|
Zetra Festival
The Juan Antonio Samaranch Olympic Hall ( Bosnian, Croatian and Serbian: ''Olimpijska dvorana Juan Antonio Samaranch'' / Олимпијска дворана Хуан Антонио Самаран; formerly Zetra Olympic Hall) is an indoor multi-purpose arena in Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Named in honor of Juan Antonio Samaranch in 2010 after his death, it was used for various sporting events at the 1984 Winter Olympics, and as the main venue of the 2019 European Youth Olympic Winter Festival. History The building of the complex started in June 1981 and was officially opened by then-President of the International Olympic Committee, Juan Antonio Samaranch, on February 14, 1982. Olympic venue Zetra Olympic Hall was constructed specifically for the 1984 Winter Olympics, hosted in Sarajevo, and was completed in 1982. Its first major event was the 1983 World Junior Speed Skating Championships. It was described as an "ultramodern, angular edifice" [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centar Municipality, Sarajevo
Centar (Cyrillic: Центар, lit. ”Center") is a municipality of the city of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located between the older parts of the city under Stari Grad, and the newer more modern parts of the city under the municipalities Novi Grad and Novo Sarajevo. The Centar municipality, according to the government website, is the administrative, business, commercial, cultural, educational, and medical centre of Sarajevo. Although some of these may be disputed, Centar is certainly the most important part of Sarajevo, housing most major branches of the city and national governments. The municipality of Centar occupies 3,313 hectrates of land, of which close to 17% is housing. The amount of private and state owned land is nearly equal, with 1600 and 1713 hectrates respectively. The municipality celebrates May 2 as "Centar Municipality Day", in commemoration of the heroic defense by citizens of the aggressor's assault on the Building of the Presidency of Bosnia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stability Pact Summit
Stability may refer to: Mathematics *Stability theory, the study of the stability of solutions to differential equations and dynamical systems **Asymptotic stability **Linear stability **Lyapunov stability **Orbital stability **Structural stability *Stability (probability), a property of probability distributions *Stability (learning theory), a property of machine learning algorithms *Stability, a property of sorting algorithms *Numerical stability, a property of numerical algorithms which describes how errors in the input data propagate through the algorithm *Stability radius, a property of continuous polynomial functions *Stable theory, concerned with the notion of stability in model theory *Stability, a property of points in geometric invariant theory *K-Stability, a stability condition for algebraic varieties. *Bridgeland stability conditions, a class of stability conditions on elements of a triangulated category. *Stability (algebraic geometry) Engineering *In atmospheric flui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drina Martyrs Beatification
The Drina ( sr-Cyrl, Дрина, ) is a long Balkans river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava, Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps which belongs to the Danube river watershed. Its name is derived from the Ancient Rome, Roman name of the river ( la, Drinus) which in turn is derived from Greek language, Greek (Ancient Greek: ). The Drina originates from the confluence of the rivers Tara (river), Tara and Piva (river), Piva, in the glen between the slopes of the Maglić (mountain), Maglić, Hum (Pešter), Hum and Piva_(river)#Piva Plateau, Pivska Planina mountains, in the area of Šćepan Polje (in Montenegro) and Hum, Foča, Hum (Bosnia and Herzegovina) villages. Hydrological characteristics The Drina is a very fast and cold alpine river, with a very high 175:346 meandering ratio, and relatively clean water, which has particularly intensive green coloration, a usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . The euro is divided into 100 cents. The currency is also used officially by the institutions of the European Union, by four European microstates that are not EU members, the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, as well as unilaterally by Montenegro and Kosovo. Outside Europe, a number of special territories of EU members also use the euro as their currency. Additionally, over 200 million people worldwide use currencies pegged to the euro. As of 2013, the euro is the second-largest reserve currency as well as the second-most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar. , with more than €1.3 trillion in circulation, the euro has one of the highest combined values of banknotes and coins in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Mark
The Deutsche Mark (; English: ''German mark''), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it was typically called the "Deutschmark" (). One Deutsche Mark was divided into 100 pfennigs. It was first issued under Allied occupation in 1948 to replace the Reichsmark and served as the Federal Republic of Germany's official currency from its founding the following year. On 31 December 1998, the Council of the European Union fixed the irrevocable exchange rate, effective 1 January 1999, for German mark to euros as DM 1.95583 = €1. In 1999, the Deutsche Mark was replaced by the euro; its coins and banknotes remained in circulation, defined in terms of euros, until the introduction of euro notes and coins on 1 January 2002. The Deutsche Mark ceased to be legal tender immediately upon the introduction of the euro—in contrast to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss Civil Code (articles 60–79). Founded by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas in 1894, it is the authority responsible for organising the modern ( Summer, Winter, and Youth) Olympic Games. The IOC is the governing body of the National Olympic Committees (NOCs) and of the worldwide "Olympic Movement", the IOC's term for all entities and individuals involved in the Olympic Games. As of 2020, there are 206 NOCs officially recognised by the IOC. The current president of the IOC is Thomas Bach. The stated mission of the IOC is to promote the Olympics throughout the world and to lead the Olympic Movement: *To encourage and support the organization, development, and coordination of sport and sports competitions; *To ensure the regular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SFOR
The Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina (SFOR) was a NATO-led multinational peacekeeping force deployed to Bosnia and Herzegovina after the Bosnian war. Although SFOR was led by NATO, several non-NATO countries contributed troops. It was replaced by EUFOR Althea in December 2004. Mission The stated mission of SFOR was to "deter hostilities and stabilise the peace, contribute to a secure environment by providing a continued military presence in the Area Of Responsibility (AOR), target and co-ordinate SFOR support to key areas including primary civil implementation organisations, and progress towards a lasting consolidation of peace, without further need for NATO-led forces in Bosnia and Herzegovina". Structure and history SFOR was established in United Nations Security Council Resolution 1088, Security Council Resolution 1088 on 12 December 1996. It succeeded the much larger Implementation Force IFOR which was deployed to Bosnia and Herzegovina on 20 December 1995 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
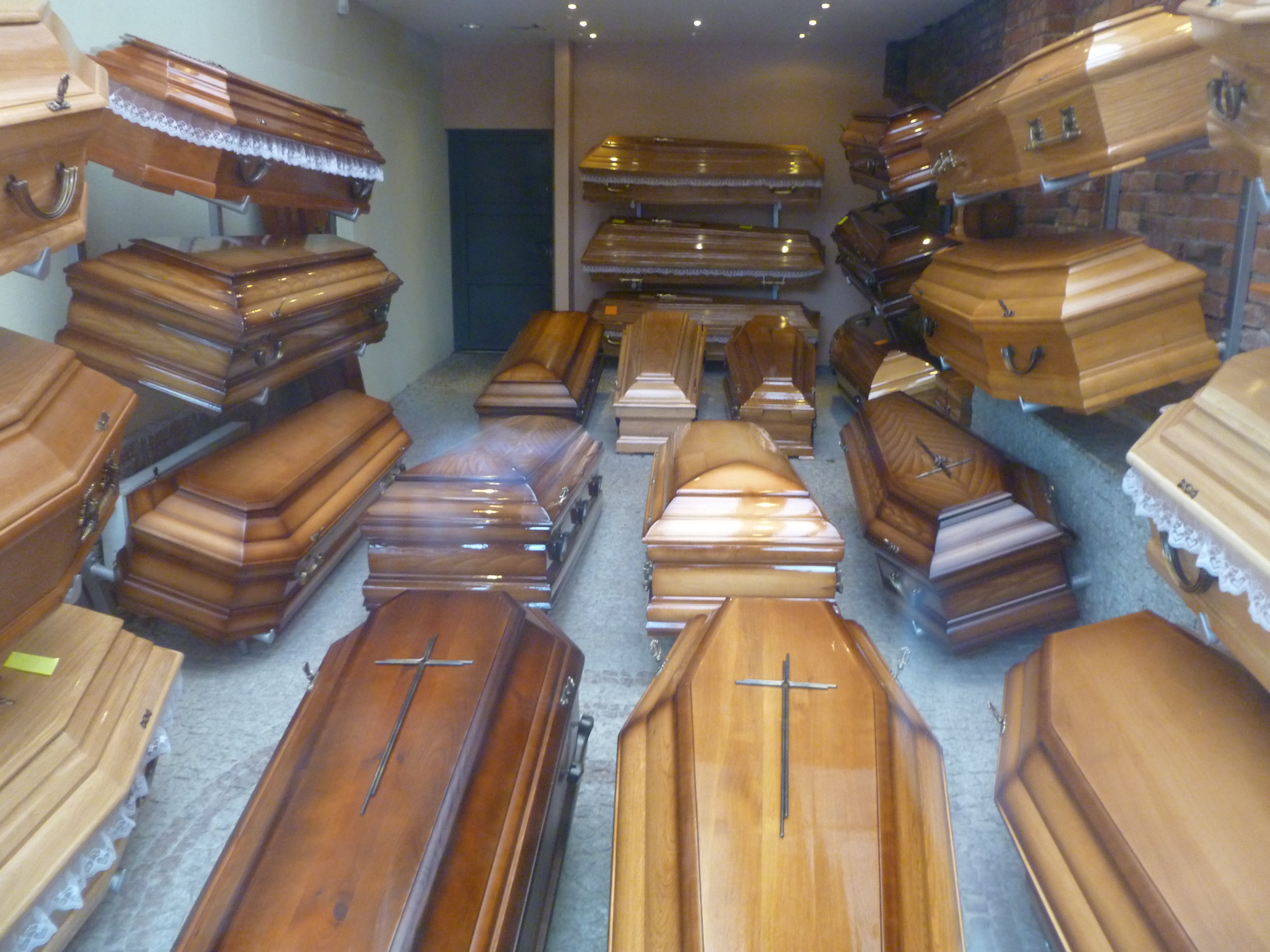
Coffin
A coffin is a funerary box used for viewing or keeping a corpse, either for burial or cremation. Sometimes referred to as a casket, any box in which the dead are buried is a coffin, and while a casket was originally regarded as a box for jewelry, use of the word "casket" in this sense began as a euphemism introduced by the undertaker's trade. A distinction is commonly drawn between "coffins" and "caskets", using "coffin" to refer to a tapered hexagonal or octagonal (also considered to be anthropoidal in shape) box and "casket" to refer to a rectangular box, often with a split lid used for viewing the deceased as seen in the picture. Receptacles for cremated and cremulated human ashes (sometimes called cremains) are called urns. Etymology First attested in English in 1380, the word ''coffin'' derives from the Old French , from Latin , which means ''basket'', which is the latinisation of the Greek κόφινος (''kophinos''), ''basket''. The earliest attested form of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgue
A morgue or mortuary (in a hospital or elsewhere) is a place used for the storage of human corpses awaiting identification (ID), removal for autopsy, respectful burial, cremation or other methods of disposal. In modern times, corpses have customarily been refrigerated to delay decomposition. Etymology and lexicology The term ''mortuary'' dates from the early 14th century, from Anglo-French ''mortuarie'', meaning "gift to a parish priest from a deceased parishioner," from Medieval Latin mortuarium, noun use of neuter of Late Latin adjective mortuarius "pertaining to the dead," from Latin ''mortuus'', pp. of ''mori'' "to die" (see mortal (adj.)). The meaning of "place where the deceased are kept temporarily" was first recorded in 1865, as a euphemism for the earlier English term "deadhouse". The term ''morgue'' comes from the French. First used to describe the inner wicket of a prison, where new prisoners were kept so that jailers and turnkeys could recognize them in the futu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started on 6 April 1992, following a number of earlier violent incidents. The war ended on 14 December 1995 when the Dayton accords were signed. The main belligerents were the forces of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and those of Herzeg-Bosnia and Republika Srpska, proto-states led and supplied by Croatia and Serbia, respectively. The war was part of the breakup of Yugoslavia. Following the Slovenian and Croatian secessions from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1991, the multi-ethnic Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina – which was inhabited by mainly Muslim Bosniaks (44%), Orthodox Serbs (32.5%) and Catholic Croats (17%) – passed a referendum for independence on 29 February 1992. Political representatives of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SR Bosnia
The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina, Социјалистичка Pепублика Босна и Херцеговина), commonly referred to as Socialist Bosnia or simply Bosnia, was one of the six constituent federal states forming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. It was a predecessor of the modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, existing between 1945 and 1992, under a number of different formal names, including Democratic Bosnia and Herzegovina (1943–1946) and People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1946–1963). Within Yugoslavia, Bosnia and Herzegovina was a unique federal state with no dominant ethnic group, as was the case in other constituent states, all of which were also nation states of Ethnic groups in Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia's South Slavic ethnic groups. It was administered under strict terms of sanctioned consociationalism, known locally as "ethnic key" ( sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


