|
Yeovilton And District
Yeovilton is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Yeovilton and District, in Somerset, England, east of Ilchester and north of Yeovil, in South Somerset district. The parish had a population of 1,226 in the 2011 census, estimated at 1,418 in 2019. This includes Podimore (also known as Puddimore or Milton Podimore) and the hamlets of Speckington and Bridgehampton. The village includes RNAS Yeovilton (HMS Heron) and the associated Fleet Air Arm Museum. History Yeovilton is close to the route of the Fosse Way, a Roman road that linked Exeter (''Isca Dumnoniorum'') in South West England to Lincoln ('' Lindum Colonia'') in the East Midlands, via Ilchester (''Lindinis''), Bath (''Aquae Sulis''), Cirencester ('' Corinium''), Leicester (''Ratae Corieltauvorum'') and Newark-on-Trent. There is evidence of a Romano-British farmstead under what is now an airfield. Between 899 and 925, an estate in Yeovilton was granted by King Edward and between 955 and 959 King E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
River Yeo (South Somerset)
The River Yeo, also known as the River Ivel, is a tributary of the River Parrett in north Dorset and south Somerset, England. The river's names derive from the Celtic river-name ''gifl'' 'forked river'. The name Yeo appears to have been influenced by Old English ''ēa'' 'river'. The river rises in the North Dorset Downs region. It flows through the town of Sherborne and Sherborne Lake in north Dorset, and the Somerset towns of Yeovil, Yeovilton and Ilchester, to which it gives its name, and joins the River Parrett near Langport. For a few miles east of Yeovil, it forms the county boundary between Somerset and Dorset. The river is navigable for light craft for from the Parrett to Ilchester. The Yeo's tributaries include the River Gascoigne, which rises near Milborne Wick and joins the Yeo near Sherborne, the River Wriggle, Trent Brook, Hornsey Brook, the River Cam The River Cam () is the main river flowing through Cambridge in eastern England. After leaving Cambri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lindum Colonia
Lindum Colonia was the Latin name for the settlement which is now the City of Lincoln in Lincolnshire. It was founded as a Roman Legionary Fortress during the reign of the Emperor Nero (58–68 AD) or possibly later. Evidence from Roman tombstones suggests that Lincoln was first garrisoned by the Ninth Legion ''Hispana'', which probably moved from Lincoln to found the fortress at York around c. 71 AD. Lindum was then garrisoned by the Second Legion ''Adiutrix'', which then went on to Chester in 77–78 AD. Probably under the reign of Domitian and most likely after 86 AD, the fortress became a colonia, a settlement for retired soldiers sanctioned by the Emperor. The colonia now developed and a second enclosure, often referred to as the ''Lower Colonia'' was added between the ''Upper Colonia'' and the River Witham. Evidence has been uncovered for the Forum, baths, temples, buildings and shops of the colonia which was enclosed by walls. The walls of the Upper Colonia started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Brihtric
Beorhtric (meaning "magnificent ruler"; also spelled Brihtric) (died 802) was the King of Wessex from 786 to 802, succeeding Cynewulf. During his rule, however, his wife and father-in-law had most of the power. Early life The names of his parents are unknown but the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' claims that he was descended from Cerdic. In 786, Cynewulf, the King of Wessex, was killed by Cyneheard, brother of the former King Sigeberht. Cyneheard died soon after.Mike Ashley, ''The Mammoth Book of British Kings and Queens'' (New york: Carroll & Graf, 1999), p. 312 Reign Becoming king Either with help of his close ally Offa, the King of Mercia, or quickly coming under his influence, Beorhtric became King of Wessex in 786, but he had to still contend the throne with Ecgberht whom Beorhtric and Offa drove to exile. In 787, Beorhtric held the Synod of Chelsea jointly with Offa, and in 789, he married one of Offa's daughters, Eadburh. Also in 789, it was during Beorhtric's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Eadwig Of England
Eadwig (also Edwy or Eadwig All-Fair, 1 October 959) was King of England from 23 November 955 until his death in 959. He was the elder son of Edmund I and his first wife Ælfgifu, who died in 944. Eadwig and his brother Edgar were young children when their father was killed trying to rescue his seneschal from attack by an outlawed thief on 26 May 946. As Edmund's sons were too young to rule he was succeeded by his brother Eadred, who suffered from ill health and died unmarried in his early 30s. Eadwig became king in 955 aged about fifteen and was no more than twenty when he died in 959. He clashed at the beginning of his reign with Dunstan, the powerful Abbot of Glastonbury and future Archbishop of Canterbury, and exiled him to Flanders. He later came to be seen as an enemy of monasteries, but most historians think that this reputation is unfair. In 956 he issued more than sixty charters transferring land, a yearly total unmatched by any other European king before the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
_-_BL_Stowe_MS_944%2C_f_30v.jpg) |
Edward The Elder
Edward the Elder (17 July 924) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin Æthelwold, who had a strong claim to the throne as the son of Alfred's elder brother and predecessor, Æthelred I. Alfred had succeeded Æthelred as king of Wessex in 871, and almost faced defeat against the Danish Vikings until his decisive victory at the Battle of Edington in 878. After the battle, the Vikings still ruled Northumbria, East Anglia and eastern Mercia, leaving only Wessex and western Mercia under Anglo-Saxon control. In the early 880s Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians, the ruler of western Mercia, accepted Alfred's lordship and married his daughter Æthelflæd, and around 886 Alfred adopted the new title King of the Anglo-Saxons as the ruler of all Anglo-Saxons not subject to Danish rule. Edward inherited the new title w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent or Newark () is a market town and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district in Nottinghamshire, England. It is on the River Trent, and was historically a major inland port. The A1 road bypasses the town on the line of the ancient Great North Road. The town's origins are likely to be Roman, as it lies on a major Roman road, the Fosse Way. It grew up round Newark Castle and as a centre for the wool and cloth trades. In the English Civil War, it was besieged by Parliamentary forces and relieved by Royalist forces under Prince Rupert. Newark has a market place lined with many historical buildings and one of its most notable landmark is St Mary Magdalene church with its towering spire at high and the highest structure in the town. The church is the tallest church in Nottinghamshire and can be seen when entering Newark or bypassing it. History Early history The place-name Newark is first attested in the cartulary of Eynsham Abbey in Oxfordshire, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
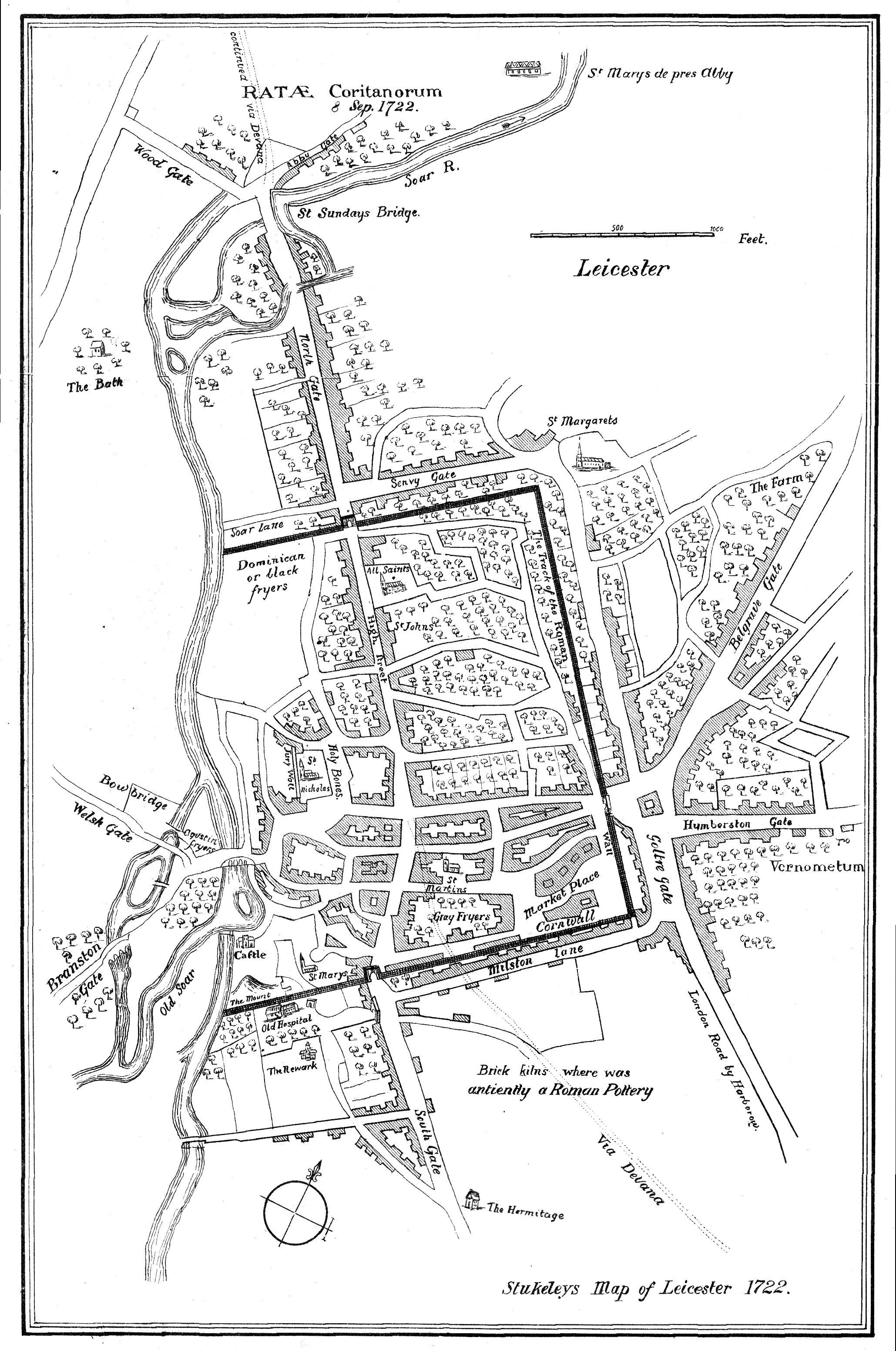 |
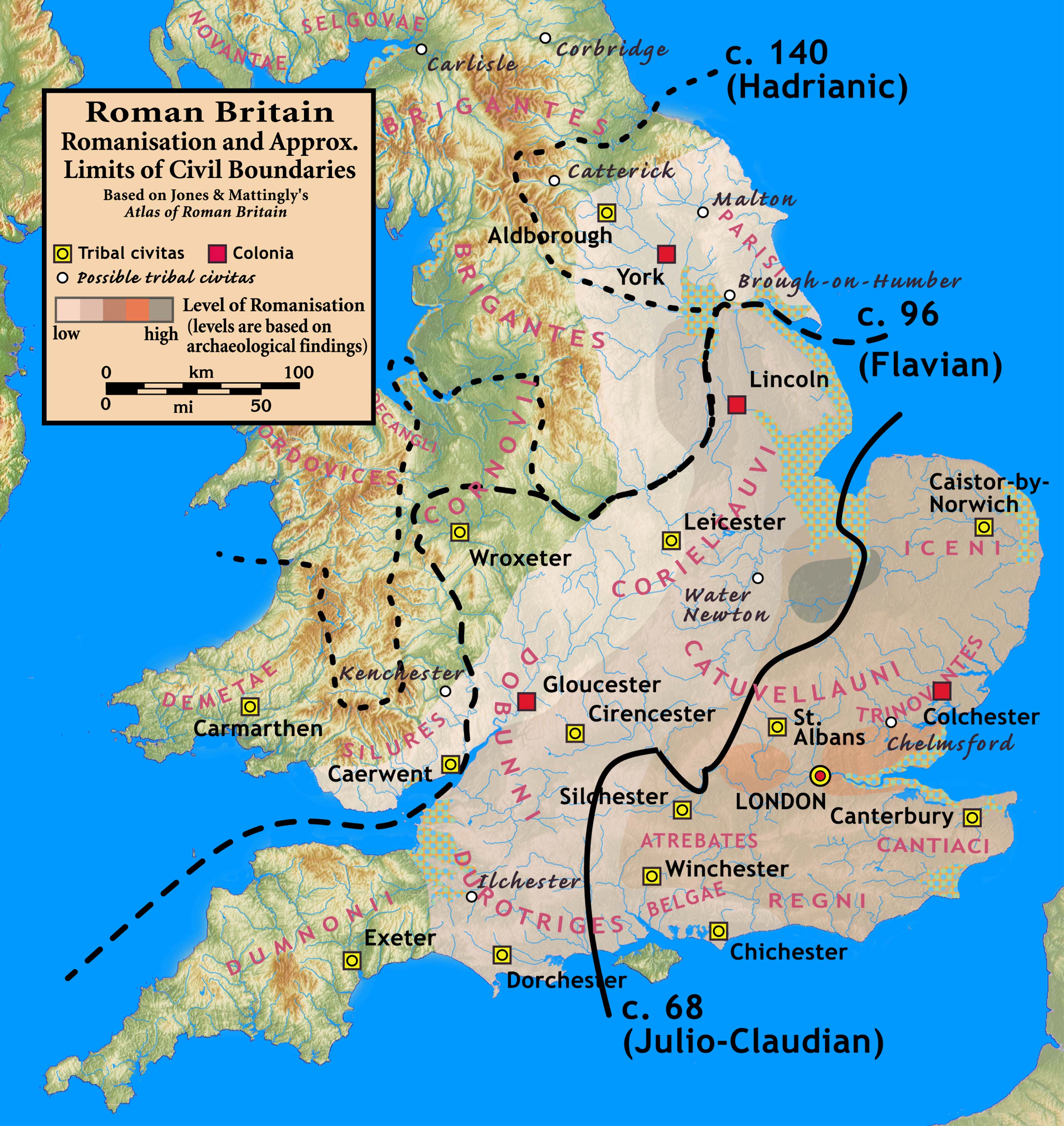
Ratae Corieltauvorum
Ratae Corieltauvorum or simply Ratae was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Leicester, located in the English county of Leicestershire. Name ''Ratae'' is a latinate form of the Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf. Gaelic '' rath''), suggesting the site was an Iron Age oppidum. This generic name was distinguished by "of the Corieltauvians", the name of the Celtic tribe whose capital it served as under the Romans. The town was mistakenly known as Ratae Coritanorum in later records. However, an inscription recovered in 1983 showed that it was corrupt and "Corieltauvorum" was the proper form of the name. History Prehistory The native settlement encountered by the Romans at the site seems to have developed in the 2nd or 1st centuries BC. This area of the Soar was split into two channels: a main stream to the east and a narrower channel on the west, with a presumably marshy island between. The settlement seems to have controlled a ford ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands. The city lies on the River Soar and close to the eastern end of the National Forest, England, National Forest. It is situated to the north-east of Birmingham and Coventry, south of Nottingham and west of Peterborough. The population size has increased by 38,800 ( 11.8%) from around 329,800 in 2011 to 368,600 in 2021 making it the most populous municipality in the East Midlands region. The associated Urban area#United Kingdom, urban area is also the 11th most populous in England and the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, 13th most populous in the United Kingdom. Leicester is at the intersection of two railway lines: the Midland Main Line and the Birmingham to London Stansted Airport line. It is also at the confluence of the M1 motorway, M1/M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Corinium Dobunnorum
Corinium Dobunnorum was the Romano-British settlement at Cirencester in the present-day English county of Gloucestershire. Its 2nd-century walls enclosed the second-largest area of a city in Roman Britain. It was the tribal capital of the Dobunni and is usually thought to have been the capital of the Diocletian-era province of First Britain (''Britannia I'' ). Roman fort A Roman fort was established at Corinium in the territory of the friendly tribe of the Dobunni about a year after the Roman conquest of Britain. The main settlement in the area at the time was the hillfort at Bagendon. Three main Roman roads met in Corinium: the Fosse Way, Akeman Street, and Ermin Street. Tribal capital By the mid-70s CE, the military had abandoned the fort and the site became the tribal capital (''civitas'') of the Dobunni. Over the next twenty years, a street grid was laid out and the town was furnished with an array of large public stone buildings, two market places, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cirencester
Cirencester (, ; see below for more variations) is a market town in Gloucestershire, England, west of London. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames, and is the largest town in the Cotswolds. It is the home of the Royal Agricultural University, the oldest agricultural college in the English-speaking world, founded in 1840. The town had a population of 20,229 in 2021. The Roman name for the town was Corinium, which is thought to have been associated with the ancient British tribe of the '' Dobunni'', having the same root word as the River Churn. The earliest known reference to the town was by Ptolemy in AD 150. The town's Corinium Museum has an extensive Roman collection. Cirencester is twinned with the town of Itzehoe, in the Steinburg region of Germany. Local geography Cirencester lies on the lower dip slopes of the Cotswold Hills, an outcrop of oolitic limestone. Natural drainage is into the River Churn, which flows roughly north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Aquae Sulis
Aquae Sulis (Latin for ''Waters of Sulis'') was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is the English city of Bath, Somerset. The Antonine Itinerary register of Roman roads lists the town as ''Aquis Sulis.'' Ptolemy records the town as ''Aquae calidae'' (warm waters) in his 2nd-century work ''Geographia''. Development Baths and temple complex The Romans probably began building a formal temple complex at Aquae Sulis in the AD 60s. The Romans had probably arrived in the area shortly after their arrival in Britain in AD 43 and there is evidence that their military road, the Fosse Way, crossed the river Avon at Bath. An early Roman military presence has been found just to the North-East of the bath complex in the Walcot area of modern Bath. Not far from the crossing point of their road, they would have been attracted by the large natural hot spring which had been a shrine of the Celtic Brythons, dedicated to their goddess Sulis. This spring is a natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |