|
Zoigê County
Zoigê County or Ruo'ergai County (; zh, s=若尔盖县 , p=Ruò'ěrgài Xiàn) is a county of Ngawa Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan, China, bordering Gansu to the north. It is the northernmost county of the province. It is part of the Tibetan traditional region of Amdo. It has an area of and a population of , 90.4% of which are Tibetan people. Governance Ruo'ergai County Public Security Bureau () is the primary law enforcement agency of Ruo'ergai county. It operates police stations in , and . On 14 July 2022, the Ruo'ergai County Public Security Bureau began a major operation to crack down on firearms and explosives, seizing a total of 198 firearms, 4,300 rounds of ammunition, 10 hand grenades, 20 kg of explosives and an improvised mortar. The Ruo'ergai County Fire and Rescue Battalion () provides fire and rescue services in Ruo'ergai county. Geography Ruo'ergai County is found in the easternmost sections of the Tibetan Plateau. The county is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code Of China
Postal codes in the China, People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the provinces of China, province, province-equivalent direct-controlled municipalities of China, municipality, or autonomous regions of China, autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures of the People's Republic of China, prefectures or prefecture-level city, prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000–009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min Mountains
Min Mountains or Minshan () are a mountain range in central China. It runs in the general north-south direction through northern Sichuan (the eastern part of the Ngawa Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture and adjacent areas of Mianyang Prefecture-level city) and southernmost borderlands of Gansu. The highest elevation is Mount Xuebaoding ("Snow Treasure Peak"), 5588 m and the second highest is Mt Little Xuebaoding ("Little Snow Treasure Peak"), 5443m. Geography The Min mountain range is a southern prolongation of the Kunlun Mountains that separates the basins of two major rivers of Sichuan: the Min River (to the west) and the Jialing River (to the east). Both rivers flow in the general southern direction, and are tributaries of the Yangtze. The Min Mountains are part of a wider mountainous region: * Amne Machin: The range located to the far west, known to the ancient Chinese as Mount Jishi (積石山, 积石山, Jīshíshān), part of the Kunlun Mountains. * Xiqing Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Script
The Tibetan script is a segmental writing system, or '' abugida'', forming a part of the Brahmic scripts, and used to write certain Tibetic languages, including Tibetan, Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Ladakhi, Jirel and Balti. Its exact origins are a subject of research but is traditionally considered to be developed by Thonmi Sambhota for King Songtsen Gampo. The printed form is called uchen script while the hand-written form used in everyday writing is called umê script. This writing system is especially used across the Himalayan Region. History Little is known about the exact origins of Tibetan script. According to Tibetan historiography, it was developed during the reign of King Songtsen Gampo by his minister Thonmi Sambhota, who was sent to India along with other scholars to study Buddhism along with Sanskrit and other brahmi languages. They developed the Tibetan script from the Gupta script while at the Pabonka Hermitage. This occurred , towards the beginning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townships Of The People's Republic Of China
Townships ( zh, s=乡, labels=no), formally township-level divisions ( zh, s=乡级行政区, labels=no), are the basic level (fourth-level administrative units) of Administrative divisions of China#Township level, political divisions in the China, People's Republic of China. They are similar to municipalities and communes in other countries and in turn may contain village committees and villages. In 1995 there were 29,648 townships and 17,570 towns (a total of 47,218 township-level divisions) in China which included the territories Free area of the Republic of China, held by the Taiwan, Republic of China and claimed by the PRC. Much like other levels of government in mainland China, the township's governance is divided between the Communist Party Township Secretary, and the "County magistrate (China), county magistrate" ( zh, s=乡长, hp=xiāngzhǎng, links=no). The township party secretary, along with the township's party committee, determines policy. The magistrate is in char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town (China)
When referring to Administrative divisions of China#Township level (4th), political divisions of China, town is the standard English translation of the Chinese (traditional: ; zh, p=zhèn , w=chen4). The Constitution of the People's Republic of China classifies towns as fourth-level administrative units, along with, for example, Townships of China, townships ( zh, s=乡 , p=xiāng). A township is typically smaller in population and more remote than a town. Similar to higher-level administrative units, the borders of a town would typically include an urban core (a small town with the population on the order of 10,000 people), as well as a rural area with some Villages of China, villages ( zh, labels=no, s=村 , p=cūn, or zh, labels=no, s=庄 , p=zhuāng). Map representation A typical provincial map would merely show a town as a circle centered at its urban area and labeled with its name, while a more detailed one (e.g., a map of a single county-level division) would also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Highway 248
The China National Highways (CNH/Guodao) () is a network of trunk roads across mainland China. Established to facilitate transportation and economic development, the system includes north-south and east-west arterial highways, expressways, and local roads. By 2024, the network encompasses over 1.9 million kilometers of highways, making it one of the most extensive in the world. Key milestones include the completion of major expressways by 2008 and ongoing expansions to enhance connectivity, especially in western and less developed areas. Apart from the expressways of China that were planned and constructed later, most of the CNH are not controlled-access highways. History The building of highways is seen as key to accelerating infrastructure construction. In 2003, completed investment in highway construction was 350 billion yuan and 219 key highway projects progressed, focusing mainly on the five north–south and seven east–west national arterial highways as well as highw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Highway 213
China National Highway 213 (G213) runs from Ceke, Inner Mongolia, to Mohan, on the border with Laos, in Yunnan. It is in length and runs via Chengdu, Sichuan and Kunming, Yunnan. Before the 2013 Highway Planning, the route started in Lanzhou, Gansu. This route was a key transportation route into the disaster zone during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, and was referred to as a "lifeline" by rescue workers. On 6 July 2011, it was damaged by mudslide A mudflow, also known as mudslide or mud flow, is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris and dirt that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/ ...s and collapses, including a stretch which was damaged as a result of the nearby river being diverted by a mudslide. For the extension to Ceke, a tunnel is being constructed on the pass on the Gansu-Qinghai border near Sunan County. Route and distance See also * China Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Meteorological Administration
The China Meteorological Administration (CMA) is the national weather service of the People's Republic of China. The institution is located in Beijing. History The agency was originally established in December 1949 as the Central Military Commission Meteorological Bureau. It replaced the Central Weather Bureau formed in 1941. In 1994, the CMA was transformed from a subordinate governmental body into one of the public service agencies under the State Council.CMA.gov history Meteorological bureaus are established in 31 provinces, autonomous regions and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
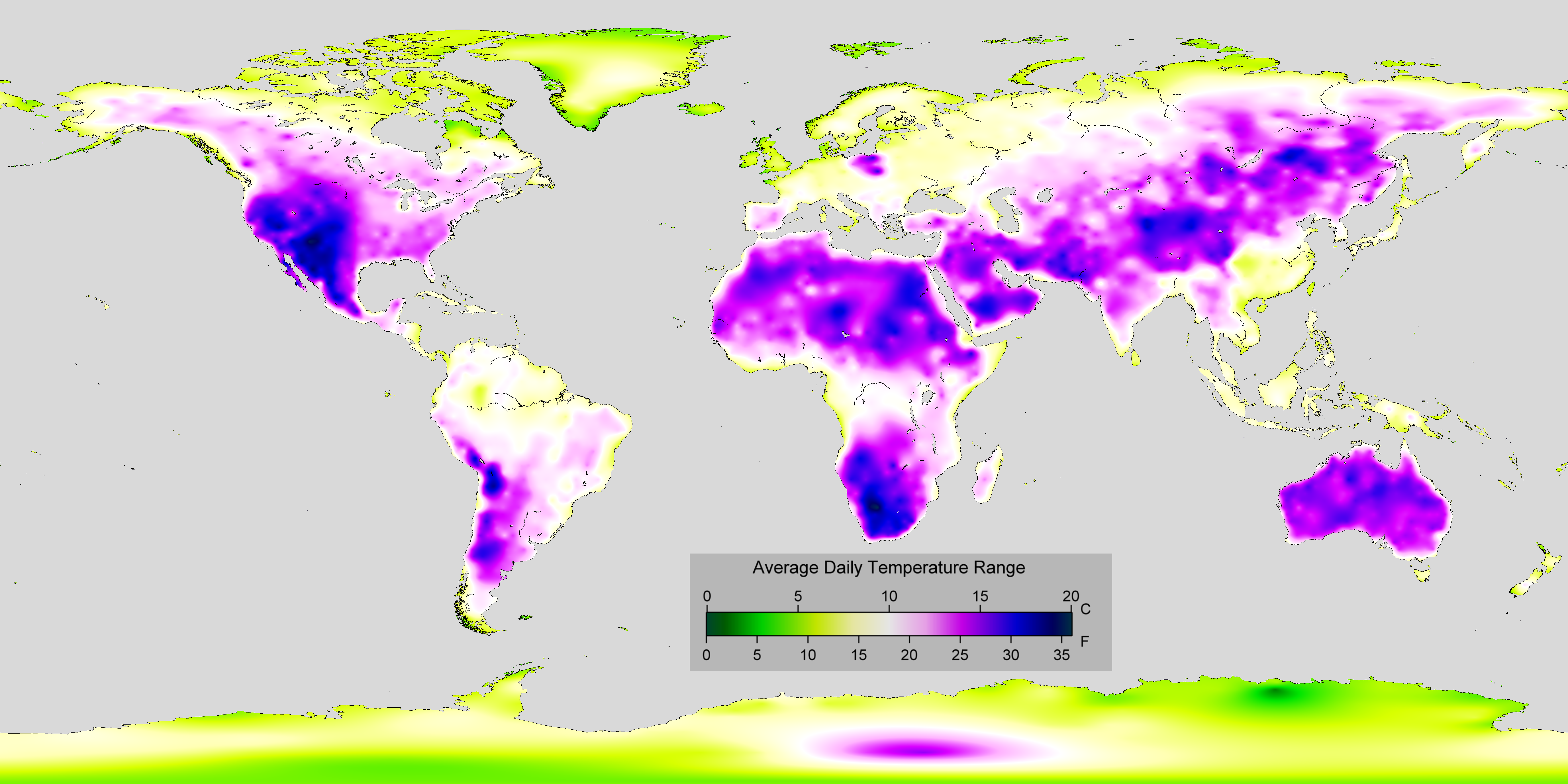
Diurnal Temperature Range
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a continental climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Like other Class D climates, they are rare in the Southern Hemisphere, only found at some isolated highland elevations. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese language, Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat language, Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |