|
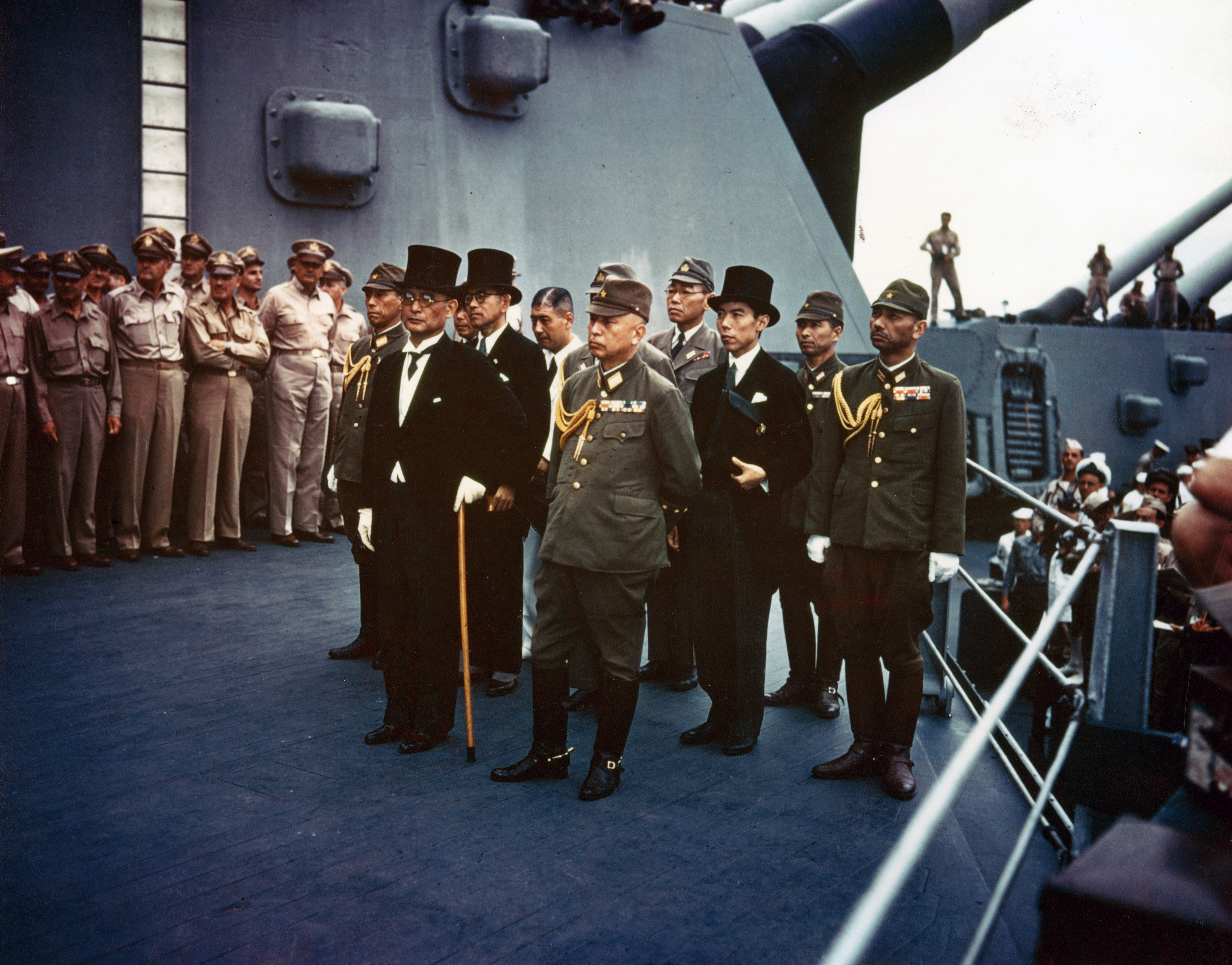
Yoshijirō Umezu
(January 4, 1882 – January 8, 1949) was a Japanese general in World War II and Chief of the Army General Staff during the final years of the conflict. He was convicted of war crimes and sentenced to life imprisonment. Biography Early life and career Umezu was born in Nakatsu, Ōita, Japan, where his family ran a bookstore since the 18th century. During his years at the Kumamoto Prefectural Seiseikou High School in Kumamoto, he decided to pursue a military career. He graduated from the 15th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy on November 30, 1903 and was commissioned a second lieutenant in the infantry the following February 12, 1904. Promoted to lieutenant on June 30, 1905, he entered the 23rd class of the Army Staff College, graduating first in 1911. Following his promotion to captain on March 25, 1912, he was sent to Europe for further studies in Germany and Denmark. While in Denmark, he was also a military observer from Japan, during the course of World War I, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
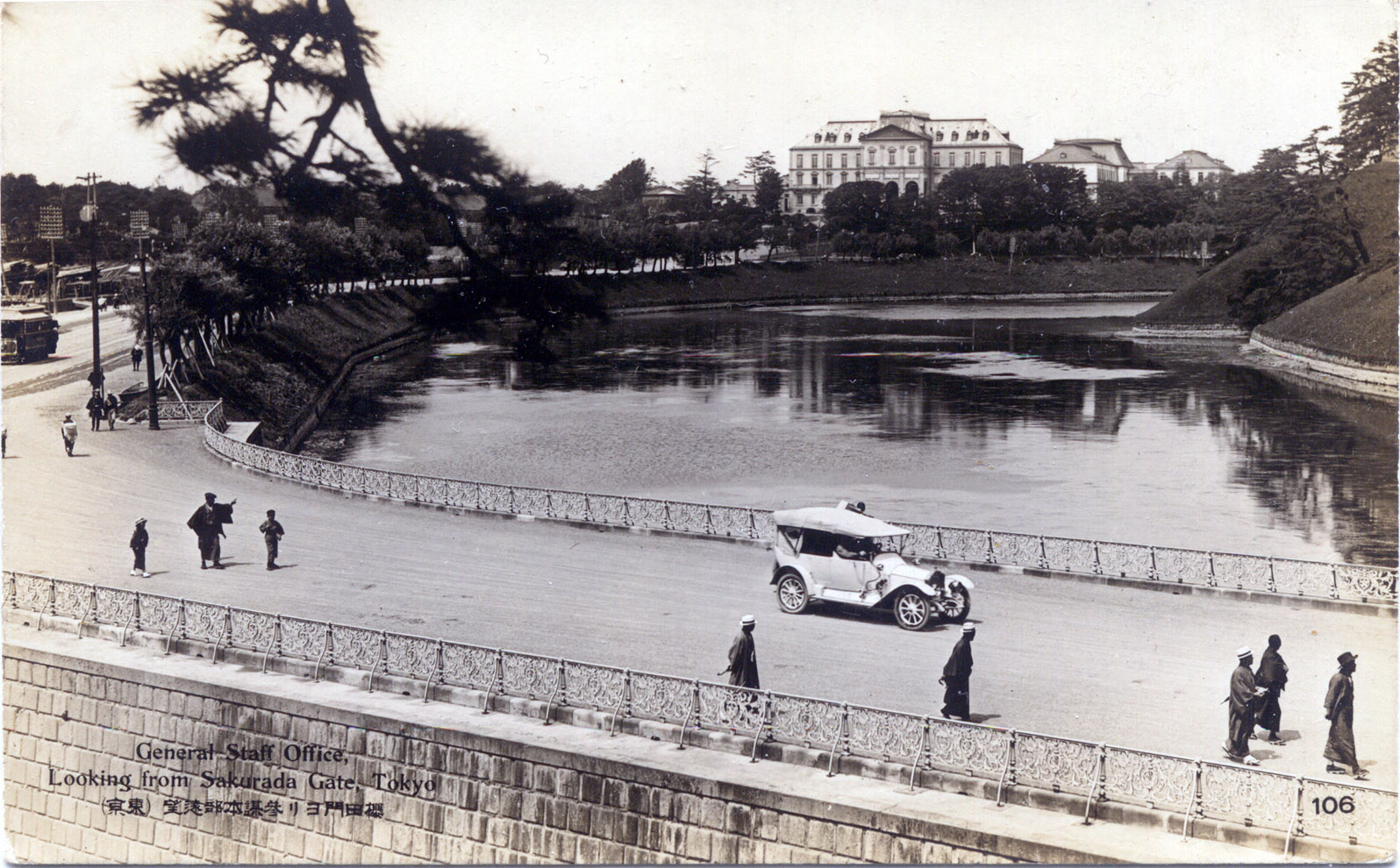
Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office
The , also called the Army General Staff, was one of the two principal agencies charged with overseeing the Imperial Japanese Army. Role The was created in April 1872, along with the Navy Ministry, to replace the Ministry of Military Affairs (''Hyōbushō'') of the early Meiji government. Initially, the Army Ministry was in charge of both administration and operational command of the Imperial Japanese Army however, from December 1878, the Imperial Army General Staff Office took over all operational control of the Army, leaving the Army Ministry only with administrative functions. The Imperial Army General Staff was thus responsible for the preparation of war plans; the military training and employment of combined arms military intelligence; the direction of troop maneuvers; troop deployments; and the compilation of field service military regulations, military histories, and cartography. The Chief of the Army General Staff was the senior ranking uniformed officer in the Imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army General Staff
The , also called the Army General Staff, was one of the two principal agencies charged with overseeing the Imperial Japanese Army. Role The was created in April 1872, along with the Navy Ministry, to replace the Ministry of Military Affairs (''Hyōbushō'') of the early Meiji government. Initially, the Army Ministry was in charge of both administration and operational command of the Imperial Japanese Army however, from December 1878, the Imperial Army General Staff Office took over all operational control of the Army, leaving the Army Ministry only with administrative functions. The Imperial Army General Staff was thus responsible for the preparation of war plans; the military training and employment of combined arms military intelligence; the direction of troop maneuvers; troop deployments; and the compilation of field service military regulations, military histories, and cartography. The Chief of the Army General Staff was the senior ranking uniformed officer in the Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a " presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army War College (Japan)
:''This article deals with the Empire of Japan's Army War College. For other war colleges, see: War college.'' The ; Short form: of the Empire of Japan was founded in 1882 in Minato, Tokyo, Minato, Tokyo to modernization, modernize and Westernization, Westernize the Imperial Japanese Army. Much of the empire's elite including Prime Minister of Japan, prime ministers during the period of Japanese militarism were graduates of the college. History Supported by influential pro-German ministers and army officers, the Army War College was modeled after the Prussian ''Preußische Kriegsakademie'', with German officers hired as Oyatoi gaikokujin to provide training. The most prominent of these instructors was Major Jakob Meckel, Klemens W.J. Meckel. He was influential in assisting in the reorganization of the standing army from a garrison-based system into a division (military), divisional system. Reporting directly to the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Headquarters, the college ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army Academy
The was the principal officer's training school for the Imperial Japanese Army. The programme consisted of a junior course for graduates of local army cadet schools and for those who had completed four years of middle school, and a senior course for officer candidates. History and background Established as the ''Heigakkō'' in 1868 in Kyoto, the officer training school was renamed the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1874 and relocated to Ichigaya, Tokyo. After 1898, the Academy came under the supervision of the Army Education Administration. In 1937 the Academy was divided, with the Senior Course Academy being relocated to Sagamihara in Kanagawa prefecture, and the Junior Course School moved to Asaka, Saitama. The 50th graduation ceremony was held in the new Academy buildings in Sagamihara on 20 December 1937, and was attended by the Shōwa Emperor ( Emperor Hirohito) himself. In 1938, a separate school was established for military aviation officers. During World War II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumamoto
is the capital city of Kumamoto Prefecture on the island of Kyushu, Japan. , the city has an estimated population of 738,907 and a population density of 1,893 people per km2. The total area is 390.32 km2. had a population of 1,461,000, as of the 2000 census. , Kumamoto Metropolitan Employment Area has a GDP of US$39.8 billion. It is not considered part of the Fukuoka–Kitakyushu metropolitan area, despite their shared border. The city was designated on April 1, 2012, by government ordinance. History Early modern period Shokuhō period Katō Kiyomasa, a contemporary