and a total route length of (), and 28 bus lines, with a total line length of approximately . It is also responsible for two funicular railways and three ferries across the River Elbe. The DVB network carries some 142 million passenger journeys each year. In 2007, it generated €96.5m of revenue, covering 76% of costs. Tramways The Dresden tramway system is the backbone of public transport in Dresden. DVB operates twelve tram routes, with a current total combined line length of . , there was of track, which translated into of actual tram route, serving 154 tram stops. The tram fleet is made up of 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Dresden
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoos In Germany
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for Conservation biology, conservation purposes. The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zoology, the study of animals. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek language, Greek , , 'animal', and the suffix , , 'study of'. The abbreviation ''zoo'' was first used of the London Zoological Gardens, which was opened for scientific study in 1828 and to the public in 1847."Landmarks in ZSL History" , Zoological Society of London. In the United States alone, zoos are visited by over 181 million people annually. Etymology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Dresden
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saki
Hector Hugh Munro (18 December 1870 – 14 November 1916), better known by the pen name Saki and also frequently as H. H. Munro, was a British writer whose witty, mischievous and sometimes macabre stories satirize Edwardian society and culture. He is considered by English teachers and scholars a master of the short story and is often compared to O. Henry and Dorothy Parker. Influenced by Oscar Wilde, Lewis Carroll and Rudyard Kipling, he himself influenced A. A. Milne, Noël Coward and P. G. Wodehouse. Besides his short stories (which were first published in newspapers, as was customary at the time, and then collected into several volumes), he wrote a full-length play, ''The Watched Pot'', in collaboration with Charles Maude; two one-act plays; a historical study, ''The Rise of the Russian Empire'' (the only book published under his own name); a short novel, ''The Unbearable Bassington''; the episodic ''The Westminster Alice'' (a parliamentary parody of '' Alice in Wonderlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Gauge Railway
Minimum-gauge railways have a gauge of most commonly , , , , , or . The notion of minimum-gauge railways was originally developed by estate railways and the French company of Decauville for light railways, trench railways, mining, and farming applications. History The term was originally conceived by Sir Arthur Percival Heywood, who used it in 1874 to describe the principle behind his Duffield Bank Railway, specifically its gauge, distinguishing it from a "narrow gauge" railway. Having previously built a small railway of gauge, he settled on as the minimum that he felt was practical. The original text of Heywood's article defining minimum gauge railways is available online. In general, minimum-gauge railways maximize their loading gauge, where the dimension of the equipment is made as large as possible with respect to the track gauge while still providing enough stability to keep it from tipping over. Standard gauge railways have vehicles that are approximately twice, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresdner Parkeisenbahn
The Dresden park railway (german: Dresdner Parkeisenbahn) is a minimum gauge railway in Dresden, Germany. The line opened in 1950 and was previously known as the ''Kindereisenbahn'' and the ''Pioniereisenbahn''. As these names suggest, the line is largely operated by children, and is a survivor of the many children's railways that were built in the former Eastern Bloc countries. The railway operates within the ''Großer Garten'', a large city centre park. History In 1925, a series of three identical gauge miniature steam locomotives and matching trains were designed by the engineer Roland Martens, following a study trip to England. The locomotives were based on full sized Pacific locomotives of the Deutsche Reichsbahn, and built by Krauss & Co., who subsequently went on to build 15 locomotives of this type, most of which are still in use on various miniature railways around the world. Originally, the three locomotives were used on temporary tracks at various trade fairs or e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Association Of Zoos And Aquariums
The World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA) is the "umbrella" organization for the world zoo and aquarium community. Its mission is to provide leadership and support for zoos, aquariums, and partner organizations of the world in animal care and welfare, conservation of biodiversity, environmental education and global sustainability. History After the ''International Union of Directors of Zoological Gardens'' (IUDZG), founded in 1935 at Basel, Switzerland, ceased to exist during World War II, it was refounded in Rotterdam in 1946 by a group of zoo directors from allied or neutral countries. In 1950 IUDZG became an international organisation member of International Union for the Protection of Nature. In 1991 the IUDZG adopted a new name, ''World Zoo Organization'', and revised its membership rules to include regional zoo associations. In 2000 the organization got its current name, the ''World Association of Zoos and Aquariums'', to reflect a more modern institution work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großer Garten
The Großer Garten (English: Great Garden) is a Baroque style park in central Dresden. It is rectangular in shape and covers about 1.8 km². Originally established in 1676 on the orders of John George III, Elector of Saxony, it has been a public garden since 1814. Pathways and avenues are arranged symmetrically throughout the park. The ''Sommerpalais'', a small Lustschloss is at the center of the park. Originally established outside the old walls of the city, the park was surrounded by urban areas by the second half of the 19th century. Dresden Zoo and Dresden Botanical Garden were added late in the 19th century. A miniature railway, known as the Parkeisenbahn, operates in the park from April to October. Volkswagen's Transparent Factory is the newest building in the park, completed in 2002. It is on ''Straßburger Platz'', in the northwest corner of the park. Image:Großer Garten1.jpg, Park seen from the south-western corner Image:Parkeisenbahn Dresden Dampflokomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
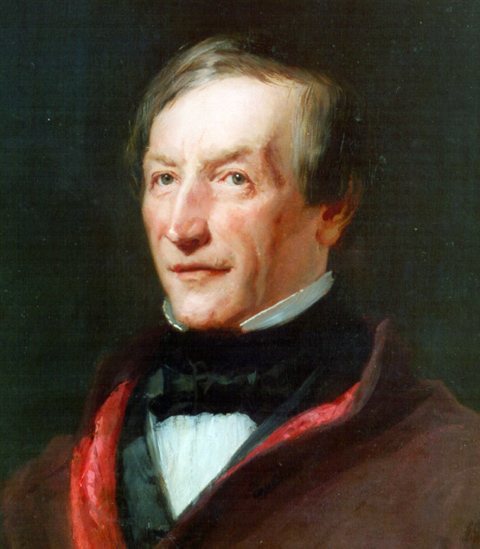
Peter Joseph Lenné
Peter Joseph Lenné (the Younger) (29 September 1789 – 23 January 1866) was a Prussian gardener and landscape architect. As director general of the Royal Prussian palaces and parks in Potsdam and Berlin, his work shaped the development of 19th-century German garden design in the Neoclassical style. Laid out according to the principles of the English landscape garden, his parks are now World Heritage Sites. Life and works Lenné was born in Bonn, then part of the Electorate of Cologne, the son of the court and university gardener Peter Joseph Lenné the Elder (1756–1821), and his wife, Anna Catharina Potgieter (also Potgeter), daughter of the mayor of Rheinberg. The Lenné family descended from the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Circa 1665, Peter Joseph's ancestor Augustin Le Neu had settled in Poppelsdorf near Bonn as court gardener of Archbishop-Elector Maximilian Henry of Bavaria. Childhood and development Having obtained his ''Abitur'' degree, Peter Joseph Lenné decided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |