|
Zalzal
Manṣūr Zalzal al-Ḍārib (منصور زلزل; died after 842 CE) or simply Zalzal, was an Iranian musician during the early Abbasid period. The renowned musician Ishaq al-Mawsili was his student; he declared Zalzal to be the most outstanding lutenist of his time. He contributed musical scales that were later named after him (the Mansouri scale, Arabic, المقياس المنصوري) and introduced positions (intervals) within scales on the fretboard The fingerboard (also known as a fretboard on fretted instruments) is an important component of most stringed instrument String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating s ... of an oud (neutral 3rd frets, between major 3rd frets and minor third frets), called ''wasati-zalzal''. Mansour is credited by the Encyclopedia of Islam with making improvements on the design of the barbat lute, which was then called the ūd shabbūt. References Arabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishaq Al-Mawsili
Ishaq al-Mawsili ( ar, إسحاق الموصلي; 767/772 – March 850) was an Arab musician of Persian origin active as a composer, singer, music theorist and writer on music. The leading musician of his time in the Abbasid Caliphate, he served under six successive Abbasid caliphs: Harun al-Rashid, Al-Amin, Al-Ma'mun, Al-Mu'tasim, Al-Wathiq and Al-Mutawakkil. The caliphs and Abbasid court held him in high regard, and his diverse intellect elevated him to a social status that was highly unusual for musicians of the time. Taught by his similarly renowned father Ibrahim al-Mawsili and the noted lutenist Zalzal, he succeeded his father in leading the conservative musical establishment, putting him at odds with progressive musicians such as Ibrahim ibn al-Mahdi and Ziryab. He has appeared in the ''Maqamat'' of Al-Hariri of Basra and ''One Thousand and One Nights''. Life and career Early life Modern sources vary on the exact location and birthdate of Ishaq al-Mawsili. The arabist Ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbat (lute)
The ''barbat'' ( fa, بربت) or ''barbud'' was a lute of Central Asian or Greater Iranian or Persian origin. Barbat is characterized as carved from a single piece of wood, including the neck and a wooden sound board. Possibly a skin-topped instrument for part of its history, it is ancestral to the wood-topped oud and biwa and the skin-topped Yemeni qanbus. Although the original barbat disappeared, modern Iranian luthiers have re-created the instrument, looking at historical images for details. The modern re-created instrument (Iranian Barbat) resembles the oud, although differences include a smaller body, longer neck, a slightly raised fingerboard, and a sound that is distinct from that of the oud. History The ''barbat'' probably originated in Central Asia. The earliest image of the ''barbat'' dates back to the 1st century BC from ancient northern Bactria. While in his book (''Les instruments de musique de l’Inde ancienne'') musicologist Claudie Marcel-Dubois pointed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
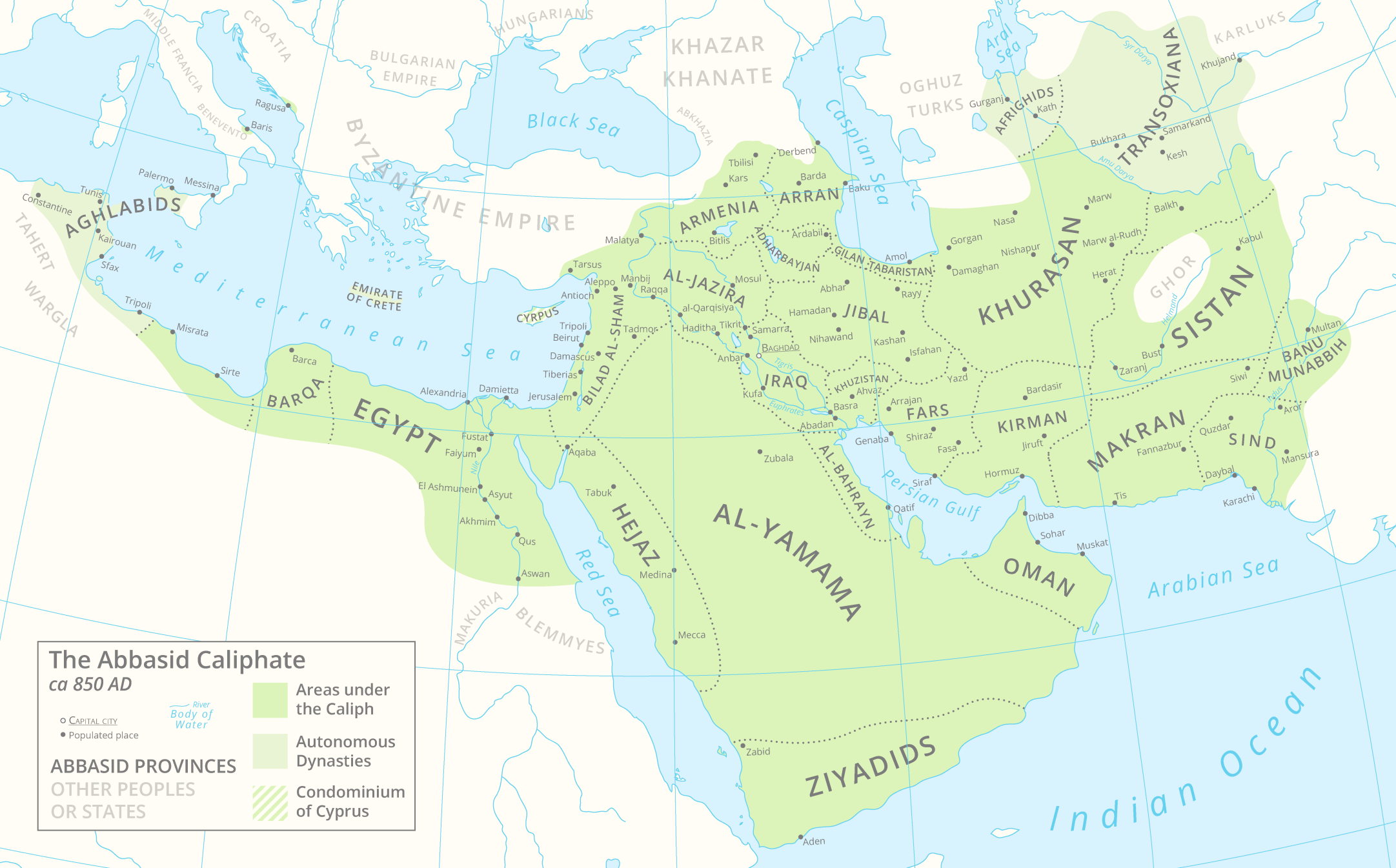
Abbasid Period
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Music Online
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theory of music. Earlier editions were published under the titles ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', and ''Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians''; the work has gone through several editions since the 19th century and is widely used. In recent years it has been made available as an electronic resource called ''Grove Music Online'', which is now an important part of ''Oxford Music Online''. ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' was first published in London by Macmillan and Co. in four volumes (1879, 1880, 1883, 1889) edited by George Grove with an Appendix edited by J. A. Fuller Maitland in the fourth volume. An Index edited by Mrs. E. Wodehouse was issued as a separate volume in 1890. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Scale
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale. Often, especially in the context of the common practice period, most or all of the melody and harmony of a musical work is built using the notes of a single scale, which can be conveniently represented on a staff with a standard key signature. Due to the principle of octave equivalence, scales are generally considered to span a single octave, with higher or lower octaves simply repeating the pattern. A musical scale represents a division of the octave space into a certain number of scale steps, a scale step being the recognizable distance (or interval) between two successive notes of the scale. However, there is no need for scale steps to be equal within any scale and, particularly as demonstrated by microtonal music, there is no limit to how many notes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerboard
The fingerboard (also known as a fretboard on fretted instruments) is an important component of most stringed instruments. It is a thin, long strip of material, usually wood, that is laminated to the front of the neck of an instrument. The strings run over the fingerboard, between the nut and bridge. To play the instrument, a musician presses strings down to the fingerboard to change the vibrating length, changing the pitch. This is called '' stopping'' the strings. Depending on the instrument and the style of music, the musician may pluck, strum or bow one or more strings with the hand that is not fretting the notes. On some instruments, notes can be sounded by the fretting hand alone, such as with hammer ons, an electric guitar technique. The word "fingerboard" in other languages sometimes occurs in musical directions. In particular, the direction ''sul tasto'' (Ital., also ''sulla tastiera'', Fr. ''sur la touche'', G. ''am Griffbrett'') for bowed string instruments to play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic-language Singers
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)