of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, was made ''daimyō'' of half of the (old) administrative region of Higo in 1588. Afterwards, Kiyomasa built Kumamoto Castle. Due to its many innovative defensive designs, Kumamoto Castle was considered impenetrable, and Kiyomasa enjoyed a reputation as one of the finest castle-builders in Japanese history. Edo period After Kiyomasa died in 1611, his son, Tadahiro, succeede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumamoto Prefectural Seiseikou High School
Kumamoto Prefectural Seiseikou High School is a co-educational public senior high school located in Kumamoto, Kumamoto prefecture. It is one of the Super Global High Schools in Japan. Notable alumni Academic * Einosuke Harada * Jun-Ichiro Mukai * Kang Sang-jung Fine Art * Tetsuya Noda Politics * Adachi Kenzō * Korekiyo Otsuka * Toshio Ōtsu * Morio Takahashi * Toshikatsu Matsuoka was a Japanese politician who served as the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries from 2006 until his suicide in 2007 amid a financial scandal. Early life and education He was born in Aso, Kumamoto, Kyūshū on 25 February 1945. His ... * Minoru Kihara References External links Seiseiko High School {{coord missing, Kumamoto Prefecture Kumamoto Schools in Kumamoto Prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakatsu, Ōita
is a city on the northern border of Ōita Prefecture in Kyushu, Japan. The city is on the border with Fukuoka Prefecture. Nakatsu was founded on April 20, 1929. As of March 2017, the city has an estimated population of 84,701 and a population density of 170 people per km2. The total area is 491.09 km2. History *1587: Kuroda Yoshitaka (Josui) built Nakatsu Castle as a flatland castle near the Yamaguni River. *April 1925: The village of Ōe was merged with Toyoda to become the town of Nakatsu. *April 1919: The village of Ogusu and the town of Nakatsu were merged to become the city of Nakatsu. *August 1933: The villages of Tsurui, Ōhata and Josui were merged into Nakatsu. *April 1951: The village of Miho was merged into Nakatsu. *October 1954: The village of Wada was merged into Nakatsu. *February 1955: The village of Imazu was merged into Nakatsu. *March, 2005: The towns of Hon'yabakei, Yabakei and Yamakuni, and the village of Sankō (all from Shimoge District) were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Imprisonment
Life imprisonment is any sentence (law), sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for which, in some countries, a person could receive this sentence include murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, drug trafficking, drug possession, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated criminal damage, arson, kidnapping, burglary, and robbery, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or any three felony, felonies in case of three-strikes law. Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death. Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
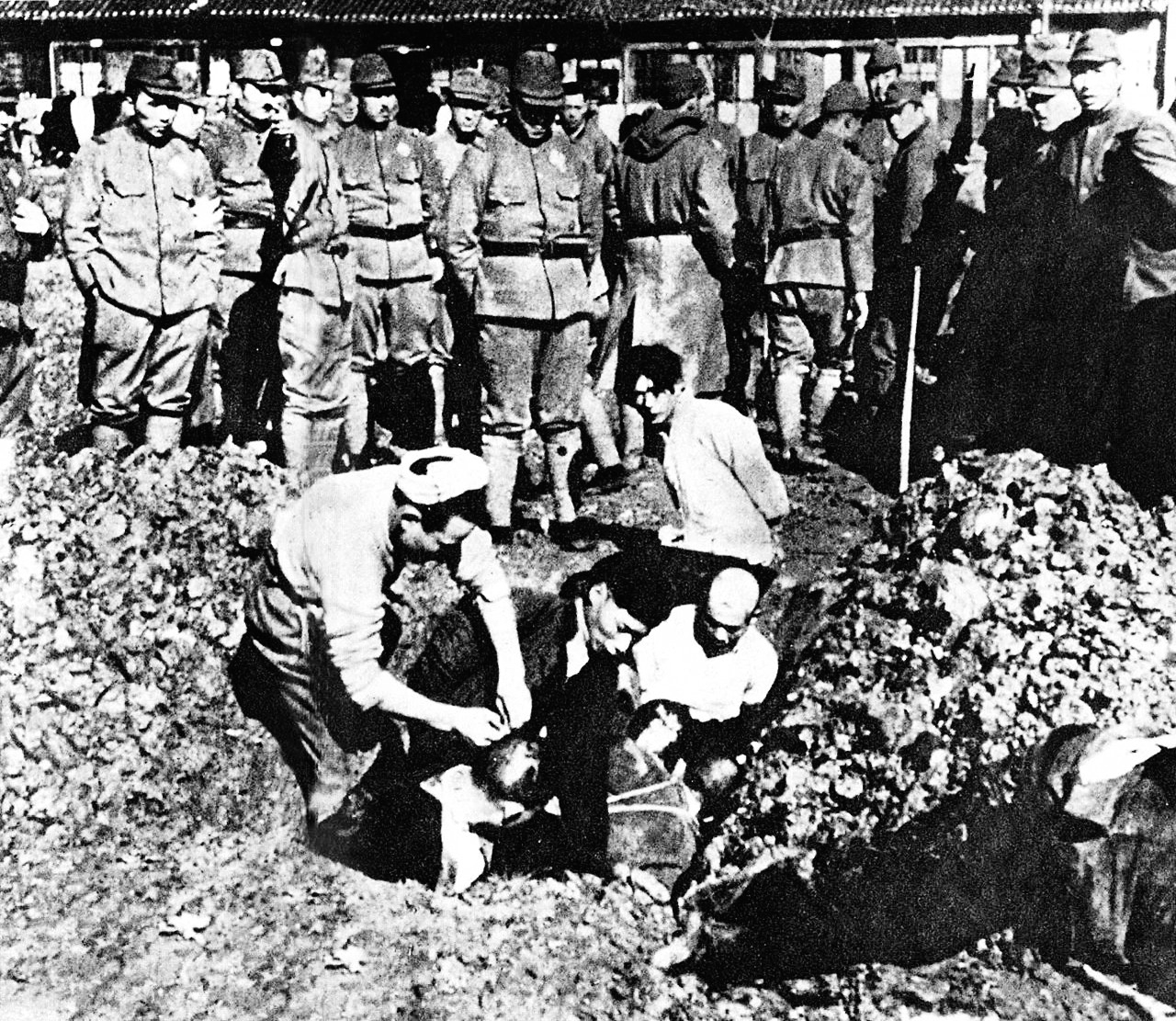
Japanese War Crimes
The Empire of Japan committed war crimes in many Asian-Pacific countries during the period of Japanese imperialism, primarily during the Second Sino-Japanese and Pacific Wars. These incidents have been described as an "Asian Holocaust". Some war crimes were committed by Japanese military personnel during the late 19th century, but most were committed during the first part of the Shōwa era, the name given to the reign of Emperor Hirohito. Under Emperor Hirohito, the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) perpetrated numerous war crimes which resulted in the deaths of millions of people. Estimates of the number of deaths range from three to 30 million through massacres, human experimentation, starvation, and forced labor directly perpetrated or condoned by the Japanese military and government. Japanese veterans have admitted war crimes and have provided oral testimonies and written evidence, which includes diaries and war journals. Airmen of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |