|
Yogin Dalal
Instead of having a single "inventor", the Internet was developed by many people over many years. The following are some Internet pioneers who contributed to its early and ongoing development. These include early theoretical foundations, specifying original protocols, and expansion beyond a research tool to wide deployment. The pioneers Claude Shannon Claude Shannon (1916–2001) called the "father of modern information theory", published "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" in 1948. His paper gave a formal way of studying communication channels. It established fundamental limits on the efficiency of communication over noisy channels, and presented the challenge of finding families of codes to achieve capacity. Vannevar Bush Vannevar Bush (1890–1974) helped to establish a partnership between U.S. military, university research, and independent think tanks. He was appointed Chairman of the National Defense Research Committee in 1940 by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers. The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the 1970s to enable resource shari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-Computer Symbiosis
"Man-Computer Symbiosis" is the title of a work by J.C.R. Licklider, which was published in 1960. The paper represented what we would today consider a fundamental, or key text of the modern computing revolution. The work describes something of Lickliders' vision for a complementary (symbiotic) relationship between humans and computers at a potential time of the future. According to ''Bardini'', Licklider envisioned a future time when machine cognition (''cerebration'') would surpass and become independent of human direction, as a basic stage of development within human evolution. ''Jacucci'' gives the description of Lickliders' vision as being the ''very tight coupling of human brains and computing machines'' (c.f. ''brain'', the term '' cohesion'' & the general definitions of the term '' coupling''). As a necessary ''pre-requisite'' of human-computer symbiosis, Licklider conceived of a thing known as the ''Thinking centre''. Altogether these things were pre-conditions for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPL Network
The NPL network, or NPL Data Communications Network, was a local area computer network operated by a team from the National Physical Laboratory in London that pioneered the concept of packet switching. Based on designs first conceived by Donald Davies in 1965, development work began in 1968. Elements of the first version of the network, the Mark I, became operational during 1969 then fully operational in January 1970, and the Mark II version operated from 1973 until 1986. The NPL network and the ARPANET in the United States were the first two computer networks that implemented packet switching and the NPL network was the first to use high-speed links. Origins In 1965, Donald Davies, who was later appointed to head of the NPL Division of Computer Science, proposed a commercial national data network based on packet switching in ''Proposal for the Development of a National Communications Service for On-line Data Processing''. After the proposal was not taken up nationally, during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Roberts (scientist)
Lawrence Gilman Roberts (December 21, 1937 – December 26, 2018) was an American engineer who received the Draper Prize in 2001 "for the development of the Internet", and the Principe de Asturias Award in 2002. As a program manager and later office director at the Advanced Research Projects Agency, Roberts and his team created the ARPANET using packet switching techniques invented by British computer scientist Donald Davies and American Paul Baran. The ARPANET, which was built by the Massachusetts-based company Bolt Beranek and Newman (BBN), was a predecessor to the modern Internet. He asked Leonard Kleinrock to apply mathematical models to simulate the performance of the network. Roberts later served as CEO of the commercial packet-switching network Telenet. Early life and education Roberts, who was known as Larry, was born and raised in Westport, Connecticut. He was the son of Elizabeth (Gilman) and Elliott John Roberts, both of whom had doctorates in chemistry. It is said t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symposium On Operating Systems Principles
In ancient Greece, the symposium ( grc-gre, συμπόσιον ''symposion'' or ''symposio'', from συμπίνειν ''sympinein'', "to drink together") was a part of a banquet that took place after the meal, when drinking for pleasure was accompanied by music, dancing, recitals, or conversation.Peter Garnsey, ''Food and Society in Classical Antiquity'' (Cambridge University Press, 1999), p. 13online Sara Elise Phang, ''Roman Military Service: Ideologies of Discipline in the Late Republic and Early Principate'' (Cambridge University Press, 2008), pp. 263–264. Literary works that describe or take place at a symposium include two Socratic dialogues, Plato's ''Symposium'' and Xenophon's ''Symposium'', as well as a number of Greek poems such as the elegies of Theognis of Megara. Symposia are depicted in Greek and Etruscan art that shows similar scenes. In modern usage, it has come to mean an academic conference or meeting such as a scientific conference. The equivalent of a Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Scantlebury
Roger Anthony Scantlebury (born August 1936) is a British computer scientist who worked at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) and later at Logica. Scantlebury participated in pioneering work to develop packet switching and associated communication protocols at the NPL in the late 1960s. He proposed the use of the technology in the ARPANET, the forerunner of the Internet, at the inaugural Symposium on Operating Systems Principles in 1967. During the 1970s, he was an active member of international working groups that developed concepts for the interconnection of computer networks. Early life Roger Scantlebury was born in Ealing in 1936. Career National Physical Laboratory Scantlebury worked at the National Physical Laboratory in south-west London, in collaboration with the National Research Development Corporation (NRDC). His early work was on the Automatic Computing Engine and English Electric DEUCE computers. Following this he worked with Donald Davies on his pioneering p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 70,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing" division. Routledge is headquartered in the main T&F office in Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfordshire and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datagram
A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network. Datagrams are typically structured in header and payload sections. Datagrams provide a connectionless communication service across a packet-switched network. The delivery, arrival time, and order of arrival of datagrams need not be guaranteed by the network. History In the early 1970s, the term ''datagram'' was created by combining the words ''data'' and ''telegram'' by the CCITT rapporteur on packet switching, Halvor Bothner-By. While the word was new, the concept had already a long history. In 1962, Paul Baran described, in a RAND Corporation report, a hypothetical military network having to resist a nuclear attack. Small standardized "message blocks", bearing source and destination addresses, were stored and forwarded in computer nodes of a highly redundant meshed computer network. "The network user who has called up a "virtual connection" to an end station and has transmitted messages ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Protocol
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics (computer science), semantics and synchronization of communication and possible Error detection and correction, error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by Computer hardware, hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be Implementation, implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Router (computing)
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions between networks and on the global Internet. Data sent through a network, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork (e.g. the Internet) until it reaches its destination node. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different IP networks. When a data packet comes in on one of the lines, the router reads the network address information in the packet header to determine the ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network on its journey. The most familiar type of IP routers are home and small office routers that simply forward IP packets between the home computers and the Internet. More sophisticated routers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom)
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is the national measurement standards laboratory of the United Kingdom. It is one of the most extensive government laboratories in the UK and has a prestigious reputation for its role in setting and maintaining physical standards for British industry. Founded in 1900, it is one of the oldest metrology institutes in the world. Research and development work at NPL has contributed to the advancement of many disciplines of science, including the development early computers in the late 1940s and 1950s, construction of the first accurate atomic clock in 1955, and the invention and pioneering implementation of packet switching in the 1960s, which is today one of the fundamental technologies of the Internet. The former heads of NPL include many individuals who were pillars of the British scientific establishment. NPL is based at Bushy Park in Teddington, west London. It is under the management of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
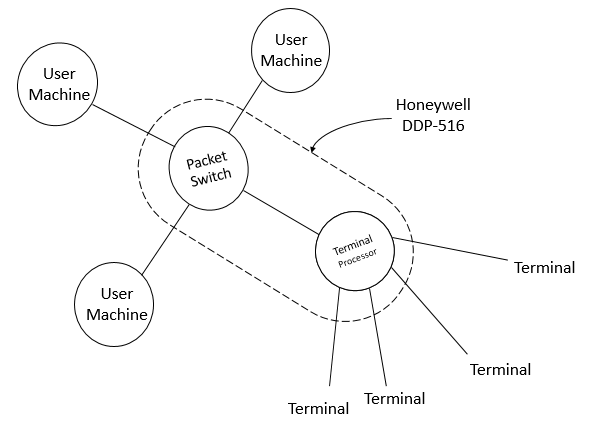
Packet Switching
In telecommunications, packet switching is a method of grouping Data (computing), data into ''network packet, packets'' that are transmitted over a digital Telecommunications network, network. Packets are made of a header (computing), header and a payload (computing), payload. Data in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination, where the payload is extracted and used by an operating system, application software, or protocol suite, higher layer protocols. Packet switching is the primary basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide. In the early 1960s, American computer scientist Paul Baran developed the concept that he called "distributed adaptive message block switching", with the goal of providing a fault-tolerant, efficient routing method for telecommunication messages as part of a research program at the RAND Corporation, funded by the United States Department of Defense. His ideas contradicted then-established principles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |