|
Yijing
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yi Jing'' (, ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. Originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou period (1000750), the ''I Ching'' was transformed over the course of the Warring States and early imperial periods (500200) into a cosmological text with a series of philosophical commentaries known as the " Ten Wings". After becoming part of the Five Classics in the 2nd century BC, the ''I Ching'' was the subject of scholarly commentary and the basis for divination practice for centuries across the Far East, and eventually took on an influential role in Western understanding of East Asian philosophical thought. As a divination text, the ''I Ching'' is used for a traditional Chinese form of cleromancy known as ''I Ching'' divination, in which bundles of yarrow stalks are manipulated to produce sets of six apparently random numbers r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wen Sequence
The King Wen sequence () is an arrangement of the sixty-four divination figures in 易經 Yì Jīng, the I Ching or Book of Changes. They are called ''hexagrams'' in English because each figure is composed of six 爻 yáo—broken or unbroken lines, that represent 陰 yin or 陽 yang respectively. The King Wen sequence is also known as the ''received'' or ''classical'' sequence because it is the oldest surviving arrangement of the hexagrams. Its true age and authorship are unknown. Traditionally, it is said that 周文王 Zhōu Wén Wáng (King Wen) arranged the hexagrams in this sequence while imprisoned by 商紂王 Shāng Zhòu Wáng in the 12th century BC. A different arrangement, the ''binary sequence'' named in honor of the mythic culture hero 伏羲 Fú Xī, originated in the Song Dynasty. It is believed to be the work of scholar 邵雍 Shào Yōng (1011–1077 AD). As mirrored by the 先天 Earlier Heaven and 後天 Later Heaven arrangements of the eight tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The '' Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the Three Treasures: , compassio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a way of life, Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius (551–479 BCE). Confucius considered himself a transmitter of cultural values inherited from the Xia (c. 2070–1600 BCE), Shang (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and Western Zhou dynasties (c. 1046–771 BCE). Confucianism was suppressed during the Legalist and autocratic Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE), but survived. During the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), Confucian approaches edged out the "proto-Taoist" Huang–Lao as the official ideology, while the emperors mixed both with the realist techniques of Legalism. A Confucian revival began during the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE). In the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
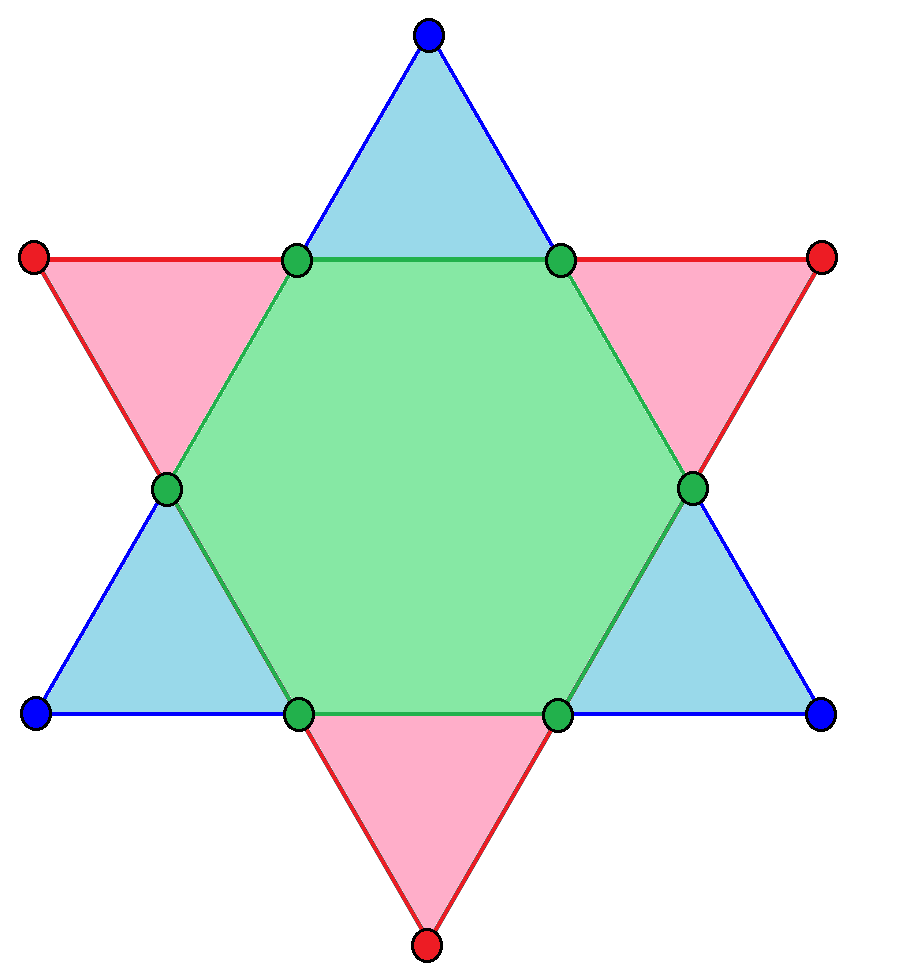
Hexagrams
, can be seen as a compound composed of an upwards (blue here) and downwards (pink) facing equilateral triangle, with their intersection as a regular hexagon (in green). A hexagram ( Greek language, Greek) or sexagram (Latin) is a six-pointed geometric star figure with the Schläfli symbol , 2, or . Since there are no true regular continuous hexagrams, the term is instead used to refer to a compound figure of two equilateral triangles. The intersection is a regular hexagon. The hexagram is part of an infinite series of shapes which are compounds of two n-dimensional simplices. In three dimensions, the analogous compound is the stellated octahedron, and in four dimensions the compound of two 5-cells is obtained. It has been historically used in religious and cultural contexts and as decorative motifs. The symbol was used as a decorative motif in medieval Christian churches and Jewish synagogues. It was first used as a mystic symbol by Muslims in the medieval period, known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guicang
''Guicang'' (歸藏, "Return to the Hidden") is a divination text dating to the Zhou dynasty, which was once used in place of the ''I Ching''. The text of ''Guicang'' was rediscovered in a rural bog in 1993; it had been lost for roughly two thousand years. ''Guicang'' contains the sixty-four hexagrams and stories relating to each of them. For example, Hexagram 54 of the ''I Ching'', "Returning Maiden", is accompanied by the story of how the maiden Chang'e stole the medicine of immortality from Xi Wangmu The Queen Mother of the West, known by various local names, is a mother goddess in Chinese religion and mythology, also worshipped in neighbouring Asian countries, and attested from ancient times. From her name alone some of her most importan ... and, upon returning home, used the hexagrams to determine that she should flee to the moon. Footnotes I Ching Taoist texts Confucian texts Chinese classic texts Chinese books of divination Chinese folk religion {{taois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rites Of Zhou
The ''Rites of Zhou'' (), originally known as "Officers of Zhou" () is a work on bureaucracy and organizational theory. It was renamed by Liu Xin to differentiate it from a chapter in the '' Book of History'' by the same name. To replace a lost work, it was included along with the '' Book of Rites'' and the '' Etiquette and Ceremonial'' becoming one of three ancient ritual texts (the "Three Rites") listed among the classics of Confucianism. In comparison with other works of its type, the Rite's ruler, though a sage, does not create the state, but merely organizes a bureaucracy. It could not have been composed during the Western Zhou, and was probably based on Warring States period societies. Michael Puett and Mark Edward Lewis compares its system of duties and ranks to the "Legalism" of Shang Yang. Authorship The book appeared in the middle of the 2nd century BC, when it was found and included in the collection of Old Texts in the library of Prince Liu De (; d. 130 BC), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo And Wooden Slips
Bamboo and wooden slips () were the main media for writing documents in China before the widespread introduction of paper during the first two centuries AD. (Silk was occasionally used, for example in the Chu Silk Manuscript, but was prohibitively expensive for most documents.) The earliest surviving examples of wood or bamboo slips date from the 5th century BC during the Warring States period. However, references in earlier texts surviving on other media make it clear that some precursor of these Warring States period bamboo slips was in use as early as the late Shang period (from about 1250 BC). Bamboo or wooden strips were the standard writing material during the Han dynasty and excavated examples have been found in abundance. Subsequently, the invention of paper by Cai Lun during the Han dynasty began to displace bamboo and wooden strips from mainstream uses, and by the 4th century AD bamboo had been largely abandoned as a medium for writing in China. The long, narrow str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai Museum
The Shanghai Museum is a museum of ancient Chinese art, situated on the People's Square in the Huangpu District of Shanghai, China. Rebuilt at its current location in 1996, it is considered one of China's first world-class modern museums and famous for its large collection of rare cultural pieces. History The museum was founded in 1952 and was first open to the public in the former Shanghai Racecourse club house, now at 325 West Nanjing Road. The founding collections came principally from three sources: a batch of artifacts gathered by the Communist 3rd Field Army during the civil war from accidental finds and confiscations of private property and brought to Shanghai upon the Communists' conquest of the city; artifacts confiscated by the customs service; items sold by private collectors due to political pressure during political purges and purchased by the government. The former Shanghai Municipal Museum was also merged into the new Shanghai Museum. In the next few years, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xuan Of Zhou
__NOTOC__ King Xuan of Zhou, personal name Ji Jing, was the eleventh king of the Chinese Zhou Dynasty. Estimated dates of his reign are 827/25–782 BC. He worked to restore royal authority after the Gong He interregnum. He fought the 'Western Barbarians' (probably Xianyun) and another group on the Huai River to the southeast. In his ninth year he called a meeting of all the lords. Later he intervened militarily in succession struggles in the states of Lu, Wey and Qi. Sima Qian says "from this time on, the many lords mostly rebelled against royal commands." According to Zhang Shoujie's annotation ''Correct Meanings'' (史記正義) to Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian, quote: "周春秋云宣王殺杜伯" king Xuan is said to have killed the innocent Du Bo (D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward L
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Bronze Inscriptions
Chinese bronze inscriptions, also commonly referred to as bronze script or bronzeware script, are writing in a variety of Chinese scripts on ritual bronzes such as ''zhōng'' bells and '' dǐng'' tripodal cauldrons from the Shang dynasty (2nd millennium BC) to the Zhou dynasty (11th–3rd century BC) and even later. Early bronze inscriptions were almost always cast (that is, the writing was done with a stylus in the wet clay of the piece-mold from which the bronze was then cast), while later inscriptions were often engraved after the bronze was cast. The bronze inscriptions are one of the earliest scripts in the Chinese family of scripts, preceded by the oracle bone script. Terminology For the early Western Zhou to early Warring States period, the bulk of writing which has been unearthed has been in the form of bronze inscriptions. As a result, it is common to refer to the variety of scripts of this period as "bronze script", even though there is no single such script. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |