|
Zamua
Zamua (also Mazamua) was an ancient Pre-Iranian kingdom, corresponding with the earlier kingdom of Lullubi,''The Cambridge History of Iran'', Volume 2, (1985) Cambridge University Press, p. 59Direct link Last retrieved 11.12.2013 which stretched from lake Urmia to the upper reaches of the Diyala River, roughly corresponding with the modern Sulaimania governorate (still called Zamua/Zamwa by the Kurds) in Iraqi Kurdistan. It was centered at Sharazur plain. Ameka and Arashtua were two southern Zamuan kingdoms. A tribal chief (''Nasiku'') bearing the Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to: * Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire * Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language * Akkadian literature, literature in this language * Akkadian cuneiform Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ... name of ''Nūr-Adad'' was a Zamuan leader who launched a failed resistance against Assyrian domination. Its inhabitants were most probably related to the Gutians living east and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lullubi
Lullubi, Lulubi ( akk, 𒇻𒇻𒉈: ''Lu-lu-bi'', akk, 𒇻𒇻𒉈𒆠: ''Lu-lu-biki'' "Country of the Lullubi"), more commonly known as Lullu, were a group of tribes during the 3rd millennium BC, from a region known as ''Lulubum'', now the Sharazor plain of the Zagros Mountains of modern Kurdistan, Lullubi was neighbour and sometimes ally with the Simurrum kingdom. Frayne (1990) identified their city ''Lulubuna'' or ''Luluban'' with the region's modern town of Halabja. The language of the Lullubi is regarded as an unclassified language because it is unattested. The term ''Lullubi'' though, appears to be of Hurrian origin. Historical references Legends The early Sumerian legend "''Lugalbanda and the Anzud Bird''", set in the reign of Enmerkar of Uruk, alludes to the "mountains of Lulubi" as being where the character of Lugalbanda encounters the gigantic ''Anzû'' bird while searching for the rest of Enmerkar's army ''en route'' to siege Aratta. Akkadian empire and Gutian dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharazur
Shahrizor or Shahrazur () is a region part of Kurdistan Region, Iraq situated in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate and west of Avroman. Shahrizor is a fertile plain watered by the Tributary, tributaries of Tandjaro river which flows to Diyala River, Diyala and Tigris rivers. Etymology The name ''Shahrazur'' is likely derived from two Iranian languages, Iranian words: ''shah'' (king) and (forest), hence sharazur meaning ''kingly forest''. Ernst Herzfeld, Herzfeld based on the fact that in classical sources the name was spelt with an initial /s/ rather /sh/, suggested ''white forest'', which he connected with the Avestan legends. Indeed, to this day the plain of Sharazur has an important status among adherents of native religion of Yarsan as a holy and sacred region where God descends for the Last Judgement. The 12th century geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi, based on folk etymology interpreted origin of name Sharazur, from the name of the son of Zahhak, whom he mentions as founder of the famo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
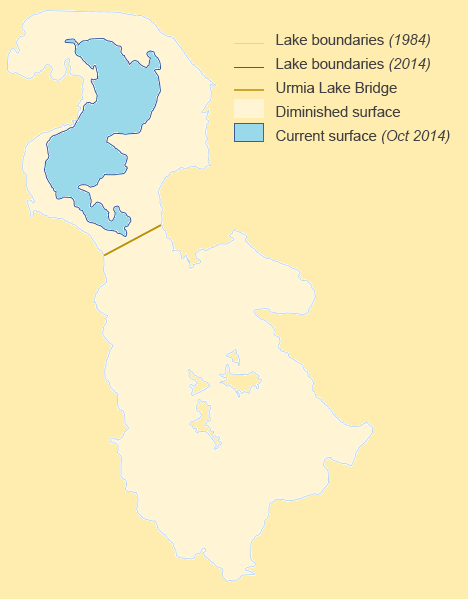
Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia; az, اۇرمۇ گؤلۆ, script=Arab, italic=no, Urmu gölü; ku, گۆلائوو رمیەیێ, Gola Ûrmiyeyê; hy, Ուրմիա լիճ, Urmia lich; arc, ܝܡܬܐ ܕܐܘܪܡܝܐ is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East and the sixth-largest saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately , a length of , a width of , and a maximum depth of . By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size (and 1/60 of water volume in 1998) due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again, due to both increased rain and water diversion from the Zab River by the Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diyala River
The Diyala River (Arabic: ; ku, Sîrwan; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjaro river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of . Course It rises near Hamadan, in the Zagros Mountains of Iran. It then descends through the mountains, where for some 32 km it forms the border between the two countries. It finally feeds into the Tigris below Baghdad. Navigation of the upper reaches of the Diyala is not possible because of its narrow defiles, but the river's valley provides an important trade route between Iran and Iraq. The river flows southwest of the Hamrin Mountains. Name Its Aramaic origin is "Diyalas" and in Kurdish it is called "Sirwan", meaning 'roaring sea' or 'shouting river'. In early Islamic period, the lower course of the river formed part of the Nahrawan Canal. The Diyala Governorate in Iraq is named after the river. History The river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulaimania Governorate
ar, محافظة السليمانية , other_name = , settlement_type = Governorate , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_caption = Clockwise, from left: Sulaymaniyah with Dukan Lake, Halabja and Ranya , image_map = As-Sulaymaniyyah in Iraq.svg , map_alt = , map_caption = , image_map1 = Kurdistan_governorates_2015.png , map_alt1 = , map_caption1 = Sulaymaniyah Governorate within the Kurdistan Region , image_flag = Flag of Sulaymaniyah Governorate.png , image_seal = Sulaymaniyah Governorate logo.png , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Autonomous region , subdivision_name1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurds
ug:كۇردلار Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northern Syria. There are exclaves of Kurds in Central Anatolia, Khorasan, and the Caucasus, as well as significant Kurdish diaspora communities in the cities of western Turkey (in particular Istanbul) and Western Europe (primarily in Germany). The Kurdish population is estimated to be between 30 and 45 million. Kurds speak the Kurdish languages and the Zaza–Gorani languages, which belong to the Western Iranian branch of the Iranian languages. After World War I and the defeat of the Ottoman Empire, the victorious Western allies made provision for a Kurdish state in the 1920 Treaty of Sèvres. However, that promise was broken three years later, when the Treaty of Lausanne set the boundaries of modern Turkey and made no s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Kurdistan
Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan ( ku, باشووری کوردستان, Başûrê Kurdistanê) refers to the Kurdish-populated part of northern Iraq. It is considered one of the four parts of "Kurdistan" in Western Asia, which also includes parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdistan), northern Syria (Western Kurdistan), and northwestern Iran (Eastern Kurdistan). Much of the geographical and cultural region of Iraqi Kurdistan is part of the Kurdistan Region (KRI), an autonomous region recognized by the Constitution of Iraq. As with the rest of Kurdistan, and unlike most of the rest of Iraq, the region is inland and mountainous. Etymology The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an Iranian term for region. The literal translation for Kurdistan is "Region of Kurds". The name was also formerly spelled ''Curdistan''. One of the ancient names of Kurdistan is '' Corduene''.A.D. Lee, ''The Role of Hostages in Roman Diplomacy with Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameka
Ameka is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Felix Ameka, Ghanaian linguist *Louis Ameka (born 1996), Gabonese footballer See also *Emeka Emeka is a name of Nigerian origins. It is an abbreviation of the Igbo name Chukwuemeka, meaning "God has done so much". Notable people with the surname "Emeka" include * Anthony Emeka (born 1990), Nigerian footballer * Chinonso Emeka (born 2001) ... {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa and Babylonia) from the third millennium BC until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BC. It is the earliest documented Semitic language. It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BC). The mutual influence between Sumerian and Akkadian had led scholars to describe the languages as a '' Sprachbund''. Akkadian proper names were first attested in Sumerian texts from around the mid 3rd-mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
