|
Zoltán Decleva
Zoltán Decleva (30 July 188717 July 1950) was a Hungarian military officer, who served as commander of the Hungarian Third Army during the Second World War. He commanded the Hungarian I Corps during the Invasion of Yugoslavia. In 1941, he was deputy chief of General Staff (May–October) and deputy commander in chief of the Army (November). Between 1 November 1941 and 3 December 1942, he commanded the 3rd Army, which occupied a part of Yugoslavia. He retired on 1 February 1943. Biography Zoltán was born on 30 July 1887 in Alsószemeréd (now Dolné Semerovce) in province of Lower Austria, Austria-Hungary (now Slovakia). Raised into an impoverished noble family, whose origins goes back to Joannes Decleva, illegitimate son of John II, Duke of Cleves and a Hungarian jewish women. After he graduated in Defense Force Academy of Pécs, he served in 1906 at 19º Regiment of Infantry of Army in Pécs. At the First World War, during forty months, he fought at the front. He got a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolné Semerovce
Dolné Semerovce ( hu, Alsószemeréd) is a village and municipality in the Levice District in the Nitra Region of Slovakia. History In history, historical records the village was first mentioned in 1268. Geography The village lies at an altitude of 174 metres and covers an area of 11.861 km². It has a population of about 500 people. Ethnicity The village is approximately 60% Hungarian people, Magyar, 20% Slovaks, Slovak and 20% Romani people, Gypsy in ethnicity. Facilities The village has a public library and a Association football pitch, football pitch. Genealogical resources The records for genealogical research are available at the state archive "Statny Archiv in Banska Bystrica, Nitra, Slovakia" * Roman Catholic church records (births/marriages/deaths): 1703-1896 (parish A) * Lutheran church records (births/marriages/deaths): 1721-1900 (parish B) See also * List of municipalities and towns in Slovakia External links *https://web.archive.org/web/20071116010355/ht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
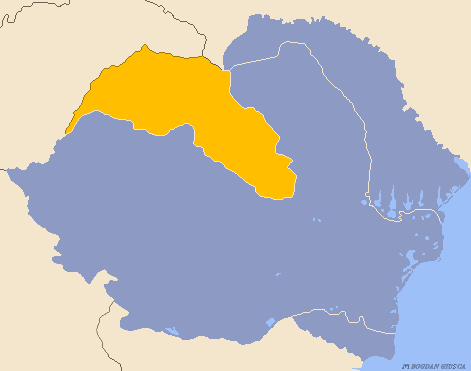
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania ( ro, Transilvania de Nord, hu, Észak-Erdély) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary. With an area of , the population was largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians. In October 1944, Soviet and Romanian forces gained control of the territory, and by March 1945 Northern Transylvania returned to Romanian administration. After the war, this was confirmed by the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. Background The region has a varied history. It was once the nucleus of the Kingdom of Dacia (82 BC–106 AD). In 106 AD the Roman Empire conquered the territory, systematically exploiting its resources. After the Roman legions withdrew in 271 AD, it was overrun by a succession of various tribes, bringing it under the control of the Carpi, Visigoths, Huns, Gepids, Avars, and Slavs. During the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Crișana, from Romania to Hungary. Background After World War I, the multiethnic Kingdom of Hungary was divided by the 1920 Treaty of Trianon to form several new nation states, but Hungary noted that the new state borders did not follow ethnic boundaries. The new nation state of Hungary was about a third the size of prewar Hungary, and millions of ethnic Hungarians were left outside the new Hungarian borders. Many historically-important areas of Hungary were assigned to other countries, and the distribution of natural resources was uneven. The various non-Hungarian populations generally saw the treaty as justice for their historically-marginalised nationalities, but the Hungarians considered the treaty to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decleva Zoltán
Decleva is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Enrico Decleva (1941–2020), Italian historian *Zoltán Decleva Zoltán Decleva (30 July 188717 July 1950) was a Hungarian military officer, who served as commander of the Hungarian Third Army during the Second World War. He commanded the Hungarian I Corps during the Invasion of Yugoslavia. In 1941, he was ... (1887–1950), Hungarian military officer {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
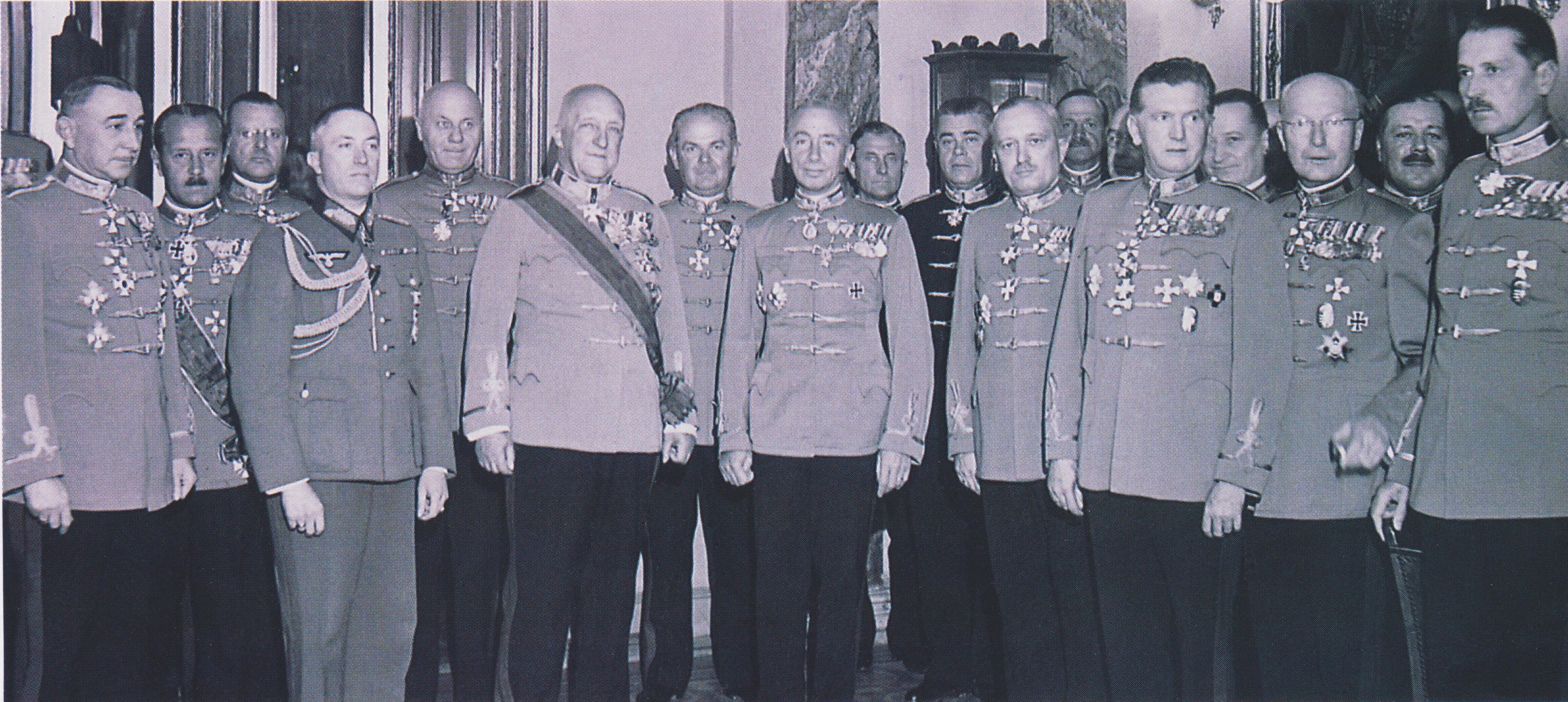
General Staff Of The Hungarian Royal Army 1944
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 October 1990. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from eleven states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The FRG's provisional capital was the city of Bonn, and the Cold War era country is retrospectively designated as the Bonn Republic. At the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided between the Western and Eastern blocs. Germany was divided into the two countries. Initially, West Germany claimed an exclusive mandate for all of Germany, representing itself as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the fourth-largest city in the State of Bavaria after Munich, Nuremberg and Augsburg. From its foundation as an imperial Roman river fort, the city has been the political, economic and cultural centre of the surrounding region; it is still known in the Romance languages by a cognate of its Latin name of "Ratisbona" (the version "Ratisbon" was long current in English). Later, under the rule of the Holy Roman Empire, it housed the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. The medieval centre of the city was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006 because of its well-preserved architecture and the city's historical importance for assemblies during the Holy Roman Empire. In 2014, Regensburg was among the top sights and travel attractions in Germany. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary In World War II
During World War II, the Kingdom of Hungary was a member of the Axis powers. While according to the Romanian estimations in 1940 prior to the Second Vienna Award, about 1,300,000 people or 50% of the population was Romanian and according to the Hungarian estimations in 1940 shortly following the Second Vienna Award, about 1,150,000 people or 48% of the population was Romanian. The establishment of Hungarian rule met sometimes insurgency, most notable cases are the Ip massacre, Ip and Treznea massacre, Treznea incidents in Northern Transylvania. Occupation and annexation of Yugoslav territories After invasion of Yugoslavia, invading Yugoslavia on 11 April 1941, Hungary annexed sections of Baranya (region), Baranja, Bačka, Međimurje, and Prekmurje. The returned territories – 11,417 km² – had a population of 1,025,508 which comprised 36.6% Hungarians, 19% Germans, 16% Serbs and 28.4% others. Nearly one year later the Novi Sad raid was conducted initially targeting Yugoslav Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
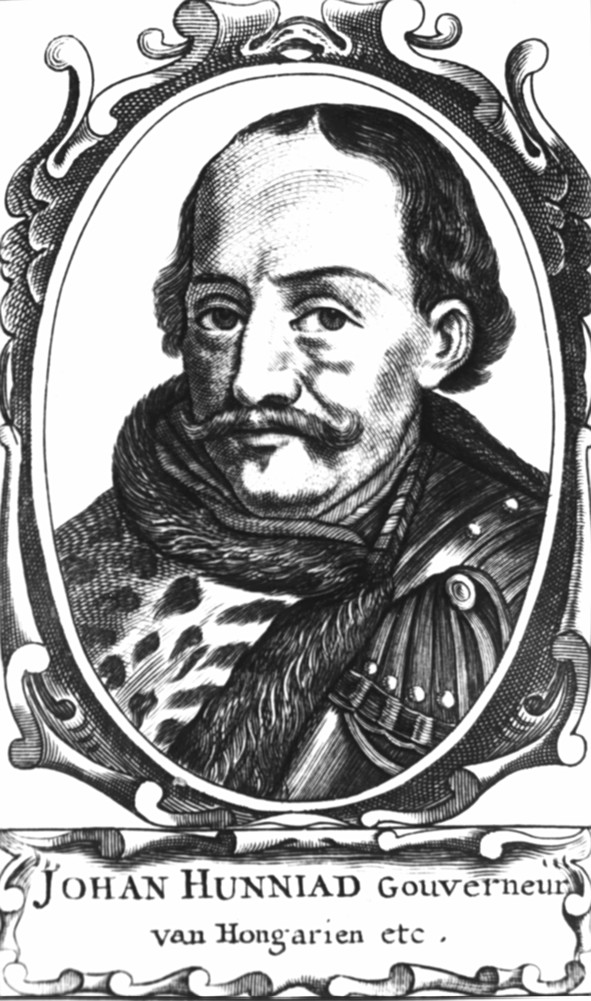
Regent Of Hungary
The Regent of Hungary was a position established in 1446 and renewed in 1920. It was held by Admiral Miklós Horthy until 1944. Under Hungary's Constitution there were two regents, one a regent of the ruling house, called the Nádor, and another called "Kormányzó" (which can mean "governor"). As the Entente had banned the legitimate Nádor from taking his place, the choice fell on electing a governor-regent: Admiral Horthy was chosen. Thus, he was regent of the post-World War I state called the Kingdom of Hungary and served as the head of state in the absence of a monarch, while a prime minister served as head of government. Horthy was styled "His Serene Highness the Regent of the Kingdom of Hungary" (Hungarian: ''Ő Főméltósága a Magyar Királyság Kormányzója''). History of the position Historical examples John Hunyadi On the untimely death of Albert in 1439, John Hunyadi was of the opinion that Hungary was best served by a warrior king and lent his support to the candid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke Joseph August Of Austria
Archduke Joseph August Viktor Klemens Maria of Austria, Prince of Hungary and Bohemia (9 August 1872 – 6 July 1962) was a ''Feldmarschall'' (field marshal) of the Austro-Hungarian Army and for a short period head of state of Hungary. He was a member of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, the eldest son of Archduke Joseph Karl of Austria (1833–1905) and his wife Princess Clotilde of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1846–1927). Joseph August's grandfather had been Palatine Joseph of Hungary (1776–1847), Palatine and Viceroy of Hungary, a younger son of Emperor Leopold II. The Archduke Joseph Diamond, a 76.02 carat colourless diamond with internal flawless clarity, is named after the Archduke and officially recorded as his property. Early life August was born at Alcsút, Kingdom of Hungary. On 15 November 1893, in Munich, he married Princess Augusta Maria Louise of Bavaria (1877–1964), daughter of Prince Leopold of Bavaria (1846–1930) and his wife Archduchess Gisela of Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduchess
Archduke (feminine: Archduchess; German: ''Erzherzog'', feminine form: ''Erzherzogin'') was the title borne from 1358 by the Habsburg rulers of the Archduchy of Austria, and later by all senior members of that dynasty. It denotes a rank within the former Holy Roman Empire (962–1806), which was below that of Emperor and King, roughly equal to Grand Duke, but above that of a Prince and Duke. The territory ruled by an Archduke or Archduchess was called an Archduchy. All remaining Archduchies ceased to exist in 1918. The current head of the House of Habsburg is Karl von Habsburg. Terminology The English word is first recorded in 1530, derived from Middle French ', a 15th-century derivation from Medieval Latin ', from Latin ''-'' (Greek ) meaning "authority" or "primary" (see '' arch-'') and ' "duke" (literally "leader"). "Archduke" (german: Erzherzog; nl, Aartshertog) is a title distinct from "Grand Duke" (french: Grand-Duc; lb, Groussherzog; german: Großherzog; nl, Groother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |