|
Yevpatoria
Yevpatoria ( uk, Євпаторія, Yevpatoriia; russian: Евпатория, Yevpatoriya; crh, , , gr, Ευπατορία) is a city of regional significance in Western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of History Greek settlement The first recorded settlement in the area, called ''Kerkinitis'' (), was built by Greek colonists around 500 BCE. Along with the rest of the Crimea, Kerkinitis formed part of the dominions of King Mithridates VI Eupator ( BCE), from whose nickname, ''Eupator'' "of noble father" the city's modern name derives. Khanate period From roughly the 7th through the 10th centuries, Yevpatoria was a Khazar settlement; its name in Khazar language was probably ''Güzliev'' (literally "beautiful house"). It was later subject to the Cumans ( Kipchaks), the Mongols and the Crimean Khanate. During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevpatoria Municipality
The Yevpatoria City Municipality ( uk, Євпаторійська міськрада, Romanization of Ukrainian, translit. ''Yevpatoriis'ka mis'krada'') is one of the 25 regions of the Crimea, Autonomous Republic of Crimea, a territory recognized by almost all countries as part of Ukraine but occupied by Russia as the Republic of Crimea. The region is located on the western coast of Crimea on the Black Sea's shore. Its Administrative centre, administrative center is the city of Yevpatoria. Population: Name The Yevpatoria City Municipality is also known by its two other native official names; in Russian language, Russian as ''Evpatoriyskiy gorsovet'' (), and in Crimean Tatar language, Crimean Tatar as . Colloquially, the municipality is known as "the territory governed by the Yevpatoria City Council ( uk, Євпаторійська міська рада). History The Yevpatoria City Municipality was formed on February 11, 1963 when the territory of the Yevpatoria Raion was absorbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juma-Jami Mosque
The Juma-Jami Mosque, ( uk, Мечеть Джума-Джамі, crh, Cuma Cami, russian: Мечеть Джума-Джами, tr, Cuma Han Camii) also known as the Friday Mosque, is located in Yevpatoria, Crimea. Built between 1552 and 1564, and designed by the Ottoman architect Mimar Sinan. History The Juma-Jami is the largest mosque of Crimea and was founded by Khan Devlet I Giray in 1552. The Khan commissioned Istanbul architect Mimar Sinan (1489–1588) to build the mosque. Sinan was the chief architect of the Ottoman Empire. He designed the Sinan Pasha Mosque and the Şehzade Mosque in Istanbul. Construction of the Juma-Jami Mosque was a long process. At the time, Mimar Sinan was busy with construction of the Süleymaniye Mosque, in Istanbul, which was also plagued by financial difficulties due to money being spent on a war with Ivan the Terrible. Photos File:JumaMosqueEupatoria.jpg, Main entrance to the Juma-Jami Mosque Image:Eupatoria-mosque.jpg Image:MeczetPiatkowy2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimar Sinan
Mimar Sinan ( ota, معمار سينان, translit=Mi'mâr Sinân, , ) ( 1488–1490 – 17 July 1588) also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, ("Sinan Agha (title), Agha the Grand Architect" or "Grand Sinan") was the chief Ottoman Empire, Ottoman architect ( tr, links=no, mimar) and civil engineer for sultans Suleiman the Magnificent, Selim II and Murad III. He was responsible for the construction of more than 300 major structures and other more modest projects, such as schools. His apprentices would later design the Sultan Ahmed Mosque in Istanbul and Stari Most in Mostar. The son of a stonemason, he received a technical education and became a military engineer. He rose rapidly through the ranks to become first an officer and finally a Janissary commander, with the honorific title of Sinan.Goodwin (2001), p. 87 He refined his architectural and engineering skills while on campaign with the Janissaries, becoming expert at constructing fortifications of all kinds, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Western Asia, Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the Early Middle Ages, early medieval world, commanding the western March (territory), marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965) the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Colonisation
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC. This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that it consisted of organised direction (see Oikistes) by the originating metropolis instead of the simple movement of tribes which characterized the earlier migrations. Many colonies () that were founded in this period evolved into strong city-states and became independent of their metropolis. Reasons for colonization Reasons for colonization had to do with the demographic explosion of this period, the development of the emporium, the need for a secure supply of raw materials, but also with the emerging politics of the period that drove sections of the population into exile. Population growth created a scarcity of farmland and a restriction of the ability of smallholders to farm it, which was similar in every city-state. In places with surp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalamita Bay
__NOTOC__ The Kalamita Bay (russian: Каламитский залив, uk, Каламітська затока, crh, Kalamita körfezi, Каламита корьфези), also known as Gulf of Kalamita, is a bay and a gulf in the Black Sea south of Yevpatoria, Crimea. Kalamita was likewise a name used for Inkerman. History On 18 September 1854, French and British forces landed here in pursuit of their objective of besieging and destroying the Russian naval base of Sevastopol. The sighting of the allied fleet immediately caused local Tatars to form armed bands in support of the invaders, while local Russians and Greeks fled in panic. The landing took five days and was unopposed, though several Cossack scouts observed from a distance. The beach was well-protected, by the respective navies on the seaward side, and by a saltwater lagoon to landward. Wells were dug for water, which proved however to be extremely brackish. Soldiers either drank from puddles or took wine from near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious and ruthless ruler who sought to dominate Asia Minor and the Black Sea region, waging several hard-fought but ultimately unsuccessful wars (the Mithridatic Wars) to break Roman dominion over Asia and the Hellenic world. He has been called the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus. He cultivated an immunity to poisons by regularly ingesting sub-lethal doses; this practice, now called mithridatism, is named after him. After his death he became known as Mithridates the Great. Etymology ''Mithridates'' is the Greek attestation of the Persian name ''Mihrdāt'', meaning "given by Mithra", the name of the ancient Iranian sun god. The name itself is derived from Old Iranian ''Miθra-dāta-''. Ancestry, family and ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), also known as ''Karaims'' and ''Qarays'', are an ethnicity of Turkic-speaking adherents of Karaite Judaism in Central and Eastern Europe, especially in the territory of the old Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Crimea. "Karaim" is a Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Polish and Lithuanian name for the community. Origins Turkic-speaking Karaite Jews (in the Crimean Tatar language, ''Qaraylar'') have lived in Crimea for centuries. Their origin is a matter of great controversy. Most modern scientists regard them as descendants of Karaite Jews who settled in Crimea and adopted a Kypchak language. Others view them as descendants of Khazar or Cuman, Kipchak converts to Karaite Judaism. Today, many Crimean Karaites reject ethnic Semitic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupatoria 04-14 Img16 Karaimskaya Street
Eupatoria may refer to: * Eupatoria or Yevpatoria, a city of Crimea ** the Battle of Eupatoria, 1855 * Eupatoria (Pontus), an ancient city of Pontus * ''Agrimonia eupatoria'', common agrimony {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
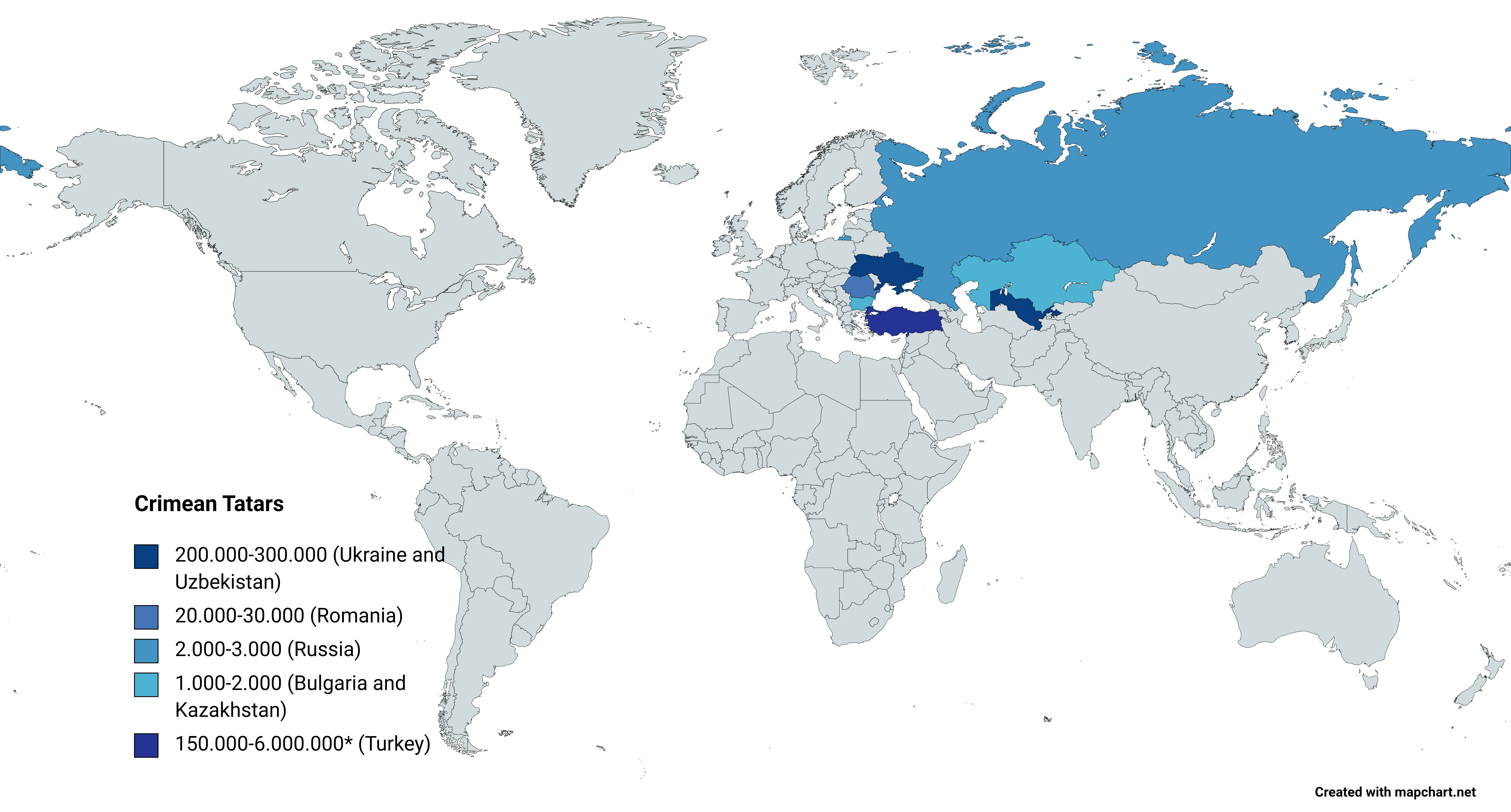
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Cumania, Desht-i-Kipchak. In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Russian Empire Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Empire, annexed the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance. Naming and geography Crimean khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of the Golden Horde and Desht-i Kipchak, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |