|
Ziklag
Ziklag ( he, צִקְלַג) is the biblical name of a town that was located in the Negev region in the south-west of what was the Kingdom of Judah. It was a provincial town within the Philistine kingdom of Gath when Achish was king. Its exact location has not been identified with any certainty. Identification At the end of the 19th century, both Haluza (by Wadi Asluj, south of Beersheba)Cheyne and Black, ''Encyclopedia Biblica'' and Khirbet Zuheiliqah (located north-west of Beersheba and south-southeast of Gaza city) had been suggested as possible locations. Khirbet Zuheiliqah was identified by Conder and Kitchener as the location on the basis of ''Ziklag'' being a corruption of ''Zahaliku'', whence also ''Zuheiliqah''. The more recently proposed identifications for Ziklag are: * Albrecht Alt (1883–1956) proposed Tel Halif/ Tell el-Khuweilifeh, just beside kibbutz Lahav, some northeast of Beersheba. Due to this identification, for some time Lahav was officially named Tzekl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khirbet A-Ra'i
Khirbet er-Ra'i, also Khirbet al-Ra'i, (formerly ''Tôr el Hiry'', ) is an archaeological site in the Shephelah region of Israel. It is located 4 km west of Lachish.Garfinkel, Yosef & Keimer, Kyle & Ganor, & Rollston, Christopher. (2021). 2019Khirbet al-Ra‘i in the Judean Shephelah: The 2015–2019 Excavation Seasons 37. 13-50. Archeological excavations conducted in Khirbet er-Ra'i in the past decade have uncovered remains dating back to the 12th-10th centuries BCE. According to the site's excavators, it was mainly a Canaanite site, but with a strong Philistine influence. Location Khirbet e-Ra'i is situated on a hill on the Lachish River's southern bank, between the upper and lower parts of the Shfela (Shephelah). The hill is overlooking the Coastal Plain in the west, the Mount Hebron and Jerusalem in the east and Tell ej-Judeideh and Maresha to the north. Khirbet er-Ra'i controls the main road connecting the coastal plain with the Shephelah and Judea. According to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (Septuagint, LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and Archaeology, archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their Bible, biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramesses III, Ramses III at Medinet Habu (temple), Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cogna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cognate with Hebrew ); the parallel Assyrian term is , , or . Etymology The English te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshe Garsiel
Moshe Garsiel ( he, משה גרסיאל) (born 1936) is professor emeritus of Bible at Bar-Ilan University."Moshe Garsiel", Bible commentaries, p. 15. Early life and education Moshe Garsiel born and raised in Tel Aviv. Most of his academic studies were completed at Tel Aviv University: B.A. in Hebrew Bible and Hebrew Literature (1965), M.A. in Hebrew Bible (1968), Ph.D in Hebrew Bible (1974), Post-doctorate in Biblical Archaeology (1974-5). Career Garsiel's major teaching and research positions were at Bar-Ilan University: Instructor, The Department of Bible (1968-1973); lecturer, The Department of Bible (1974-1977); senior lecture (status-tenure) (1978-1980); associate professor (1984); full professor and a senate member (1992—2005). In 2006 he retired from Bar-Ilan as professor emeritus, but continues teaching voluntarily to this day and delivers seminars for graduate students (MA and Ph.D. students). He held different administrative positions at Bar-Ilan University: chair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Halif
Tel H̱alif, formerly Tel H̱alifa ( he, תל חליף, Arabic name: Tel el-Khuweilifeh) is an archaeological site, a mound ( tell) in northern Negev area, west from kibbutz Lahav, Israel. Albrecht Alt suggested that it is the location of the biblical town of Ziklag Ziklag ( he, צִקְלַג) is the biblical name of a town that was located in the Negev region in the south-west of what was the Kingdom of Judah. It was a provincial town within the Philistine kingdom of Gath when Achish was king. Its exact loca .... Other evidence suggests Rimmon. Excavcations around Tel Halif was among the research activities of the Cobb Institute of Archaeology as part of the Lahav Research Project arranged by Joe Seger in 1974. See also * Battle of Tel el Khuweilfe References {{infobox mapframe, coord={{coord, 31.383062, 34.866140, zoom=14 archaeological sites in Israel Negev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
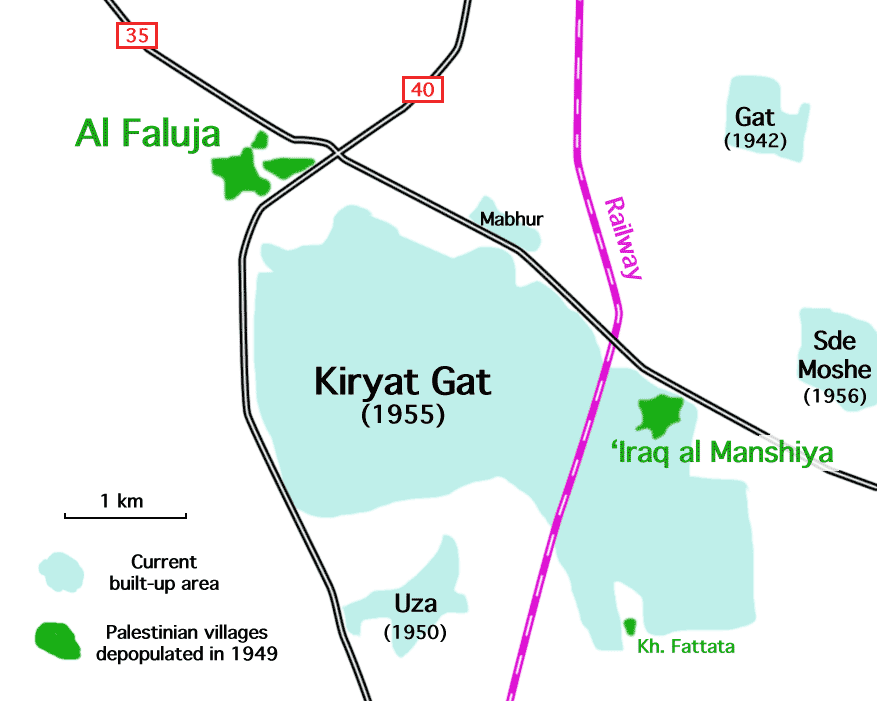
Kiryat Gat
Kiryat Gat, also spelled Qiryat Gat ( he, קִרְיַת גַּת), is a city in the Southern District of Israel. It lies south of Tel Aviv, north of Beersheba, and from Jerusalem. In it had a population of . The city hosts one of the most advanced semiconductor fabrication plants in the world, Intel's Fab 28 plant producing 7 nm process chips and the currently under construction Fab 38 planned to open in 2024 and to produce 5 nm process using EUV lithography. Etymology Kiryat Gat is named for Gath, one of the five major cities of the Philistines. In Hebrew, "gat" means "winepress". In the 1950s, archaeologists found ruins at a nearby tell ( Tel Erani) which were mistaken for the Philistine city of Gath. The location most favored for Gath now is Tel es-Safi, thirteen kilometers () to the northeast. History Kiryat Gat was founded in 1954, initially as a ma'abara. The following year it was established as a development town by 18 families from Morocco. It was founded j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell El-Khuweilifeh
Tel H̱alif, formerly Tel H̱alifa ( he, תל חליף, Arabic name: Tel el-Khuweilifeh) is an archaeological site, a mound ( tell) in northern Negev area, west from kibbutz Lahav, Israel. Albrecht Alt suggested that it is the location of the biblical town of Ziklag Ziklag ( he, צִקְלַג) is the biblical name of a town that was located in the Negev region in the south-west of what was the Kingdom of Judah. It was a provincial town within the Philistine kingdom of Gath when Achish was king. Its exact loca .... Other evidence suggests Rimmon. Excavcations around Tel Halif was among the research activities of the Cobb Institute of Archaeology as part of the Lahav Research Project arranged by Joe Seger in 1974. See also * Battle of Tel el Khuweilfe References {{infobox mapframe, coord={{coord, 31.383062, 34.866140, zoom=14 archaeological sites in Israel Negev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahav
Lahav ( he, לַהַב, ''lit. blade'') is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located around 20 km north of Beersheba and covering 33,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Bnei Shimon Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The kibbutz was established in 1952 and was initially named Tziklag ( he, צקלג) after the Biblical city of Ziklag, which was thought to have been located nearby. Originally the founders had been unsure whether to settle in the Negev or Galilee, but accepted a government decision that settling on Tel Halif (''Tell el-Khuweilifeh'') in the Negev was more important. After a few years, the kibbutz was renamed Lahav in honour of the Nahal group which established it. Archaeology The ancient settlement of Tel Halif flourished at the time of ancient Egypt. It was a 7-acre site, and it was occupied from Chalcolithic times. Also, significant Early Bronze Age remains have been found. During the Late Bronze period, an Egyptian “residence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achish
Achish ( he, אָכִישׁ ''ʾāḵīš'', Philistine: 𐤀𐤊𐤉𐤔 *''ʾāḵayūš'', Akkadian: 𒄿𒅗𒌑𒋢 ''i-ka-ú-su'') is a name used in the Hebrew Bible for two Philistine rulers of Gath. It is perhaps only a general title of royalty, applicable to the Philistine kings. The two kings of Gath, which is identified by most scholars as Tell es-Safi, are: * The monarch, described as "Achish the king of Gath", with whom David sought refuge when he fled from Saul. He is called Abimelech (meaning "father of the king") in the superscription of Psalm 34. It was probably this same king, or his son with the same name, described as "Achish, the son of Maoch", to whom David reappeared a second time at the head of a band of 600 warriors. The king assigned David to Ziklag, whence he carried on war against the surrounding tribes whilst lying to Achish that he was waging war against Israel to garner his support. Achish had great confidence in the valour and fidelity of David, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gath (city)
Gath or Gat ( he, גַּת, translit=Gaṯ, lit= wine press; la, Geth, Philistine: 𐤂𐤕 *''Gīt''), often referred to as Gath of the Philistines, was a major Philistine city and one of the five Philistine city-states during the Iron Age. It was located in northeastern Philistia, close to the border with Judah. Gath is often mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and its existence is confirmed by Egyptian inscriptions. Already of significance during the Bronze Age, the city is believed to be mentioned in the El-Amarna letters as Gimti/Gintu, ruled by the two Shuwardata and 'Abdi-Ashtarti. Another Gath, known as Ginti-kirmil (Gath of Carmel) also appears in the Amarna letters.Naʼaman, Nadav (2005), p207/ref> The site most favored as the location of Gath is the archaeological mound or tell known as Tell es-Safi in Arabic and Tel Zafit in Hebrew (sometimes written Tel Tzafit), located inside Tel Zafit National Park, but a stone inscription disclosing the name of the city has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Post
''The Jerusalem Post'' is a broadsheet newspaper based in Jerusalem, founded in 1932 during the British Mandate of Palestine by Gershon Agron as ''The Palestine Post''. In 1950, it changed its name to ''The Jerusalem Post''. In 2004, the paper was bought by Mirkaei Tikshoret, a diversified Israeli media firm controlled by investor Eli Azur. In April 2014, Azur acquired the newspaper '' Maariv''. The newspaper is published in English and previously also printed a French edition. Originally a left-wing newspaper, it underwent a noticeable shift to the political right in the late 1980s. From 2004 editor David Horovitz moved the paper to the center, and his successor in 2011, Steve Linde, pledged to provide balanced coverage of the news along with views from across the political spectrum. In April 2016, Linde stepped down as editor-in-chief and was replaced by Yaakov Katz, a former military reporter for the paper who previously served as an adviser to former Prime Minister Naf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casluhim
The Casluhim or Casluhites ( he, כסלחים) were an ancient Egyptian people mentioned in the Bible and related literature. Biblical accounts According to the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles (), the Casluhim were descendants of Mizraim (Egypt) son of Ham, out of whom originated the Philistines. Archaeology The Egyptian form of their name is preserved in the inscriptions of the Temple of Kom Ombo as the region name ''Kasluḥet''. In the Aramaic ''Targum''s their region is called ''Pentpolitai'' understood to be derived from the Greek ''Pentapolis'' which locates the area as the north west in what is now the Cyrenaica region of Libya. Another name for their region is ''Pekosim'' used in Bereshit Rabbah 37. In Saadia Gaon's Judeo-Arabic translation of the Pentateuch, the '' Sa'idi people'' (i.e. the people of Upper Egypt) are listed in the position of the Casluhim in , while ''Albiyim'' is listed in the position of Pathrusim, however the ordering of Casluhim and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |