|
Yodong Fortress
Xiangping ( zh, иҘ„е№і) is a historical name of Liaoyang, Liaoning province. Xiangping was first mentioned in history as the capital of the Liaodong Commandery in the state of Yan, and the eastern terminus of the Great Wall of Yan established in 284 BC. After the unification of China by the Qin dynasty, Xiangping became the political and cultural center of what is now Northeastern China. From the 4th century onward, Xiangping was successively ruled by the Former Yan and Later Yan. The city was taken by Goguryeo in AD 404 and renamed to Liaodong/Yodong (йҒјжқұ) City. It saw several major battles during the GoguryeoвҖ“Sui War and GoguryeoвҖ“Tang Wars before eventually falling to the Tang dynasty. Warring States Before the Yan conquest, the area was inhabited by the Donghu people, Shanrong, and Gija Joseon. In 300 BC, the Yan general Qin Kai established Liaodong Commandery, with Xiangping as its capital. The Yan subsequently constructed its Great Wall, and Xiangping was the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoyang
Liaoyang () is a prefecture-level city of east-central Liaoning province, China, situated on the Taizi River. It is approximately one hour south of Shenyang, the provincial capital, by car. Liaoyang is home to Liaoning University's College of Foreign Studies and a number of vocational colleges. The city hosts a limited number of professional basketball and volleyball games in a modern sports facility. According to the latest statistics in 2020, the age distribution of the population in Liaoyang is as follows: 0-14 years old account for 9.83% of the population; 15-59 years old account for 62.26% of the population; 60 years old and above account for 27.91% of the population; 65 years old and above account for 27.91% of the population 19.46% of the population. History Liaoyang is one of the oldest continuously-inhabited cities in northeast China, dating back to before the Warring States period, and the site of the city has not changed ever since. Under the Yan state and the Qin an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Zhao Of Yan
King Zhao of Yan (, died 279 BC), ancestral name JД« (姬), clan name YДҒn (зҮ•), personal name ZhГӯ (иҒ·), was the fourth king of the state of Yan in Warring States period of Chinese history. He ruled the kingdom between 311 BC until his death in 279 BC. ZhГӯ was a son of Kuai, King of Yan. In early years, he was chosen to serve as a political hostage in the Kingdom of Han. In 314 BC, Yan was attacked and practically conquered by Qi, both Kuai and the usurper Zizhi (еӯҗд№Ӣ) were killed. However, Qi was unable to put down the rebellion in Yan area and had to withdraw. Finally, the Yan Kingdom was restored. ZhГӯ was installed as the new king by King Wuling of Zhao, and sent back to Yan. King Zhao was judicious and measured in his actions toward his subordinates. He hired talents with high salary, these talents include: Yue Yi from Wei, Zou Yan (й„’иЎҚ) from Qi, and Ju Xin (еҠҮиҫӣ) from Zhao. Yan became a powerful kingdom and was able to take revenge on Qi. In 284, he plo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongsun Yuan
Gongsun Yuan () (died September 238Cao Rui's biography in ''Sanguozhi'' indicated that Sima Yi laid siege to Xiangping on the ''bingyin'' day of the 8th month of the 2nd year of the ''Jing'chu'' era. However, there is no ''bingyin'' day in that month; the next ''bingyin'' day is in the 9th month of that year and corresponds to 3 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar. Volume 74 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' placed the fall of Xiangping on the ''renwu'' day of the 8th month of that year. However, there is also no ''renwu'' day in that month; the next ''renwu'' day is also in the 9th month and corresponds to 19 Sep 238 in the Julian calendar.), courtesy name Wenyi, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He rebelled against Wei in 237 and declared himself "King of Yan" (). In 238, the Cao Wei general Sima Yi led forces to Liaodong and successfully conquered Yan. Life Gongsun Yuan was a son of Gongsun Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
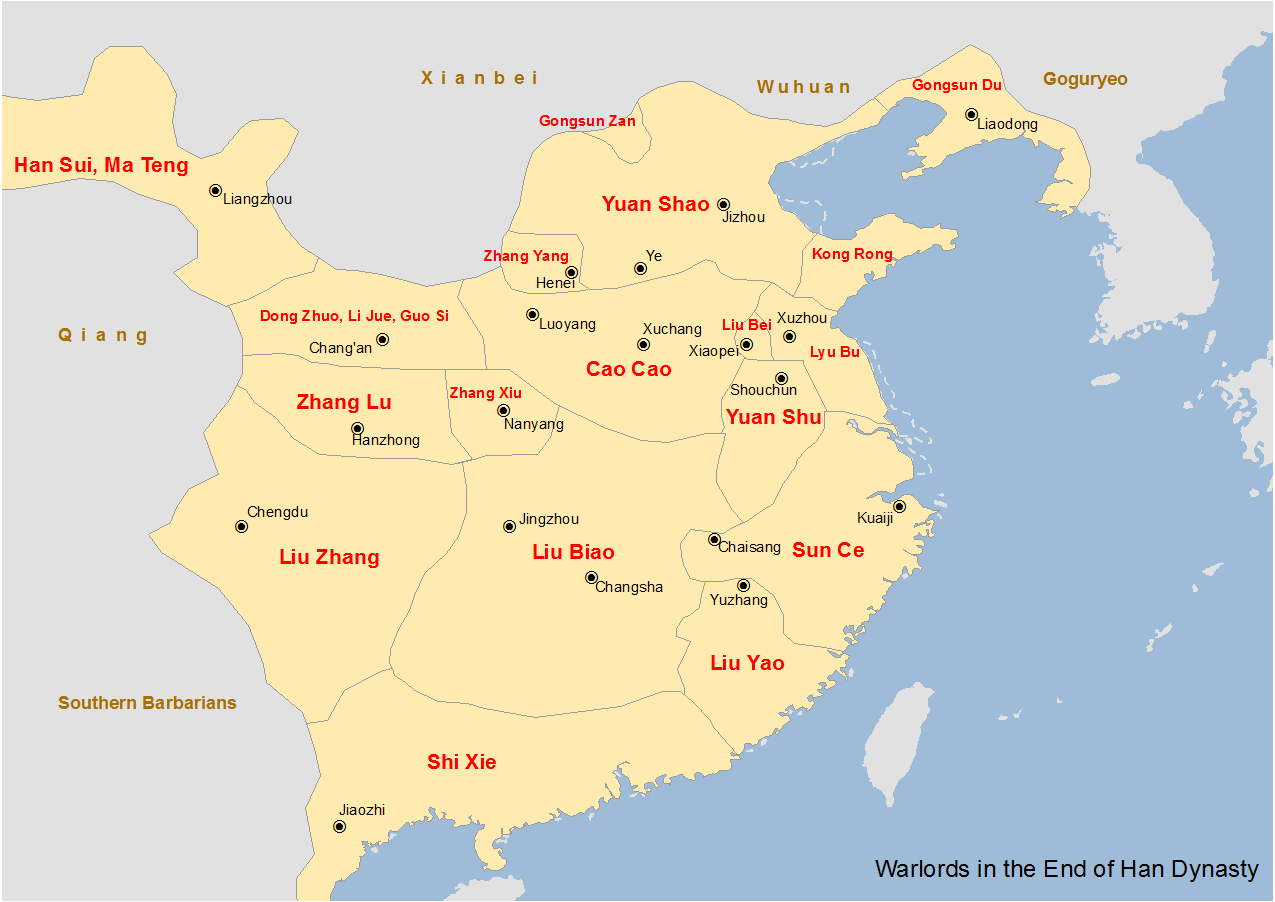
Gongsun Du
Gongsun Du () (150? вҖ“ 2049th year of the ''Jian'an'' era, per vol. 08 of ''Sanguozhi''), courtesy name Shengji, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was not able to participate in battle until Dong Zhuo seized power from Emperor Shao. Dong Zhuo, hoping to expand the empire, gave Gongsun Du the command to attack present-day Korea from across the sea. Gongsun Du was successful in his attack and also took control of the existing Daifang and Lelang commanderies established during the earlier period of the Han dynasty, among others. Under another order from Dong Zhuo, Gongsun Du took over Liaoning. This presaged the development of Gongsun Du's power base in the northeast. Gongsun Du later sent Gongsun Muo and Zhang Pi to present-day South Korea in an attempt to gain more land. He died in 204 and was succeeded by his son, Gongsun Kang, who continued to rule northeastern China. See also * Lists of peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 вҖ“ 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (еҠүеҚ”), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian fell u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buyeo
Buyeo or PuyЕҸ (Korean: л¶Җм—¬; Korean pronunciation: u.jКҢ or жү¶йӨҳ ''FГәyГә''), also rendered as Fuyu, was an ancient kingdom that was centered in northern Manchuria in modern-day northeast China. It is sometimes considered a Korean kingdom, and had ties to the Yemaek people, who are considered to be the ancestors of modern Koreans. Buyeo is a major predecessor of the Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo and Baekje. According to the ''Book of the Later Han'', Buyeo was initially placed under the jurisdiction of the Xuantu Commandery, one of Four Commanderies of Han in the later Western Han. Buyeo entered into formal diplomatic relations with the Eastern Han dynasty by the mid-1st century AD as an important ally of that empire to check the Xianbei and Goguryeo threats. Jurisdiction of Buyeo was then placed under the Liaodong Commandery of the Eastern Han. After an incapacitating Xianbei invasion in 285, Buyeo was restored with help from the Jin dynasty. This, however, marked th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Commanderies Of Han
The Four Commanderies of Han (; ) were Chinese commanderies located in the north of the Korean Peninsula and part of the Liaodong Peninsula from around the end of the second century BC through the early 4th AD, for the longest lasting. The commanderies were set up to control the populace in the former Gojoseon area as far south as the Han River, with a core area at Lelang near present-day Pyongyang by Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty in early 2nd century BC after his conquest of Wiman Joseon. As such, these commanderies are seen as Chinese colonies by some scholars. Though disputed by North Korean scholars, Western sources generally describe the Lelang Commandery as existing within the Korean peninsula, and extend the rule of the four commanderies as far south as the Han River. However, South Korean scholars assumed its administrative areas to Pyongan and Hwanghae provinces. Three of the commanderies fell or retreated westward within a few decades, but the Lelang commandery remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC вҖ“ 9 AD, 25вҖ“220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221вҖ“207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206вҖ“202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220вҖ“280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9вҖ“23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periodsвҖ”the Western Han (202 BC вҖ“ 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25вҖ“220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jГ№n (йғЎ) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jГ№n''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiГ n''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5th- to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Shihuang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259вҖ“210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wГЎng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor () of the Qin dynasty from 221 to 210 BC. His self-invented title "emperor" ( ') would continue to be borne by Chinese rulers for the next two millennia. Historically, he was often portrayed as a tyrannical ruler and strict Legalist, in part from the Han dynasty's scathing assessments of him. Since the mid 20th-century, scholars have begun to question this evaluation, inciting considerable discussion on the actual nature of his policies and reforms. Regardless, according to sinologist Michael Loewe "few would contest the view that the achievements of his reign have exercised a paramount influence on the whole of China's subsequent history, marking the start of an epoch that closed in 1911". Born in the Zhao state capital Handan, as Ying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
еҢҲеҘҙ
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complexвҖ”alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five Barba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
еҸІиЁҳ
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |