German Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The German Empire (), Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a " presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –
The German Empire
" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a
/ref> The dominance of the German Empire in the natural sciences, especially in physics and chemistry, was such that one-third of all Nobel Prizes went to German inventors and researchers. During its 47 years of existence, the German Empire became the industrial, technological, and scientific giant of Europe, and by 1913, Germany was the largest economy in Continental Europe and the third-largest in the world. Germany also became a great power, it built up the longest railway network of Europe, the world's strongest army, and a fast-growing industrial base. Starting very small in 1871, in a decade, the
 The German Confederation had been created by an act of the
The German Confederation had been created by an act of the
 On 10 December 1870, the North German Confederation Reichstag renamed the Confederation the "German Empire" and gave the title of
On 10 December 1870, the North German Confederation Reichstag renamed the Confederation the "German Empire" and gave the title of
 Bismarck's post-1871 foreign policy was conservative and sought to preserve the balance of power in Europe. British historian
Bismarck's post-1871 foreign policy was conservative and sought to preserve the balance of power in Europe. British historian
 Germans had dreamed of colonial imperialism since 1848. Although Bismarck had little interest in acquiring overseas possessions, most Germans were enthusiastic, and by 1884 he had acquired German New Guinea. By the 1890s, German colonial expansion in Asia and the Pacific ( Kiauchau in China, Tientsin in China, the
Germans had dreamed of colonial imperialism since 1848. Although Bismarck had little interest in acquiring overseas possessions, most Germans were enthusiastic, and by 1884 he had acquired German New Guinea. By the 1890s, German colonial expansion in Asia and the Pacific ( Kiauchau in China, Tientsin in China, the
 For 30 years, Germany struggled against Britain to be Europe's leading industrial power. Representative of Germany's industry was the steel giant
For 30 years, Germany struggled against Britain to be Europe's leading industrial power. Representative of Germany's industry was the steel giant
 Prussia in 1871 included 16,000,000 Protestants, both Reformed and Lutheran, and 8,000,000 Catholics. Most people were generally segregated into their own religious worlds, living in rural districts or city neighbourhoods that were overwhelmingly of the same religion, and sending their children to separate public schools where their religion was taught. There was little interaction or intermarriage. On the whole, the Protestants had a higher social status, and the Catholics were more likely to be peasant farmers or unskilled or semiskilled industrial workers. In 1870, the Catholics formed their own political party, the Centre Party, which generally supported unification and most of Bismarck's policies. However, Bismarck distrusted parliamentary democracy in general and opposition parties in particular, especially when the Centre Party showed signs of gaining support among dissident elements such as the Polish Catholics in Silesia. A powerful intellectual force of the time was anti-Catholicism, led by the liberal intellectuals who formed a vital part of Bismarck's coalition. They saw the Catholic Church as a powerful force of reaction and anti-modernity, especially after the proclamation of papal infallibility in 1870, and the tightening control of the Vatican over the local bishops.
The Kulturkampf launched by Bismarck 1871–1880 affected Prussia; although there were similar movements in Baden and Hesse, the rest of Germany was not affected. According to the new imperial constitution, the states were in charge of religious and educational affairs; they funded the Protestant and Catholic schools. In July 1871 Bismarck abolished the Catholic section of the Prussian Ministry of ecclesiastical and educational affairs, depriving Catholics of their voice at the highest level. The system of strict government supervision of schools was applied only in Catholic areas; the Protestant schools were left alone.
Much more serious were the May laws of 1873. One made the appointment of any priest dependent on his attendance at a German university, as opposed to the seminaries that the Catholics typically used. Furthermore, all candidates for the ministry had to pass an examination in German culture before a state board which weeded out intransigent Catholics. Another provision gave the government a veto power over most church activities. A second law abolished the jurisdiction of the Vatican over the Catholic Church in Prussia; its authority was transferred to a government body controlled by Protestants.
Nearly all German bishops, clergy, and laymen rejected the legality of the new laws, and were defiant in the face of heavier and heavier penalties and imprisonments imposed by Bismarck's government. By 1876, all the Prussian bishops were imprisoned or in exile, and a third of the Catholic parishes were without a priest. In the face of systematic defiance, the Bismarck government increased the penalties and its attacks, and were challenged in 1875 when a papal encyclical declared the whole ecclesiastical legislation of Prussia was invalid, and threatened to excommunicate any Catholic who obeyed. There was no violence, but the Catholics mobilized their support, set up numerous civic organizations, raised money to pay fines, and rallied behind their church and the Centre Party. The "Old Catholic Church", which rejected the First Vatican Council, attracted only a few thousand members. Bismarck, a devout pietistic Protestant, realized his Kulturkampf was backfiring when secular and socialist elements used the opportunity to attack all religion. In the long run, the most significant result was the mobilization of the Catholic voters, and their insistence on protecting their religious identity. In the elections of 1874, the Centre party doubled its popular vote, and became the second-largest party in the national parliament—and remained a powerful force for the next 60 years, so that after Bismarck it became difficult to form a government without their support.
Prussia in 1871 included 16,000,000 Protestants, both Reformed and Lutheran, and 8,000,000 Catholics. Most people were generally segregated into their own religious worlds, living in rural districts or city neighbourhoods that were overwhelmingly of the same religion, and sending their children to separate public schools where their religion was taught. There was little interaction or intermarriage. On the whole, the Protestants had a higher social status, and the Catholics were more likely to be peasant farmers or unskilled or semiskilled industrial workers. In 1870, the Catholics formed their own political party, the Centre Party, which generally supported unification and most of Bismarck's policies. However, Bismarck distrusted parliamentary democracy in general and opposition parties in particular, especially when the Centre Party showed signs of gaining support among dissident elements such as the Polish Catholics in Silesia. A powerful intellectual force of the time was anti-Catholicism, led by the liberal intellectuals who formed a vital part of Bismarck's coalition. They saw the Catholic Church as a powerful force of reaction and anti-modernity, especially after the proclamation of papal infallibility in 1870, and the tightening control of the Vatican over the local bishops.
The Kulturkampf launched by Bismarck 1871–1880 affected Prussia; although there were similar movements in Baden and Hesse, the rest of Germany was not affected. According to the new imperial constitution, the states were in charge of religious and educational affairs; they funded the Protestant and Catholic schools. In July 1871 Bismarck abolished the Catholic section of the Prussian Ministry of ecclesiastical and educational affairs, depriving Catholics of their voice at the highest level. The system of strict government supervision of schools was applied only in Catholic areas; the Protestant schools were left alone.
Much more serious were the May laws of 1873. One made the appointment of any priest dependent on his attendance at a German university, as opposed to the seminaries that the Catholics typically used. Furthermore, all candidates for the ministry had to pass an examination in German culture before a state board which weeded out intransigent Catholics. Another provision gave the government a veto power over most church activities. A second law abolished the jurisdiction of the Vatican over the Catholic Church in Prussia; its authority was transferred to a government body controlled by Protestants.
Nearly all German bishops, clergy, and laymen rejected the legality of the new laws, and were defiant in the face of heavier and heavier penalties and imprisonments imposed by Bismarck's government. By 1876, all the Prussian bishops were imprisoned or in exile, and a third of the Catholic parishes were without a priest. In the face of systematic defiance, the Bismarck government increased the penalties and its attacks, and were challenged in 1875 when a papal encyclical declared the whole ecclesiastical legislation of Prussia was invalid, and threatened to excommunicate any Catholic who obeyed. There was no violence, but the Catholics mobilized their support, set up numerous civic organizations, raised money to pay fines, and rallied behind their church and the Centre Party. The "Old Catholic Church", which rejected the First Vatican Council, attracted only a few thousand members. Bismarck, a devout pietistic Protestant, realized his Kulturkampf was backfiring when secular and socialist elements used the opportunity to attack all religion. In the long run, the most significant result was the mobilization of the Catholic voters, and their insistence on protecting their religious identity. In the elections of 1874, the Centre party doubled its popular vote, and became the second-largest party in the national parliament—and remained a powerful force for the next 60 years, so that after Bismarck it became difficult to form a government without their support.
 One of the effects of the unification policies was the gradually increasing tendency to eliminate the use of non-German languages in public life, schools and academic settings with the intent of pressuring the non-German population to abandon their national identity in what was called "
One of the effects of the unification policies was the gradually increasing tendency to eliminate the use of non-German languages in public life, schools and academic settings with the intent of pressuring the non-German population to abandon their national identity in what was called "
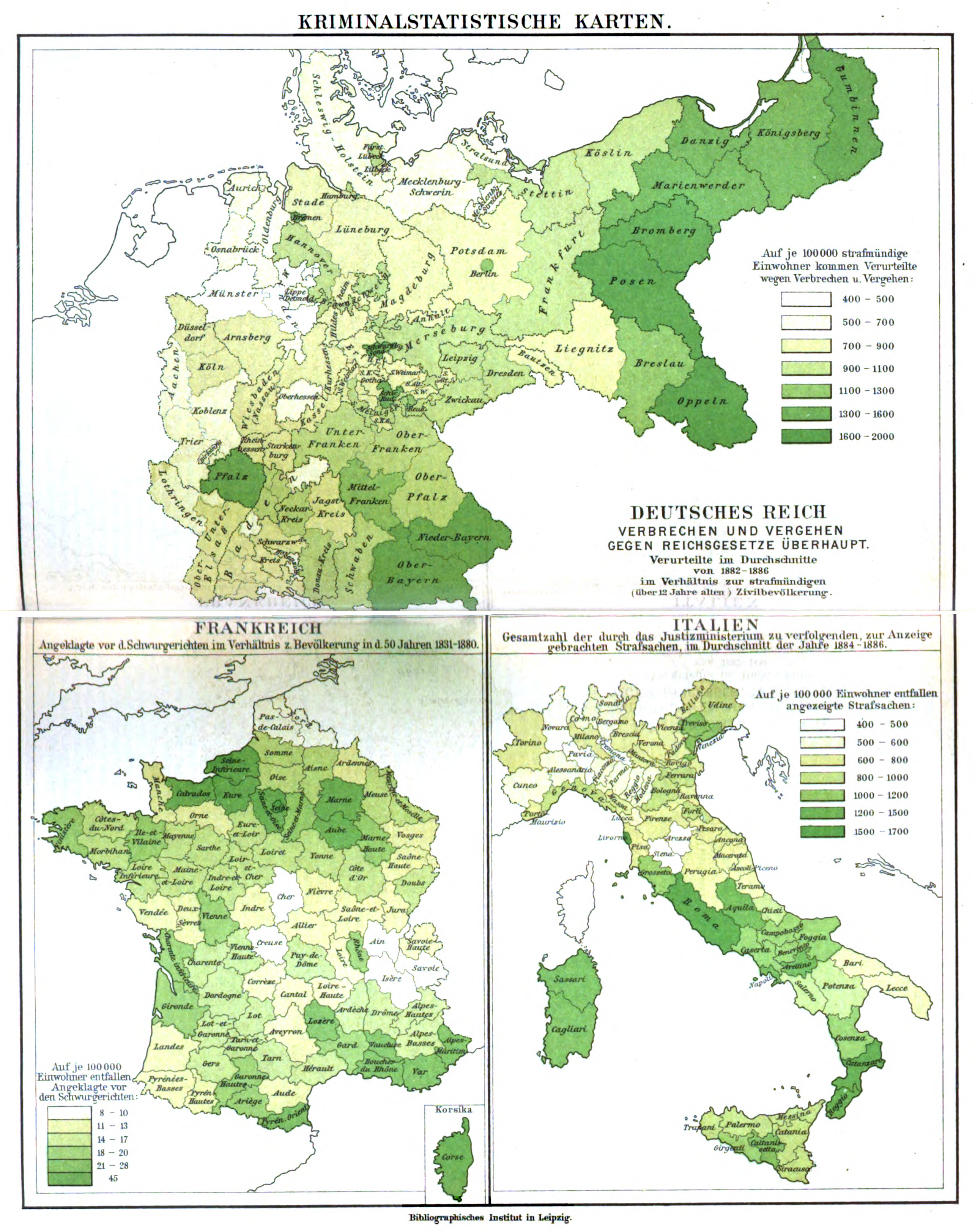 Bismarck's efforts also initiated the levelling of the enormous differences between the German states, which had been independent in their evolution for centuries, especially with legislation. The completely different legal histories and judicial systems posed enormous complications, especially for national trade. While a common trade code had already been introduced by the Confederation in 1861 (which was adapted for the Empire and, with great modifications, is still in effect today), there was little similarity in laws otherwise.
In 1871, a common was introduced; in 1877, common court procedures were established in the court system by the , code of civil procedure () and code of criminal procedure (). In 1873 the constitution was amended to allow the Empire to replace the various and greatly differing Civil Codes of the states (If they existed at all; for example, parts of Germany formerly occupied by Napoleon's France had adopted the French Civil Code, while in Prussia the of 1794 was still in effect). In 1881, a first commission was established to produce a common Civil Code for all of the Empire, an enormous effort that would produce the (BGB), possibly one of the most impressive legal works in the world; it was eventually put into effect on 1 January 1900. All of these codifications are, albeit with many amendments, still in effect today.
Bismarck's efforts also initiated the levelling of the enormous differences between the German states, which had been independent in their evolution for centuries, especially with legislation. The completely different legal histories and judicial systems posed enormous complications, especially for national trade. While a common trade code had already been introduced by the Confederation in 1861 (which was adapted for the Empire and, with great modifications, is still in effect today), there was little similarity in laws otherwise.
In 1871, a common was introduced; in 1877, common court procedures were established in the court system by the , code of civil procedure () and code of criminal procedure (). In 1873 the constitution was amended to allow the Empire to replace the various and greatly differing Civil Codes of the states (If they existed at all; for example, parts of Germany formerly occupied by Napoleon's France had adopted the French Civil Code, while in Prussia the of 1794 was still in effect). In 1881, a first commission was established to produce a common Civil Code for all of the Empire, an enormous effort that would produce the (BGB), possibly one of the most impressive legal works in the world; it was eventually put into effect on 1 January 1900. All of these codifications are, albeit with many amendments, still in effect today.
Deutsche Rechts- und Gerichtskarte (1895).jpg, Different legal systems in Germany prior to 1900
DR Fields of Law.png, Fields of law in the German Empire
 On 9 March 1888, Wilhelm I died shortly before his 91st birthday, leaving his son Frederick III as the new emperor. Frederick was a liberal and an admirer of the British constitution, while his links to Britain strengthened further with his marriage to Princess Victoria, eldest child of Queen Victoria. With his ascent to the throne, many hoped that Frederick's reign would lead to a liberalization of the Reich and an increase of parliament's influence on the political process. The dismissal of Robert von Puttkamer, the highly conservative Prussian interior minister, on 8 June was a sign of the expected direction and a blow to Bismarck's administration.
By the time of his accession, however, Frederick had developed incurable
On 9 March 1888, Wilhelm I died shortly before his 91st birthday, leaving his son Frederick III as the new emperor. Frederick was a liberal and an admirer of the British constitution, while his links to Britain strengthened further with his marriage to Princess Victoria, eldest child of Queen Victoria. With his ascent to the throne, many hoped that Frederick's reign would lead to a liberalization of the Reich and an increase of parliament's influence on the political process. The dismissal of Robert von Puttkamer, the highly conservative Prussian interior minister, on 8 June was a sign of the expected direction and a blow to Bismarck's administration.
By the time of his accession, however, Frederick had developed incurable
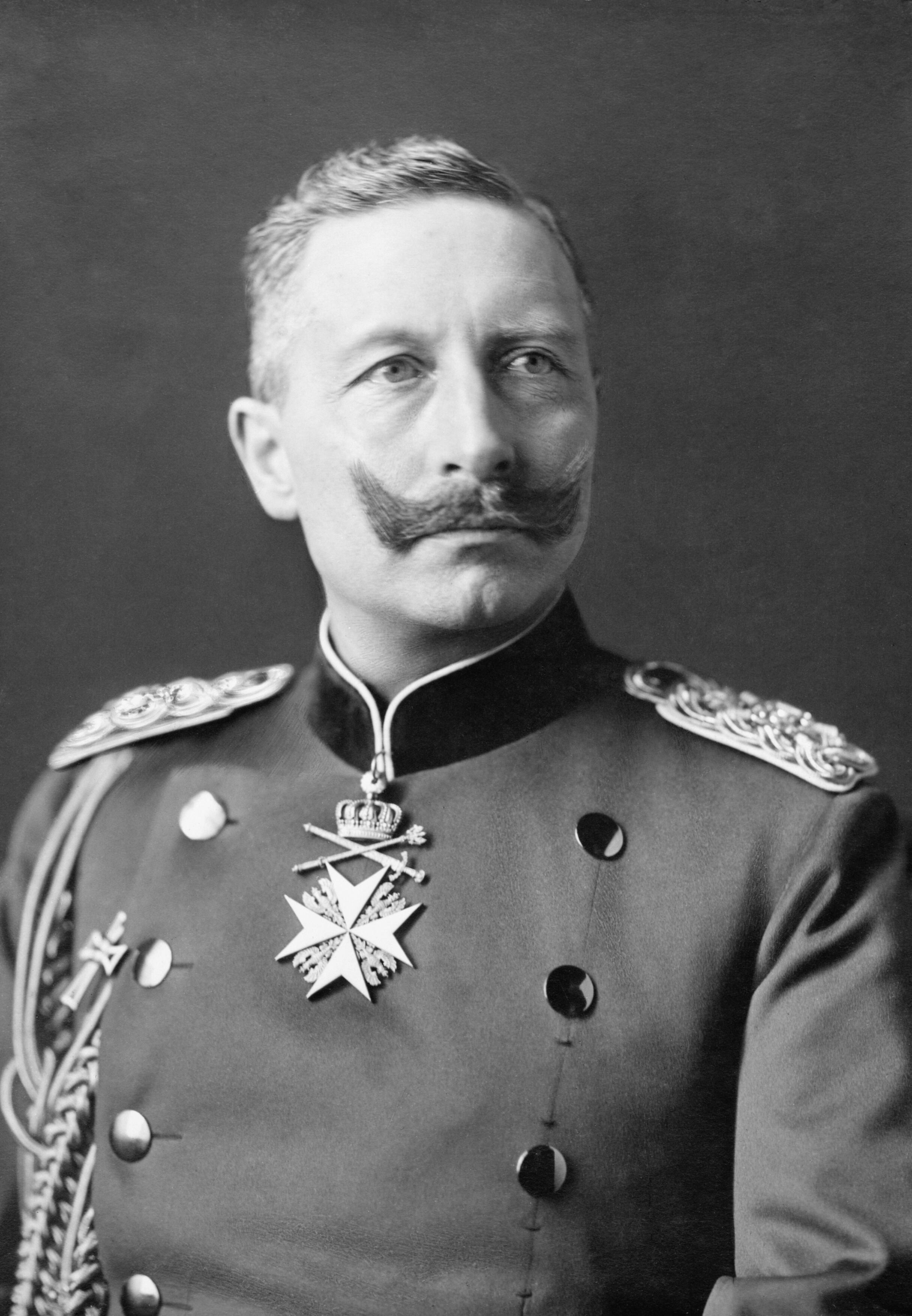 Wilhelm II wanted to reassert his ruling prerogatives at a time when other monarchs in Europe were being transformed into constitutional figureheads. This decision led the ambitious Kaiser into conflict with Bismarck. The old chancellor had hoped to guide Wilhelm as he had guided his grandfather, but the emperor wanted to be the master in his own house and had many sycophants telling him that Frederick the Great would not have been great with a Bismarck at his side. A key difference between Wilhelm II and Bismarck was their approaches to handling political crises, especially in 1889, when German coal miners went on strike in Upper Silesia. Bismarck demanded that the
Wilhelm II wanted to reassert his ruling prerogatives at a time when other monarchs in Europe were being transformed into constitutional figureheads. This decision led the ambitious Kaiser into conflict with Bismarck. The old chancellor had hoped to guide Wilhelm as he had guided his grandfather, but the emperor wanted to be the master in his own house and had many sycophants telling him that Frederick the Great would not have been great with a Bismarck at his side. A key difference between Wilhelm II and Bismarck was their approaches to handling political crises, especially in 1889, when German coal miners went on strike in Upper Silesia. Bismarck demanded that the
 Under Wilhelm II, Germany no longer had long-ruling strong chancellors like Bismarck. The new chancellors had difficulty in performing their roles, especially the additional role as Prime Minister of Prussia assigned to them in the German Constitution. The reforms of Chancellor Leo von Caprivi, which liberalized trade and so reduced unemployment, were supported by the Kaiser and most Germans except for Prussian landowners, who feared loss of land and power and launched several campaigns against the reforms.
While Prussian aristocrats challenged the demands of a united German state, in the 1890s several organizations were set up to challenge the authoritarian conservative Prussian militarism which was being imposed on the country. Educators opposed to the German state-run schools, which emphasized military education, set up their own independent liberal schools, which encouraged individuality and freedom. However nearly all the schools in Imperial Germany had a very high standard and kept abreast with modern developments in knowledge.
Artists began experimental art in opposition to Kaiser Wilhelm's support for traditional art, to which Wilhelm responded "art which transgresses the laws and limits laid down by me can no longer be called art". It was largely thanks to Wilhelm's influence that most printed material in Germany used blackletter instead of the Roman type used in the rest of Western Europe. At the same time, a new generation of cultural creators emerged.
Under Wilhelm II, Germany no longer had long-ruling strong chancellors like Bismarck. The new chancellors had difficulty in performing their roles, especially the additional role as Prime Minister of Prussia assigned to them in the German Constitution. The reforms of Chancellor Leo von Caprivi, which liberalized trade and so reduced unemployment, were supported by the Kaiser and most Germans except for Prussian landowners, who feared loss of land and power and launched several campaigns against the reforms.
While Prussian aristocrats challenged the demands of a united German state, in the 1890s several organizations were set up to challenge the authoritarian conservative Prussian militarism which was being imposed on the country. Educators opposed to the German state-run schools, which emphasized military education, set up their own independent liberal schools, which encouraged individuality and freedom. However nearly all the schools in Imperial Germany had a very high standard and kept abreast with modern developments in knowledge.
Artists began experimental art in opposition to Kaiser Wilhelm's support for traditional art, to which Wilhelm responded "art which transgresses the laws and limits laid down by me can no longer be called art". It was largely thanks to Wilhelm's influence that most printed material in Germany used blackletter instead of the Roman type used in the rest of Western Europe. At the same time, a new generation of cultural creators emerged.
 From the 1890s onwards, the most effective opposition to the monarchy came from the newly formed
From the 1890s onwards, the most effective opposition to the monarchy came from the newly formed
 Wilhelm II wanted Germany to have her " place in the sun", like Britain, which he constantly wished to emulate or rival. With German traders and merchants already active worldwide, he encouraged colonial efforts in Africa and the Pacific (" new imperialism"), causing the German Empire to vie with other European powers for remaining "unclaimed" territories. With the encouragement or at least the acquiescence of Britain, which at this stage saw Germany as a counterweight to her old rival France, Germany acquired German Southwest Africa (modern Namibia), German Kamerun (modern
Wilhelm II wanted Germany to have her " place in the sun", like Britain, which he constantly wished to emulate or rival. With German traders and merchants already active worldwide, he encouraged colonial efforts in Africa and the Pacific (" new imperialism"), causing the German Empire to vie with other European powers for remaining "unclaimed" territories. With the encouragement or at least the acquiescence of Britain, which at this stage saw Germany as a counterweight to her old rival France, Germany acquired German Southwest Africa (modern Namibia), German Kamerun (modern  Bismarck had originally dismissed the agitation for colonies with contempt; he favoured a Eurocentric foreign policy, as the treaty arrangements made during his tenure in office show. As a latecomer to colonization, Germany repeatedly came into conflict with the established colonial powers and also with the United States, which opposed German attempts at colonial expansion in both the Caribbean and the Pacific. Native insurrections in German territories received prominent coverage in other countries, especially in Britain; the established powers had dealt with such uprisings decades earlier, often brutally, and had secured firm control of their colonies by then. The Boxer Rising in China, which the Chinese government eventually sponsored, began in the Shandong province, in part because Germany, as colonizer at Kiautschou, was an untested power and had only been active there for two years. Eight western nations, including the United States, mounted a joint relief force to rescue westerners caught up in the rebellion. During the departure ceremonies for the German contingent, Wilhelm II urged them to behave like the
Bismarck had originally dismissed the agitation for colonies with contempt; he favoured a Eurocentric foreign policy, as the treaty arrangements made during his tenure in office show. As a latecomer to colonization, Germany repeatedly came into conflict with the established colonial powers and also with the United States, which opposed German attempts at colonial expansion in both the Caribbean and the Pacific. Native insurrections in German territories received prominent coverage in other countries, especially in Britain; the established powers had dealt with such uprisings decades earlier, often brutally, and had secured firm control of their colonies by then. The Boxer Rising in China, which the Chinese government eventually sponsored, began in the Shandong province, in part because Germany, as colonizer at Kiautschou, was an untested power and had only been active there for two years. Eight western nations, including the United States, mounted a joint relief force to rescue westerners caught up in the rebellion. During the departure ceremonies for the German contingent, Wilhelm II urged them to behave like the  Upon acquiring Southwest Africa, German settlers were encouraged to cultivate land held by the
Upon acquiring Southwest Africa, German settlers were encouraged to cultivate land held by the
 Following the assassination of the Austro-Hungarian Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, the Kaiser offered Emperor Franz Joseph full support for Austro-Hungarian plans to invade the
Following the assassination of the Austro-Hungarian Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, the Kaiser offered Emperor Franz Joseph full support for Austro-Hungarian plans to invade the
 Germany did not want to risk lengthy battles along the Franco-German border and instead adopted the Schlieffen Plan, a military strategy designed to cripple France by invading Belgium and
Germany did not want to risk lengthy battles along the Franco-German border and instead adopted the Schlieffen Plan, a military strategy designed to cripple France by invading Belgium and  German attempts to break through failed at the two battles of Ypres (
German attempts to break through failed at the two battles of Ypres (
 While the
While the
 The defeat of Russia in 1917 enabled Germany to transfer hundreds of thousands of troops from the Eastern to the Western Front, giving it a numerical advantage over the Allies. By retraining the soldiers in new infiltration tactics, the Germans expected to unfreeze the battlefield and win a decisive victory before the army of the United States, which had now entered the war on the side of the Allies, arrived in strength. In what was known as the "kaiserschlacht", Germany converged their troops and delivered multiple blows that pushed back the allies. However, the repeated German offensives in the spring of 1918 all failed, as the Allies fell back and regrouped and the Germans lacked the reserves needed to consolidate their gains. Meanwhile, soldiers had become radicalised by the
The defeat of Russia in 1917 enabled Germany to transfer hundreds of thousands of troops from the Eastern to the Western Front, giving it a numerical advantage over the Allies. By retraining the soldiers in new infiltration tactics, the Germans expected to unfreeze the battlefield and win a decisive victory before the army of the United States, which had now entered the war on the side of the Allies, arrived in strength. In what was known as the "kaiserschlacht", Germany converged their troops and delivered multiple blows that pushed back the allies. However, the repeated German offensives in the spring of 1918 all failed, as the Allies fell back and regrouped and the Germans lacked the reserves needed to consolidate their gains. Meanwhile, soldiers had become radicalised by the
Karte Deutsches Reich, Verwaltungsgliederung 1900-01-01.png, Administrative map
Meyers b4 s0812a.jpg, Population density ()
Karte der Reichstagswahlkreise farbig-2011-11-09.svg, Election constituencies for the Reichstag
Deutsches Kaiserreich 1893.jpg, Detailed map in 1893 with cities and larger towns
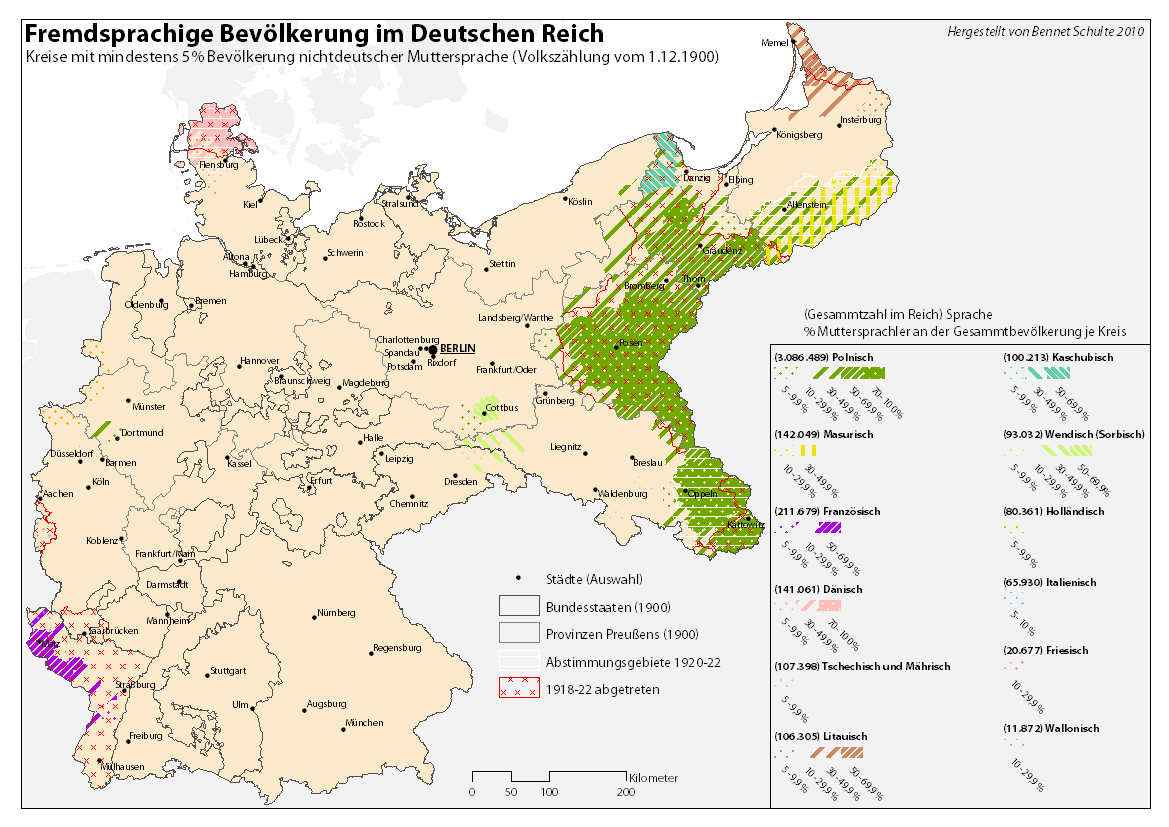 About 92% of the population spoke German as their first language. The only minority language with a significant number of speakers (5.4%) was Polish (a figure that rises to over 6% when including the related
About 92% of the population spoke German as their first language. The only minority language with a significant number of speakers (5.4%) was Polish (a figure that rises to over 6% when including the related
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 dänisch.png, Danish
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 niederländisch.png, Dutch
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 friesisch.png, Frisian
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 polnisch.png, Polish
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 tschechisch.png, Czech (and Moravian)
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 masurisch.png, Masurian
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 kaschubisch.png,
 Generally, religious demographics of the early modern period hardly changed. Still, there were almost entirely Catholic areas (Lower and Upper Bavaria, northern Westphalia, Upper Silesia, etc.) and almost entirely Protestant areas (Schleswig-Holstein, Pomerania, Saxony, etc.). Confessional prejudices, especially towards mixed marriages, were still common. Bit by bit, through internal migration, religious blending was more and more common. In eastern territories, confession was almost uniquely perceived to be connected to one's ethnicity and the equation "Protestant = German, Catholic = Polish" was held to be valid. In areas affected by immigration in the Ruhr area and Westphalia, as well as in some large cities, religious landscape changed substantially. This was especially true in largely Catholic areas of Westphalia, which changed through Protestant immigration from the eastern provinces.
Politically, the confessional division of Germany had considerable consequences. In Catholic areas, the Centre Party had a big electorate. On the other hand, Social Democrats and Free Trade Unions usually received hardly any votes in the Catholic areas of the Ruhr. This began to change with the secularization arising in the last decades of the German Empire.
In Germany's overseas colonial empire, millions of subjects practiced various
Generally, religious demographics of the early modern period hardly changed. Still, there were almost entirely Catholic areas (Lower and Upper Bavaria, northern Westphalia, Upper Silesia, etc.) and almost entirely Protestant areas (Schleswig-Holstein, Pomerania, Saxony, etc.). Confessional prejudices, especially towards mixed marriages, were still common. Bit by bit, through internal migration, religious blending was more and more common. In eastern territories, confession was almost uniquely perceived to be connected to one's ethnicity and the equation "Protestant = German, Catholic = Polish" was held to be valid. In areas affected by immigration in the Ruhr area and Westphalia, as well as in some large cities, religious landscape changed substantially. This was especially true in largely Catholic areas of Westphalia, which changed through Protestant immigration from the eastern provinces.
Politically, the confessional division of Germany had considerable consequences. In Catholic areas, the Centre Party had a big electorate. On the other hand, Social Democrats and Free Trade Unions usually received hardly any votes in the Catholic areas of the Ruhr. This began to change with the secularization arising in the last decades of the German Empire.
In Germany's overseas colonial empire, millions of subjects practiced various
Verbreitung der Konfessionen im deutschen Reich.jpg, Distribution of Protestants and Catholics in Imperial Germany
Meyers b4 s0817a.jpg, Distribution of Protestants, Catholics and Jews in Imperial Germany (Meyers Konversationslexikon)
Verbreitung der Juden im deutschen Reich.jpg, Distribution of Jews in Imperial Germany
Greater imperial coat of arms of Germany.svg, Greater Imperial coat of arms of Germany
Middle imperial coat of arms of Germany.svg, Middle Imperial coat of arms of Germany
Wappen Deutsches Reich - Reichsadler 1889.svg, Lesser Imperial coat of arms of Germany
 Under Bismarck, a united German state had finally been achieved, but it remained a Prussian-dominated state and did not include German Austria as Pan-German nationalists had desired. The influence of Prussian militarism, the Empire's colonial efforts and its vigorous, competitive industrial prowess all gained it the dislike and envy of other nations. The German Empire enacted a number of progressive reforms, such as Europe's first social welfare system and freedom of press. There was also a modern system for electing the federal parliament, the Reichstag, in which every adult man had one vote. This enabled the Socialists and the Catholic Centre Party to play considerable roles in the empire's political life despite the continued hostility of Prussian aristocrats.
The era of the German Empire is well remembered in Germany as one of great cultural and intellectual vigour. Thomas Mann published his novel '' Buddenbrooks'' in 1901. Theodor Mommsen received the Nobel prize for literature a year later for his Roman history. Painters like the groups Der Blaue Reiter and Die Brücke made a significant contribution to modern art. The AEG turbine factory in Berlin by Peter Behrens from 1909 was a milestone in classic modern architecture and an outstanding example of emerging functionalism. The social, economic, and scientific successes of this '' Gründerzeit'', or founding epoch, have sometimes led the Wilhelmine era to be regarded as a golden age.
In the field of economics, the "''Kaiserzeit''" laid the foundation of Germany's status as one of the world's leading economic powers. The iron and coal industries of the
Under Bismarck, a united German state had finally been achieved, but it remained a Prussian-dominated state and did not include German Austria as Pan-German nationalists had desired. The influence of Prussian militarism, the Empire's colonial efforts and its vigorous, competitive industrial prowess all gained it the dislike and envy of other nations. The German Empire enacted a number of progressive reforms, such as Europe's first social welfare system and freedom of press. There was also a modern system for electing the federal parliament, the Reichstag, in which every adult man had one vote. This enabled the Socialists and the Catholic Centre Party to play considerable roles in the empire's political life despite the continued hostility of Prussian aristocrats.
The era of the German Empire is well remembered in Germany as one of great cultural and intellectual vigour. Thomas Mann published his novel '' Buddenbrooks'' in 1901. Theodor Mommsen received the Nobel prize for literature a year later for his Roman history. Painters like the groups Der Blaue Reiter and Die Brücke made a significant contribution to modern art. The AEG turbine factory in Berlin by Peter Behrens from 1909 was a milestone in classic modern architecture and an outstanding example of emerging functionalism. The social, economic, and scientific successes of this '' Gründerzeit'', or founding epoch, have sometimes led the Wilhelmine era to be regarded as a golden age.
In the field of economics, the "''Kaiserzeit''" laid the foundation of Germany's status as one of the world's leading economic powers. The iron and coal industries of the
 }), an uninhabited hill and some nearby slivers of land, annexed by the Netherlands after WWII
, -
, style="background: white; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" ,
}), an uninhabited hill and some nearby slivers of land, annexed by the Netherlands after WWII
, -
, style="background: white; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" ,
Modern Germany; her political and economic problems, her foreign and domestic policy, her ambitions, and the causes of her success
' (1907) * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. ''Modern Germany: society, economy, and politics in the twentieth century'' (1987
ACLS E-book
* Berghahn, Volker Rolf. ''Imperial Germany, 1871–1914: Economy, Society, Culture, and Politics'' (2nd ed. 2005) * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. "German Colonialism and Imperialism from Bismarck to Hitler". ''German Studies Review'', vol. 40, no. 1 (2017) pp. 147–16
Online
* Blackbourn, David. ''The Long Nineteenth Century: A History of Germany, 1780–1918'' (1998
excerpt and text search
* Blackbourn, David, and Geoff Eley. ''The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany (1984) * Blanke, Richard. ''Prussian Poland in the German Empire'' (1981) * Brandenburg, Erich. ''From Bismarck to the World War: A History of German Foreign Policy 1870–1914'' (1927
online
* Carroll, E. Malcolm.
Germany and the great powers, 1866–1914: A study in public opinion and foreign policy
' (1938); 862pp; written for advanced students. * Cecil, Lamar. ''Wilhelm II: Prince and Emperor, 1859–1900'' (1989); vol 2: ''Wilhelm II: Emperor and Exile, 1900–1941'' (1996
vol 2 online
* Chickering, Roger. ''Imperial Germany and the Great War, 1914–1918'' (2nd ed. 2004
excerpt and text search
* Clark, Christopher. '' Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947'' (2006), the standard scholarly survey
online
* Dawson, William Harbutt.
The Evolution of Modern Germany
' (1908), 503 pages, covers 1871–1906 with focus on social and economic history and colonies * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Bismarck and state socialism; an exposition of the social and economic legislation of Germany since 1870
' (1890) 175 pages * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Municipal life and government in Germany
' (1914); 507 pages, describes the workings of local government and bureaucracy * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Germany and the Germans
' (1894) 387pp; politics and parties, Volume 2 * Eyck, Erich. ''Bismarck and the German Empire'' (1964
excerpt and text search
* Fife, Robert Herndon. (1916). ''The German Empire between Two Wars; a Study of the Political and Social Development of the Nation between 1871 and 1914.'' New York: Macmillan Company. *
excerpt
* Haardt, Oliver FR. "The Kaiser in the Federal State, 1871–1918." ''German History'' 34.4 (2016): 529–554
online
* * Hewitson, Mark. "Germany and France before the First World War: a reassessment of Wilhelmine foreign policy." ''English Historical Review'' 115.462 (2000): 570–606; argues Germany had a growing sense of military superiority * Holborn, Hajo. ''A History of Modern Germany: 1840–1945'' (1969), pp. 173–53
online
* Hoyer, Katja. ''Blood and Iron: The Rise and Fall of the German Empire 1871-1918'' (2021) * Jefferies, Mattew. ''Imperial Culture in Germany, 1871–1918''. (Palgrave, 2003) . * Kennedy, Paul
''The Rise of the Anglo-German Antagonism, 1860–1914''
(2nd ed. 1988) * Koch, Hannsjoachim W. ''A constitutional history of Germany in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries'' (1984). * Kurlander, Eric. ''The Price of Exclusion: Ethnicity, National Identity, and the Decline of German Liberalism, 1898–1933'' (2007). * Levy, Richard S. ''The Downfall of the Anti-Semitic Political Parties in Imperial Germany'' (Yale University Press, 1975). * Levy, Richard S. ed. ''Antisemitism: A historical encyclopedia of prejudice and persecution'' (2 vol Abc-clio, 2005). * Milward, Alan S. and S. B. Saul. ''The Development of the Economies of Continental Europe: 1850–1914'' (1977) pp. 17–70. * Mombauer, Annika and Wilhelm Deist, eds. ''The Kaiser: New Research on Wilhelm II's Role in Imperial Germany'' (2003) * Mommsen, Wolfgang. ''Imperial Germany 1867–1918: Politics, Culture, and Society in an Authoritarian State''. (1995). . * Nipperdey, Thomas. ''Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck'' (1996) dense coverage of chief topics
online
* Padfield, Peter. ''The Great Naval Race: Anglo-German Naval Rivalry 1900–1914'' (2005) * Ragins, Sanford. ''Jewish Responses to Anti-Semitism in Germany, 1870–1914: A Study in the History of Ideas'' (ISD, 1980). * * Retallack, James. ''Germany in the Age of Kaiser Wilhelm II'', (1996) . * Retallack, James. ''Imperial Germany 1871–1918'' (2008) * Rich, Norman. "The Question of National Interest in Imperial German Foreign Policy: Bismarck, William II, and the Road to World War I." ''Naval War College Review'' (1973) 26#1: 28-41
online
* Ritter, Gerhard. ''The Sword and the Scepter; the Problem of Militarism in Germany''. (4 vol University of Miami Press 1969–1973) * Richie, Alexandra. ''Faust's Metropolis: A History of Berlin'' (1998), 1139 pages, pp. 188–233 * Sagarra, Eda. ''A Social History of Germany, 1648–1914'' (1977
online
* Scheck, Raffael
(2008), a brief textbook by a leading scholar * Schollgen, Gregor. ''Escape into War? The Foreign Policy of Imperial Germany''. (Berg, 1990) . * Smith, Helmut Walser, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern German History'' (2011), 862 pp; 35 essays by specialists; Germany since 176
excerpt
* Smith, Woodruff D. ''The German Colonial Empire'' (1978 * Sperber, Jonathan. ''The Kaiser's Voters: Electors and Elections in Imperial Germany'' (1997
online review
* Stern, Fritz. ''Gold and Iron: Bismarck, Bleichroder, and the Building of the German Empire'' (1979) Bismarck worked closely with this leading banker and financie
excerpt and text search
* Steinberg, Jonathan. ''Bismarck: A Life'' (2011), a recent scholarly biography; emphasis on Bismarck's personalit
online
* Steinmetz, George (2007) ''The Devil's Handwriting: Precoloniality and the German Colonial State in Qingdao, Samoa, and Southwest Africa''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. * Taylor, A.J.P. ''Bismarck: The Man and the Statesman'' (1967
online
* Wehler, Hans-Ulrich. ''The German Empire, 1871–1918''. (Berg, 1985). * Wildenthal, Lora. ''German Women for Empire, 1884–1945'' (2001) ::Historiography * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. "Structure and Agency in Wilhelmine Germany: The history of the German Empire, Past, present and Future," in Annika Mombauer and Wilhelm Deist, eds. ''The Kaiser: New Research on Wilhelm II's Role in Imperial Germany'' (2003) pp. 281–293, historiography * Chickering, Roger, ed. ''Imperial Germany: A Historiographical Companion'' (1996), 552pp; 18 essays by specialists * Dickinson, Edward Ross. "The German Empire: an Empire?" ''History Workshop Journal'' Issue 66, (Autumn 2008
online
in Project MUSE, with guide to recent scholarship * * Jefferies, Matthew. ''Contesting the German Empire 1871–1918'' (2008
excerpt and text search
* Müller, Sven Oliver, and Cornelius Torp, ed. ''Imperial Germany Revisited: Continuing Debates and New Perspectives'' (2011) * Reagin, Nancy R. "Recent Work on German National Identity: Regional? Imperial? Gendered? Imaginary?" ''Central European History'' (2004) v 37, pp. 273–289 ::Primary sources * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Germany at Home
' (1908) 275 pp; popular description of social life in villages and cities * Vizetelly, Henry.
Berlin Under the New Empire: Its Institutions, Inhabitants, Industry, Monuments, Museums, Social Life, Manners, and Amusements
' (2 vol. London, 1879) Volume 2
Ravenstein's Atlas of the German Empire
, Library.wis.edu
Gemeindeverzeichnis.de
German Reich map of states 1913 (300 dpi)
Dissemination of the German Language 1913 (map, 300 dpi)
Dissemination of the main foreign mother tongues in the German Reich 1913 (map, 300 dpi)
{{Authority control Former countries in Europe Former empires Former monarchies of Europe Former monarchies Modern history of Germany . . . . . Germanic empires States and territories established in 1871 States and territories disestablished in 1918 * * 19th century in Germany 20th century in Germany by period
The German Empire
" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a
republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
.
The empire was founded
Founding may refer to:
* The formation of a corporation, government, or other organization
* The laying of a building's Foundation
* The casting of materials in a mold
See also
* Foundation (disambiguation)
* Incorporation (disambiguation)
In ...
on 18 January 1871, when the south German states, except for Austria, joined the North German Confederation and the new constitution came into force on April 16, changing the name of the federal state to the German Empire and introducing the title of German Emperor
The German Emperor (german: Deutscher Kaiser, ) was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the off ...
for Wilhelm I, King of Prussia from the House of Hohenzollern. Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
remained its capital, and Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
, Minister President of Prussia, became Chancellor, the head of government. As these events occurred, the Prussian-led North German Confederation and its southern German allies, such as Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, Württemburg and Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Da ...
, were still engaged in the Franco-Prussian War.
The German Empire consisted of 25 states, each with their own nobility, four constituent kingdoms, six grand duchies
A grand duchy is a country or territory whose official head of state or ruler is a monarch bearing the title of grand duke or grand duchess.
Relatively rare until the abolition of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the term was often used in the o ...
, five duchies (six before 1876), seven principalities, three free
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything
* Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism
* Emancipate, to procur ...
Hanseatic cities, and one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds of the Empire's population and territory, and Prussian dominance was also constitutionally established, since the King of Prussia was also the German Emperor (''Deutscher Kaiser'').
After 1850, the states of Germany had rapidly become industrialized, with particular strengths in coal, iron (and later steel), chemicals, and railways. In 1871, Germany had a population of 41 million people; by 1913, this had increased to 68 million. A heavily rural collection of states in 1815, the now united Germany became predominantly urban. The success of German industrialization manifested itself in two ways since the early 20th century: the German factories were larger and more modern than their British and French counterparts.Germany article of Encyclopedia Britannia, Link /ref> The dominance of the German Empire in the natural sciences, especially in physics and chemistry, was such that one-third of all Nobel Prizes went to German inventors and researchers. During its 47 years of existence, the German Empire became the industrial, technological, and scientific giant of Europe, and by 1913, Germany was the largest economy in Continental Europe and the third-largest in the world. Germany also became a great power, it built up the longest railway network of Europe, the world's strongest army, and a fast-growing industrial base. Starting very small in 1871, in a decade, the
navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
became second only to Britain's Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
.
From 1871 to 1890, Otto von Bismarck's tenure as the first and to this day longest-serving Chancellor was marked by relative liberalism at its start, but in time grew more conservative. Broad reforms and the Kulturkampf
(, 'culture struggle') was the conflict that took place from 1872 to 1878 between the Catholic Church led by Pope Pius IX and the government of Prussia led by Otto von Bismarck. The main issues were clerical control of education and ecclesiastic ...
marked his period in the office. Despite his hatred of liberalism and socialism – he called liberals and socialists "enemies of the Reich" – social programs introduced by Bismarck included old-age pensions, accident insurance, medical care and unemployment insurance, all aspects of the modern European welfare state.
Late in Bismarck's chancellorship and in spite of his earlier personal opposition, Germany became involved in colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their rel ...
. Claiming much of the leftover territory that was yet unclaimed in the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
, it managed to build the third-largest colonial empire at the time, after the British and the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
ones. As a colonial state, it sometimes clashed with the interests of other European powers, especially the British Empire. During its colonial expansion, the German Empire committed the Herero and Namaqua genocide.
After the removal of Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
by Wilhelm II in 1890, the empire embarked on '' Weltpolitik'' ("world politics") – a bellicose new course that ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War I. Bismarck's successors were incapable of maintaining their predecessor's complex, shifting, and overlapping alliances which had kept Germany from being diplomatically isolated. This period was marked by various factors influencing the Emperor's decisions, which were often perceived as contradictory or unpredictable by the public. In 1879, the German Empire consolidated the Dual Alliance with Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, followed by the Triple Alliance Triple Alliance may refer to:
* Aztec Triple Alliance (1428–1521), Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan and in central Mexico
* Triple Alliance (1596), England, France, and the Dutch Republic to counter Spain
* Triple Alliance (1668), England, the ...
with Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in 1882. It also retained strong diplomatic ties to the Ottoman Empire. When the great crisis of 1914 arrived, Italy left the alliance and the Ottoman Empire formally allied with Germany.
In the First World War, German plans to capture Paris quickly in the autumn of 1914 failed, and the war on the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
became a stalemate. The Allied naval blockade caused severe shortages of food and supplements. However, Imperial Germany had success on the Eastern Front; it occupied a large amount of territory to its east following the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. The German declaration of unrestricted submarine warfare in early 1917 contributed to bringing the United States into the war. In October 1918, after the failed Spring Offensive, the German armies were in retreat, allies Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire had collapsed, and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
had surrendered. The empire collapsed in the November 1918 Revolution with the abdications of its monarch, which left the post-war federal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected representatives ...
to govern a devastated populace. The Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
imposed post-war reparation costs of 132 billion gold marks (around US$269 billion or €240 billion in 2019, or roughly US$32 billion in 1921), as well as limiting the army to 100,000 men and disallowing conscription, armored vehicles, submarines, aircraft, and more than six battleships. The consequential economic devastation, later exacerbated by the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion ...
, as well as humiliation and outrage experienced by the German population are considered leading factors in the rise of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
and Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
.
History
Background
 The German Confederation had been created by an act of the
The German Confederation had been created by an act of the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
on 8 June 1815 as a result of the Napoleonic Wars, after being alluded to in Article 6 of the 1814 Treaty of Paris.
The liberal Revolutions of 1848 were crushed after the relations between the educated, well-off middle-class liberals and the urban artisans broke down; Otto von Bismarck's pragmatic '' Realpolitik'', which appealed to peasants as well as the traditional aristocracy, took its place. Bismarck sought to extend Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
hegemony throughout the German states; to do so meant unification of the German states and the exclusion of Prussia's main German rival, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, from the subsequent German Empire. He envisioned a conservative, Prussian-dominated Germany. The Second Schleswig War against Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
in 1864, the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, and the Franco-Prussian War in 1870–1871 sparked a growing pan-German ideal and contributed to the formation of a German State.
The German Confederation ended as a result of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 between the constituent Confederation entities of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
and its allies on one side and Prussia and its allies on the other. The war resulted in the partial replacement of the Confederation in 1867 by a North German Confederation, comprising the 22 states north of the river Main. The patriotic fervor generated by the Franco-Prussian War overwhelmed the remaining opposition to a unified Germany (aside from Austria) in the four states south of the Main, and during November 1870, they joined the North German Confederation by treaty.
Foundation
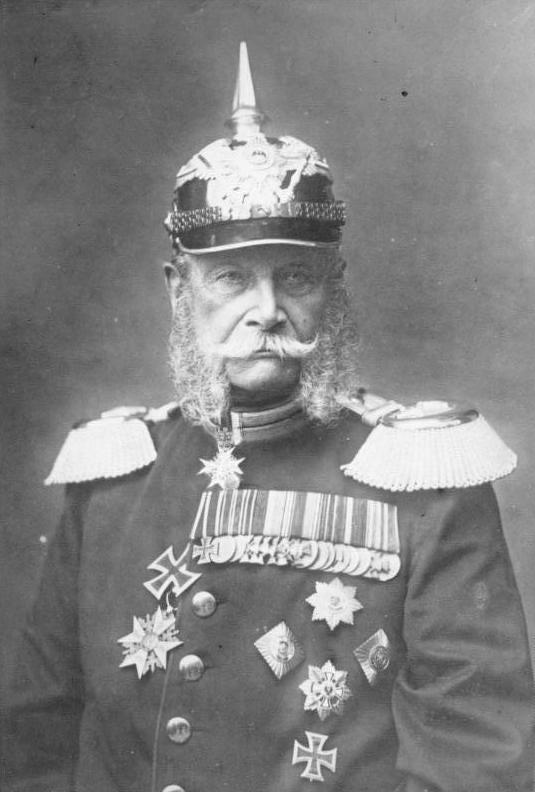
 On 10 December 1870, the North German Confederation Reichstag renamed the Confederation the "German Empire" and gave the title of
On 10 December 1870, the North German Confederation Reichstag renamed the Confederation the "German Empire" and gave the title of German Emperor
The German Emperor (german: Deutscher Kaiser, ) was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the off ...
to William I, the King of Prussia, as ''Bundespräsidium'' of the Confederation. The new constitution ( Constitution of the German Confederation) and the title Emperor came into effect on 1 January 1871. During the Siege of Paris on 18 January 1871, William accepted to be proclaimed Emperor in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 19 ...
.
The second German Constitution, adopted by the Reichstag on 14 April 1871 and proclaimed by the Emperor on 16 April, was substantially based upon Bismarck's North German Constitution The North German Constitution was the constitution of the North German Confederation, which existed as a country from 1 July 1867 to 31 December 1870. The Constitution of the German Empire (1871) was closely based on it.
A constituent Reichstag w ...
. The political system remained the same. The empire had a parliament called the '' Reichstag'', which was elected by universal male suffrage. However, the original constituencies drawn in 1871 were never redrawn to reflect the growth of urban areas. As a result, by the time of the great expansion of German cities in the 1890s and 1900s, rural areas were grossly over-represented.
The legislation also required the consent of the '' Bundesrat'', the federal council of deputies from the 27 states. Executive power was vested in the emperor, or ''Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
'', who was assisted by a Chancellor responsible only to him. The emperor was given extensive powers by the constitution. He alone appointed and dismissed the chancellor (so in practice, the emperor ruled the empire through the chancellor), was supreme commander-in-chief of the armed forces, and final arbiter of all foreign affairs, and could also disband the ''Reichstag'' to call for new elections. Officially, the chancellor was a one-man cabinet and was responsible for the conduct of all state affairs; in practice, the State Secretaries (top bureaucratic officials in charge of such fields as finance, war, foreign affairs, etc.) functioned much like ministers in other monarchies. The ''Reichstag'' had the power to pass, amend, or reject bills and to initiate legislation. However, as mentioned above, in practice, the real power was vested in the emperor, who exercised it through his chancellor.
Although nominally a federal empire and league of equals, in practice, the empire was dominated by the largest and most powerful state, Prussia. Prussia stretched across the northern two-thirds of the new ''Reich'' and contained three-fifths of its population. The imperial crown was hereditary in the ruling house of Prussia, the House of Hohenzollern. With the exception of 1872–1873 and 1892–1894, the chancellor was always simultaneously the prime minister of Prussia. With 17 out of 58 votes in the ''Bundesrat'', Berlin needed only a few votes from the smaller states to exercise effective control.
The other states retained their own governments but had only limited aspects of sovereignty. For example, both postage stamps and currency were issued for the empire as a whole. Coins through one mark were also minted in the name of the empire, while higher-valued pieces were issued by the states. However, these larger gold and silver issues were virtually commemorative coins and had limited circulation.
While the states issued their own decorations and some had their own armies, the military forces of the smaller ones were put under Prussian control. Those of the larger states, such as the Kingdoms of Bavaria and Saxony, were coordinated along Prussian principles and would, in wartime, be controlled by the federal government.
The evolution of the German Empire is somewhat in line with parallel developments in Italy, which became a united nation-state a decade earlier. Some key elements of the German Empire's authoritarian political structure were also the basis for conservative modernization in Imperial Japan under Meiji and the preservation of an authoritarian political structure under the tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
s in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
.
One factor in the social anatomy of these governments was the retention of a very substantial share in political power by the landed elite, the Junkers, resulting from the absence of a revolutionary breakthrough by the peasants in combination with urban areas.
Although authoritarian in many respects, the empire had some democratic features. Besides universal suffrage, it permitted the development of political parties. Bismarck intended to create a constitutional façade that would mask the continuation of authoritarian policies. In the process, he created a system with a serious flaw. There was a significant disparity between the Prussian and German electoral systems. Prussia used a highly restrictive three-class voting system in which the richest third of the population could choose 85% of the legislature, all but assuring a conservative majority. As mentioned above, the king and (with two exceptions) the prime minister of Prussia was also the emperor and chancellor of the empire – meaning that the same rulers had to seek majorities from legislatures elected from completely different franchises. Universal suffrage was significantly diluted by gross over-representation of rural areas from the 1890s onward. By the turn of the century, the urban-rural population balance was completely reversed from 1871; more than two-thirds of the empire's people lived in cities and towns.
Bismarck era
Bismarck's domestic policies played an important role in forging the authoritarian political culture of the ''Kaiserreich''. Less preoccupied with continental power politics following unification in 1871, Germany's semi-parliamentary government carried out a relatively smooth economic and political revolution from above that pushed them along the way towards becoming the world's leading industrial power of the time. Bismarck's "revolutionary conservatism" was a conservative state-building strategy designed to make ordinary Germans—not just the Junker elite—more loyal to the throne and empire. According to Kees van Kersbergen and Barbara Vis, his strategy was: Bismarck created the modern welfare state in Germany in the 1880s and enacted universal male suffrage in 1871. He became a great hero to German conservatives, who erected many monuments to his memory and tried to emulate his policies.Foreign policy
 Bismarck's post-1871 foreign policy was conservative and sought to preserve the balance of power in Europe. British historian
Bismarck's post-1871 foreign policy was conservative and sought to preserve the balance of power in Europe. British historian Eric Hobsbawm
Eric John Ernest Hobsbawm (; 9 June 1917 – 1 October 2012) was a British historian of the rise of industrial capitalism, socialism and nationalism. A life-long Marxist, his socio-political convictions influenced the character of his work. H ...
concludes that he "remained undisputed world champion at the game of multilateral diplomatic chess for almost twenty years after 1871, evoting
Electronic voting (also known as e-voting) is voting that uses electronic means to either aid or take care of casting and counting ballots.
Depending on the particular implementation, e-voting may use standalone ''electronic voting machines'' ( ...
himself exclusively, and successfully, to maintaining peace between the powers". This was a departure from his adventurous foreign policy for Prussia, where he favored strength and expansion, punctuating this by saying, "The great questions of the age are not settled by speeches and majority votes – this was the error of 1848–49 – but by iron and blood."
Bismarck's chief concern was that France would plot revenge after its defeat in the Franco-Prussian War. As the French lacked the strength to defeat Germany by themselves, they sought an alliance with Russia, which would trap Germany between the two in a war (as would ultimately happen in 1914). Bismarck wanted to prevent this at all costs and maintain friendly relations with the Russians and thereby formed an alliance with them and Austria-Hungary, the ''Dreikaiserbund
The League of the Three Emperors or Union of the Three Emperors (german: Dreikaiserbund) was an alliance between the German, Russian and Austro-Hungarian Empires, from 1873 to 1887. Chancellor Otto von Bismarck took full charge of German foreign p ...
'' (League of Three Emperors), in 1881. The alliance was further cemented by a separate non-aggression pact with Russia called Reinsurance Treaty, which was signed in 1887. During this period, individuals within the German military were advocating a preemptive strike against Russia, but Bismarck knew that such ideas were foolhardy. He once wrote that "the most brilliant victories would not avail against the Russian nation, because of its climate, its desert, and its frugality, and having but one frontier to defend", and because it would leave Germany with another bitter, resentful neighbor.
Meanwhile, the chancellor remained wary of any foreign policy developments that looked even remotely warlike. In 1886, he moved to stop an attempted sale of horses to France because they might be used for cavalry and also ordered an investigation into large Russian purchases of medicine from a German chemical works. Bismarck stubbornly refused to listen to Georg Herbert Münster, ambassador to France, who reported back that the French were not seeking a revanchist war and were desperate for peace at all costs.
Bismarck and most of his contemporaries were conservative-minded and focused their foreign policy attention on Germany's neighboring states. In 1914, 60% of German foreign investment was in Europe, as opposed to just 5% of British investment. Most of the money went to developing nations such as Russia that lacked the capital or technical knowledge to industrialize on their own. The construction of the Berlin–Baghdad railway, financed by German banks, was designed to eventually connect Germany with the Ottoman Empire and the Persian Gulf, but it also collided with British and Russian geopolitical interests. Conflict over the Baghdad Railway was resolved in June 1914.
Many consider Bismarck's foreign policy as a coherent system and partly responsible for the preservation of Europe's stability. It was also marked by the need to balance circumspect defensiveness and the desire to be free from the constraints of its position as a major European power. Bismarck's successors did not pursue his foreign policy legacy. For instance, Kaiser Wilhelm II, who dismissed the chancellor in 1890, let the treaty with Russia lapse in favor of Germany's alliance with Austria, which finally led to a stronger coalition-building between Russia and France.
Colonies
 Germans had dreamed of colonial imperialism since 1848. Although Bismarck had little interest in acquiring overseas possessions, most Germans were enthusiastic, and by 1884 he had acquired German New Guinea. By the 1890s, German colonial expansion in Asia and the Pacific ( Kiauchau in China, Tientsin in China, the
Germans had dreamed of colonial imperialism since 1848. Although Bismarck had little interest in acquiring overseas possessions, most Germans were enthusiastic, and by 1884 he had acquired German New Guinea. By the 1890s, German colonial expansion in Asia and the Pacific ( Kiauchau in China, Tientsin in China, the Marianas
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
, the Caroline Islands, Samoa) led to frictions with the UK, Russia, Japan, and the US. The largest colonial enterprises were in Africa, where the Herero Wars in what is now Namibia in 1906–1907 resulted in the Herero and Namaqua genocide.
Economy
By 1900, Germany became the largest economy in continentalEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
and the third-largest in the world behind the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
and the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
, which were also its main economic rivals. Throughout its existence, it experienced economic growth and modernization led by heavy industry. In 1871, it had a largely rural population of 41 million, while by 1913, this had increased to a predominantly urban population of 68 million.
Industrial power
 For 30 years, Germany struggled against Britain to be Europe's leading industrial power. Representative of Germany's industry was the steel giant
For 30 years, Germany struggled against Britain to be Europe's leading industrial power. Representative of Germany's industry was the steel giant Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krup ...
, whose first factory was built in Essen
Essen (; Latin: ''Assindia'') is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and D ...
. By 1902, the factory alone became "A great city with its own streets, its own police force, fire department and traffic laws. There are 150 kilometers of rail, 60 different factory buildings, 8,500 machine tools, seven electrical stations, 140 kilometers of underground cable, and 46 overhead."
Under Bismarck, Germany was a world innovator in building the welfare state. German workers enjoyed health, accident and maternity benefits, canteens, changing rooms, and a national pension scheme.E. P. Hennock, ''The Origin of the Welfare State in England and Germany, 1850–1914: Social Policies Compared'' (2007)
Industrialisation progressed dynamically in Germany, and German manufacturers began to capture domestic markets from British imports, and also to compete with British industry abroad, particularly in the U.S. The German textile and metal industries had by 1870 surpassed those of Britain in organisation and technical efficiency and superseded British manufacturers in the domestic market. Germany became the dominant economic power on the continent and was the second-largest exporting nation after Britain.
Technological progress during German industrialisation occurred in four waves: the railway wave (1877–1886), the dye wave (1887–1896), the chemical wave (1897–1902), and the wave of electrical engineering (1903–1918). Since Germany industrialised later than Britain, it was able to model its factories after those of Britain, thus making more efficient use of its capital and avoiding legacy methods in its leap to the envelope of technology. Germany invested more heavily than the British in research, especially in chemistry, motors and electricity. Germany's dominance in physics and chemistry was such that one-third of all Nobel Prizes went to German inventors and researchers.
The German cartel system (known as ''Konzerne''), being significantly concentrated, was able to make more efficient use of capital. Germany was not weighted down with an expensive worldwide empire that needed defense. Following Germany's annexation of Alsace-Lorraine in 1871, it absorbed parts of what had been France's industrial base.
Germany overtook British steel production in 1893 and pig iron production in 1903. The German steel and pig iron production continued its rapid expansion: Between 1911 and 1913, the German steel and pig iron output reached one quarter of total global production.
By 1900, the German chemical industry dominated the world market for synthetic dyes
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
. The three major firms BASF, Bayer and Hoechst produced several hundred different dyes, along with the five smaller firms. Imperial Germany built up the world's largest chemical industry, the production of German chemical industry was 60% higher than that of the United States. In 1913, these eight firms produced almost 90% of the world supply of dyestuffs and sold about 80% of their production abroad. The three major firms had also integrated upstream into the production of essential raw materials and they began to expand into other areas of chemistry such as pharmaceuticals
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and rel ...
, photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of th ...
, agricultural chemicals and electrochemicals. Top-level decision-making was in the hands of professional salaried managers; leading Chandler to call the German dye companies "the world's first truly managerial industrial enterprises". There were many spinoffs from research—such as the pharmaceutical industry, which emerged from chemical research.
German factories were larger and more modern than their British and French counterparts. By 1913, the German electricity production was higher than the combined electricity production of Britain, France, Italy and Sweden.
By the start of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
(1914–1918), German industry switched to war production. The heaviest demands were on coal and steel for artillery and shell production, and on chemicals for the synthesis of materials that were subject to import restrictions and for chemical weapons and war supplies.
Railways
Lacking a technological base at first, the Germans imported their engineering and hardware from Britain but quickly learned the skills needed to operate and expand the railways. In many cities, the new railway shops were the centers of technological awareness and training, so that by 1850, Germany was self-sufficient in meeting the demands of railroad construction, and the railways were a major impetus for the growth of the new steel industry. However, German unification in 1870 stimulated consolidation, nationalisation into state-owned companies, and further rapid growth. Unlike the situation in France, the goal was support of industrialisation, and so heavy lines crisscrossed theRuhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
and other industrial districts and provided good connections to the major ports of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
and Bremen. By 1880, Germany had 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight, and forged ahead of France. The total length of German railroad tracks expanded from 21,000 km, (13,000 miles) in 1871 to 63,000 km, (39,000 miles) by 1913, establishing the largest rail network in the world after the United States The German rail network was followed by Austria-Hungary (), France (), the United Kingdom (), Italy () and Spain ().
Consolidation
The creation of the Empire under Prussian leadership was a victory for the concept of ''Kleindeutschland
{{more citations needed, date=April 2017
The term Lesser Germany (German: ''Kleindeutschland'') or Lesser German solution (German: Kleindeutsche Lösung) denoted essentially exclusion of Austria of the Habsburgs from the planned German unification ...
'' (Smaller Germany) over the ''Großdeutschland'' concept. This meant that Austria-Hungary, a multi-ethnic Empire with a considerable German-speaking population, would remain outside of the German nation state. Bismarck's policy was to pursue a solution diplomatically. The effective alliance between Germany and Austria played a major role in Germany's decision to enter World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in 1914.
Bismarck announced there would be no more territorial additions to Germany in Europe, and his diplomacy after 1871 was focused on stabilizing the European system and preventing any wars. He succeeded, and only after his departure from office in 1890 did the diplomatic tensions start rising again.
Social issues
After achieving formal unification in 1871, Bismarck devoted much of his attention to the cause of national unity. He opposed Catholic civil rights and emancipation, especially the influence of the Vatican underPope Pius IX
Pope Pius IX ( it, Pio IX, ''Pio Nono''; born Giovanni Maria Mastai Ferretti; 13 May 1792 – 7 February 1878) was head of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian ch ...
, and working-class radicalism, represented by the emerging Social Democratic Party.
Kulturkampf
 Prussia in 1871 included 16,000,000 Protestants, both Reformed and Lutheran, and 8,000,000 Catholics. Most people were generally segregated into their own religious worlds, living in rural districts or city neighbourhoods that were overwhelmingly of the same religion, and sending their children to separate public schools where their religion was taught. There was little interaction or intermarriage. On the whole, the Protestants had a higher social status, and the Catholics were more likely to be peasant farmers or unskilled or semiskilled industrial workers. In 1870, the Catholics formed their own political party, the Centre Party, which generally supported unification and most of Bismarck's policies. However, Bismarck distrusted parliamentary democracy in general and opposition parties in particular, especially when the Centre Party showed signs of gaining support among dissident elements such as the Polish Catholics in Silesia. A powerful intellectual force of the time was anti-Catholicism, led by the liberal intellectuals who formed a vital part of Bismarck's coalition. They saw the Catholic Church as a powerful force of reaction and anti-modernity, especially after the proclamation of papal infallibility in 1870, and the tightening control of the Vatican over the local bishops.
The Kulturkampf launched by Bismarck 1871–1880 affected Prussia; although there were similar movements in Baden and Hesse, the rest of Germany was not affected. According to the new imperial constitution, the states were in charge of religious and educational affairs; they funded the Protestant and Catholic schools. In July 1871 Bismarck abolished the Catholic section of the Prussian Ministry of ecclesiastical and educational affairs, depriving Catholics of their voice at the highest level. The system of strict government supervision of schools was applied only in Catholic areas; the Protestant schools were left alone.
Much more serious were the May laws of 1873. One made the appointment of any priest dependent on his attendance at a German university, as opposed to the seminaries that the Catholics typically used. Furthermore, all candidates for the ministry had to pass an examination in German culture before a state board which weeded out intransigent Catholics. Another provision gave the government a veto power over most church activities. A second law abolished the jurisdiction of the Vatican over the Catholic Church in Prussia; its authority was transferred to a government body controlled by Protestants.
Nearly all German bishops, clergy, and laymen rejected the legality of the new laws, and were defiant in the face of heavier and heavier penalties and imprisonments imposed by Bismarck's government. By 1876, all the Prussian bishops were imprisoned or in exile, and a third of the Catholic parishes were without a priest. In the face of systematic defiance, the Bismarck government increased the penalties and its attacks, and were challenged in 1875 when a papal encyclical declared the whole ecclesiastical legislation of Prussia was invalid, and threatened to excommunicate any Catholic who obeyed. There was no violence, but the Catholics mobilized their support, set up numerous civic organizations, raised money to pay fines, and rallied behind their church and the Centre Party. The "Old Catholic Church", which rejected the First Vatican Council, attracted only a few thousand members. Bismarck, a devout pietistic Protestant, realized his Kulturkampf was backfiring when secular and socialist elements used the opportunity to attack all religion. In the long run, the most significant result was the mobilization of the Catholic voters, and their insistence on protecting their religious identity. In the elections of 1874, the Centre party doubled its popular vote, and became the second-largest party in the national parliament—and remained a powerful force for the next 60 years, so that after Bismarck it became difficult to form a government without their support.
Prussia in 1871 included 16,000,000 Protestants, both Reformed and Lutheran, and 8,000,000 Catholics. Most people were generally segregated into their own religious worlds, living in rural districts or city neighbourhoods that were overwhelmingly of the same religion, and sending their children to separate public schools where their religion was taught. There was little interaction or intermarriage. On the whole, the Protestants had a higher social status, and the Catholics were more likely to be peasant farmers or unskilled or semiskilled industrial workers. In 1870, the Catholics formed their own political party, the Centre Party, which generally supported unification and most of Bismarck's policies. However, Bismarck distrusted parliamentary democracy in general and opposition parties in particular, especially when the Centre Party showed signs of gaining support among dissident elements such as the Polish Catholics in Silesia. A powerful intellectual force of the time was anti-Catholicism, led by the liberal intellectuals who formed a vital part of Bismarck's coalition. They saw the Catholic Church as a powerful force of reaction and anti-modernity, especially after the proclamation of papal infallibility in 1870, and the tightening control of the Vatican over the local bishops.
The Kulturkampf launched by Bismarck 1871–1880 affected Prussia; although there were similar movements in Baden and Hesse, the rest of Germany was not affected. According to the new imperial constitution, the states were in charge of religious and educational affairs; they funded the Protestant and Catholic schools. In July 1871 Bismarck abolished the Catholic section of the Prussian Ministry of ecclesiastical and educational affairs, depriving Catholics of their voice at the highest level. The system of strict government supervision of schools was applied only in Catholic areas; the Protestant schools were left alone.
Much more serious were the May laws of 1873. One made the appointment of any priest dependent on his attendance at a German university, as opposed to the seminaries that the Catholics typically used. Furthermore, all candidates for the ministry had to pass an examination in German culture before a state board which weeded out intransigent Catholics. Another provision gave the government a veto power over most church activities. A second law abolished the jurisdiction of the Vatican over the Catholic Church in Prussia; its authority was transferred to a government body controlled by Protestants.
Nearly all German bishops, clergy, and laymen rejected the legality of the new laws, and were defiant in the face of heavier and heavier penalties and imprisonments imposed by Bismarck's government. By 1876, all the Prussian bishops were imprisoned or in exile, and a third of the Catholic parishes were without a priest. In the face of systematic defiance, the Bismarck government increased the penalties and its attacks, and were challenged in 1875 when a papal encyclical declared the whole ecclesiastical legislation of Prussia was invalid, and threatened to excommunicate any Catholic who obeyed. There was no violence, but the Catholics mobilized their support, set up numerous civic organizations, raised money to pay fines, and rallied behind their church and the Centre Party. The "Old Catholic Church", which rejected the First Vatican Council, attracted only a few thousand members. Bismarck, a devout pietistic Protestant, realized his Kulturkampf was backfiring when secular and socialist elements used the opportunity to attack all religion. In the long run, the most significant result was the mobilization of the Catholic voters, and their insistence on protecting their religious identity. In the elections of 1874, the Centre party doubled its popular vote, and became the second-largest party in the national parliament—and remained a powerful force for the next 60 years, so that after Bismarck it became difficult to form a government without their support.
Social reform
Bismarck built on a tradition of welfare programs in Prussia and Saxony that began as early as in the 1840s. In the 1880s he introduced old-age pensions, accident insurance, medical care and unemployment insurance that formed the basis of the modernEuropean welfare state
The European social model is a concept that emerged in the discussion of economic globalization and typically contrasts the degree of employment regulation and social protection in European countries to conditions in the United States. It is comm ...
. He came to realize that this sort of policy was very appealing, since it bound workers to the state, and also fit in very well with his authoritarian nature. The social security systems installed by Bismarck (health care in 1883, accident insurance in 1884, invalidity and old-age insurance in 1889) at the time were the largest in the world and, to a degree, still exist in Germany today.
Bismarck's paternalistic programs won the support of German industry because its goals were to win the support of the working classes for the Empire and reduce the outflow of immigrants to America, where wages were higher but welfare did not exist. Bismarck further won the support of both industry and skilled workers by his high tariff policies, which protected profits and wages from American competition, although they alienated the liberal intellectuals who wanted free trade.
Antisemitism
As it was throughout Europe at the time, Antisemitism was endemic in Germany during the period. BeforeNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's decrees ended the ghettos in Confederation of the Rhine, it had been religiously motivated, but by the 19th century, it was a factor in German nationalism. In the popular mind Jews became a symbol of capitalism and wealth. On the other hand, the constitution and legal system protected the rights of Jews as German citizens. Antisemitic parties were formed but soon collapsed. But after the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
, and Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's rise to power in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, Antisemitism in Germany would increase.
Germanization
 One of the effects of the unification policies was the gradually increasing tendency to eliminate the use of non-German languages in public life, schools and academic settings with the intent of pressuring the non-German population to abandon their national identity in what was called "
One of the effects of the unification policies was the gradually increasing tendency to eliminate the use of non-German languages in public life, schools and academic settings with the intent of pressuring the non-German population to abandon their national identity in what was called "Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationa ...
". These policies often had the reverse effect of stimulating resistance, usually in the form of homeschooling and tighter unity in the minority groups, especially the Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
.
The Germanisation policies were targeted particularly against the significant Polish minority of the empire, gained by Prussia in the partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
. Poles were treated as an ethnic minority
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
even where they made up the majority, as in the Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (german: Provinz Posen, pl, Prowincja Poznańska) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920. Posen was established in 1848 following the Greater Poland Uprising as a successor to the Grand Duchy of Posen, w ...
, where a series of anti-Polish measures was enforced. Numerous anti-Polish laws had no great effect especially in the province of Posen where the German-speaking population dropped from 42.8% in 1871 to 38.1% in 1905, despite all efforts.
Law
 Bismarck's efforts also initiated the levelling of the enormous differences between the German states, which had been independent in their evolution for centuries, especially with legislation. The completely different legal histories and judicial systems posed enormous complications, especially for national trade. While a common trade code had already been introduced by the Confederation in 1861 (which was adapted for the Empire and, with great modifications, is still in effect today), there was little similarity in laws otherwise.
In 1871, a common was introduced; in 1877, common court procedures were established in the court system by the , code of civil procedure () and code of criminal procedure (). In 1873 the constitution was amended to allow the Empire to replace the various and greatly differing Civil Codes of the states (If they existed at all; for example, parts of Germany formerly occupied by Napoleon's France had adopted the French Civil Code, while in Prussia the of 1794 was still in effect). In 1881, a first commission was established to produce a common Civil Code for all of the Empire, an enormous effort that would produce the (BGB), possibly one of the most impressive legal works in the world; it was eventually put into effect on 1 January 1900. All of these codifications are, albeit with many amendments, still in effect today.
Bismarck's efforts also initiated the levelling of the enormous differences between the German states, which had been independent in their evolution for centuries, especially with legislation. The completely different legal histories and judicial systems posed enormous complications, especially for national trade. While a common trade code had already been introduced by the Confederation in 1861 (which was adapted for the Empire and, with great modifications, is still in effect today), there was little similarity in laws otherwise.
In 1871, a common was introduced; in 1877, common court procedures were established in the court system by the , code of civil procedure () and code of criminal procedure (). In 1873 the constitution was amended to allow the Empire to replace the various and greatly differing Civil Codes of the states (If they existed at all; for example, parts of Germany formerly occupied by Napoleon's France had adopted the French Civil Code, while in Prussia the of 1794 was still in effect). In 1881, a first commission was established to produce a common Civil Code for all of the Empire, an enormous effort that would produce the (BGB), possibly one of the most impressive legal works in the world; it was eventually put into effect on 1 January 1900. All of these codifications are, albeit with many amendments, still in effect today.
Year of the three emperors
 On 9 March 1888, Wilhelm I died shortly before his 91st birthday, leaving his son Frederick III as the new emperor. Frederick was a liberal and an admirer of the British constitution, while his links to Britain strengthened further with his marriage to Princess Victoria, eldest child of Queen Victoria. With his ascent to the throne, many hoped that Frederick's reign would lead to a liberalization of the Reich and an increase of parliament's influence on the political process. The dismissal of Robert von Puttkamer, the highly conservative Prussian interior minister, on 8 June was a sign of the expected direction and a blow to Bismarck's administration.
By the time of his accession, however, Frederick had developed incurable
On 9 March 1888, Wilhelm I died shortly before his 91st birthday, leaving his son Frederick III as the new emperor. Frederick was a liberal and an admirer of the British constitution, while his links to Britain strengthened further with his marriage to Princess Victoria, eldest child of Queen Victoria. With his ascent to the throne, many hoped that Frederick's reign would lead to a liberalization of the Reich and an increase of parliament's influence on the political process. The dismissal of Robert von Puttkamer, the highly conservative Prussian interior minister, on 8 June was a sign of the expected direction and a blow to Bismarck's administration.
By the time of his accession, however, Frederick had developed incurable laryngeal cancer
Laryngeal cancers are mostly squamous-cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the epithelium of the larynx.
Cancer can develop in any part of the larynx. The prognosis is affected by the location of the tumour. For the purposes of staging, ...
, which had been diagnosed in 1887. He died on the 99th day of his rule, on 15 June 1888. His son Wilhelm II became emperor.
Wilhelmine era
Bismarck's resignation
 Wilhelm II wanted to reassert his ruling prerogatives at a time when other monarchs in Europe were being transformed into constitutional figureheads. This decision led the ambitious Kaiser into conflict with Bismarck. The old chancellor had hoped to guide Wilhelm as he had guided his grandfather, but the emperor wanted to be the master in his own house and had many sycophants telling him that Frederick the Great would not have been great with a Bismarck at his side. A key difference between Wilhelm II and Bismarck was their approaches to handling political crises, especially in 1889, when German coal miners went on strike in Upper Silesia. Bismarck demanded that the
Wilhelm II wanted to reassert his ruling prerogatives at a time when other monarchs in Europe were being transformed into constitutional figureheads. This decision led the ambitious Kaiser into conflict with Bismarck. The old chancellor had hoped to guide Wilhelm as he had guided his grandfather, but the emperor wanted to be the master in his own house and had many sycophants telling him that Frederick the Great would not have been great with a Bismarck at his side. A key difference between Wilhelm II and Bismarck was their approaches to handling political crises, especially in 1889, when German coal miners went on strike in Upper Silesia. Bismarck demanded that the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, '' ...
be sent in to crush the strike, but Wilhelm II rejected this authoritarian measure, responding "I do not wish to stain my reign with the blood of my subjects." Instead of condoning repression, Wilhelm had the government negotiate with a delegation from the coal miners, which brought the strike to an end without violence. The fractious relationship ended in March 1890, after Wilhelm II and Bismarck quarrelled, and the chancellor resigned days later. Bismarck's last few years had seen power slip from his hands as he grew older, more irritable, more authoritarian, and less focused.
With Bismarck's departure, Wilhelm II became the dominant ruler of Germany. Unlike his grandfather, Wilhelm I, who had been largely content to leave government affairs to the chancellor, Wilhelm II wanted to be fully informed and actively involved in running Germany, not an ornamental figurehead, although most Germans found his claims of divine right to rule amusing. Wilhelm allowed politician Walther Rathenau to tutor him in European economics and industrial and financial realities in Europe.
As Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
(2004) notes, Bismarckian foreign policy "was too sedate for the reckless Kaiser". Wilhelm became internationally notorious for his aggressive stance on foreign policy and his strategic blunders (such as the Tangier Crisis
The First Moroccan Crisis or the Tangier Crisis was an international crisis between March 1905 and May 1906 over the status of Morocco. German Empire, Germany wanted to challenge French Third Republic, France's growing control over Morocco, aggr ...
), which pushed the German Empire into growing political isolation and eventually helped to cause World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
Domestic affairs
 Under Wilhelm II, Germany no longer had long-ruling strong chancellors like Bismarck. The new chancellors had difficulty in performing their roles, especially the additional role as Prime Minister of Prussia assigned to them in the German Constitution. The reforms of Chancellor Leo von Caprivi, which liberalized trade and so reduced unemployment, were supported by the Kaiser and most Germans except for Prussian landowners, who feared loss of land and power and launched several campaigns against the reforms.
While Prussian aristocrats challenged the demands of a united German state, in the 1890s several organizations were set up to challenge the authoritarian conservative Prussian militarism which was being imposed on the country. Educators opposed to the German state-run schools, which emphasized military education, set up their own independent liberal schools, which encouraged individuality and freedom. However nearly all the schools in Imperial Germany had a very high standard and kept abreast with modern developments in knowledge.
Artists began experimental art in opposition to Kaiser Wilhelm's support for traditional art, to which Wilhelm responded "art which transgresses the laws and limits laid down by me can no longer be called art". It was largely thanks to Wilhelm's influence that most printed material in Germany used blackletter instead of the Roman type used in the rest of Western Europe. At the same time, a new generation of cultural creators emerged.
Under Wilhelm II, Germany no longer had long-ruling strong chancellors like Bismarck. The new chancellors had difficulty in performing their roles, especially the additional role as Prime Minister of Prussia assigned to them in the German Constitution. The reforms of Chancellor Leo von Caprivi, which liberalized trade and so reduced unemployment, were supported by the Kaiser and most Germans except for Prussian landowners, who feared loss of land and power and launched several campaigns against the reforms.
While Prussian aristocrats challenged the demands of a united German state, in the 1890s several organizations were set up to challenge the authoritarian conservative Prussian militarism which was being imposed on the country. Educators opposed to the German state-run schools, which emphasized military education, set up their own independent liberal schools, which encouraged individuality and freedom. However nearly all the schools in Imperial Germany had a very high standard and kept abreast with modern developments in knowledge.
Artists began experimental art in opposition to Kaiser Wilhelm's support for traditional art, to which Wilhelm responded "art which transgresses the laws and limits laid down by me can no longer be called art". It was largely thanks to Wilhelm's influence that most printed material in Germany used blackletter instead of the Roman type used in the rest of Western Europe. At the same time, a new generation of cultural creators emerged.
 From the 1890s onwards, the most effective opposition to the monarchy came from the newly formed
From the 1890s onwards, the most effective opposition to the monarchy came from the newly formed Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been the ...
(SPD), whose radicals advocated Marxism. The threat of the SPD to the German monarchy and industrialists caused the state both to crack down on the party's supporters and to implement its own programme of social reform to soothe discontent. Germany's large industries provided significant social welfare programmes and good care to their employees, as long as they were not identified as socialists or trade-union members. The larger industrial firms provided pensions, sickness benefits and even housing to their employees.
Having learned from the failure of Bismarck's Kulturkampf
(, 'culture struggle') was the conflict that took place from 1872 to 1878 between the Catholic Church led by Pope Pius IX and the government of Prussia led by Otto von Bismarck. The main issues were clerical control of education and ecclesiastic ...
, Wilhelm II maintained good relations with the Roman Catholic Church and concentrated on opposing socialism. This policy failed when the Social Democrats won a third of the votes in the 1912 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 1912.
Asia
* 1912 Chinese National Assembly election (first election for the newly founded National Assembly of the Republic of China)
* 1912 Philippine Assembly elections
Europe
* 1912 German federal ...
to the ''Reichstag'', and became the largest political party in Germany. The government remained in the hands of a succession of conservative coalitions supported by right-wing liberals or Catholic clerics and heavily dependent on the Kaiser's favour. The rising militarism under Wilhelm II caused many Germans to emigrate to the U.S. and the British colonies to escape mandatory military service.
During World War I, the Kaiser increasingly devolved his powers to the leaders of the German High Command, particularly future President of Germany, Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg and ''Generalquartiermeister'' Erich Ludendorff. Hindenburg took over the role of commander–in–chief from the Kaiser, while Ludendorff became de facto general chief of staff. By 1916, Germany was effectively a military dictatorship run by Hindenburg and Ludendorff, with the Kaiser reduced to a mere figurehead.
Foreign affairs
=Colonialism
= Wilhelm II wanted Germany to have her " place in the sun", like Britain, which he constantly wished to emulate or rival. With German traders and merchants already active worldwide, he encouraged colonial efforts in Africa and the Pacific (" new imperialism"), causing the German Empire to vie with other European powers for remaining "unclaimed" territories. With the encouragement or at least the acquiescence of Britain, which at this stage saw Germany as a counterweight to her old rival France, Germany acquired German Southwest Africa (modern Namibia), German Kamerun (modern
Wilhelm II wanted Germany to have her " place in the sun", like Britain, which he constantly wished to emulate or rival. With German traders and merchants already active worldwide, he encouraged colonial efforts in Africa and the Pacific (" new imperialism"), causing the German Empire to vie with other European powers for remaining "unclaimed" territories. With the encouragement or at least the acquiescence of Britain, which at this stage saw Germany as a counterweight to her old rival France, Germany acquired German Southwest Africa (modern Namibia), German Kamerun (modern Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west- central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; th ...
), Togoland (modern Togo) and German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
(modern Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
, Burundi, and the mainland part of current Tanzania). Islands were gained in the Pacific through purchase and treaties and also a 99-year lease for the territory of Kiautschou in northeast China. But of these German colonies only Togoland and German Samoa (after 1908) became self-sufficient and profitable; all the others required subsidies from the Berlin treasury for building infrastructure, school systems, hospitals and other institutions.
Hun
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
invaders of continental Europe – an unfortunate remark that would later be resurrected by British propagandists to paint Germans as barbarians during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. On two occasions, a French-German conflict over the fate of Morocco seemed inevitable.
 Upon acquiring Southwest Africa, German settlers were encouraged to cultivate land held by the
Upon acquiring Southwest Africa, German settlers were encouraged to cultivate land held by the Herero
Herero may refer to:
* Herero people, a people belonging to the Bantu group, with about 240,000 members alive today
* Herero language, a language of the Bantu family (Niger-Congo group)
* Herero and Namaqua Genocide
* Herero chat, a species of b ...
and Nama. Herero and Nama tribal lands were used for a variety of exploitative goals (much as the British did before in Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of S ...
), including farming, ranching, and mining for minerals and diamonds. In 1904, the Herero and the Nama revolted against the colonists in Southwest Africa, killing farm families, their laborers and servants. In response to the attacks, troops were dispatched to quell the uprising which then resulted in the Herero and Namaqua Genocide. In total, some 65,000 Herero (80% of the total Herero population), and 10,000 Nama (50% of the total Nama population) perished. The commander of the punitive expedition, General Lothar von Trotha, was eventually relieved and reprimanded for his usurpation of orders and the cruelties he inflicted. These occurrences were sometimes referred to as "the first genocide of the 20th century" and officially condemned by the United Nations in 1985. In 2004 a formal apology by a government minister of the Federal Republic of Germany followed.
=Middle East
= Bismarck and Wilhelm II after him sought closer economic ties with the Ottoman Empire. Under Wilhelm II, with the financial backing of the Deutsche Bank, the Baghdad Railway was begun in 1900, although by 1914 it was still short of its destination in Baghdad. In an interview with Wilhelm in 1899, Cecil Rhodes had tried "to convince the Kaiser that the future of the German empire abroad lay in the Middle East" and not in Africa; with a grand Middle-Eastern empire, Germany could afford to allow Britain the unhindered completion of the Cape-to-Cairo railway that Rhodes favoured. Britain initially supported the Baghdad Railway; but by 1911 British statesmen came to fear it might be extended toBasra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
on the Persian Gulf, threatening Britain's naval supremacy in the Indian Ocean. Accordingly, they asked to have construction halted, to which Germany and the Ottoman Empire acquiesced.
=South America
= In South America, Germany's primary interest was in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Uruguay and viewed the countries of northern South America –Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar language, Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechuan ...
, Colombia, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
– as a buffer to protect its interest from the growing influence of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
. Policymakers in Germany analysed the possibility of establishing bases in Margarita Island and showed interest in the Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands ( es, Islas Galápagos) are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the Equator west of the mainland of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador, with ...
but soon abandoned any such designs given that far-flung bases in northern South America would be very vulnerable.Mitchell, Nancy. ''The danger of dreams: German and American imperialism in Latin America'' (U of North Carolina Press, 1999), p. 67 Germany attempted to promote Chile, a country that was heavily influenced by Germany, into a regional counterweight to the United States. Germany and Britain managed through Chile to have Ecuador deny the United States a naval base in the Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands ( es, Islas Galápagos) are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the Equator west of the mainland of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador, with ...
.
Claims that German communities in South America acted as extensions of the German Empire were ubiquituous by 1900 but it has never been proved that these communities acted in such way to any significant degree. German political, cultural and scientific influence was particularly intense in Chile in the decades before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, and the prestige of Germany and German things in Chile remained high after the war but did not recover to its pre-war levels.
=Pre-war Europe
= Berlin was deeply suspicious of a supposed conspiracy of its enemies: that year-by-year in the early 20th century it was systematically encircled by enemies. There was a growing fear that the supposed enemy coalition of Russia, France and Britain was getting stronger militarily every year, especially Russia. The longer Berlin waited the less likely it would prevail in a war. According to American historian Gordon A. Craig, it was after the set-back in Morocco in 1905 that the fear of encirclement began to be a potent factor in German politics." Few outside observers agreed with the notion of Germany as a victim of deliberate encirclement. English historian G. M. Trevelyan expressed the British viewpoint:The encirclement, such as it was, was of Germany's own making. She had encircled herself by alienating France over Alsace-Lorraine, Russia by her support of Austria-Hungary's anti--Slav policy in the Balkans, England by building her rival fleet. She had created with Austria-Hungary a military bloc in the heart of Europe so powerful and yet so restless that her neighbors on each side had no choice but either to become her vassals or to stand together for protection....They used their central position to create fear in all sides, in order to gain their diplomatic ends. And then they complained that on all sides they had been encircled.Wilhelm II, under pressure from his new advisors after Bismarck left, committed a fatal error when he decided to allow the " Reinsurance Treaty" that Bismarck had negotiated with Tsarist Russia to lapse. It allowed Russia to make a new alliance with France. Germany was left with no firm ally but
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, and her support for action in annexing Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
in 1908 further soured relations with Russia. Berlin missed the opportunity to secure an alliance with Britain in the 1890s when it was involved in colonial rivalries with France, and he alienated British statesmen further by openly supporting the Boers in the South African War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sout ...
and building a navy to rival Britain's. By 1911, Wilhelm had completely picked apart the careful power balance established by Bismarck and Britain turned to France in the Entente Cordiale. Germany's only other ally besides Austria was the Kingdom of Italy, but it remained an ally only ''pro forma''. When war came, Italy saw more benefit in an alliance with Britain, France, and Russia, which, in the secret Treaty of London The Treaty of London or London Convention or similar may refer to:
*Treaty of London (1358), established a truce between England and France following the Battle of Poitiers
*Treaty of London (1359), which ceded western France to England
*Treaty of ...
in 1915 promised it the frontier districts of Austria and also colonial concessions. Germany did acquire a second ally in 1914 when the Ottoman Empire entered the war on its side, but in the long run, supporting the Ottoman war effort only drained away German resources from the main fronts.
World War I
Origins
 Following the assassination of the Austro-Hungarian Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, the Kaiser offered Emperor Franz Joseph full support for Austro-Hungarian plans to invade the
Following the assassination of the Austro-Hungarian Archduke Franz Ferdinand by Gavrilo Princip, the Kaiser offered Emperor Franz Joseph full support for Austro-Hungarian plans to invade the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
, which Austria-Hungary blamed for the assassination. This unconditional support for Austria-Hungary was called a "blank cheque" by historians, including German Fritz Fischer. Subsequent interpretation – for example at the Versailles Peace Conference – was that this "blank cheque" licensed Austro-Hungarian aggression regardless of the diplomatic consequences, and thus Germany bore responsibility for starting the war, or at least provoking a wider conflict.
Germany began the war by targeting its chief rival, France. Germany saw the French Republic as its principal danger on the European continent as it could mobilize much faster than Russia and bordered Germany's industrial core in the Rhineland. Unlike Britain and Russia, the French entered the war mainly for revenge against Germany, in particular for France's loss of Alsace-Lorraine to Germany in 1871. The German high command knew that France would muster its forces to go into Alsace-Lorraine. Aside from the very unofficial Septemberprogramm, the Germans never stated a clear list of goals that they wanted out of the war.
Western Front
 Germany did not want to risk lengthy battles along the Franco-German border and instead adopted the Schlieffen Plan, a military strategy designed to cripple France by invading Belgium and
Germany did not want to risk lengthy battles along the Franco-German border and instead adopted the Schlieffen Plan, a military strategy designed to cripple France by invading Belgium and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
, sweeping down to encircle and crush both Paris and the French forces along the Franco-German border in a quick victory. After defeating France, Germany would turn to attack Russia. The plan required violating the official neutrality of Belgium and Luxembourg, which Britain had guaranteed by treaty. However, the Germans had calculated that Britain would enter the war regardless of whether they had formal justification to do so. At first the attack was successful: the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, '' ...
swept down from Belgium and Luxembourg and advanced on Paris, at the nearby river Marne. However, the evolution of weapons over the last century heavily favored defense over offense, especially thanks to the machine gun, so that it took proportionally more offensive force to overcome a defensive position. This resulted in the German lines on the offense contracting to keep up the offensive timetable while correspondingly the French lines were extending. In addition, some German units that were originally slotted for the German far-right were transferred to the Eastern Front in reaction to Russia mobilizing far faster than anticipated. The combined effect had the German right flank sweeping down in front of Paris instead of behind it exposing the German Right flank to the extending French lines and attack from strategic French reserves stationed in Paris. Attacking the exposed German right flank, the French Army and the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
put up a strong resistance to the defense of Paris at the First Battle of the Marne, resulting in the German Army retreating to defensive positions along the river Aisne. A subsequent Race to the Sea resulted in a long-held stalemate between the German Army and the Allies in dug-in trench warfare positions from Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it ha ...
to Flanders.
 German attempts to break through failed at the two battles of Ypres (
German attempts to break through failed at the two battles of Ypres (1st
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
/ 2nd) with huge casualties. A series of allied offensives in 1915 against German positions in Artois and Champagne resulted in huge allied casualties and little territorial change. German Chief of Staff Erich von Falkenhayn decided to exploit the defensive advantages that had shown themselves in the 1915 Allied offensives by attempting to goad France into attacking strong defensive positions near the ancient city of Verdun. Verdun had been one of the last cities to hold out against the German Army in 1870, and Falkenhayn predicted that as a matter of national pride the French would do anything to ensure that it was not taken. He expected that he could take strong defensive positions in the hills overlooking Verdun on the east bank of the River Meuse to threaten the city and the French would launch desperate attacks against these positions. He predicted that French losses would be greater than those of the Germans and that continued French commitment of troops to Verdun would "bleed the French Army white." In February 1916, the Battle of Verdun began, with the French positions under constant shelling and poison gas attack and taking large casualties under the assault of overwhelmingly large German forces. However, Falkenhayn's prediction of a greater ratio of French killed proved to be wrong as both sides took heavy casualties. Falkenhayn was replaced by Erich Ludendorff, and with no success in sight, the German Army pulled out of Verdun in December 1916 and the battle ended.
Eastern Front
Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
was a stalemate for the German Army, the Eastern Front eventually proved to be a great success. Despite initial setbacks due to the unexpectedly rapid mobilisation of the Russian army, which resulted in a Russian invasion of East Prussia and Austrian Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, the badly organised and supplied Russian Army
The Russian Ground Forces (russian: Сухопутные войска �В Sukhoputnyye voyska V, also known as the Russian Army (, ), are the Army, land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.
The primary responsibilities of the Russian Gro ...
faltered and the German and Austro-Hungarian armies thereafter steadily advanced eastward. The Germans benefited from political instability in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
and its population's desire to end the war. In 1917 the German government allowed Russia's communist Bolshevik leader Vladimir Lenin to travel through Germany from Switzerland
; rm, citad federala, links=no). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzon ...
into Russia. Germany believed that if Lenin could create further political unrest, Russia would no longer be able to continue its war with Germany, allowing the German Army to focus on the Western Front.
In March 1917, the Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
was ousted from the Russian throne, and in November a Bolshevik government came to power under the leadership of Lenin. Facing political opposition from the Bolsheviks, he decided to end Russia's campaign against Germany, Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
to redirect Bolshevik energy to eliminating internal dissent. In March 1918, by the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, the Bolshevik government gave Germany and the Ottoman Empire enormous territorial and economic concessions in exchange for an end to war on the Eastern Front. All of present-day Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
was given over to the German occupation authority '' Ober Ost'', along with Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Ukraine. Thus Germany had at last achieved its long-wanted dominance of "Mitteleuropa" (Central Europe) and could now focus fully on defeating the Allies on the Western Front. In practice, however, the forces that were needed to garrison and secure the new territories were a drain on the German war effort.
Colonies
Germany quickly lost almost all its colonies. However, inGerman East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
, an impressive guerrilla campaign was waged by the colonial army leader there, General Paul Emil von Lettow-Vorbeck. Using Germans and native Askaris, Lettow-Vorbeck launched multiple guerrilla raids against British forces in Kenya and Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of S ...
. He also invaded Portuguese Mozambique to gain his forces supplies and to pick up more Askari recruits. His force was still active at war's end.
1918
 The defeat of Russia in 1917 enabled Germany to transfer hundreds of thousands of troops from the Eastern to the Western Front, giving it a numerical advantage over the Allies. By retraining the soldiers in new infiltration tactics, the Germans expected to unfreeze the battlefield and win a decisive victory before the army of the United States, which had now entered the war on the side of the Allies, arrived in strength. In what was known as the "kaiserschlacht", Germany converged their troops and delivered multiple blows that pushed back the allies. However, the repeated German offensives in the spring of 1918 all failed, as the Allies fell back and regrouped and the Germans lacked the reserves needed to consolidate their gains. Meanwhile, soldiers had become radicalised by the
The defeat of Russia in 1917 enabled Germany to transfer hundreds of thousands of troops from the Eastern to the Western Front, giving it a numerical advantage over the Allies. By retraining the soldiers in new infiltration tactics, the Germans expected to unfreeze the battlefield and win a decisive victory before the army of the United States, which had now entered the war on the side of the Allies, arrived in strength. In what was known as the "kaiserschlacht", Germany converged their troops and delivered multiple blows that pushed back the allies. However, the repeated German offensives in the spring of 1918 all failed, as the Allies fell back and regrouped and the Germans lacked the reserves needed to consolidate their gains. Meanwhile, soldiers had become radicalised by the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
and were less willing to continue fighting. The war effort sparked civil unrest in Germany, while the troops, who had been constantly in the field without relief, grew exhausted and lost all hope of victory. In the summer of 1918, the British Army was at its peak strength with as many as 4.5 million men on the western front and 4,000 tanks for the Hundred Days Offensive, the Americans arriving at the rate of 10,000 a day, Germany's allies facing collapse and the German Empire's manpower exhausted, it was only a matter of time before multiple Allied offensives destroyed the German army.
Home front
The concept of " total war" meant that supplies had to be redirected towards the armed forces and, with German commerce being stopped by the Allied naval blockade, German civilians were forced to live in increasingly meagre conditions. First food prices were controlled, then rationing was introduced. During the war about 750,000 German civilians died from malnutrition. Towards the end of the war, conditions deteriorated rapidly on the home front, with severe food shortages reported in all urban areas. The causes included the transfer of many farmers and food workers into the military, combined with the overburdened railway system, shortages of coal, and the British blockade. The winter of 1916–1917 was known as the "turnip winter", because the people had to survive on a vegetable more commonly reserved for livestock, as a substitute for potatoes and meat, which were increasingly scarce. Thousands of soup kitchens were opened to feed the hungry, who grumbled that the farmers were keeping the food for themselves. Even the army had to cut the soldiers' rations. The morale of both civilians and soldiers continued to sink.Spanish Flu Pandemic
The population of Germany was already suffering from outbreaks of disease due to malnutrition due to Allied blockade preventing food imports. Spanish flu arrived in Germany with returning troops. Around 287,000 people died of Spanish flu in Germany between 1918 and 1920.Revolt and demise
Many Germans wanted an end to the war and increasing numbers began to associate with the political left, such as the Social Democratic Party and the more radicalIndependent Social Democratic Party
The Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Unabhängige Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, USPD) was a short-lived political party in Germany during the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. The organization was establis ...
, which demanded an end to the war. The entry of the U.S. into the war in April 1917 tipped the long-run balance of power even more in favour of the Allies.
The end of October 1918, in Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland pe ...
, in northern Germany, saw the beginning of the German Revolution of 1918–1919
The German Revolution or November Revolution (german: Novemberrevolution) was a civil conflict in the German Empire at the end of the First World War that resulted in the replacement of the German federal constitutional monarchy with a dem ...
. Units of the German Navy refused to set sail for a last, large-scale operation in a war which they saw as good as lost, initiating the uprising. On 3 November, the revolt spread to other cities and states of the country, in many of which workers' and soldiers' councils were established. Meanwhile, Hindenburg and the senior generals lost confidence in the Kaiser and his government.
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
signed the Armistice of Salonica on 29 September 1918. The Ottoman Empire signed the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by ...
on 30 October 1918. Between 24 October and 3 November 1918, Italy defeated Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
in the battle of Vittorio Veneto, which forced Austria-Hungary to sign the Armistice of Villa Giusti on 3 November 1918. So, in November 1918, with internal revolution, the Allies advancing toward Germany on the Western Front, Austria-Hungary falling apart from multiple ethnic tensions, its other allies out of the war and pressure from the German high command, the Kaiser and all German ruling kings, dukes, and princes abdicated, and German nobility was abolished. On 9 November, the Social Democrat Philipp Scheidemann proclaimed a republic. The new government led by the German Social Democrats
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
** ...
called for and received an armistice on 11 November. It was succeeded by the Weimar Republic. Those opposed, including disaffected veterans, joined a diverse set of paramilitary and underground political groups such as the Freikorps, the Organisation Consul, and the Communists.
Constitution
The Empire was aconstitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies di ...
, with the Emperor – commonly referred as the "Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
" – as its Head of State
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state (polity), state#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international p ...
and ultimate authority. The government exercised executive power, and was led by a Chancellor, who was appointed by the Emperor and directly reported to him; he was not responsible to the legislature as in other parliamentary systems. The longest ruling Chancellor was Otto Von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
, who ruled from 1871 to 1890, and led to the unification of Germany and to its consolidation as Europe's most powerful country.
The Empire's legislative power was vested in two bodies, the upper house was the Bundesrat and the lower one the Reichstag or parliament; legislation had to pass both houses. There was universal male suffrage for the election of members to the Reichstag. The Bundesrat contained the appointed representatives of the governments of each individual state of the Empire, with an unequal distribution of votes as specified in the Constitution – Prussia, for instance, the largest state in size and population, had 17 votes, while no other state had more than 6 votes; thus, Prussia dominated the house, which was presided over by the Chancellor.
Constituent states
Before unification, German territory (excluding Austria and Switzerland) was made up of 27 constituent states. These states consisted of kingdoms, grand duchies, duchies, principalities, free Hanseatic cities and one imperial territory. The free cities had a republican form of government on the state level, even though the Empire at large was constituted as a monarchy, and so were most of the states. Prussia was the largest of the constituent states, covering two-thirds of the empire's territory. Several of these states had gained sovereignty following the dissolution of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and had been ''de facto'' sovereign from the mid-1600s onward. Others were created as sovereign states after the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815. Territories were not necessarily contiguous—many existed in several parts, as a result of historical acquisitions, or, in several cases, divisions of the ruling families. Some of the initially existing states, in particular Hanover, were abolished and annexed by Prussia as a result of the war of 1866.
Each component of the German Empire sent representatives to the Federal Council (''Bundesrat'') and, via single-member districts, the Imperial Diet (''Reichstag''). Relations between the Imperial centre and the Empire's components were somewhat fluid and were developed on an ongoing basis. The extent to which the German Emperor could, for example, intervene on occasions of disputed or unclear succession was much debated on occasion—for example in the inheritance crisis of the Lippe-Detmold.
Unusually for a federation and/or a nation-state, the German states maintained limited autonomy over foreign affairs and continued to exchange ambassadors and other diplomats (both with each other and directly with foreign nations) for the Empire's entire existence. Shortly after the Empire was proclaimed, Bismarck implemented a convention in which his sovereign would only send and receive envoys to and from other German states as the King of Prussia, while envoys from Berlin sent to foreign nations always received credentials from the monarch in his capacity as German Emperor. In this way, the Prussian foreign ministry was largely tasked with managing relations with the other German states while the Imperial foreign ministry managed Germany's external relations.
Map and table
Other maps
Language
 About 92% of the population spoke German as their first language. The only minority language with a significant number of speakers (5.4%) was Polish (a figure that rises to over 6% when including the related
About 92% of the population spoke German as their first language. The only minority language with a significant number of speakers (5.4%) was Polish (a figure that rises to over 6% when including the related Kashubian Kashubian can refer to:
* Pertaining to Kashubia, a region of north-central Poland
* Kashubians, an ethnic group of north-central Poland
* Kashubian language
See also
*Kashubian alphabet
The Kashubian or Cassubian alphabet (''kaszëbsczi alf ...
and Masurian languages).
The non-German Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
(0.5%), like Danish, Dutch and Frisian, were located in the north and northwest of the empire, near the borders with Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
, the Netherlands, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small land ...
. Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle L ...
was spoken throughout northern Germany and, though linguistically as distinct from High German (''Hochdeutsch'') as from Dutch and English, was considered "German", hence also its name. Danish and Frisian were spoken predominantly in the north of the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein and Dutch in the western border areas of Prussia ( Hanover, Westphalia, and the Rhine Province
The Rhine Province (german: Rheinprovinz), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. It ...
).
Polish and other West Slavic languages (6.28%) were spoken chiefly in the east.
A few (0.5%) spoke French, the vast majority of these in the Reichsland Elsass-Lothringen where francophones formed 11.6% of the total population.
1900 census results
Linguistic maps
Kashubian Kashubian can refer to:
* Pertaining to Kashubia, a region of north-central Poland
* Kashubians, an ethnic group of north-central Poland
* Kashubian language
See also
*Kashubian alphabet
The Kashubian or Cassubian alphabet (''kaszëbsczi alf ...
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 sorbisch.png, Sorbian
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 französisch.png, French
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 wallonisch.png, Walloon
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 italienisch.png, Italian
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 litauisch.png, Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
Sprachen deutsches reich 1900 nichtdeutsch.png, non-German
Religion
 Generally, religious demographics of the early modern period hardly changed. Still, there were almost entirely Catholic areas (Lower and Upper Bavaria, northern Westphalia, Upper Silesia, etc.) and almost entirely Protestant areas (Schleswig-Holstein, Pomerania, Saxony, etc.). Confessional prejudices, especially towards mixed marriages, were still common. Bit by bit, through internal migration, religious blending was more and more common. In eastern territories, confession was almost uniquely perceived to be connected to one's ethnicity and the equation "Protestant = German, Catholic = Polish" was held to be valid. In areas affected by immigration in the Ruhr area and Westphalia, as well as in some large cities, religious landscape changed substantially. This was especially true in largely Catholic areas of Westphalia, which changed through Protestant immigration from the eastern provinces.
Politically, the confessional division of Germany had considerable consequences. In Catholic areas, the Centre Party had a big electorate. On the other hand, Social Democrats and Free Trade Unions usually received hardly any votes in the Catholic areas of the Ruhr. This began to change with the secularization arising in the last decades of the German Empire.
In Germany's overseas colonial empire, millions of subjects practiced various
Generally, religious demographics of the early modern period hardly changed. Still, there were almost entirely Catholic areas (Lower and Upper Bavaria, northern Westphalia, Upper Silesia, etc.) and almost entirely Protestant areas (Schleswig-Holstein, Pomerania, Saxony, etc.). Confessional prejudices, especially towards mixed marriages, were still common. Bit by bit, through internal migration, religious blending was more and more common. In eastern territories, confession was almost uniquely perceived to be connected to one's ethnicity and the equation "Protestant = German, Catholic = Polish" was held to be valid. In areas affected by immigration in the Ruhr area and Westphalia, as well as in some large cities, religious landscape changed substantially. This was especially true in largely Catholic areas of Westphalia, which changed through Protestant immigration from the eastern provinces.
Politically, the confessional division of Germany had considerable consequences. In Catholic areas, the Centre Party had a big electorate. On the other hand, Social Democrats and Free Trade Unions usually received hardly any votes in the Catholic areas of the Ruhr. This began to change with the secularization arising in the last decades of the German Empire.
In Germany's overseas colonial empire, millions of subjects practiced various indigenous religions
Indigenous religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the religious belief systems of communities described as being "indigenous". This category is often juxtaposed against others such as the "world religions" and "new re ...
in addition to Christianity. Over two million Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
also lived under German colonial rule, primarily in German East Africa
German East Africa (GEA; german: Deutsch-Ostafrika) was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozam ...
.
Coat of arms
Legacy
The defeat and aftermath of the First World War and the penalties imposed by theTreaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
shaped the positive memory of the Empire, especially among Germans who distrusted and despised the Weimar Republic. Conservatives, liberals, socialists, nationalists, Catholics and Protestants all had their own interpretations, which led to a fractious political and social climate in Germany in the aftermath of the empire's collapse.
Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; german: Ruhrgebiet , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr area, sometimes Ruhr district, Ruhr region, or Ruhr valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 2,800/km ...
, the Saar
Saar or SAAR has several meanings:
People Given name
*Saar Boubacar (born 1951), Senegalese professional football player
*Saar Ganor, Israeli archaeologist
*Saar Klein (born 1967), American film editor
Surname
* Ain Saar (born 1968), Esto ...
and Upper Silesia especially contributed to that process. The first motorcar was built by Karl Benz in 1886. The enormous growth of industrial production and industrial potential also led to a rapid urbanisation of Germany, which turned the Germans into a nation of city dwellers. More than 5 million people left Germany for the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
during the 19th century.
Sonderweg
Many historians have emphasized the central importance of a German or "special path" (or "exceptionalism") as the root of Nazism and the German catastrophe in the 20th century. According to the historiography by Kocka (1988), the process of nation-building from above had very grievous long-term implications. In terms of parliamentary democracy, Parliament was kept weak, the parties were fragmented, and there was a high level of mutual distrust. The Nazis built on the illiberal, anti-pluralist elements of Weimar's political culture. The Junker elites (the large landowners in the east) and senior civil servants used their great power and influence well into the twentieth century to frustrate any movement toward democracy. They played an especially negative role in the crisis of 1930–1933. Bismarck's emphasis on military force amplified the voice of the officer corps, which combined advanced modernisation of military technology with reactionary politics. The rising upper-middle-class elites, in the business, financial and professional worlds, tended to accept the values of the old traditional elites. The German Empire was for Hans-Ulrich Wehler a strange mixture of highly successful capitalist industrialisation and socio-economic modernisation on the one hand, and of surviving pre-industrial institutions, power relations and traditional cultures on the other. Wehler argues that it produced a high degree of internal tension, which led on the one hand to the suppression of socialists, Catholics and reformers, and on the other hand to a highly aggressive foreign policy. For these reasons Fritz Fischer and his students emphasised Germany's primary guilt for causing the First World War. Hans-Ulrich Wehler, a leader of the Bielefeld School of social history, places the origins of Germany's path to disaster in the 1860s–1870s, when economic modernisation took place, but political modernisation did not happen and the old Prussian rural elite remained in firm control of the army, diplomacy and the civil service. Traditional, aristocratic, premodern society battled an emerging capitalist, bourgeois, modernising society. Recognising the importance of modernising forces in industry and the economy and in the cultural realm, Wehler argues that reactionary traditionalism dominated the political hierarchy of power in Germany, as well as social mentalities and in class relations (). The catastrophic German politics between 1914 and 1945 are interpreted in terms of a delayed modernisation of its political structures. At the core of Wehler's interpretation is his treatment of "the middle class" and "revolution", each of which was instrumental in shaping the 20th century. Wehler's examination of Nazi rule is shaped by his concept of "charismatic domination", which focuses heavily on Hitler. The historiographical concept of a German has had a turbulent history. 19th-century scholars who emphasised a separate German path to modernity saw it as a positive factor that differentiated Germany from the "western path" typified by Great Britain. They stressed the strong bureaucratic state, reforms initiated by Bismarck and other strong leaders, the Prussian service ethos, the high culture of philosophy and music, and Germany's pioneering of a social welfare state. In the 1950s, historians in West Germany argued that the led Germany to the disaster of 1933–1945. The special circumstances of German historical structures and experiences, were interpreted as preconditions that, while not directly causing National Socialism, did hamper the development of a liberal democracy and facilitate the rise of fascism. The paradigm has provided the impetus for at least three strands of research in German historiography: the " long 19th century", the history of the bourgeoisie, and comparisons with the West. After 1990, increased attention to cultural dimensions and to comparative and relational history moved German historiography to different topics, with much less attention paid to the . While some historians have abandoned the thesis, they have not provided a generally accepted alternative interpretation.Military
The Empire of Germany had two armed forces: * theImperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (german: Deutsches Heer), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the l ...
, which included
** the Imperial German Stormtroopers,
** the Imperial German Air Service, and
* the Imperial German Navy
Territorial legacy
In addition to present-day Germany, large parts of what comprised the German Empire now belong to several other modern European countries.World War I
! scope="row" style="background: #ffffff; font-weight: normal;" , Northern Schleswig
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
, South Jutland County (excluding towns of Taps, Hejle and Vejstrup), and the towns of Hviding, Roager and Spandet
, -
, style="background: #c0c0c0; width: 1em; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" , Both World Wars
! scope="row" style="background: transparent; font-weight: normal;" , Hultschin Region
, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
, Hlučín Region, on the Czech–Polish border in Silesia, whose German population was partially deported following WWII; part of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
until its dissolution in 1992
, -
, style="background: #c0c0c0; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" , Both World Wars
! scope="row" style="background: transparent; font-weight: normal;" , Memel Territory
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Klaipėda Region, annexed by Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
in 1923, retaken by Nazi Germany in 1939, from which Germans were deported following WWII by the Soviet authorities; now part of independent Lithuania since 1990
, -
, style="background: #c0c0c0; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" , Both World Wars
! scope="row" style="background: transparent; font-weight: normal;" , Most of West Prussia and Posen, a part of Upper Silesia, parts of the districts of Bütow, Lauenburg and Stolp in Pomerania,''Der Große Brockhaus''. 15th edition, vol. 14, Leipzig 1933, p. 741. Soldau in East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, Silesian Silesian as an adjective can mean anything from or related to Silesia. As a noun, it refers to an article, item, or person of or from Silesia.
Silesian may also refer to:
People and languages
* Silesians, inhabitants of Silesia, either a West S ...
, Pomeranian and Greater Poland Voivodeships, the towns of Bytów
Bytów (; csb, Bëtowò; formerly german: Bütow ) is a town in the Gdańsk Pomerania region of northern Poland with 16,730 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the capital of Bytów County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
The origins of By ...
, Lębork, Słupsk and Działdowo (the German population was deported following WWII)
, -
, style="background: #696969; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" , World War II
! scope="row" style="background: transparent; font-weight: normal;" , Silesia, East Brandenburg, Warmia, Masuria, southern East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, central and eastern parts of Pomerania
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, Northern and western parts of the country, including Pomerania, Silesia, Lubusz Land, Warmia and Masuria, from all of which Germans were deported following WWII
, -
, style="background: #696969; width: 1em; overflow: hidden;" , World War II
! scope="row" style="background: transparent; font-weight: normal;" , Northern East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, The Kaliningrad Oblast exclave on the Baltic, from which Germans were deported following WWII. Transferred to the Russian SFSR and continued as a part of Russia following the collapse of the Soviet Union
See also
*Economic history of Germany
Until the early 19th century, Germany, a federation of numerous states of varying size and development, retained its pre-industrial character, where trade centered around a number of free cities. After the extensive development of the railway ...
* Kingdom of Germany
* List of German monarchs
* List of German monarchs in 1918
References
Informational notes CitationsFurther reading
* Barker, J. Ellis.Modern Germany; her political and economic problems, her foreign and domestic policy, her ambitions, and the causes of her success
' (1907) * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. ''Modern Germany: society, economy, and politics in the twentieth century'' (1987
ACLS E-book
* Berghahn, Volker Rolf. ''Imperial Germany, 1871–1914: Economy, Society, Culture, and Politics'' (2nd ed. 2005) * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. "German Colonialism and Imperialism from Bismarck to Hitler". ''German Studies Review'', vol. 40, no. 1 (2017) pp. 147–16
Online
* Blackbourn, David. ''The Long Nineteenth Century: A History of Germany, 1780–1918'' (1998
excerpt and text search
* Blackbourn, David, and Geoff Eley. ''The Peculiarities of German History: Bourgeois Society and Politics in Nineteenth-Century Germany (1984) * Blanke, Richard. ''Prussian Poland in the German Empire'' (1981) * Brandenburg, Erich. ''From Bismarck to the World War: A History of German Foreign Policy 1870–1914'' (1927
online
* Carroll, E. Malcolm.
Germany and the great powers, 1866–1914: A study in public opinion and foreign policy
' (1938); 862pp; written for advanced students. * Cecil, Lamar. ''Wilhelm II: Prince and Emperor, 1859–1900'' (1989); vol 2: ''Wilhelm II: Emperor and Exile, 1900–1941'' (1996
vol 2 online
* Chickering, Roger. ''Imperial Germany and the Great War, 1914–1918'' (2nd ed. 2004
excerpt and text search
* Clark, Christopher. '' Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600–1947'' (2006), the standard scholarly survey
online
* Dawson, William Harbutt.
The Evolution of Modern Germany
' (1908), 503 pages, covers 1871–1906 with focus on social and economic history and colonies * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Bismarck and state socialism; an exposition of the social and economic legislation of Germany since 1870
' (1890) 175 pages * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Municipal life and government in Germany
' (1914); 507 pages, describes the workings of local government and bureaucracy * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Germany and the Germans
' (1894) 387pp; politics and parties, Volume 2 * Eyck, Erich. ''Bismarck and the German Empire'' (1964
excerpt and text search
* Fife, Robert Herndon. (1916). ''The German Empire between Two Wars; a Study of the Political and Social Development of the Nation between 1871 and 1914.'' New York: Macmillan Company. *
Fischer, Fritz
Fritz Fischer (5 March 1908 – 1 December 1999) was a German historian best known for his analysis of the causes of World War I. In the early 1960s Fischer advanced the controversial thesis at the time that responsibility for the outbreak of the ...
. ''From Kaiserreich to Third Reich: Elements of Continuity in German History, 1871–1945''. (1986). .
* Geiss, Imanuel. ''German Foreign Policy, 1871–1914'' (1979excerpt
* Haardt, Oliver FR. "The Kaiser in the Federal State, 1871–1918." ''German History'' 34.4 (2016): 529–554
online
* * Hewitson, Mark. "Germany and France before the First World War: a reassessment of Wilhelmine foreign policy." ''English Historical Review'' 115.462 (2000): 570–606; argues Germany had a growing sense of military superiority * Holborn, Hajo. ''A History of Modern Germany: 1840–1945'' (1969), pp. 173–53
online
* Hoyer, Katja. ''Blood and Iron: The Rise and Fall of the German Empire 1871-1918'' (2021) * Jefferies, Mattew. ''Imperial Culture in Germany, 1871–1918''. (Palgrave, 2003) . * Kennedy, Paul
''The Rise of the Anglo-German Antagonism, 1860–1914''
(2nd ed. 1988) * Koch, Hannsjoachim W. ''A constitutional history of Germany in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries'' (1984). * Kurlander, Eric. ''The Price of Exclusion: Ethnicity, National Identity, and the Decline of German Liberalism, 1898–1933'' (2007). * Levy, Richard S. ''The Downfall of the Anti-Semitic Political Parties in Imperial Germany'' (Yale University Press, 1975). * Levy, Richard S. ed. ''Antisemitism: A historical encyclopedia of prejudice and persecution'' (2 vol Abc-clio, 2005). * Milward, Alan S. and S. B. Saul. ''The Development of the Economies of Continental Europe: 1850–1914'' (1977) pp. 17–70. * Mombauer, Annika and Wilhelm Deist, eds. ''The Kaiser: New Research on Wilhelm II's Role in Imperial Germany'' (2003) * Mommsen, Wolfgang. ''Imperial Germany 1867–1918: Politics, Culture, and Society in an Authoritarian State''. (1995). . * Nipperdey, Thomas. ''Germany from Napoleon to Bismarck'' (1996) dense coverage of chief topics
online
* Padfield, Peter. ''The Great Naval Race: Anglo-German Naval Rivalry 1900–1914'' (2005) * Ragins, Sanford. ''Jewish Responses to Anti-Semitism in Germany, 1870–1914: A Study in the History of Ideas'' (ISD, 1980). * * Retallack, James. ''Germany in the Age of Kaiser Wilhelm II'', (1996) . * Retallack, James. ''Imperial Germany 1871–1918'' (2008) * Rich, Norman. "The Question of National Interest in Imperial German Foreign Policy: Bismarck, William II, and the Road to World War I." ''Naval War College Review'' (1973) 26#1: 28-41
online
* Ritter, Gerhard. ''The Sword and the Scepter; the Problem of Militarism in Germany''. (4 vol University of Miami Press 1969–1973) * Richie, Alexandra. ''Faust's Metropolis: A History of Berlin'' (1998), 1139 pages, pp. 188–233 * Sagarra, Eda. ''A Social History of Germany, 1648–1914'' (1977
online
* Scheck, Raffael
(2008), a brief textbook by a leading scholar * Schollgen, Gregor. ''Escape into War? The Foreign Policy of Imperial Germany''. (Berg, 1990) . * Smith, Helmut Walser, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern German History'' (2011), 862 pp; 35 essays by specialists; Germany since 176
excerpt
* Smith, Woodruff D. ''The German Colonial Empire'' (1978 * Sperber, Jonathan. ''The Kaiser's Voters: Electors and Elections in Imperial Germany'' (1997
online review
* Stern, Fritz. ''Gold and Iron: Bismarck, Bleichroder, and the Building of the German Empire'' (1979) Bismarck worked closely with this leading banker and financie
excerpt and text search
* Steinberg, Jonathan. ''Bismarck: A Life'' (2011), a recent scholarly biography; emphasis on Bismarck's personalit
online
* Steinmetz, George (2007) ''The Devil's Handwriting: Precoloniality and the German Colonial State in Qingdao, Samoa, and Southwest Africa''. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. * Taylor, A.J.P. ''Bismarck: The Man and the Statesman'' (1967
online
* Wehler, Hans-Ulrich. ''The German Empire, 1871–1918''. (Berg, 1985). * Wildenthal, Lora. ''German Women for Empire, 1884–1945'' (2001) ::Historiography * Berghahn, Volker Rolf. "Structure and Agency in Wilhelmine Germany: The history of the German Empire, Past, present and Future," in Annika Mombauer and Wilhelm Deist, eds. ''The Kaiser: New Research on Wilhelm II's Role in Imperial Germany'' (2003) pp. 281–293, historiography * Chickering, Roger, ed. ''Imperial Germany: A Historiographical Companion'' (1996), 552pp; 18 essays by specialists * Dickinson, Edward Ross. "The German Empire: an Empire?" ''History Workshop Journal'' Issue 66, (Autumn 2008
online
in Project MUSE, with guide to recent scholarship * * Jefferies, Matthew. ''Contesting the German Empire 1871–1918'' (2008
excerpt and text search
* Müller, Sven Oliver, and Cornelius Torp, ed. ''Imperial Germany Revisited: Continuing Debates and New Perspectives'' (2011) * Reagin, Nancy R. "Recent Work on German National Identity: Regional? Imperial? Gendered? Imaginary?" ''Central European History'' (2004) v 37, pp. 273–289 ::Primary sources * Dawson, William Harbutt.
Germany at Home
' (1908) 275 pp; popular description of social life in villages and cities * Vizetelly, Henry.
Berlin Under the New Empire: Its Institutions, Inhabitants, Industry, Monuments, Museums, Social Life, Manners, and Amusements
' (2 vol. London, 1879) Volume 2
External links
Ravenstein's Atlas of the German Empire
, Library.wis.edu
Gemeindeverzeichnis.de
German Reich map of states 1913 (300 dpi)
Dissemination of the German Language 1913 (map, 300 dpi)
Dissemination of the main foreign mother tongues in the German Reich 1913 (map, 300 dpi)
{{Authority control Former countries in Europe Former empires Former monarchies of Europe Former monarchies Modern history of Germany . . . . . Germanic empires States and territories established in 1871 States and territories disestablished in 1918 * * 19th century in Germany 20th century in Germany by period