|
Yellow Bear
Yellow Bear, ''Mato Ǧí'' ( 1844–1913), was an Oglala Lakota leader. The first Yellow Bear The first Yellow Bear was a prominent headman among the Tapisleca Tiyóšpaye (translated as the Spleen or Melt Band), one of the major divisions of the southern Oglala Lakota. He accompanied the first Oglala delegation to Washington, D.C. in 1870. By the following year, Colonel John E. Smith rated the size of this leader's village at about 40 lodges, one of the largest family groups within the Tapisleca Band. Yellow Bear was murdered in 1872 near Fort Laramie during a fight with the controversial white trader John Richard Jr. As the Lakota reservations were being established following the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868, the majority of the Tapisleca gave up their buffalo hunting way of life and settled at the Red Cloud Agency. By 1874, leadership of Yellow Bear's band appears to have passed to his younger brother, Black Hawk. At about this same time, another Oglala named Yellow Bear began t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oglala Lakota
The Oglala (pronounced , meaning "to scatter one's own" in Lakota language) are one of the seven subtribes of the Lakota people who, along with the Dakota people, Dakota, make up the Sioux, Očhéthi Šakówiŋ (Seven Council Fires). A majority of the Oglala live on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, the eighth-largest Indian reservation, Native American reservation in the United States. The Oglala are a List of federally recognized tribes, federally recognized tribe whose official title is the Oglala Sioux Tribe (previously called the Oglala Sioux Tribe of the Pine Ridge Reservation, South Dakota). However, many Oglala reject the term "Sioux" due to the hypothesis (among Sioux#Names, other possible theories) that its origin may be a derogatory word meaning "snake" in Ojibwe language, the language of the Ojibwe, who were among the historical enemies of the Lakota. They are also known as Oglála Lakhóta Oyáte. History Oglala elders relate stories about the orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Cheyenne
The Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation ( chy, Tsėhéstáno; formerly named the Tongue River) is the federally recognized Northern Cheyenne tribe. Located in southeastern Montana, the reservation is approximately in size and home to approximately 5,000 Cheyenne people. The tribal and government headquarters are located in Lame Deer, also the home of the annual Northern Cheyenne pow wow. The reservation is bounded on the east by the Tongue River and on the west by the Crow Reservation. There are small parcels of non-contiguous off-reservation trust lands in Meade County, South Dakota, northeast of the city of Sturgis. Its timbered ridges that extend into northwestern South Dakota are part of Custer National Forest and it is approximately east of the site of the 1876 Battle of the Little Bighorn. According to tribal enrollment figures as of March 2013, there were approximately 10,050 enrolled tribal members, of which about 4,939 were residing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1913 Deaths
Events January * January 5 – First Balkan War: Battle of Lemnos – Greek admiral Pavlos Kountouriotis forces the Turkish fleet to retreat to its base within the Dardanelles, from which it will not venture for the rest of the war. * January 13 – Edward Carson founds the (first) Ulster Volunteer Force, by unifying several existing loyalist militias to resist home rule for Ireland. * January 23 – 1913 Ottoman coup d'état: Ismail Enver comes to power. * January – Stalin (whose first article using this name is published this month) travels to Vienna to carry out research. Until he leaves on February 16 the city is home simultaneously to him, Hitler, Trotsky and Tito alongside Berg, Freud and Jung and Ludwig and Paul Wittgenstein. February * February 1 – New York City's Grand Central Terminal, having been rebuilt, reopens as the world's largest railroad station. * February 3 – The 16th Amendment to the United States Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1844 Births
In the Philippines, it was the only leap year with 365 days, as December 31 was skipped when 1845 began after December 30. Events January–March * January 15 – The University of Notre Dame, based in the city of the same name, receives its charter from Indiana. * February 27 – The Dominican Republic gains independence from Haiti. * February 28 – A gun on the USS ''Princeton'' explodes while the boat is on a Potomac River cruise, killing two United States Cabinet members and several others. * March 8 ** King Oscar I ascends to the throne of Sweden–Norway upon the death of his father, Charles XIV/III John. ** The Althing, the parliament of Iceland, is reopened after 45 years of closure. * March 9 – Giuseppe Verdi's opera ''Ernani'' debuts at Teatro La Fenice, Venice. * March 12 – The Columbus and Xenia Railroad, the first railroad planned to be built in Ohio, is chartered. * March 13 – The dictator Carlos Antonio López becomes first President of Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen, South Dakota
Allen (Lakota: ''Wagmíza Wakpála''; "corn creek") is a census-designated place on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in Bennett County, South Dakota, United States, that was named for the Allen Township (civil township), which it encompasses. As of the 2020 census, the CDP had a population of 460. It is one of two places which are closest to the North American continental pole of inaccessibility. History The CDP is named for the Allen Township, which in turn was named for Charles W. Allen, the town's first merchant. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , all land. Allen has been assigned the ZIP code 57714 throughout the CDP. In North America, the continental pole of inaccessibility is between Kyle and Allen, located from the nearest coastline at . Demographics 2020 As of the census of 2020. there were 460 people and 84 households in the CDP. The population density was . There were 87 housing units (84 occupied) at an avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford Hayes
Rutherford may refer to: Places Australia * Rutherford, New South Wales, a suburb of Maitland * Rutherford (Parish), New South Wales, a civil parish of Yungnulgra County Canada * Mount Rutherford, Jasper National Park * Rutherford, Edmonton, neighbourhood * Rutherford House, in Edmonton, Alberta * Rutherford Library, University of Alberta United Kingdom * Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Oxfordshire United States * Rutherford, California, in Napa County * East Rutherford, New Jersey * Rutherford, New Jersey * Rutherford, Pennsylvania * Rutherford, Virginia * Rutherford, West Virginia * Rutherford County, North Carolina * Rutherford County, Tennessee People * Rutherford (name), people with the surname or given name ** Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937), 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, known as the father of nuclear physics ** Rutherford B. Hayes (1822–1893), 19th president of the United States (1877–1881) Fiction * Rutherford the Brave, a character from Gamehen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
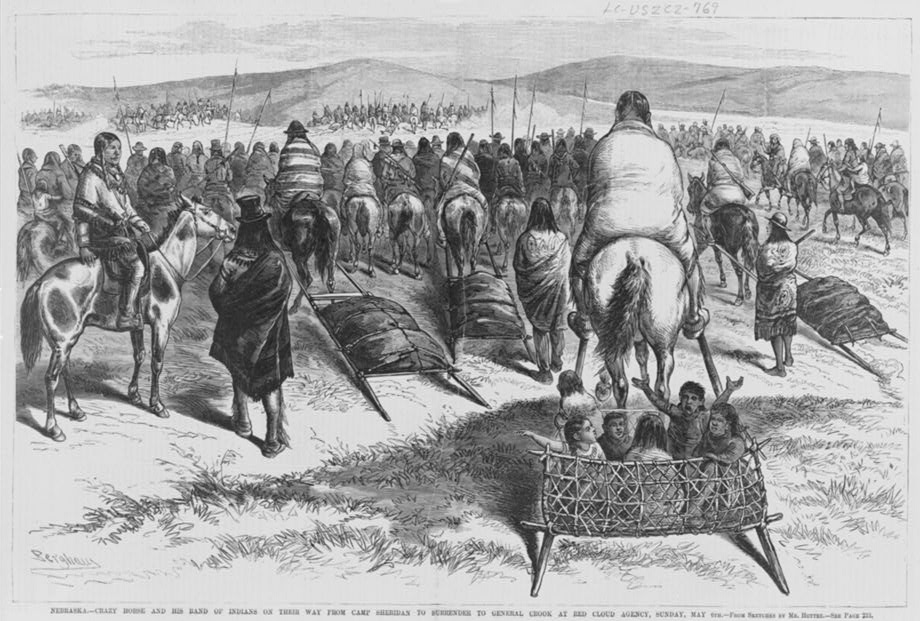
Red Cloud
Red Cloud ( lkt, Maȟpíya Lúta, italic=no) (born 1822 – December 10, 1909) was a leader of the Oglala Lakota from 1868 to 1909. He was one of the most capable Native American opponents whom the United States Army faced in the western territories. He defeated the United States during Red Cloud's War, which was a fight over control of the Powder River Country in northeastern Wyoming and southern Montana. The largest action of the war was the Fetterman Fight, with 81 US soldiers killed; it was the worst military defeat suffered by the US Army on the Great Plains until the Battle of the Little Bighorn 10 years later. After signing the Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868), Red Cloud led his people in the transition to reservation life. Some of his opponents mistakenly thought of him as the overall leader of the Sioux groups (Dakota, Lakota, and Nakota), but the large tribe had several major divisions and was highly decentralized. Bands among the Oglala and other divisions operated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crazy Horse
Crazy Horse ( lkt, Tȟašúŋke Witkó, italic=no, , ; 1840 – September 5, 1877) was a Lakota war leader of the Oglala band in the 19th century. He took up arms against the United States federal government to fight against encroachment by white American settlers on Native American territory and to preserve the traditional way of life of the Lakota people. His participation in several famous battles of the Black Hills War on the northern Great Plains, among them the Fetterman Fight in 1866, in which he acted as a decoy, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876, in which he led a war party to victory, earned him great respect from both his enemies and his own people. In September 1877, four months after surrendering to U.S. troops under General George Crook, Crazy Horse was fatally wounded by a bayonet-wielding military guard while allegedly resisting imprisonment at Camp Robinson in present-day Nebraska. He was honored by the U.S. Postal Service in 1982 with a 13¢ Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dull Knife Fight
The Dull Knife Fight, or the Battle on the Red Fork, part of the Great Sioux War of 1876, was a battle that was fought on November 25, 1876, in present-day Johnson County, Wyoming between soldiers and scouts of the United States Army and warriors of the Northern Cheyenne. The battle essentially ended the Northern Cheyennes' ability to continue the fight for their freedom on the Great Plains. Background After soldiers from Fort Fetterman in Wyoming Territory under Brigadier General George Crook fought the Northern Cheyenne at the Battle of Powder River, on March 17, 1876, the Battle of Prairie Dog Creek on June 9, 1876, the Battle of the Rosebud on June 17, 1876, and the Battle of Slim Buttes on September 9–10, 1876, General Crook received reinforcements at his Goose Creek, Wyoming supply base and began to move up the old Bozeman Trail towards Crazy Horse. After learning of a village of Cheyennes in October, 1876, Crook sent Colonel Ranald S. Mackenzie into the Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Crook
George R. Crook (September 8, 1828 – March 21, 1890) was a career United States Army officer, most noted for his distinguished service during the American Civil War and the Indian Wars. During the 1880s, the Apache nicknamed Crook ''Nantan Lupan'', which means "Grey Wolf." Early life and military career Crook was born to Thomas and Elizabeth Matthews Crook on a farm near Taylorsville, Ohio. Nominated to the United States Military Academy by Congressman Robert Schenck, he graduated in 1852, ranking near the bottom of his class. He was assigned to the 4th U.S. infantry as brevet second lieutenant, serving in California, 1852–61. He served in Oregon and northern California, alternately protecting or fighting against several Native American tribes. He commanded the Pitt River Expedition of 1857 and, in one of several engagements, was severely wounded by an Indian arrow. He established a fort in Northeast California that was later named in his honor; and later, Fort Ter-W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
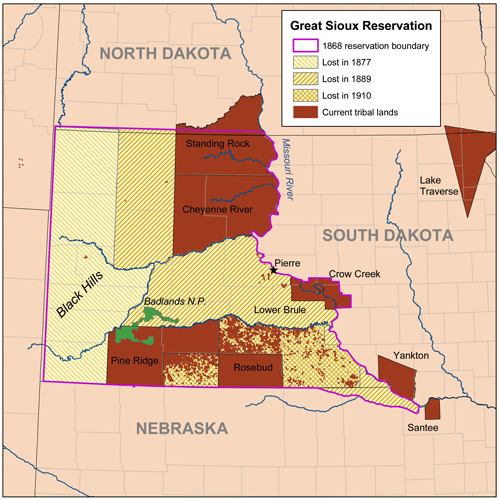
South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota people, Dakota Sioux Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population with nine Indian reservation, reservations currently in the state and have historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, seventeenth largest by area, but the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 5th least populous, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, 5th least densely populated of the List of U.S. states, 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. They are the 39th and 40th states admitted to the union; Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sioux War Of 1876-77
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the desire of the US government to obtain ownership of the Black Hills. Gold had been discovered in the Black Hills, settlers began to encroach onto Native American lands, and the Sioux and the Cheyenne refused to cede ownership. Traditionally, American military and historians place the Lakota at the center of the story, especially because of their numbers, but some Native Americans believe the Cheyenne were the primary target of the American campaign. Among the many battles and skirmishes of the war was the Battle of the Little Bighorn; often known as Custer's Last Stand, it is the most storied of the many encounters between the US Army and mounted Plains Indians. Despite the Indian victory, the Americans leveraged national resources to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)