|
Yutu (Lunar Rover)
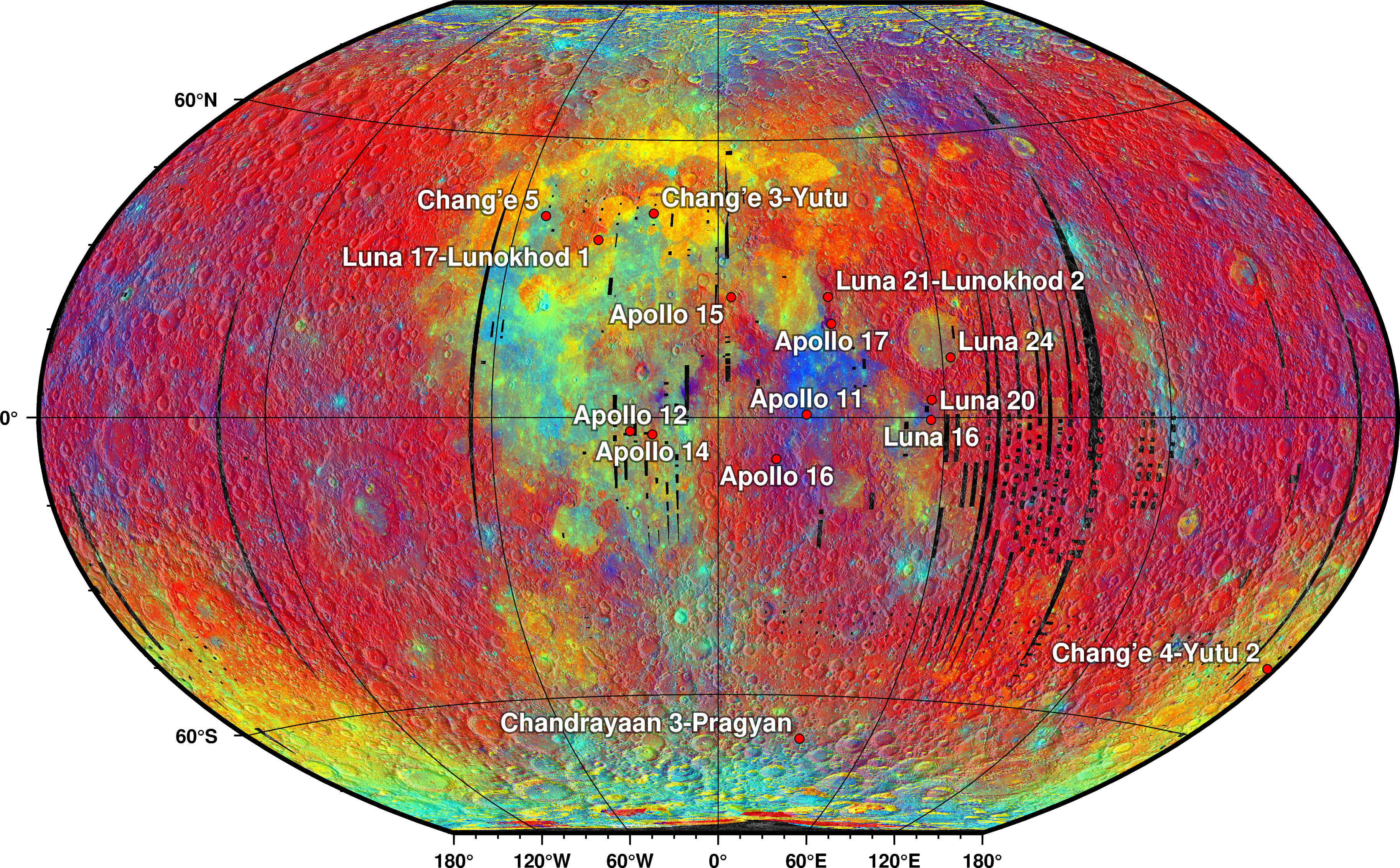
''Yutu'' () was a robotic lunar rover that formed part of the Chinese Chang'e 3 mission to the Moon. It was launched at 17:30 UTC on 1 December 2013, and reached the Moon's surface on 14 December 2013. The mission marks the first soft landing on the Moon since 1976 and the first rover to operate there since the Soviet Lunokhod 2 ceased operations on 11 May 1973. The rover encountered operational difficulties toward the end of the second lunar day after surviving and recovering successfully from the first 14-day lunar night. It was unable to move after the end of the second lunar night, though it continued to gather useful information for some months afterward. In October 2015, ''Yutu'' set the record for the longest operational period for a rover on the Moon. On 31 July 2016, ''Yutu'' ceased to operate after a total of 31 months, well beyond its original expected lifespan of three months. In total, while working on the Moon, the rover was able to travel a distance of 114 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods and the Chinese '' Yutus''. Three countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States and China. An Indian mission failed while Japan and Greece currently have planned missions. Past missions Lunokhod 1 Lunokhod 1 (Луноход) was the first of two polycrystalline-panel-powered robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program after a previous unsuccessful attempt of a launch probe with Lunokhod 0 (No.201) in 1969. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains on November 1970. Lunokhod was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e
Chang'e ( ; , alternatively rendered as Chang-Er or Ch‘ang-o), originally known as Heng'e, is the Chinese goddess of the Moon. She is the subject of several legends in Chinese mythology, most of which incorporate several of the following elements: Houyi the archer, a benevolent or malevolent emperor, an elixir of life, and the Moon. She was married to Houyi. In modern times, Chang'e has been the namesake of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. Tales There are many tales about Chang'e, including a well-known story about her that is given as the origin of the Mid-Autumn Festival. In one version, in a very distant past, Chang'e was a beautiful woman. Ten suns had risen together into the skies and scorched the Earth, thus causing hardship for the people. Houyi the archer shot down nine of them, leaving just one Sun, and was given either two or one with enough for two elixirs of immortality as a reward. He did not consume it straight away, but let Chang'e keep it with her, as he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photovoltaic system or solar array. Solar panels capture sunlight as a source of radiant energy, which is converted into electric energy in the form of direct current (DC) electricity. Arrays of a photovoltaic system can be used to generate solar electricity that supplies electrical equipment directly, or grid-connected photovoltaic system, feeds power back into an alternate current (AC) electric grid, grid via an solar inverter, inverter system. History In 1839, the ability of some materials to create an electrical charge from light exposure was first observed by the French physicist Edmond Becquerel. Though these initial solar panels were too inefficient for even simple electric devices, they were used as an instrument to measure light. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.'' An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha particles and fluorescent X-rays after a sample is irradiated with alpha particles and X-rays from radioactive sources. This method of analysing the elemental composition of a sample is most often used on space missions, which require low weight, small size, and minimal power consumption. Other methods (e.g. mass spectrometry) are faster, and do not require the use of radioactive materials, but require larger equipment with greater power requirements. A variation is the alpha proton X-ray spectrometer, such as on the Pathfinder mission, which also detects protons. Over the years several modified versions of this type of instrument such as APS (without X-ray spectrometer) or APXS have been flown: Surveyor 5-7, Mars Pathfinder, Mars 96, Mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectrometer
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunokhod 1
''Lunokhod 1'' ( Russian: Луноход-1 ("Moonwalker 1"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 203 ("Device 8EL No. 203")) was the first of two robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program. The ''Luna 17'' spacecraft carried ''Lunokhod 1'' to the Moon in 1970. ''Lunokhod 1'' was the first remote-controlled robot "rover" to freely move across the surface of an astronomical object beyond the Earth. It was also the first wheeled craft on another celestial body. Lunokhod 0 (No.201), the previous and first attempt to do so, launched in February 1969 but failed to reach orbit. Although only designed for a lifetime of three lunar days (approximately three Earth months), ''Lunokhod 1'' operated on the lunar surface for eleven lunar days (321 Earth days) and traversed a total distance of 10.54 km. Rover description ''Lunokhod 1'' was a lunar vehicle formed of a tub-like compartment with a large convex lid on eight independently p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rover (space exploration), rovers to explore the Martian surface and Geology of Mars, geology; both landed on Mars at separate locations in January 2004. Both rovers far outlived their planned missions of 90 Timekeeping on Mars#Sols, Martian solar days: MER-A ''Spirit'' was active until March 22, 2010, while MER-B ''Opportunity'' was active until June 10, 2018. Objectives The mission's scientific objective was to search for and characterize a wide range of rock (geology), rocks and soils that hold clues to past Water on Mars, water activity on Mars. The mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program, which includes three previous successful landers: the two Viking program landers in 1976 and Mars Pathfinder probe in 1997. The total cost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 5
Chang'e 5 () was the fifth lunar exploration mission of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and China's first lunar sample-return mission. Like its predecessors, the spacecraft is named after the Chinese moon goddess Chang'e. It launched at 20:30 UTC on 23 November 2020 from Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on Hainan Island, landed on the Moon on 1 December 2020, collected ~ of lunar samples (including from a core ~1 m deep), and returned to the Earth at 17:59 UTC on 16 December 2020. Chang'e-5 was the first lunar sample-return mission since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 in 1976. The mission made China the third country to return samples from the Moon after the United States and the Soviet Union. Overview The Chinese Lunar Exploration Program has four phases, with incremental technological advancement: * Phase one: orbiting the Moon, completed by Chang'e 1 in 2007 and Chang'e 2 in 2010. * Phase two: soft landing and deploying rover on the Moon, completed by Chang'e 3 (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese unmanned lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and conducted research from a 100-km-high lunar orbit in preparation for the December 2013 soft landing by the Chang'e 3 lander and rover. Chang'e 2 was similar in design to Chang'e 1, although it featured some technical improvements, including a more advanced onboard camera. Like its predecessor, the probe was named after Chang'e, an ancient Chinese moon goddess. After completing its primary objective, the probe left lunar orbit for the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point, to test the Chinese tracking and control network, making the China National Space Administration the third space agency after NASA and ESA to have visited this point. It entered orbit around L2 on 25 August 2011, and began transmitting data from its new position in September 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 1
Chang'e 1 (; ) was an unmanned Chinese lunar-orbiting spacecraft, part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The spacecraft was named after the Chinese Moon goddess, Chang'e. Chang'e 1 was launched on 24 October 2007 at 10:05:04 UTC from Xichang Satellite Launch Center. It left lunar transfer orbit on 31 October and entered lunar orbit on 5 November. The first picture of the Moon was relayed on 26 November 2007. On 12 November 2008, a map of the entire lunar surface was released, produced from data collected by Chang'e 1 between November 2007 and July 2008. The mission was scheduled to continue for a year, but was later extended and the spacecraft operated until 1 March 2009, when it was taken out of orbit. It impacted the surface of the Moon at 08:13 UTC. Data gathered by Chang'e 1 was used to create an accurate and high resolution 3-D map of the lunar surface. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |