|
Zapodidae
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China. Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs of cheek-teeth in each jaw. There are five toes to all the feet, but the first in the fore-feet is rudimentary, and furnished with a flat nail. The tail makes up about 60% of its body length and is used to gain balance while jumping. The cheeks have pouches. The Sichuan jumping "yeti" mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') from China can be identified by the ‘Y’ marking on its belly. Jumping mice live in wooded areas, grassy fields and alpine meadows. When disturbed, they start, in enormous bounds of eight or ten feet in length, which soon diminish to three or four, and in leaping the feet scarcely seem to touch the ground. They are nocturnal and generally live alone. The nest is placed in clefts of rocks, among timber, or in hollow trees, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipodoidea
Dipodoidea is a superfamily of rodents, also known as dipodoids, found across the Northern Hemisphere. This superfamily includes over 50 species among the 16 genera in 3 families. They include the jerboas (family Dipodidae), jumping mice (family Zapodidae), and birch mice (family Sminthidae). Different species are found in grassland, deserts, and forests. They are all capable of saltation (jumping while in a bipedal stance), a feature that is most highly evolved in the desert-dwelling jerboas. Taxonomy Formerly, Dipodoidea contained only a single large family, Dipodidae, which contained jerboas, jumping mice, and birch mice as subfamilies. However, phylogenetic evidence found all three to be distinct families from one another, and thus they were split into three different families within Dipodoidea. Characteristics Dipodoids are small to medium-sized rodents, ranging from in body length, excluding the tail. They are all adapted for jumping, although to varying degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
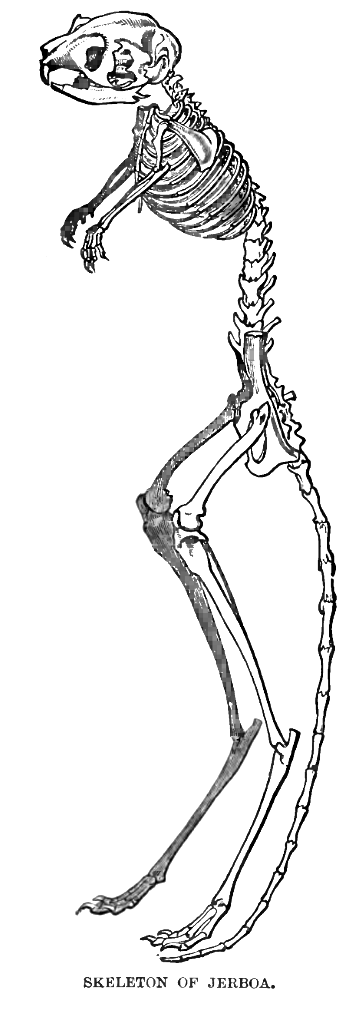
Dipodidae
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert Rodent, rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be Paraphyly, paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and Birch mouse, birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerboa
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Jumping Mouse
The woodland jumping mouse (''Napaeozapus insignis'') is a species of jumping mouse found in North America. It can jump up to using its extremely strong feet and long tail. Taxonomy Representatives of the family Dipodidae are found in the northern regions of the Old and New Worlds, and are characterized by very large infraorbital foramen, and, in one of the two North American genera, ''Zapus'', by four upper cheek teeth. Incisors are compressed and deeply grooved. These animals are common and noted for very long tails and long hind legs adapted for leaping. They live in forests, meadows, and swamps and are profound hibernators. The woodland jumping mouse was originally classified as '' Zapus insignis'' in 1891, but differences detected in dental morphology, ear ossicles, and the baculum resulted in the creation of two new genera, ''Napaeozapus'' and '' Euzapus''.Harrington ''N. insignis'' was in the family Dipodidae and some place it in the subfamily Zapodinae.Whitaker 268 Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meadow Jumping Mouse
The meadow jumping mouse (''Zapus hudsonius'') is the most widely distributed mouse in the family Zapodidae. Its range extends from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Great Plains west, and from the arctic tree lines in Canada and Alaska to the north, and Georgia, Alabama, Arizona, and New Mexico to the south. In mid-2014, the New Mexico subspecies of the meadow jumping mouse, ''Zapus hudsonius luteus'', was listed as an endangered species under the federal Endangered Species Act.Meadow jumping mouse is not ‘resilient’ Albuquerque Journal, July 4, 2014 Albuquerque Journal, June 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Jumping Mouse
The Chinese jumping mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Eozapus''. It is endemic to China where its natural habitat is temperate forests, steppes and meadows in mountainous regions. It is tolerant of some degree of habitat destruction, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern". Description The Chinese jumping mouse has a head-and-body length of between and a tail of . The dorsal fur has a band of dark brown running along the spine but is otherwise a reddish-brown or ochraceous colour, the flanks are pale reddish-brown and the underparts are white. In the nominate subspecies, ''E. s. setchuanus'', there is a narrow brown mid-ventral stripe, but in ''E. s. vicinus'' the belly is entirely white. The hind limbs are much longer than the fore limbs, and this mouse moves about by crawling or by a series of short hops. The long tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eozapus Setchuanus
The Chinese jumping mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Eozapus''. It is endemic to China where its natural habitat is temperate forests, steppes and meadows in mountainous regions. It is tolerant of some degree of habitat destruction, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern". Description The Chinese jumping mouse has a head-and-body length of between and a tail of . The dorsal fur has a band of dark brown running along the spine but is otherwise a reddish-brown or ochraceous colour, the flanks are pale reddish-brown and the underparts are white. In the nominate subspecies, ''E. s. setchuanus'', there is a narrow brown mid-ventral stripe, but in ''E. s. vicinus'' the belly is entirely white. The hind limbs are much longer than the fore limbs, and this mouse moves about by crawling or by a series of short hops. The long tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Jumping Mouse
The western jumping mouse (''Zapus princeps''), is a species of rodent in the family Zapodidae. It is found in Canada and the United States. Western jumping mice evolved during the Pleistocene, possibly from the fossil species '' Zapus burti'', which is known from the late Blancan. Their closest relatives appear to be Pacific jumping mice, with which they can still interbreed to produce fertile offspring. Description Western jumping mice resemble typical mice in appearance, but with long hind-feet and reduced forelimbs. They range from in total length, including a tail long, and weigh from . The mouse has coarse, dark-greyish-brown fur over the upper body, with a broad yellow to red band along the flanks, and pale yellowish-white underparts. Some individuals have white spots on the upper body, or on the tip of the tail. The two sexes are similar in appearance and size; females have four pairs of teats. Distribution and habitat Western jumping mice are found in western North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Jumping Mouse
The Pacific jumping mouse (''Zapus trinotatus'') is a species of rodent in the family Zapodidae. Found in Canada and the United States, its natural habitats are temperate grassland and swamps. Description Pacific jumping mice can be distinguished from other rodents that belong to the same genus by their larger size. They have a distinct color separation between the back and underside. Other distinctive features of the Pacific jumping mouse, especially in contrast to the Western jumping mouse, include ears fringed with light brown fur or with fur that matches the back.Gannon, L. W., (1988). Zapus trinotatus. Mammalian Species. Retrieved from . These rodents prefer to live in moist habitats and are frequently found in riparian or meadow areas near rivulets. They rely on grass seeds as their main diet, and thus they prefer inhabiting areas with thick vegetation, which provide refuge from predators as well as food resources. Besides eating grass, they feed also on fungi and insect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napaeozapus
The woodland jumping mouse (''Napaeozapus insignis'') is a species of jumping mouse found in North America. It can jump up to using its extremely strong feet and long tail. Taxonomy Representatives of the family Dipodidae are found in the northern regions of the Old and New Worlds, and are characterized by very large infraorbital foramen, and, in one of the two North American genera, ''Zapus'', by four upper cheek teeth. Incisors are compressed and deeply grooved. These animals are common and noted for very long tails and long hind legs adapted for leaping. They live in forests, meadows, and swamps and are profound hibernators. The woodland jumping mouse was originally classified as '' Zapus insignis'' in 1891, but differences detected in dental morphology, ear ossicles, and the baculum resulted in the creation of two new genera, '' Napaeozapus'' and '' Euzapus''.Harrington ''N. insignis'' was in the family Dipodidae and some place it in the subfamily Zapodinae.Whitaker 268 S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eozapus
The Chinese jumping mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Eozapus''. It is endemic to China where its natural habitat is temperate forests, steppes and meadows in mountainous regions. It is tolerant of some degree of habitat destruction, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern". Description The Chinese jumping mouse has a head-and-body length of between and a tail of . The dorsal fur has a band of dark brown running along the spine but is otherwise a reddish-brown or ochraceous colour, the flanks are pale reddish-brown and the underparts are white. In the nominate subspecies, ''E. s. setchuanus'', there is a narrow brown mid-ventral stripe, but in ''E. s. vicinus'' the belly is entirely white. The hind limbs are much longer than the fore limbs, and this mouse moves about by crawling or by a series of short hops. The long tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |