solar panel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of

 Most solar modules are currently produced from crystalline silicon (c-Si)
Most solar modules are currently produced from crystalline silicon (c-Si)


 In general with solar panels, if not enough current is taken from PVs, then power isn't maximised. If too much current is taken then the voltage collapses. The optimum current draw depends on the amount of sunlight striking the panel. Solar panel capacity is specified by the MPP (maximum power point) value of solar panels in full sunlight.
In general with solar panels, if not enough current is taken from PVs, then power isn't maximised. If too much current is taken then the voltage collapses. The optimum current draw depends on the amount of sunlight striking the panel. Solar panel capacity is specified by the MPP (maximum power point) value of solar panels in full sunlight.
 Module electrical connections are made with conducting wires that take the current off the modules and are sized according to the current rating and fault conditions.
Panels are typically connected in series of one or more panels to form strings to achieve a desired output voltage, and strings can be connected in parallel to provide the desired current capability (amperes) of the PV system.
Blocking and bypass
Module electrical connections are made with conducting wires that take the current off the modules and are sized according to the current rating and fault conditions.
Panels are typically connected in series of one or more panels to form strings to achieve a desired output voltage, and strings can be connected in parallel to provide the desired current capability (amperes) of the PV system.
Blocking and bypass
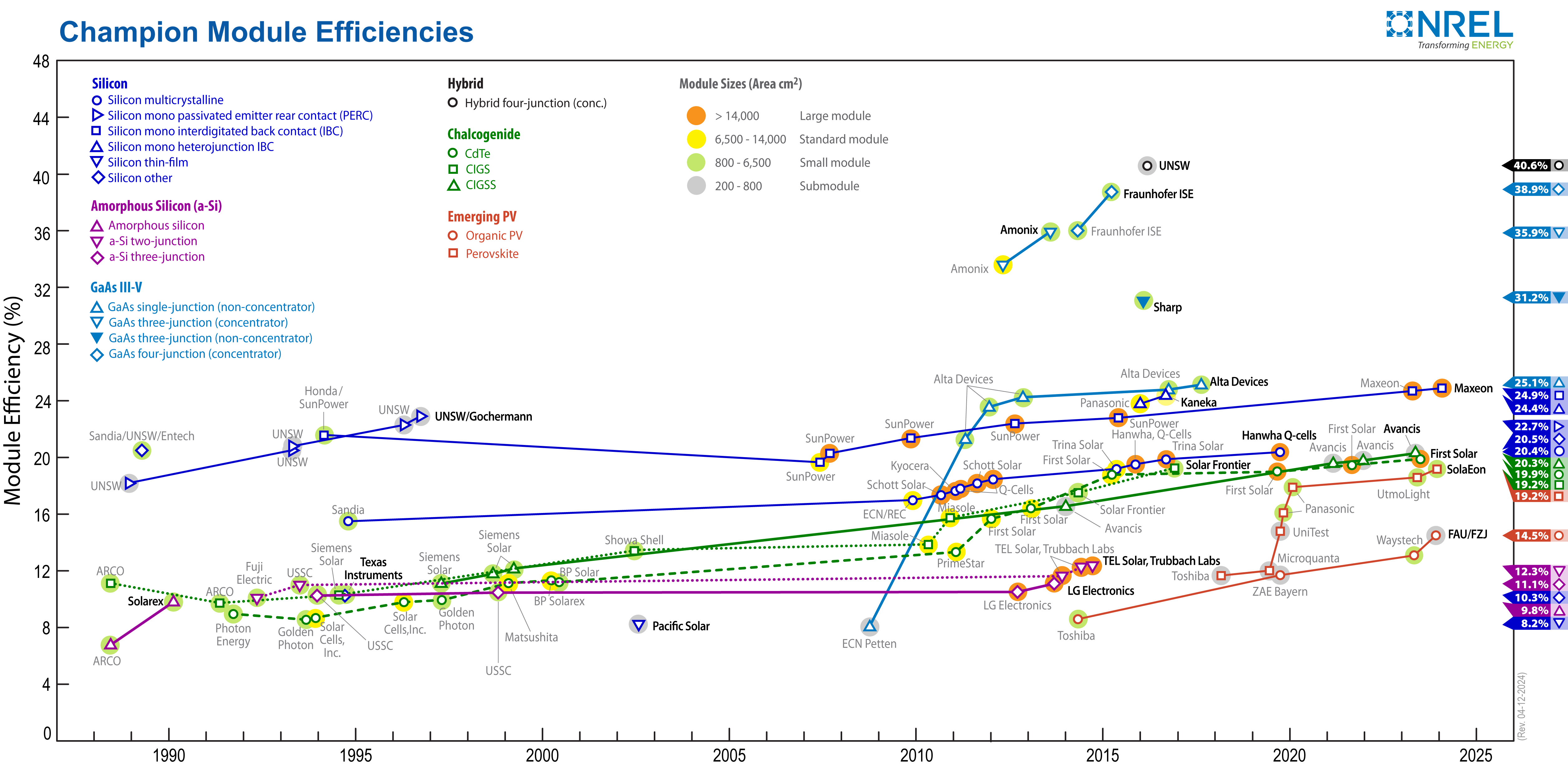 Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions (STC) and hence the on field output power might vary. Power typically ranges from 100 to 365
Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions (STC) and hence the on field output power might vary. Power typically ranges from 100 to 365

 Module performance is generally rated under standard test conditions (STC):
Module performance is generally rated under standard test conditions (STC):
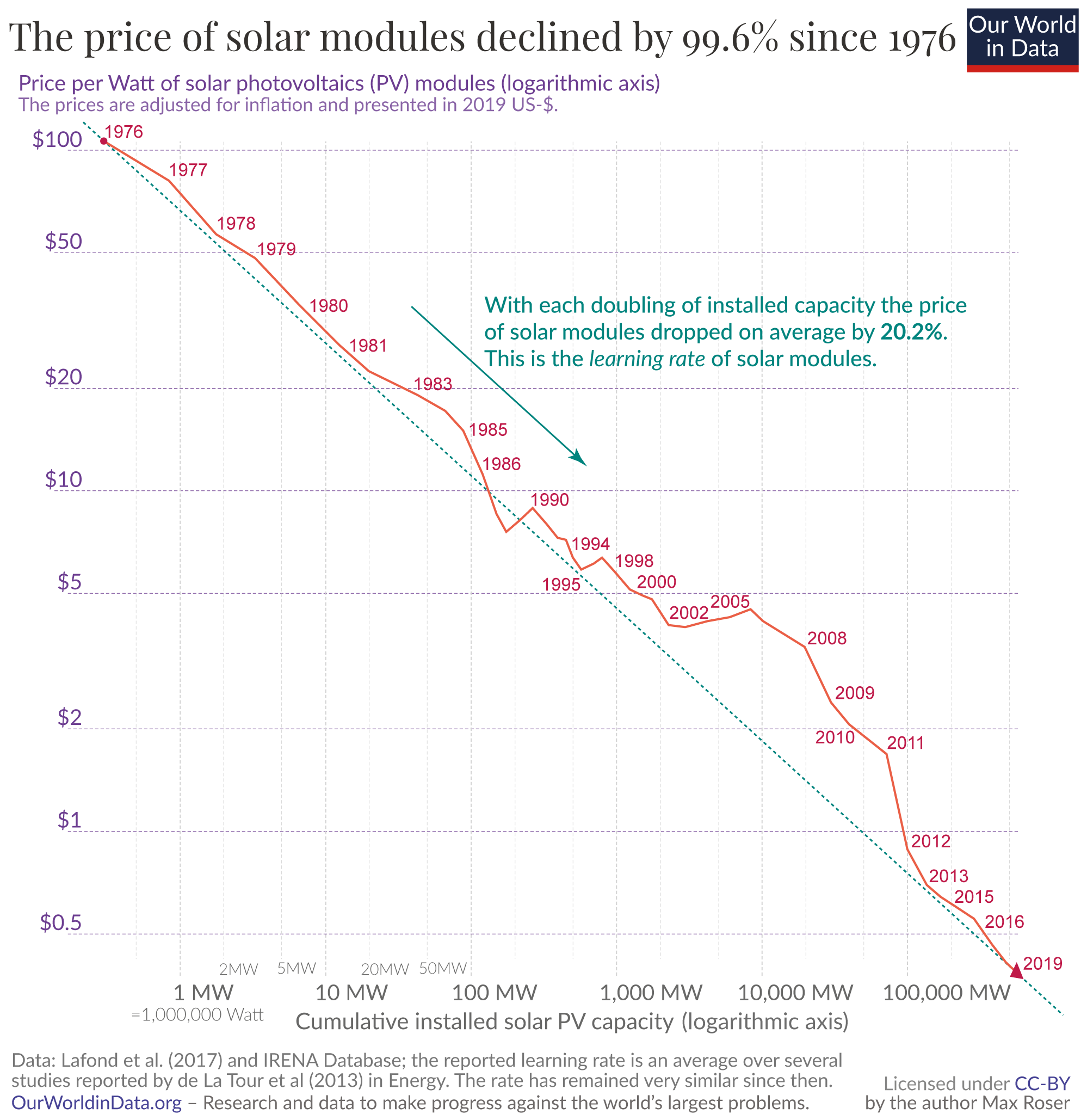 The price of solar electrical power has continued to fall so that in many countries it has become cheaper than
The price of solar electrical power has continued to fall so that in many countries it has become cheaper than  Following to RMI, Balance-of-System (BoS) elements, this is, non-module cost of non-
Following to RMI, Balance-of-System (BoS) elements, this is, non-module cost of non-
 A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
or solar array. Solar panels capture sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
as a source of radiant energy
Radiant may refer to:
Computers, software, and video games
* Radiant (software), a content management system
* GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games
* Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for '' ...
, which is converted into electric energy
Electrical energy is energy related to forces on electrically charged particles and the movement of electrically charged particles (often electrons in wires, but not always). This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electr ...
in the form of direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
(DC) electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
. Arrays of a photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
can be used to generate solar electricity
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
that supplies electrical equipment directly, or feeds power back into an alternate current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which ...
(AC) grid
Grid, The Grid, or GRID may refer to:
Common usage
* Cattle grid or stock grid, a type of obstacle is used to prevent livestock from crossing the road
* Grid reference, used to define a location on a map
Arts, entertainment, and media
* News g ...
via an inverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opp ...
system.
History
In 1839, the ability of some materials to create an electrical charge from light exposure was first observed by the French physicist Edmond Becquerel. Though these initial solar panels were too inefficient for even simple electric devices, they were used as an instrument to measure light. The observation by Becquerel was not replicated again until 1873, when the English electrical engineerWilloughby Smith
Willoughby Smith (6 April 1828, in Great Yarmouth, Norfolk – 17 July 1891, in Eastbourne, Sussex) was an English electrical engineer who discovered the photoconductivity of the element selenium. This discovery led to the invention of photoele ...
discovered that the charge could be caused by light hitting selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
. After this discovery, William Grylls Adams
William Grylls Adams (18 February 1836 in Laneast, Cornwall – 10 April 1915) was professor of Natural Philosophy at King's College, London. He was active in research on subjects ranging from light, magnetism, and astronomy to electrical power ...
and Richard Evans Day published "The action of light on selenium" in 1876, describing the experiment they used to replicate Smith's results.
In 1881, the American inventor Charles Fritts
Charles Fritts (1850 – 1903) was the American inventor credited with creating the first working selenium cell in 1883.
The world's first rooftop solar array, using Fritts' selenium cells, was installed in 1884 on a New York City rooftop.
Fritt ...
created the first commercial solar panel, which was reported by Fritts as "continuous, constant and of considerable force not only by exposure to sunlight but also to dim, diffused daylight." However, these solar panels were very inefficient, especially compared to coal-fired power plant
A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity. Worldwide, there are about 8,500 coal-fired power stations totaling over 2,000 gigawatts capacity. They generate about a th ...
s.
In 1939, Russell Ohl
Russell Shoemaker Ohl (January 30, 1898 – March 20, 1987) was an American scientist who is generally recognized for patenting the modern solar cell (, "Light sensitive device").
Ohl was a notable semiconductor researcher prior to the invention o ...
created the solar cell design that is used in many modern solar panels. He patented his design in 1941. In 1954, this design was first used by Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
to create the first commercially viable silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
solar cell.
Solar panel installers saw significant growth between 2008 and 2013. Due to that growth many installers had projects that were not "ideal" solar roof tops to work with and had to find solutions to shaded roofs and orientation difficulties. This challenge was initially addressed by the re-popularization of micro-inverter
A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial ...
s and later the invention of power optimizers.
Solar panel manufacturers partnered with micro-inverter companies to create AC modules and power optimizer companies partnered with module manufacturers to create smart modules. In 2013 many solar panel manufacturers announced and began shipping their smart module solutions.
Theory and construction
Photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
modules consist of a large number of solar cells and use light energy (photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
s) from the Sun to generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect
The photovoltaic effect is the generation of voltage and electric current in a material upon exposure to light. It is a physical property, physical and chemical phenomenon.
The photovoltaic effect is closely related to the photoelectric effect. F ...
. Most modules use wafer
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light and dry biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a garnish on some sweet dishes. Wafers can also be made into cookies with cream flavoring sandwiched between them. They ...
-based crystalline silicon
Crystalline silicon or (c-Si) Is the crystalline forms of silicon, either polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si, consisting of small crystals), or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si, a continuous crystal). Crystalline silicon is the dominant semicondu ...
cells or thin-film cells
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many ...
. The structural ( load carrying) member of a module can be either the top layer or the back layer. Cells must be protected from mechanical damage and moisture. Most modules are rigid, but semi-flexible ones based on thin-film cells are also available. The cells are usually connected electrically in series, one to another to the desired voltage, and then in parallel to increase current. The power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
(in watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
s) of the module is the mathematical product of the voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
(in volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defi ...
s) and the current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
(in ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to elect ...
s), and depends both on the amount of light and on the electrical load
An electrical load is an electrical component or portion of a circuit that consumes (active) electric power, such as electrical appliances and lights inside the home. The term may also refer to the power consumed by a circuit. This is opposed t ...
connected to the module. The manufacturing specifications on solar panels are obtained under standard conditions, which are usually not the true operating conditions the solar panels are exposed to on the installation site.
A PV junction box
An electrical junction box (also known as a "jbox") is an enclosure housing electrical connections. Junction boxes protect the electrical connections from the weather, as well as protecting people from accidental electric shocks.
Construction
...
is attached to the back of the solar panel and functions as its output interface. External connections for most photovoltaic modules use MC4 connector
MC4 connectors are single-contact electrical connectors commonly used for connecting solar panels. The MC in MC4 stands for the manufacturer Multi-Contact (now Stäubli Electrical Connectors) and the 4 for the 4 mm diameter contact pin.
...
s to facilitate easy weatherproof connections to the rest of the system. A USB power interface can also be used. Solar panels also use metal frames consisting of racking components, brackets, reflector shapes, and troughs to better support the panel structure.
Cell connection techniques
In solar modules, the cells themselves need to be connected together to form the module, with front electrodes blocking the solar cell front optical surface area slightly. To maximize frontal surface area available for sunlight and improve solar cell efficiency, manufacturers use varying rear electrode solar cell connection techniques: * Passivated emitter rear contact (PERC) adds a polymer film to capture light * Tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) adds an oxidation layer to the PERC film to capture more light * Interdigitated bulk contact (IBC)Arrays of PV modules
A single solar module can produce only a limited amount of power; most installations contain multiple modules adding their voltages or currents. A photovoltaic system typically includes an array of photovoltaic modules, aninverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opp ...
, a battery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of (preferably) identical batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage, capacity, or power density. The term battery ...
for energy storage, a charge controller, interconnection wiring, circuit breakers, fuses, disconnect switches, voltage meters, and optionally a solar tracking
A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, fresnel reflectors, lenses or the mirrors of a heliostat.
For flat-panel photovoltaic systems, trackers are used to m ...
mechanism. Equipment is carefully selected to optimize output, and energy storage, reduce power loss during power transmission, and convert from direct current to alternating current.
Smart solar modules
Smart modules are different from traditional solar panels because the power electronics embedded in the module offers enhanced functionality such as panel-levelmaximum power point tracking
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar sy ...
, monitoring, and enhanced safety. Power electronics attached to the frame of a solar module, or connected to the photovoltaic circuit through a connector, are not properly considered smart modules.
Several companies have begun incorporating into each PV module various embedded power electronics such as:
* Maximum power point tracking
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar sy ...
(, MPPT) power optimizer A power optimizer is a DC to DC converter technology developed to maximize the energy harvest from solar photovoltaic or wind turbine systems. They do this by individually tuning the performance of the panel or wind turbine through maximum power po ...
s, a DC-to-DC converter technology developed to maximize the power harvest from solar photovoltaic systems by compensating for shading effects, wherein a shadow falling on a section of a module causes the electrical output of one or more strings of cells in the module to fall to near zero, but not having the output of the entire module fall to zero.
* Solar performance monitors for data and fault detection
Technology
solar cells
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physics, physical and Chemical substance, chemical phenomenon.polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
or monocrystalline silicon
Monocrystalline silicon, more often called single-crystal silicon, in short mono c-Si or mono-Si, is the base material for silicon-based discrete components and integrated circuits used in virtually all modern electronic equipment. Mono-Si also ...
. In 2013, crystalline silicon accounted for more than 90% of worldwide PV production, while the rest of the overall market is made up of thin-film technologies using cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ca ...
(CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide
Copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS) is a I-III- VI2 semiconductor material composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium. The material is a solid solution of copper indium selenide (often abbreviated "CIS") and copper gallium selenide. ...
(CIGS) and amorphous silicon
Amorphous silicon (a-Si) is the non-crystalline form of silicon used for solar cells and thin-film transistors in LCDs.
Used as semiconductor material for a-Si solar cells, or thin-film silicon solar cells, it is deposited in thin films ont ...
.
Emerging, third-generation solar technologies use advanced thin-film cells. They produce a relatively high-efficiency conversion for a lower cost compared with other solar technologies. Also, high-cost, high-efficiency, and close-packed rectangular multi-junction (MJ) cells are usually used in solar panels on spacecraft
Spacecraft operating in the inner Solar System usually rely on the use of power electronics-managed photovoltaic solar panels to derive electricity from sunlight. Outside the orbit of Jupiter, solar radiation is too weak to produce sufficient pow ...
, as they offer the highest ratio of generated power per kilogram lifted into space. MJ-cells are compound semiconductor
Semiconductor materials are nominally small band gap insulators. The defining property of a semiconductor material is that it can be compromised by doping it with impurities that alter its electronic properties in a controllable way.
Because of ...
s and made of gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monoli ...
(GaAs) and other semiconductor materials. Another emerging PV technology using MJ-cells is concentrator photovoltaics
Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) (also known as concentration photovoltaics) is a photovoltaic technology that generates electricity from sunlight. Unlike conventional photovoltaic systems, it uses lenses or curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto ...
(CPV).
Thin film
In rigid thin-film modules, the cell and the module are manufactured on the same production line. The cell is created on a glass substrate or superstrate, and the electrical connections are created ''in situ'', a so-called "monolithic integration." The substrate or superstrate is laminated with an encapsulant to a front or back sheet, usually another sheet of glass. The main cell technologies in this category areCdTe
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with cadmi ...
, , a-Si+uc-Si tandem, and CIGS. Amorphous silicon has a sunlight conversion rate of 6–12%.
Flexible thin film cells and modules are created on the same production line by depositing the photoactive layer A photoactive layer is used in solar cells for absorbing light. It can be found in all solar cells, but with different panels the photoactive layer is made of different materials. Inorganic layers are made from inorganic materials such as silicon. T ...
and other necessary layers on a flexible substrate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and food ...
. If the substrate is an insulator (e.g. polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
or polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI) is a polymer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g ...
film) then monolithic integration can be used. If it is a conductor then another technique for electrical connection must be used. The cells are assembled into modules by laminating
Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a Raw material, material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength of materials, strength, stability, sound insulation, visual appearance, appearance, or ...
them to a transparent colourless fluoropolymer
A fluoropolymer is a fluorocarbon-based polymer with multiple carbon–fluorine bonds. It is characterized by a high resistance to solvents, acids, and bases. The best known fluoropolymer is polytetrafluoroethylene under the brand name "Teflon ...
on the front side, typically ethylene tetrafluoroethylene
Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) is a fluorine-based plastic. It was designed to have high corrosion resistance and strength over a wide temperature range. ETFE is a polymer and its source-based name is poly(ethene-co-tetrafluoroethene). It i ...
(ETFE) or fluorinated ethylene propylene
Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) is a copolymer of hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene. It differs from the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resins in that it is melt-processable using conventional injection molding and screw extrusion ...
(FEP), and a polymer suitable for bonding to the final substrate on the other side.
Mounting and tracking


Ground
Large utility-scalesolar power plants
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic ...
usually use ground-mounted photovoltaic systems. Their solar modules are held in place by racks or frames that are attached to ground-based mounting supports. Ground based mounting supports include:
* Pole mounts, which are driven directly into the ground or embedded in concrete.
* Foundation mounts, such as concrete slabs or poured footings
* Ballasted footing mounts, such as concrete or steel bases that use weight to secure the solar module system in position and do not require ground penetration. This type of mounting system is well suited for sites where excavation is not possible such as capped landfills and simplifies decommissioning or relocation of solar module systems.
Roof
Roof-mounted solar power systems consist of solar modules held in place by racks or frames attached to roof-based mounting supports. Roof-based mounting supports include: * Rail mounts, which are attached directly to the roof structure and may use additional rails for attaching the module racking or frames. * Ballasted footing mounts, such as concrete or steel bases that use weight to secure the panel system in position and do not require through penetration. This mounting method allows for decommissioning or relocation of solar panel systems with no adverse effect on the roof structure. *All wiring connecting adjacent solar modules to the energy harvesting equipment must be installed according to local electrical codes and should be run in a conduit appropriate for the climate conditionsTracking
Solar tracker
A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, fresnel reflectors, lenses or the mirrors of a heliostat.
For flat-panel photovoltaic systems, trackers are used to mi ...
s increase the energy produced per module at the cost of mechanical complexity and increased need for maintenance. They sense the direction of the Sun and tilt or rotate the modules as needed for maximum exposure to the light.
Alternatively, fixed racks can hold modules stationary throughout the day at a given tilt (zenith angle
The zenith (, ) is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction ( plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location ( nadir). The zenith is the "highe ...
) and facing a given direction (azimuth angle
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north.
Mathematically, ...
). Tilt angles equivalent to an installation's latitude are common. Some systems may also adjust the tilt angle based on the time of year.
On the other hand, east- and west-facing arrays (covering an east–west facing roof, for example) are commonly deployed. Even though such installations will not produce the maximum possible average power from the individual solar panels, the cost of the panels is now usually cheaper than the tracking mechanism and they can provided more economically valuable power during morning and evening peak demands than north or south facing systems.
Concentrator
Some special solar PV modules include concentrators in which light is focused bylenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
or mirrors onto smaller cells. This enables the use of cells with a high cost per unit area (such as gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monoli ...
) in a cost-effective way. Concentrating the sunlight can also raise the efficiency to around 45%.
Light capture
The amount of light absorbed by a solar cell depends on the angle of incidence of whatever direct sunlight hits it. This is partly because the amount falling on the panel is proportional to the cosine of the angle of incidence, and partly because at high angle of incidence more light is reflected. To maximize total energy output, modules are often oriented to face south (in the Northern Hemisphere) or north (in the Southern Hemisphere) and tilted to allow for the latitude. Solar tracking can be used to keep the angle of incidence small (see next section). Solar panels are often coated with ananti-reflective coating
An antireflective, antiglare or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses, other optical elements, and photovoltaic cells to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the effic ...
, which is one or more thin layers of substances with refractive indices intermediate between that of silicon and that of air. This causes destructive interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive ...
in the reflected light, diminishing the amount. Photovoltaic manufacturers have been working to decrease reflectance with improved anti-reflective coatings or with textured glass.
Power curve
 In general with solar panels, if not enough current is taken from PVs, then power isn't maximised. If too much current is taken then the voltage collapses. The optimum current draw depends on the amount of sunlight striking the panel. Solar panel capacity is specified by the MPP (maximum power point) value of solar panels in full sunlight.
In general with solar panels, if not enough current is taken from PVs, then power isn't maximised. If too much current is taken then the voltage collapses. The optimum current draw depends on the amount of sunlight striking the panel. Solar panel capacity is specified by the MPP (maximum power point) value of solar panels in full sunlight.
Module interconnection
 Module electrical connections are made with conducting wires that take the current off the modules and are sized according to the current rating and fault conditions.
Panels are typically connected in series of one or more panels to form strings to achieve a desired output voltage, and strings can be connected in parallel to provide the desired current capability (amperes) of the PV system.
Blocking and bypass
Module electrical connections are made with conducting wires that take the current off the modules and are sized according to the current rating and fault conditions.
Panels are typically connected in series of one or more panels to form strings to achieve a desired output voltage, and strings can be connected in parallel to provide the desired current capability (amperes) of the PV system.
Blocking and bypass diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
s may be incorporated within the module or used externally to deal with partial array shading, in order to maximize output. For series connections, bypass diodes are placed in parallel with modules to allow current to bypass shaded modules which would otherwise severely limit the current. For paralleled connections, a blocking diode may be placed in series with each module's string to prevent current flowing backwards through shaded strings thus short-circuiting other strings.
Inverters
Solar inverter
A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial ...
s convert the DC power provided by panels to AC power.
MPP (Maximum power point) of the solar panel consists of MPP voltage (V) and MPP current (I). Performing maximum power point tracking
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar sy ...
(MPPT), a solar inverter samples the output (I-V curve) from the solar cell and applies the proper electrical load to obtain maximum power.
Solar panels are wired to inverters in parallel or series (a 'string'). In string connections the voltages of the modules add, but the current is determined by the lowest performing panel. This is known as the "Christmas light effect". In parallel connections the voltages will be the same, but the currents add. Arrays are connected up to meet the voltage requirements of the inverters and to not greatly exceed the current limits.
Micro-inverters work independently to enable each panel to contribute its maximum possible output for a given amount of sunlight, but can be more expensive.
Connectors
Outdoor solar panels usually includeMC4 connector
MC4 connectors are single-contact electrical connectors commonly used for connecting solar panels. The MC in MC4 stands for the manufacturer Multi-Contact (now Stäubli Electrical Connectors) and the 4 for the 4 mm diameter contact pin.
...
s. Automotive solar panels may also include an auxiliary power outlet and/or USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply (interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers. A broad ...
adapter. Indoor panels (including solar pv glasses, thin films and windows) can integrate a microinverter
A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercia ...
(AC Solar panels).
Efficiency
 Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions (STC) and hence the on field output power might vary. Power typically ranges from 100 to 365
Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions (STC) and hence the on field output power might vary. Power typically ranges from 100 to 365 Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
s (W). The efficiency of a module determines the area of a module given the same rated output an 8% efficient 230 W module will have twice the area of a 16% efficient 230 W module. Some commercially available solar modules exceed 24% efficiency. Currently, the best achieved sunlight conversion rate (solar module efficiency) is around 21.5% in new commercial products typically lower than the efficiencies of their cells in isolation. The most efficient mass-produced solar modules have power density values of up to 175 W/m2 (16.22 W/ft2).
The current versus voltage curve of a module provides useful information about its electrical performance. Manufacturing processes often cause differences in the electrical parameters of different modules photovoltaic, even in cells of the same type. Therefore, only the experimental measurement of the I–V curve allows us to accurately establish the electrical parameters of a photovoltaic device. This measurement provides highly relevant information for the design, installation and maintenance of photovoltaic systems. Generally, the electrical parameters of photovoltaic modules are measured by indoor tests. However, outdoor testing has important advantages such as no expensive artificial light source required, no sample size limitation, and more homogeneous sample illumination.
Scientists from Spectrolab, a subsidiary of Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
, have reported development of multi-junction solar cell Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells are solar cells with multiple p–n junctions made of different semiconductor materials. Each material's p-n junction will produce electric current in response to different wavelengths of light. The use of multiple ...
s with an efficiency of more than 40%, a new world record for solar photovoltaic cells. The Spectrolab scientists also predict that concentrator solar cells could achieve efficiencies of more than 45% or even 50% in the future, with theoretical efficiencies being about 58% in cells with more than three junctions.
Capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is def ...
of solar panels is limited primarily by geographic latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and varies significantly depending on cloud cover, dust, day length and other factors. In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, seasonal capacity factor ranges from 2% (December) to 20% (July), with average annual capacity factor of 10–11%, while in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
the value reaches 18%.
Globally, capacity factor for utility-scale PV farms was 16.1% in 2019.
Overheating is the most important factor for the efficiency of the solar panel.
Radiation-dependent efficiency
Depending on construction, photovoltaic modules can produce electricity from a range of frequencies of light, but usually cannot cover the entire solar radiation range (specifically,ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
, infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
and low or diffused light). Hence, much of the incident sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
energy is wasted by solar modules, and they can give far higher efficiencies if illuminated with monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or color scheme, palette is composed of one color (or lightness, values of one color). Images using only Tint, shade and tone, shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or Black and wh ...
light. Therefore, another design concept is to split the light into six to eight different wavelength ranges that will produce a different color of light, and direct the beams onto different cells tuned to those ranges. This has been projected to be capable of raising efficiency by 50%.
Aluminum nanocylinders
Research byImperial College London
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
has shown that solar panel efficiency is improved by studding the light-receiving semiconductor surface with aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
nanocylinders, similar to the ridges
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
on Lego blocks
Lego ( , ; stylized as LEGO) is a line of plastic construction toys that are manufactured by The Lego Group, a privately held company based in Billund, Denmark. The company's flagship product, Lego, consists of variously colored interlockin ...
. The scattered light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
then travels along a longer path in the semiconductor, absorbing more photons to be converted into current. Although these nanocylinders have been used previously (aluminum was preceded by gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
), the light scattering occurred in the near-infrared region and visible light was absorbed strongly. Aluminum was found to have absorbed the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, while the visible and near-infrared parts of the spectrum were found to be scattered by the aluminum surface. This, the research argued, could bring down the cost significantly and improve the efficiency as aluminum is more abundant and less costly than gold and silver. The research also noted that the increase in current makes thinner film solar panels technically feasible without "compromising power conversion efficiencies, thus reducing material consumption".
Performance and degradation

 Module performance is generally rated under standard test conditions (STC):
Module performance is generally rated under standard test conditions (STC): irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
of 1,000 W/m2, solar spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
of AM 1.5 and module temperature at 25 °C. The actual voltage and current output of the module changes as lighting, temperature and load conditions change, so there is never one specific voltage at which the module operates. Performance varies depending on geographic location, time of day, the day of the year, amount of solar irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/ ...
, direction and tilt of modules, cloud cover, shading, soiling, state of charge, and temperature. Performance of a module or panel can be measured at different time intervals with a DC clamp meter or shunt and logged, graphed, or charted with a chart recorder or data logger.
For optimum performance, a solar panel needs to be made of similar modules oriented in the same direction perpendicular to direct sunlight. Bypass diodes are used to circumvent broken or shaded panels and optimize output. These bypass diodes are usually placed along groups of solar cells to create a continuous flow.
Electrical characteristics include nominal power (PMAX, measured in W), open-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any circuit. There is no external load connected. No external electric current f ...
(VOC), short-circuit current
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. ...
(ISC, measured in ampere
The ampere (, ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to elect ...
s), maximum power voltage (VMPP), maximum power current (IMPP), peak power, (watt-peak
The nominal power is the nameplate capacity of photovoltaic (PV) devices, such as solar cells, modules and systems, and is determined by measuring the electric current and voltage in a circuit, while varying the resistance under precisely define ...
, Wp), and module efficiency (%).
Open-circuit voltage
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC) is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of an electronic device when disconnected from any circuit. There is no external load connected. No external electric current f ...
or VOC is the maximum voltage the module can produce when not connected to an electrical circuit or system. VOC can be measured with a voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electric potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is connected in parallel. It usually has a high resistance so that it takes negligible current from the circuit.
Ana ...
directly on an illuminated module's terminals or on its disconnected cable.
The peak power rating, Wp, is the maximum output under standard test conditions (not the maximum possible output). Typical modules, which could measure approximately , will be rated from as low as 75 W to as high as 600 W, depending on their efficiency. At the time of testing, the test modules are binned according to their test results, and a typical manufacturer might rate their modules in 5 W increments, and either rate them at +/- 3%, +/-5%, +3/-0% or +5/-0%.
Influence of temperature
The performance of a photovoltaic (PV) module depends on the environmental conditions, mainly on the global incident irradiance G in the plane of the module. However, the temperature T of the p–n junction also influences the main electrical parameters: the short circuit current ISC, the open circuit voltage VOC and the maximum power Pmax. In general, it is known that VOC shows a significant inverse correlation with T, while for ISC this correlation is direct, but weaker, so that this increase does not compensate for the decrease in VOC. As a consequence, Pmax decreases when T increases. This correlation between the power output of a solar cell and the working temperature of its junction depends on the semiconductor material, and is due to the influence of T on the concentration, lifetime, and mobility of the intrinsic carriers, i.e., electrons and gaps. inside the photovoltaic cell. Temperature sensitivity is usually described by temperature coefficients, each of which expresses the derivative of the parameter to which it refers with respect to the junction temperature. The values of these parameters can be found in any data sheet of the photovoltaic module; are the following: - β: VOC variation coefficient with respect to T, given by ∂VOC/∂T. - α: Coefficient of variation of ISC with respect to T, given by ∂ISC/∂T. - δ: Coefficient of variation of Pmax with respect to T, given by ∂Pmax/∂T. Techniques for estimating these coefficients from experimental data can be found in the literatureDegradation
The ability of solar modules to withstand damage by rain,hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
, heavy snow load, and cycles of heat and cold varies by manufacturer, although most solar panels on the U.S. market are UL listed, meaning they have gone through testing to withstand hail.
Potential-induced degradation (also called PID) is a potential-induced performance degradation in crystalline photovoltaic modules, caused by so-called stray currents. This effect may cause power loss of up to 30%.
Advancements in photovoltaic technologies have brought about the process of "doping" the silicon substrate to lower the activation energy thereby making the panel more efficient in converting photons to retrievable electrons.
Chemicals such as boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
(p-type) are applied into the semiconductor crystal in order to create donor and acceptor energy levels substantially closer to the valence and conductor bands. In doing so, the addition of boron impurity allows the activation energy to decrease twenty-fold from 1.12 eV to 0.05 eV. Since the potential difference (EB) is so low, the boron is able to thermally ionize at room temperatures. This allows for free energy carriers in the conduction and valence bands thereby allowing greater conversion of photons to electrons.
The power output of a photovoltaic (PV) device decreases over time. This decrease is due to its exposure to solar radiation as well as other external conditions. The degradation index, which is defined as the annual percentage of output power loss, is a key factor in determining the long-term production of a photovoltaic plant. To estimate this degradation, the percentage of decrease associated with each of the electrical parameters. The individual degradation of a photovoltaic module can significantly influence the performance of a complete string. Furthermore, not all modules in the same installation decrease their performance at exactly the same rate. Given a set of modules exposed to long-term outdoor conditions, the individual degradation of the main electrical parameters and the increase in their dispersion must be considered. As each module tends to degrade differently, the behavior of the modules will be increasingly different over time, negatively affecting the overall performance of the plant.
There are several studies dealing with the power degradation analysis of modules based on different photovoltaic technologies available in the literature. According to a recent study, the degradation of crystalline silicon modules is very regular, oscillating between 0.8% and 1.0% per year.
On the other hand, if we analyze the performance of thin-film photovoltaic modules, an initial period of strong degradation is observed (which can last several months and even up to 2 years), followed by a later stage in which the degradation stabilizes, being then comparable to that of crystalline silicon. Strong seasonal variations are also observed in such thin-film technologies because the influence of the solar spectrum is much greater. For example, for modules of amorphous silicon, micromorphic silicon or cadmium telluride, we are talking about annual degradation rates for the first years of between 3% and 4%. However, other technologies, such as CIGS, show much lower degradation rates, even in those early years.
Maintenance
Solar panel conversion efficiency, typically in the 20% range, is reduced by the accumulation of dust, grime, pollen, and other particulates on thesolar panels
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a phot ...
, collectively referred to as soiling. "A dirty solar panel can reduce its power capabilities by up to 30% in high dust/pollen or desert areas", says Seamus Curran, associate professor of physics at the University of Houston and director of the Institute for NanoEnergy, which specializes in the design, engineering, and assembly of nanostructures.
The average soiling loss in the world in 2018 is estimated to be at least 3% – 4%.
Paying to have solar panels cleaned is a good investment in many regions, as of 2019.
However, in some regions, cleaning is not cost-effective. In California as of 2013 soiling-induced financial losses were rarely enough to warrant the cost of washing the panels. On average, panels in California lost a little less than 0.05% of their overall efficiency per day.
There are also occupational hazards with solar panel installation and maintenance. A 2015–2018 study in the UK investigated 80 PV-related incidents of fire, with over 20 "serious fires" directly caused by PV installation, including 37 domestic buildings and 6 solar farms. In of the incidents a root cause was not established and in a majority of others was caused by poor installation, faulty product or design issues. The most frequent single element causing fires was the DC isolators.
A 2021 study by kWh Analytics determined median annual degradation of PV systems at 1.09% for residential and 0.8% for non-residential ones, almost twice that previously assumed. A 2021 module reliability study found an increasing trend in solar module failure rates with 30% of manufacturers experiencing safety failures related to junction boxes (growth from 20%) and 26% bill-of-materials failures (growth from 20%).
Cleaning methods for solar panels can be divided into 5 groups: manual tools, mechanized tools (such as tractor mounted brushes), installed hydraulic systems (such as sprinklers), installed robotic systems, and deployable robots. Manual cleaning tools are by far the most prevalent method of cleaning, most likely because of the low purchase cost. However, in a Saudi Arabian study done in 2014, it was found that "installed robotic systems, mechanized systems, and installed hydraulic systems are likely the three most promising technologies for use in cleaning solar panels".
Waste and recycling
There was 30 thousand tonnes of PV waste in 2021, and the annual amount was estimated by Bloomberg NEF to rise to more than 1 million tons by 2035 and more than 10 million by 2050. Most parts of a solar module can be recycled including up to 95% of certain semiconductor materials or the glass as well as large amounts of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Some private companies and non-profit organizations are currently engaged in take-back and recycling operations for end-of-life modules. EU law requires manufacturers to ensure their solar panels are recycled properly. Similar legislation is underway inJapan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
.
A 2021 study by Harvard Business Review
''Harvard Business Review'' (''HBR'') is a general management magazine published by Harvard Business Publishing, a wholly owned subsidiary of Harvard University. ''HBR'' is published six times a year and is headquartered in Brighton, Massach ...
indicates that, unless reused, by 2035 the discarded panels would outweigh new units by a factor of 2.56. They forecast the cost of recycling a single PV panel by then would reach $20–30, which would increase the LCOE of PV by a factor 4. Analyzing the US market, where no EU-like legislation exists as of 2021, HBR noted that without mandatory recycling legislation and with the cost of sending it to a landfill being just $1–2 there was a significant financial incentive to discard the decommissioned panels. The study assumed that consumers would replace panels half way through a 30 year lifetime to make a profit. However prices of new panels increased in the year after the study. A 2022 study found that modules were lasting longer than previously estimated, and said that might result in less PV waste than had been thought.
Recycling possibilities depend on the kind of technology used in the modules:
* Silicon based modules: aluminum frames and junction boxes are dismantled manually at the beginning of the process. The module is then crushed in a mill and the different fractions are separated – glass, plastics and metals. It is possible to recover more than 80% of the incoming weight. This process can be performed by flat glass recyclers since morphology and composition of a PV module is similar to those flat glasses used in the building and automotive industry. The recovered glass, for example, is readily accepted by the glass foam and glass insulation industry.
* Non-silicon based modules: they require specific recycling technologies such as the use of chemical baths in order to separate the different semiconductor materials. For cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ca ...
modules, the recycling process begins by crushing the module and subsequently separating the different fractions. This recycling process is designed to recover up to 90% of the glass and 95% of the semiconductor materials contained. Some commercial-scale recycling facilities have been created in recent years by private companies. For aluminium flat plate reflector: the trendiness of the reflectors has been brought up by fabricating them using a thin layer (around 0.016 mm to 0.024 mm) of aluminum coating present inside the non-recycled plastic food packages.
Since 2010, there is an annual European conference bringing together manufacturers, recyclers and researchers to look at the future of PV module recycling.
Production
The production of PV systems has followed a classiclearning curve
A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how Skill, proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience ...
effect, with significant cost reduction occurring alongside large rises in efficiency and production output.
With over 100% year-on-year growth in PV system installation, PV module makers dramatically increased their shipments of solar modules in 2019. They actively expanded their capacity and turned themselves into gigawatt GW players. According to Pulse Solar, five of the top ten PV module companies in 2019 have experienced a rise in solar panel production by at least 25% compared to 2019.
The basis of producing solar panels revolves around the use of silicon cells. These silicon cells are typically 10–20% efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, with newer production models now exceeding 22%.
In 2018, the world's top five solar module producers in terms of shipped capacity during the calendar year of 2018 were Jinko Solar
JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd. () is a solar panel manufacturer headquartered in Shanghai, China. The company started out as a wafer manufacturer in 2006 and went public on the New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed ...
, JA Solar, Trina Solar
Trina Solar Co., Ltd. (SSE: 688599, ), founded in 1997, manufactures, sells and does research and development on PV products, EPC and O&M. It also develops and sells smart micro-grid and multi-energy complementary systems and energy cloud-platf ...
, Longi solar, and Canadian Solar
Canadian Solar Inc. is a publicly traded company that manufactures solar PV modules and runs large scale solar projects.
History
Founded in 2001 in Guelph, Ontario, Canada by Shawn Qu, Canadian Solar (NASDAQ: CSIQ) has subsidiaries in over 2 ...
.
Price
 The price of solar electrical power has continued to fall so that in many countries it has become cheaper than
The price of solar electrical power has continued to fall so that in many countries it has become cheaper than fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
electricity from the electricity grid since 2012, a phenomenon known as grid parity
Grid parity (or socket parity) occurs when an alternative energy source can generate power at a levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) that is less than or equal to the price of power from the electricity grid. The term is most commonly used wh ...
.
Average pricing information divides in three pricing categories: those buying small quantities (modules of all sizes in the kilowatt range annually), mid-range buyers (typically up to 10 MWp MWp or MWP may refer to:
* Medieval Warm Period, a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region
* Mega Watt peak, a solar power measure in photo-voltaic (PV) industry to describe a unit's Nominal power (photovoltaic)#Watt-peak, nominal power
* ...
annually), and large quantity buyers (self-explanatory—and with access to the lowest prices). Over the long term there is clearly a systematic reduction in the price of cells and modules. For example, in 2012 it was estimated that the quantity cost per watt was about US$0.60, which was 250 times lower than the cost in 1970 of US$150. A 2015 study shows price/kWh dropping by 10% per year since 1980, and predicts that solar could contribute 20% of total electricity consumption by 2030, whereas the International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing carb ...
predicts 16% by 2050.
Real-world energy production costs depend a great deal on local weather conditions. In a cloudy country such as the United Kingdom, the cost per produced kWh is higher than in sunnier countries like Spain.
 Following to RMI, Balance-of-System (BoS) elements, this is, non-module cost of non-
Following to RMI, Balance-of-System (BoS) elements, this is, non-module cost of non-microinverter
A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercia ...
solar modules (as wiring, converters, racking systems and various components) make up about half of the total costs of installations.
For merchant solar power stations, where the electricity is being sold into the electricity transmission network, the cost of solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essenti ...
will need to match the wholesale electricity price. This point is sometimes called 'wholesale grid parity' or 'busbar parity'.
Some photovoltaic systems, such as rooftop installations, can supply power directly to an electricity user. In these cases, the installation can be competitive when the output cost matches the price at which the user pays for their electricity consumption. This situation is sometimes called 'retail grid parity', 'socket parity' or 'dynamic grid parity'. Research carried out by UN-Energy UN-Energy is an interagency mechanism within the system of the United Nations related to energy. It was created after the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg, and its purpose is to create a coherent approach towards a sustai ...
in 2012 suggests areas of sunny countries with high electricity prices, such as Italy, Spain and Australia, and areas using diesel generators, have reached retail grid parity.
Standards
Standards generally used in photovoltaic modules: *IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
61215 (crystalline silicon
Crystalline silicon or (c-Si) Is the crystalline forms of silicon, either polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si, consisting of small crystals), or monocrystalline silicon (mono-Si, a continuous crystal). Crystalline silicon is the dominant semicondu ...
performance), 61646 (thin film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many ap ...
performance) and 61730 (all modules, safety), 61853 (Photovoltaic module performance testing & energy rating)
* ISO 9488 Solar energy—Vocabulary.
* UL 1703 from Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global safety science company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded a ...
* UL 1741 from Underwriters Laboratories
* UL 2703 from Underwriters Laboratories
* CE mark
On commercial products, the letters CE (as the logo ) mean that the manufacturer or importer affirms the good's conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is not a quality indicator or a certificat ...
* Electrical Safety Tester (EST) Series (EST-460, EST-22V, EST-22H, EST-110).
Applications
There are many practical applications for the use of solar panels or photovoltaics. It can first be used in agriculture as a power source for irrigation. In health care solar panels can be used to refrigerate medical supplies. It can also be used for infrastructure. PV modules are used inphotovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and co ...
s and include a large variety of electric devices:
* Solar canal
A solar canal is a canal fitted with solar panels, increasing their efficiency, and reducing evaporation and land usage. The first operative system was installed in Gujarat, India in 2014.
Benefits
By placing solar panels above water, evaporati ...
s
* Photovoltaic power station
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building- ...
s
* Rooftop solar PV
A rooftop solar power system, or rooftop PV system, is a photovoltaic system, photovoltaic (PV) system that has its electricity-generating solar panels mounted on the rooftop of a residential or commercial building or structure. The various compon ...
systems
* Standalone PV systems
* Solar hybrid power systems
Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.
In power engineering, the term 'hybrid' describes a combined power and energy storage system.
Examples of power producers used in hybrid power are photovoltaics, ...
* Concentrated photovoltaics
Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) (also known as concentration photovoltaics) is a photovoltaic technology that generates electricity from sunlight. Unlike conventional photovoltaic systems, it uses lenses or curved mirrors to focus sunlight on ...
* Floating solar
Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, is solar panels mounted on a structure that floats on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake.
The market for this renewable energy technology has grown rap ...
; water-borne solar panels
* Solar planes
* Solar-powered water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
* Solar-pumped lasers
* Solar vehicle
A solar vehicle or solar electric vehicle is an electric vehicle powered completely or significantly by direct solar energy. Usually, photovoltaic (PV) cells contained in solar panels convert the sun's energy directly into electric energy. T ...
s
* Solar panels on spacecraft
Spacecraft operating in the inner Solar System usually rely on the use of power electronics-managed photovoltaic solar panels to derive electricity from sunlight. Outside the orbit of Jupiter, solar radiation is too weak to produce sufficient pow ...
and space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ...
s
Limitations
Impact on electricity network
With the increasing levels of rooftop photovoltaic systems, the energy flow becomes 2-way. When there is more local generation than consumption, electricity is exported to the grid. However, an electricity network traditionally is not designed to deal with the 2- way energy transfer. Therefore, some technical issues may occur. For example, in Queensland Australia, more than 30% of households used rooftop PV by the end of 2017. Theduck curve
The duck curve is a graph of power production over the course of a day that shows the timing imbalance between peak demand and renewable energy production. Used in utility-scale electricity generation, the term was coined in 2012 by the Cali ...
appeared often for a lot of communities from 2015 onwards. An over-voltage issue may result as the electricity flows from PV households back to the network. There are solutions to manage the over voltage issue, such as regulating PV inverter power factor, new voltage and energy control equipment at the electricity distributor level, re-conducting the electricity wires, demand side management, etc. There are often limitations and costs related to these solutions.
When electric networks are down, such as during the October 2019 California power shutoff, solar panels are often insufficient to fully provide power to a house or other structure, because they are designed to supply power to the grid, not directly to homes.
Implication onto electricity bill management and energy investment
There is no silver bullet in electricity or energy demand and bill management, because customers (sites) have different specific situations, e.g. different comfort/convenience needs, different electricity tariffs, or different usage patterns. Electricity tariff may have a few elements, such as daily access and metering charge, energy charge (based on kWh, MWh) or peak demand charge (e.g. a price for the highest 30min energy consumption in a month). PV is a promising option for reducing energy charge when electricity price is reasonably high and continuously increasing, such as in Australia and Germany. However, for sites with peak demand charge in place, PV may be less attractive if peak demands mostly occur in the late afternoon to early evening, for example residential communities. Overall, energy investment is largely an economical decision and it is better to make investment decisions based on systematical evaluation of options in operational improvement, energy efficiency, onsite generation and energy storage.Solar module quality assurance
Solar module quality assurance involves testing and evaluatingsolar cells
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physics, physical and Chemical substance, chemical phenomenon.Solar module
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s (or panels) are expected to have a long service life between 20 and 40 years. They should continually and reliably convey and deliver the power anticipated. modules presented to a wide exhibit of climate conditions alongside use in various temperatures. Solar modules can be tested through a combination of physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally co ...
tests, laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
studies, and numerical analyses. Furthermore, solar modules need to be assessed throughout the different stages of their life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
. Various companies such as Southern Research Energy & Environment, SGS Consumer Testing Services, TÜV Rheinland, Sinovoltaics, Clean Energy Associates (CEA), CSA Solar International and Enertis provide services in solar module quality assurance."The implementation of consistent traceable and stable manufacturing processes becomes mandatory to safeguard and ensure the quality of the PV Modules"
Stages of testing
The lifecycle stages of testing solar modules can include: theConcept
Concepts are defined as abstract ideas. They are understood to be the fundamental building blocks of the concept behind principles, thoughts and beliefs.
They play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied by s ...
ual phase, manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a r ...
phase, transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
and installation, commissioning phase, and the in-service phase. Depending on the test phase, different test principles may apply.
Conceptual phase
The first stage can involve design verification where the expected output of the module is tested through computer simulation. Further, the modules ability to withstand natural environment conditions such astemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
, rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
, hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
,
snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
, dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes ...
, lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electric charge, electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the land, ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous ...
, horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
and near-shadow effects is tested. The layout for design
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ...
and construction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and com ...
of the module and the quality of components and installation can also be tested at this stage.
Manufacturing phase
Inspecting manufacturers of components is carried through visitation. The inspection can include assembly checks, material testing supervision and Non Destructive Testing (NDT). Certification is carried our according to ANSI/UL1703, IEC 17025, IEC 61215, IEC 61646, IEC 61701 and IEC 61730-1/-2.AC module
An AC module is aphotovoltaic module
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
which has a small AC inverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opp ...
mounted onto its back side which produces AC power with no external DC connector
A DC connector (or DC plug, for one common type of connector) is an electrical connector for supplying direct current (DC) power.
Compared to domestic AC power plugs and sockets, DC connectors have many more standard types that are not intercha ...
.
AC modules are defined by Underwriters Laboratories
The UL enterprise is a global safety science company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.
Established in 1894, the UL enterprise was founded a ...
as the smallest and most complete system for harvesting solar energy.UL1741 pp 17, Section 2.2
See also
*Daisy chain (electrical engineering)
In electrical and electronic engineering, a daisy chain is a wiring scheme in which multiple devices are wired together in sequence or in a ring, similar to a garland of daisy flowers. Daisy chains may be used for power, analog signals, digit ...
* Digital modeling and fabrication Digital modeling and fabrication is a design and production process that combines 3D modeling or computing-aided design (CAD) with additive and subtractive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing is also known as 3D printing, while subtractive manufa ...
* Domestic energy consumption
Domestic energy consumption is the total amount of energy used in a house for household work. The amount of energy used per household varies widely depending on the standard of living of the country, the climate, and the age and type of residence. ...
* Grid-tied electrical system
A grid-tied electrical system, also called ''tied to grid'' or ''grid tie system'', is a semi-autonomous electrical generation or grid energy storage system which links to the mains to feed excess capacity back to the local mains electrical grid. ...
* Growth of photovoltaics
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics has been close to exponential between 1992 and 2018.
During this period of time, photovoltaics (PV), also known as solar PV, evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricit ...
* MC4 connector
MC4 connectors are single-contact electrical connectors commonly used for connecting solar panels. The MC in MC4 stands for the manufacturer Multi-Contact (now Stäubli Electrical Connectors) and the 4 for the 4 mm diameter contact pin.
...
* Solar charger
A solar charger is a charger that employs solar energy to supply electricity to devices or batteries. They are generally portable.
Solar chargers can charge lead acid or Ni-Cd battery banks up to 48 V and hundreds of ampere hours (up to 4000 Ah ...
* Solar cooker
A solar cooker is a device which uses the energy of direct sunlight to heat, cook or pasteurize drink and other food materials. Many solar cookers currently in use are relatively inexpensive, low-tech devices, although some are as powerful or as ...
* Solar still
A solar still distills water with substances dissolved in it by using the heat of the Sun to evaporate water so that it may be cooled and collected, thereby purifying it. They are used in areas where drinking water is unavailable, so that cle ...
* Junction box
An electrical junction box (also known as a "jbox") is an enclosure housing electrical connections. Junction boxes protect the electrical connections from the weather, as well as protecting people from accidental electric shocks.
Construction
...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Solar Panel PhotovoltaicsPanel
Panel may refer to:
Arts and media Visual arts
* Panel (comics), a single image in a comic book, comic strip or cartoon; also, a comic strip containing one such image
*Panel painting, in art, either one element of a multi-element piece of art ...
Smart devices
Solar power