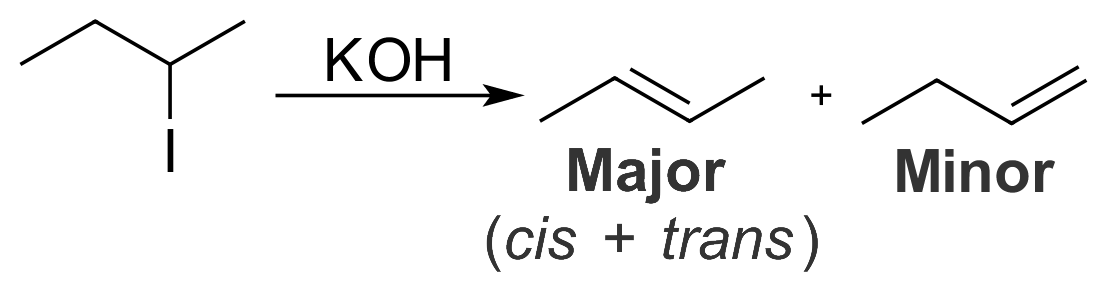|
Zaitsev's Rule
In organic chemistry, Zaitsev's rule (or Saytzeff's rule, Saytzev's rule) is an empirical rule for predicting the favored alkene product(s) in elimination reactions. While at the University of Kazan, Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev studied a variety of different elimination reactions and observed a general trend in the resulting alkenes. Based on this trend, Zaitsev proposed that the alkene formed in greatest amount is that which corresponded to removal of the hydrogen from the alpha-carbon having the fewest hydrogen substituents. For example, when 2-iodobutane is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH), 2-butene is the major product and 1-butene is the minor product. : More generally, Zaitsev's rule predicts that in an elimination reaction the most substituted product will be the most stable, and therefore the most favored. The rule makes no generalizations about the stereochemistry of the newly formed alkene, but only the regiochemistry of the elimination reaction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Vasilyevich Markovnikov
Vladimir Vasilyevich Markovnikov (russian: Влади́мир Васи́льевич Марко́вников), also spelled as Markownikoff ( – 11 February 1904), was a Russian chemist. Early life and education Markovnikov studied economics at the University of Kazan; during his studies, under the Russian cameral system, he also studied chemistry. Career After a conflict with that university, Markovnikov was appointed professor at the University of Odessa in 1871 and, two years later, at the University of Moscow, where he stayed the rest of his career. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 1901. Work Markovnikov is best known for Markovnikov's rule, elucidated in 1869 to describe addition reactions of H-X (where 'X' represents a halogen) to alkenes. According to this rule, the nucleophilic X- adds to the carbon atom with fewer hydrogen atoms, while the proton adds to the carbon atom with more hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Thus, hydrogen chlorid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperconjugation
In organic chemistry, hyperconjugation (σ-conjugation or no-bond resonance) refers to the delocalization of electrons with the participation of bonds of primarily σ-character. Usually, hyperconjugation involves the interaction of the electrons in a sigma (σ) orbital (e.g. C–H or C–C) with an adjacent unpopulated non-bonding p or antibonding σ* or π* orbitals to give a pair of extended molecular orbitals. However, sometimes, low-lying antibonding σ* orbitals may also interact with filled orbitals of lone pair character (n) in what is termed '' negative hyperconjugation''. Increased electron delocalization associated with hyperconjugation increases the stability of the system. In particular, the new orbital with bonding character is stabilized, resulting in an overall stabilization of the molecule. Only electrons in bonds that are in the β position can have this sort of direct stabilizing effect — donating from a sigma bond on an atom to an orbital in another a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral Molecular Geometry
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry, a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1(−) = 109.4712206...° ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in methane () as well as its heavier analogues. Methane and other perfectly symmetrical tetrahedral molecules belong to point group Td, but most tetrahedral molecules have lower symmetry. Tetrahedral molecules can be chiral. Tetrahedral bond angle The bond angle for a symmetric tetrahedral molecule such as CH4 may be calculated using the dot product of two vectors. As shown in the diagram, the molecule can be inscribed in a cube with the tetravalent atom (e.g. carbon) at the cube centre which is the origin of coordinates, O. The four monovalent atoms (e.g. hydrogens) are at four corners of the cube (A, B, C, D) chosen so that no two atoms are at adjacent corners linked by only one cube edge. If the edge length of the cube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen. The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions. An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalkane by removal of a hydrogen atom from a ring and has the general formula . Typically an alkyl is a part of a larger molecule. In structural formulae, the symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group. The smallest alkyl group is methyl, with the formula . Related concepts Alkylation is an important operation in refineries, for example in the production of high-octane gasoline. Alkylating antineoplastic agents are a class of compounds that are used to treat cancer. In such case, the term alkyl is used loosely. For example, nitrogen mustards are well-known alkylating agents, but they are not simple hydrocarbons. In chemistry, alkyl is a group, a substituent, that is attached to other molecular fragments. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Tetramethylethylene is a hydrocarbon with the formula Me2C=CMe2 (Me = methyl). A colorless liquid, it is the simplest tetrasubstituted alkene. Synthesis and reactions It is prepared by base-catalyzed isomerization of 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene. Tetramethylethylene forms metal-alkene complexes with low-valent metals and reacts with diborane to give the monoalkyborane known as thexylborane Thexylborane is a borane with the formula e2CHCMe2BH2sub>2 (Me = methyl). The name derives from "''t''-hexylborane" (although the group is not the standard ''tert''-hexyl group), and the formula is often abbreviated ThxBH2. A colorless liquid, ....{{cite book, doi=10.1002/9780470132593.ch22, time=Di-μ-Chloro-Bis(η4-1,5-Cyclooctadiene)-Dirhodium(I), title=Inorganic Syntheses, pages=88–90, year=1990, volume=28, last1=Giordano, first1=G., last2=Crabtree, first2=R. H., chapter=Di-μ-Chloro-Bis(η4 -1,5-Cyclooctadiene)-Dirhodium(I), isbn=9780470132593 References Alkenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-methyl-2-butene
2-Methyl-2-butene, 2m2b, 2-methylbut-2-ene, also beta-isoamylene is an alkene hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C5H10. Used as a free radical scavenger in trichloromethane (chloroform) and dichloromethane (methylene chloride). John Snow, the English physician, experimented with it in the 1840s as an anesthetic, but stopped using it for unknown reasons. See also *Pentene Pentenes are alkenes with the chemical formula . Each contains one double bond within its molecular structure. Six different compounds are in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched ... References Hydrocarbons Alkenes {{hydrocarbon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-butene Line Formula
1-Butene (or 1-Butylene) is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to give a colorless liquid. It is classified as a linear alpha-olefin. It is one of the isomers of butene (butylene). It is a precursor to diverse products. Reactions Polymerization of 1-butene give polybutene, which is used to make piping for domestic plumbing. Its main application is as a comonomer in the production of certain kinds of polyethylene, such as linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). It has also been used as a precursor to polypropylene resins, butylene oxide, and butanone. Manufacturing 1-Butene is produced by separation from crude C4 refinery streams and by ethylene dimerization. The former affords a mixture of 1-and 2-butenes, while the latter affords only the terminal alkene. It is distilled to give a very high purity product. An estimated 12 billion kilograms were produced in 2011. See also *Butene *Dimer (chemistry) *Octene Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wade
Wade, WADE, or Wades may refer to: Places in the United States * Wade, California, a former settlement * Wade, Maine, a town * Wade, Mississippi, a census-designated place * Wade, North Carolina, a town * Wade, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Wade Township, Clinton County, Illinois * Wade Township, Jasper County, Illinois * Wade County, Choctaw Nation, a former political subdivision * Wades Branch, a river in Tennessee People and figures * Wade (folklore), a being from Germanic mythology and folklore * Wade (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Wade (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters Other uses * ''Wade'' (film), a 2020 Indian animated short film * World Alliance for Decentralized Energy (WADE) * Wade Ceramics, manufacturers of porcelain and earthenware; known for making "Whimsies" * WADE (AM), a radio station in Wadesboro, North Carolina, United States * Wade–Giles, a method of Romanisation of Chinese, sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). The term ''exothermic'' was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy usually in the form of heat. The concept is frequently applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where chemical bond energy is converted to thermal energy (heat). Two types of chemical reactions Exothermic and endothermic describe two types of chemical reactions or systems found in nature, as follows: Exothermic After an exothermic reaction, more energy has been released to the surroundings than was absorbed to initiate and maintain the reaction. An example would be the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkane
In organic chemistry Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clay ..., an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like Higher alkanes#Nonatetracontane to tetrapentacontane, pentacontane () or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same catalysts and conditions that are used for hydrogenation reactions can also lead to isomerization of the alkenes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |