|
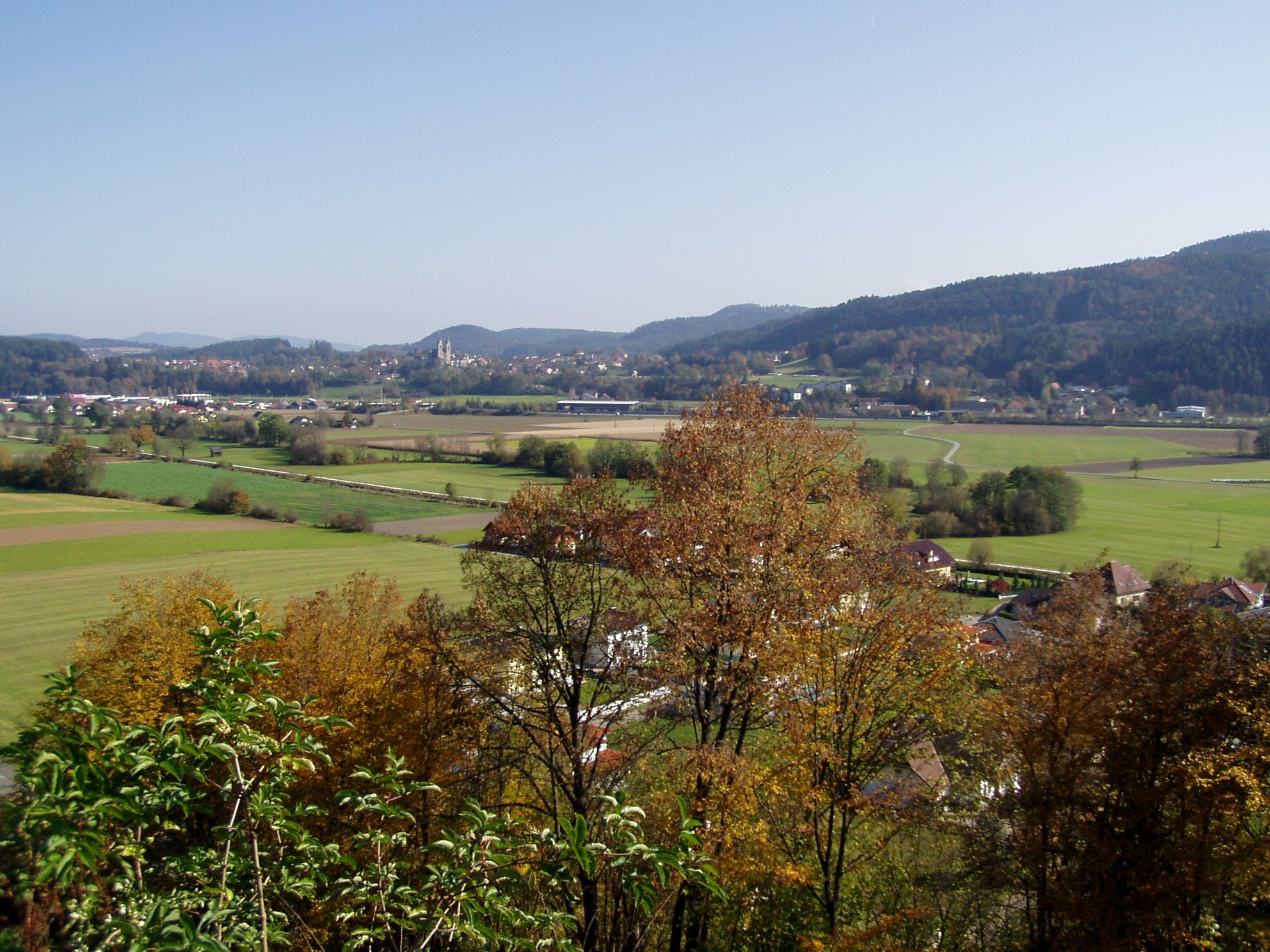
Zollfeld Plain
Zollfeld ( sl, Gosposvetsko polje) is a slightly ascending plain in Carinthia, Austria. It is one of the oldest cultural landscapes in the East Alpine region. Geography It is from to wide and about long, with an elevation between above sea level. It is situated in the larger Klagenfurt Basin of the Central Eastern Alps and extends along the Glan River from north of Klagenfurt to Sankt Veit an der Glan. The plain is confined by surrounded by four prominent peaks of the basin: the Ulrichsberg () in the south and the Magdalensberg () in the east as well as the Gößeberg () and the Lorenziberg in the north (). Since about 500 years the mountains are stops on the annual ''Vierbergelauf'' procession celebrated on second Friday after Easter. History The oldest archaeological findings at Magdalensberg originate from the time of Hallstatt culture (8th to 6th centuries BCE). The area was the cultural and political centre of the Celtic kingdom and the later Roman province of Noricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zollfeld Blick Von Karnburg Nach Maria Saal
Zollfeld ( sl, Gosposvetsko polje) is a slightly ascending plain in Carinthia, Austria. It is one of the oldest cultural landscapes in the East Alpine region. Geography It is from to wide and about long, with an elevation between above sea level. It is situated in the larger Klagenfurt Basin of the Central Eastern Alps and extends along the Glan River from north of Klagenfurt to Sankt Veit an der Glan. The plain is confined by surrounded by four prominent peaks of the basin: the Ulrichsberg () in the south and the Magdalensberg () in the east as well as the Gößeberg () and the Lorenziberg in the north (). Since about 500 years the mountains are stops on the annual ''Vierbergelauf'' procession celebrated on second Friday after Easter. History The oldest archaeological findings at Magdalensberg originate from the time of Hallstatt culture (8th to 6th centuries BCE). The area was the cultural and political centre of the Celtic kingdom and the later Roman province of Noricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virunum
Claudium Virunum was a Roman city in the province of Noricum, on today's Zollfeld in the Austrian State of Carinthia. Virunum may also have been the name of the older Celtic-Roman settlement on the hilltop of Magdalensberg nearby. Virunum (''Virunensis'') is today a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church. History Municipium Claudium Virunum, or simply, Virunum, was founded under Emperor Claudius as the capital of the province of Noricum succeeding the town upon the hilltop of Magdalensberg, perhaps also taking its name from that settlement, which is widely believed to have been the royal capital city of the pre-Roman Celtic kingdom of Noricum, a town whose name is, as yet, not known. The new Roman foundation was situated on the main route from the Adriatic to the Danube, with a branch through south eastern Carinthia connecting Virunum with the Amber Road. Established on a flood-proof terrace on the edge of Zollfeld parts of the city stretched as far as Töltschach Hill in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke's Chair
The Duke's Chair, also known as the Duke's Seat (german: Herzogstuhl, sl, vojvodski prestol or ), is a medieval stone seat dating from the ninth century and located at the Zollfeld plain near Maria Saal, north of Klagenfurt in the Austrian state of Carinthia. History The Duke's Chair, made mainly of Roman gravestones from nearby Virunum, actually consists of two stone seats, whose backrests are attached to each other. The larger seat, facing to the east, was reserved for the Dukes, the other one, slightly older and facing to the west, for the Counts palatine of the ''Meinhardiner'' dynasty. Together with the Prince's Stone, it played an important role during the installation of the Dukes of Carinthia in a Ceremony that may date back to the Early Medieval principality of Carantania. The chair was first mentioned as ''sedes Karinthani ducatus'' on the occasion of the installation of Duke Herman II of Spanheim in 1161. Here the newly installed duke had to swear an oath in German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Saal
Maria Saal ( sl, Gospa Sveta) is a market town in the district of Klagenfurt-Land in the Austrian state of Carinthia. It is located in the east of the historic Zollfeld plain (''Gosposvetsko polje''), the wide valley of the Glan river. The municipality includes the cadastral communes of Kading, Karnburg, Möderndorf, Possau and St. Michael am Zollfeld. History The Zollfeld valley has been a cultural and political centre since Celtic tribes settled in the region. When their kingdom of Noricum had become a province of the Roman Empire in 15 BC, Emperor Claudius had the city of Virunum erected as the province's capital at the foot of the nearby Magdalensberg, where on the hill top a splendid Celtic settlement had already existed. Virunum became a centre of early Christianity in the early 4th century as the see of a bishop under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch of Aquileia. When pagan Slavic tribes entered the region around 590, they settled in a place called Krnski Grad (German: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
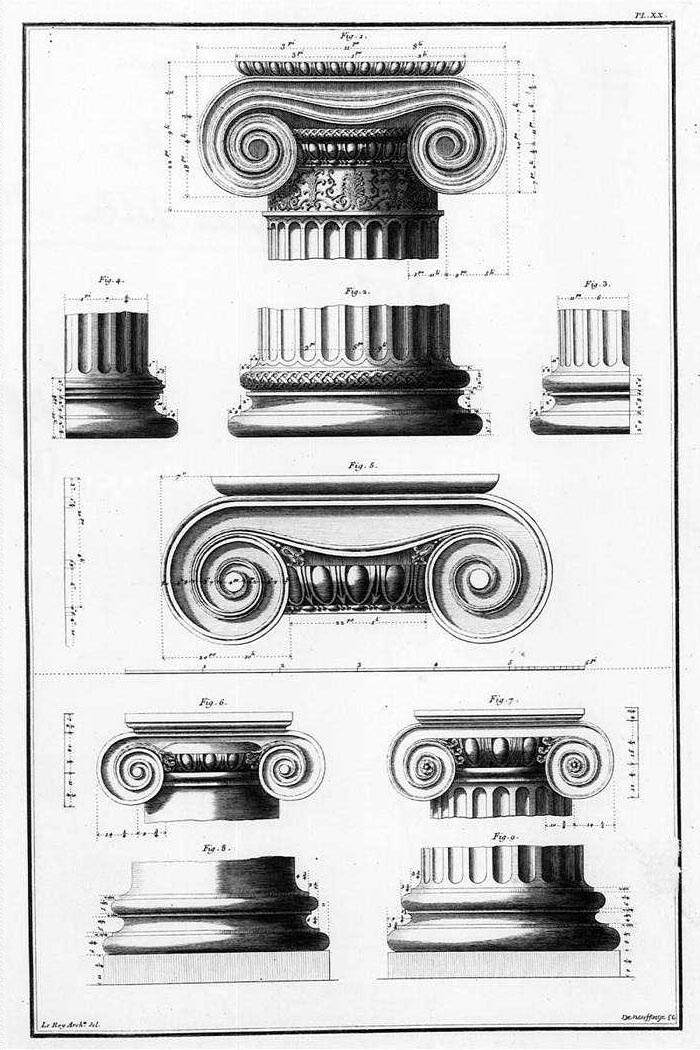
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince's Stone
The Prince's Stone (german: Fürstenstein, sl, knežji kamen) is the reversed base of an ancient Ionic column that played an important role in the ceremony surrounding the installation of the princes of Carantania in the Early Middle Ages. After the incorporation into the Frankish Empire, the procedure, held in Slovene, was continued as the first part of the coronation of the Dukes of Carinthia. It was followed by a mass at Maria Saal cathedral and the installation at the Duke's chair, where he swore an oath in German and received the homage of the estates. The stone The column probably originates from the nearby Roman city of Virunum, established as capital of the Noricum province under the reign of Emperor Claudius (AD 41–54). During the Middle Ages, the coat of arms of the Duchy of Carinthia was engraved on its top surface. Until 1862, when it was transferred to the ''Landhaus'' provincial assembly at Klagenfurt, it stood northwest of the ''Kaiserpfalz'' of Karnburg (Sloven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia (german: Herzogtum Kärnten; sl, Vojvodina Koroška) was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, and was the first newly created Imperial State after the original German stem duchies. Carinthia remained a State of the Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, though from 1335 it was ruled within the Austrian dominions of the Habsburg dynasty. A constituent part of the Habsburg monarchy and of the Austrian Empire, it remained a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary until 1918. By the Carinthian Plebiscite in October 1920, the main area of the duchy formed the Austrian state of Carinthia. History In the seventh century the area was part of the Slavic principality of Carantania, which fell under the suzerainty of Duke Odilo of Bavaria in about 743. The Bavarian stem duchy was incorporated into the Carolingian Empire when Charlemagne deposed Odilo's son Duke Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiserpfalz
The term ''Kaiserpfalz'' (, "imperial palace") or ''Königspfalz'' (, "royal palace", from Middle High German ''phal ne'' to Old High German ''phalanza'' from Middle Latin ''palatia'' luralto Latin ''palatium'' "palace") refers to a number of castles and palaces across the Holy Roman Empire that served as temporary, secondary seats of power for the Holy Roman Emperor in the Early and High Middle Ages. The term was also used more rarely for a bishop who, as a territorial lord (''Landesherr''), had to provide the king and his entourage with board and lodging, a duty referred to as ''Gastungspflicht''. Origin of the name ''Kaiserpfalz'' is a German word that is a combination of ''Kaiser'', meaning "emperor", which is derived from "caesar"; and ''Pfalz'', meaning "palace", and itself derived from the Latin ''palatium'', meaning the same (see palace). Likewise ''Königspfalz'' is a combination of ''König'', "king", and ''Pfalz'', meaning "royal palace". Description and purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of Western Europe, western and central Europe and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire around three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the Carolingian Empire. He was Canonization, canonized by Antipope Paschal III—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as Beatification, beatified (which is a step on the path to sainthood) in the Catholic Church. Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. He was born before their Marriage in the Catholic Church, canonical marriage. He became king of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from Byzantine Empire to Europe. The Carolingian Empire is considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. After a civil war (840–843) following the death of Emperor Louis the Pious, the empire was divided into autonomous kingdoms, with one king still recognised as emperor, but with little authority outside his own kingdom. The unity of the empire and the hereditary right of the Carolingians continued to be acknowledged. In 884, Charles the Fat reunited all the Carolingian kingdoms for the last time, but he died in 888 and the empire immediately split up. With the only r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odilo Of Bavaria
Odilo, also Oatilo or Uatilo (died 18th January 748) of the Agilolfing dynasty was Duke of Bavaria from 737 until his death in 748. He had the ''Lex Baiuvariorum'' compilation edited, the first ancient Germanic law collection of the Bavarians. Odilo by his Agilolfing descent was an Alemannic nobleman, a son of Duke Gotfrid (d. 709) whom he succeeded in Thurgau until 737, when with the death of Hugbert of Bavaria the older line of the dynasty became extinct and he inherited the rulership of the Duchy of Bavaria. Odilo presided over the establishment of bishoprics in Bavaria in 739, when the four dioceses of Regensburg, Freising, Passau, and Salzburg were established by St. Boniface, who in 741 also founded the Diocese of Würzburg in adjacent Franconia. His measures sparked a revolt by Bavarian nobles and the duke temporarily had to seek refuge at the court of the Frankish Mayor of the Palace Charles Martel. In 741, Odilo married Charles Martel's daughter Hiltrud, but upon the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. While the rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, and the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, the ''commenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |