|
Zellij
''Zellij'' ( ar, الزليج, translit=zillīj; also spelled zillij or zellige) is a style of mosaic tilework made from individually hand-chiseled tile pieces. The pieces were typically of different colours and fitted together to form various patterns on the basis of tessellations, most notably elaborate Islamic geometric motifs such as radiating star patterns. This form of Islamic art is one of the main characteristics of architecture in the western Islamic world. It is found in the architecture of Morocco, the architecture of Algeria, early Islamic sites in Tunisia, and in the historic monuments of al-Andalus (in the Iberian Peninsula). From the 14th century onwards, ''zellij'' became a standard decorative element along lower walls, in fountains and pools, on minarets, and for the paving of floors. After the 15th century the traditional mosaic ''zellij'' fell out of fashion in most countries except for Morocco, where it continues to be produced today. ''Zellij'' is found in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorish Architecture
Moorish architecture is a style within Islamic architecture which developed in the western Islamic world, including al-Andalus (on the Iberian peninsula) and what is now Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia (part of the Maghreb). The term "Moorish" comes from the historical Western European designation of the Muslim inhabitants of these regions as "Moors". Scholarly references on Islamic architecture often refer to this architectural tradition by a more geographic designation, such as architecture of the Islamic West or architecture of the Western Islamic lands, and some references on Islamic art and architecture consider use of the term "Moorish" to be outdated or contested. This architectural style blended influences from Berber culture in North Africa, pre-Islamic Iberia ( Roman, Byzantine, and Visigothic), and contemporary artistic currents in the Islamic Middle East to elaborate a unique style over centuries with recognizable features such as the horseshoe arch, ''riad'' gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Morocco
Moroccan architecture refers to the architecture characteristic of Morocco throughout its history and up to modern times. The country's diverse geography and long history, marked by successive waves of settlers through both migration and military conquest, are all reflected in its architecture. This architectural heritage ranges from ancient Roman and Berber (Amazigh) sites to 20th-century colonial and modern architecture. The most recognizably "Moroccan" architecture, however, is the traditional architecture that developed in the Islamic period (7th century and after) which dominates much of Morocco's documented history and its existing heritage. This "Islamic architecture" of Morocco was part of a wider cultural and artistic complex, often referred to as "Moorish" art, which characterized Morocco, al-Andalus (Muslim Spain and Portugal), and parts of Algeria and even Tunisia. It blended influences from Berber culture in North Africa, pre-Islamic Spain (Roman, Byzantine, and Vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Geometric Patterns
Islamic geometric patterns are one of the major forms of Islamic ornament, which tends to avoid using figurative images, as it is forbidden to create a representation of an important Islamic figure according to many holy scriptures. The geometric designs in Islamic art are often built on combinations of repeated squares and circles, which may be overlapped and interlaced, as can arabesques (with which they are often combined), to form intricate and complex patterns, including a wide variety of tessellations. These may constitute the entire decoration, may form a framework for floral or calligraphic embellishments, or may retreat into the background around other motifs. The complexity and variety of patterns used evolved from simple stars and lozenges in the ninth century, through a variety of 6- to 13-point patterns by the 13th century, and finally to include also 14- and 16-point stars in the sixteenth century. Geometric patterns occur in a variety of forms in Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alhambra
The Alhambra (, ; ar, الْحَمْرَاء, Al-Ḥamrāʾ, , ) is a palace and fortress complex located in Granada, Andalusia, Spain. It is one of the most famous monuments of Islamic architecture and one of the best-preserved palaces of the historic Islamic world, in addition to containing notable examples of Spanish Renaissance architecture. The complex was begun in 1238 by Muhammad I Ibn al-Ahmar, the first Nasrid emir and founder of the Emirate of Granada, the last Muslim state of Al-Andalus. It was built on the Sabika hill, an outcrop of the Sierra Nevada which had been the site of earlier fortresses and of the 11th-century palace of Samuel ibn Naghrillah. Later Nasrid rulers continuously modified the site. The most significant construction campaigns, which gave the royal palaces much of their definitive character, took place in the 14th century during the reigns of Yusuf I and Muhammad V. After the conclusion of the Christian Reconquista in 1492, the site becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azulejo
''Azulejo'' (, ; from the Arabic ''al- zillīj'', ) is a form of Spanish and Portuguese painted tin-glazed ceramic tilework. ''Azulejos'' are found on the interior and exterior of churches, palaces, ordinary houses, schools, and nowadays, restaurants, bars and even railways or subway stations. They are an ornamental art form, but also had a specific functional capacity like temperature control in homes. There is also a tradition of their production in former Spanish and Portuguese colonies in North America, South America, the Philippines, Goa (India), Lusophone Africa, East Timor, and Macau (China). ''Azulejos'' constitute a major aspect of Spanish architecture and Portuguese architecture to this day and are fixtures of buildings across Spain and Portugal and its former territories. Many azulejos chronicle major historical and cultural aspects of Spanish and Portuguese history. History 13th to 15th century The word ''azulejo'' (as well as the Ligurian ''laggio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan II Mosque
The Hassan II Mosque ( ar, مسجد الحسن الثاني, french: Grande Mosquée Hassan II) is a mosque in Casablanca, Morocco. It is the largest functioning mosque in Africa and is the 7th largest in the world. Its minaret is the world's second tallest minaret at .Kingfisher Geography encyclopedia. . Page 137 Completed in 1993, it was designed by Michel Pinseau under the guidance of King Hassan II and built by Moroccan artisans from all over the kingdom. The minaret is 60 stories high topped by a laser, the light from which is directed towards Mecca. The mosque stands on a promontory looking out to the Atlantic Ocean; worshippers can pray over the sea but there is no glass floor looking into the sea. The walls are of hand-crafted marble and the roof is retractable. A maximum of 105,000 worshippers can gather together for prayer: 25,000 inside the mosque hall and another 80,000 on the mosque's outside ground. Geography The mosque is located at Bd Sidi Mohammed Ben Abdallah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by the eastern-influenced Republic of Venice, and among the Rus. Mosaic fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansouria, Tunisia
El-Mansuriya or Mansuriya ( ar, المنصورية), near Kairouan, Tunisia, was the capital of the Fatimid Caliphate during the rule of the Ismaili Imams al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah (r. 946–953) and al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah (r. 953–975). Built between 946 and 972, el-Mansuriya was a walled city holding elaborate palaces surrounded by gardens, artificial pools and water channels. It was briefly the centre of a powerful state that encompassed most of North Africa and Sicily. It continued to serve as provincial capital of the Zirids until 1057, when it was destroyed by the invading Banu Hilal tribes. Any useful objects or relics were scavenged during the centuries that followed. Today, only faint traces remain. Background The Fatimid Caliphate originated in an Ismaili Shia movement launched in Syria by Abd Allah al-Akbar. He claimed descent through Ismail, the seventh Shia imam, from the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatimah. The Fatimid Dynasty is named after Fatimah. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Living Dictionaries
Lexico was a dictionary website that provided a collection of English and Spanish dictionaries produced by Oxford University Press (OUP), the publishing house of the University of Oxford. While the dictionary content on Lexico came from OUP, this website was operated by Dictionary.com, whose eponymous website hosts dictionaries by other publishers such as Random House. The website was closed and redirected to Dictionary.com on 26 August 2022. Before the Lexico site was launched, the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' and ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' were hosted by OUP's own website Oxford Dictionaries Online (ODO), later known as Oxford Living Dictionaries. The dictionaries' definitions have also appeared in Google definition search and the Dictionary application on macOS, among others, licensed through the Oxford Dictionaries API. History In the 2000s, OUP allowed access to content of the ''Compact Oxford English Dictionary of Current English'' on a website called AskO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco - Marrakech - Mosque Tiles (49131613737)
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
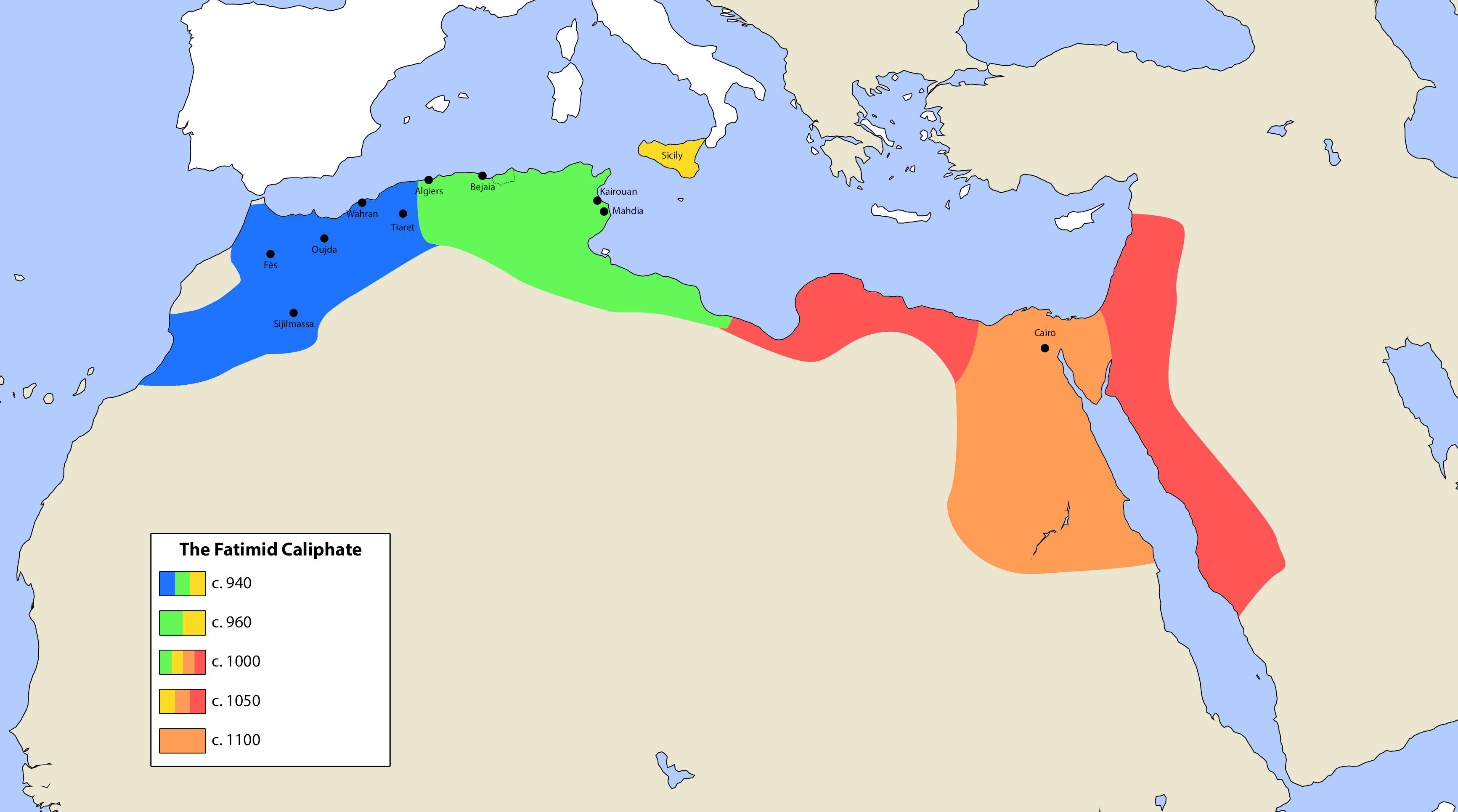
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "Mahdia, al-Mahdiyya" ( ar, المهدية). The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hijaz. Between 902 to 909 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)