|
Yellow-billed Babbler
The yellow-billed babbler (''Argya affinis'') is a member of the family Leiothrichidae endemic to southern India and Sri Lanka. The yellow-billed babbler is a common resident breeding bird in Sri Lanka and southern India. Its habitat is scrub, cultivation and garden land. This species, like most babblers, is not migratory, and has short rounded wings and a weak flight and is usually seen calling and foraging in groups. It is often mistaken for the jungle babbler, whose range overlaps in parts of southern India, although it has a distinctive call and tends to be found in more vegetated habitats. Its name is also confused with ''Turdoides leucocephala'', which is also known as white-headed babbler. Taxonomy The yellow-billed babbler was formerly placed in the genus ''Turdoides'' but following the publication of a comprehensive molecular phylogenetic study in 2018, it was moved to the resurrected genus ''Argya''. Description These birds have grey brown upperparts, a grey throa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, and southeast of the Arabian Sea; it is separated from the Indian subcontinent by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. Sri Lanka shares a maritime border with India and Maldives. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is its legislative capital, and Colombo is its largest city and financial centre. Sri Lanka has a population of around 22 million (2020) and is a multinational state, home to diverse cultures, languages, and ethnicities. The Sinhalese are the majority of the nation's population. The Tamils, who are a large minority group, have also played an influential role in the island's history. Other long established groups include the Moors, the Burghers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
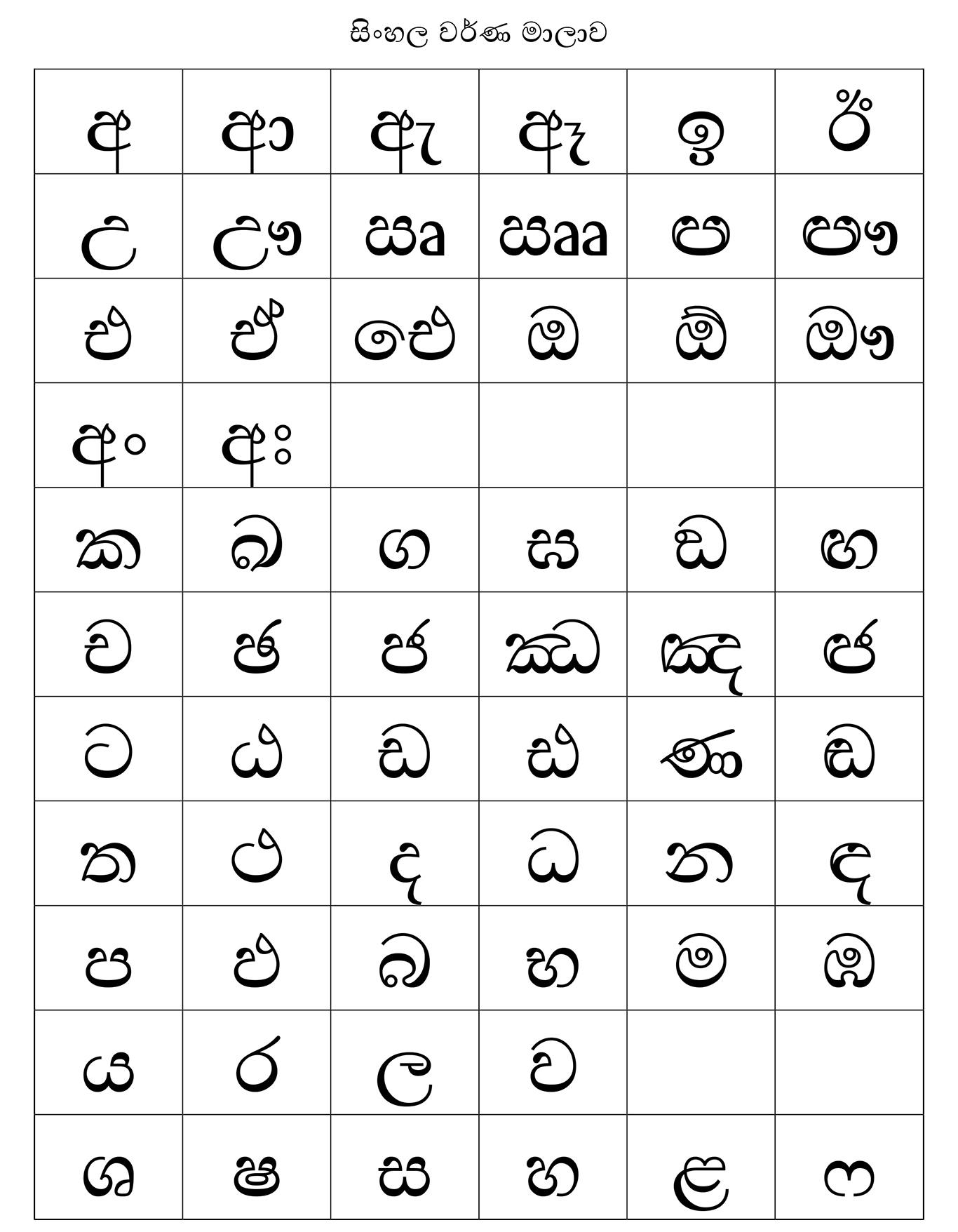
Sinhala Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada, Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptyas Mucosus
''Ptyas mucosa'', commonly known as the oriental ratsnake, Indian rat snake, ''darash'' or ''dhaman'', is a common non-venomous species of colubrid snake found in parts of South and Southeast Asia. Dhamans are large snakes. Typical mature total length is around though some exceed . The record length for this species was , second only to their cousin ''Ptyas carinata'' among living colubrid snakes.Auliya, M. (2010). ''Conservation Status and Impact of Trade on the Oriental Rat Snake Ptyas mucosa in Java, Indonesia''. TRAFFIC Southeast Asia. Despite their large size, oriental ratsnakes are usually quite slender with even a specimen of commonly measuring only around in diameter. Furthermore, the average weight of ratsnakes caught in Java was around , though larger males of over (which average mildly larger of the two sexes in the species) may easily weigh over . Their color varies from pale browns in dry regions to nearly black in moist forest areas. Rat snakes are diurnal, semi- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Coucal
The greater coucal or crow pheasant (''Centropus sinensis''), is a large non-parasitic member of the cuckoo order of birds, the Cuculiformes. A widespread resident in the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, it is divided into several subspecies, some being treated as full species. They are large, crow-like with a long tail and coppery brown wings and found in a wide range of habitats from jungle to cultivation and urban gardens. They are weak fliers, and are often seen clambering about in vegetation or walking on the ground as they forage for insects, eggs and nestlings of other birds. They have a familiar deep resonant call which is associated with omens in many parts of its range. Description This is a large species of cuckoo at 48 cm. The head is black, upper mantle and underside are black glossed with purple. The back and wings are chestnut brown. There are no pale shaft streaks on the coverts. The eyes are ruby red. Juveniles are duller black with spots on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helpers At The Nest
Helpers at the nest is a term used in behavioural ecology and evolutionary biology to describe a social structure in which juveniles and sexually mature adolescents of either one or both sexes remain in association with their parents and help them raise subsequent broods or litters, instead of dispersing and beginning to reproduce themselves. This phenomenon was first studied in birds where it occurs most frequently, but it is also known in animals from many different groups including mammals and insects. It is a simple form of co-operative breeding. The effects of helpers usually amount to a net benefit, however, benefits are not uniformly distributed by all helpers nor across all species that exhibit this behaviour. There are multiple proposed explanations for the behaviour, but its variability and broad taxonomic occurrences result in simultaneously plausible theories.Dickinson, J. L.; Hatchwell, B. J. (2004) "Fitness consequences of helping" in ''Ecology and evolution of coop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interspecific Feeding
Interspecific feeding refers to behaviour reported in wild animals, particularly birds where adults of one species feed the young of another species. This usually excludes the case of birds feeding brood parasitism, brood parasites. The behaviour has been of theoretical interest since it appears to be provide little fitness (biology), evolutionary benefit to the feeding bird. Some researchers have suggested that it is mainly male birds that are lured into feeding a fledgling that begs Such behaviour is also related to alloparenting, cross-fostering and brood adoption. Several situations have been suggested that lead to this including: # Bird raised in a mixed clutch # Original nest and brood of bird destroyed # Nests in very close proximity # Calling of young birds stimulates behaviour # Orphaned birds adopted temporarily or permanently # Male bird feeding another species while mate incubated # Feeding bird is mateless and finds a mateless bird at nest Shy (1982) listed 65 species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hawk-cuckoo
The common hawk-cuckoo (''Hierococcyx varius''), popularly known as the brainfever bird, is a medium-sized cuckoo resident in the Indian subcontinent. It bears a close resemblance to the Shikra, even in its style of flying and landing on a perch. The resemblance to hawks gives this group the generic name of hawk-cuckoo and like many other cuckoos these are brood parasites, laying their eggs in nests of babblers. During their breeding season in summer males produce loud, repetitive three note calls that are well-rendered as ''brain-fever'', the second note being longer and higher pitched. These notes rise to a crescendo before ending abruptly and repeat after a few minutes; the calling may go on through the day, well after dusk and before dawn. Description The common hawk-cuckoo is a medium- to large-sized cuckoo, about the size of a pigeon (ca. 34 cm). The plumage is ashy grey above; whitish below, cross-barred with brown. The tail is broadly barred. The sexes are alike. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pied Cuckoo
The Jacobin cuckoo (''Clamator jacobinus''), also pied cuckoo or pied crested cuckoo, is a member of the cuckoo order of birds that is found in Africa and Asia. It is partially migratory and in India, it has been considered a harbinger of the monsoon rains due to the timing of its arrival. It has been associated with a bird in Indian mythology and poetry, known as the ''chataka'' (Sanskrit: चातक) represented as a bird with a beak on its head that waits for rains to quench its thirst. Taxonomy The Jacobin cuckoo was described by the French polymath Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in his ''Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux'' in 1780. The bird was also illustrated in a hand-coloured plate engraved by François-Nicolas Martinet in the ''Planches Enluminées D'Histoire Naturelle''. This was produced under the supervision of Edme-Louis Daubenton to accompany Buffon's text. Neither the plate caption nor Buffon's description included a scientific name but in 1783 the Dutch na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Parasitism
Brood parasites are animals that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's. The evolutionary strategy relieves the parasitic parents from the investment of rearing young. This benefit comes at the cost of provoking an evolutionary arms race between parasite and host as they coevolve: many hosts have developed strong defenses against brood parasitism, such as recognizing and ejecting parasitic eggs, or abandoning parasitized nests and starting over. It is less obvious why most hosts do care for parasite nestlings, given that for example cuckoo chicks differ markedly from host chicks in size and appearance. One explanation, the mafia hypothesis, proposes that parasitic adults retaliate by destroying host nests where rejection has occurred; there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivakasi
Sivakasi () is a city and Municipal Corporation in Virudhunagar District in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. This city is known for its fireworks, firecracker, matchbox and printing industries. Sivakasi city alone meets about 90% fire cracker requirements of India. Only after Gutenberg in Germany, Sivakasi has more number of printing presses in the world. Due to its rapid industrial growth, this city is also called as ''Little Japan of India''. The industries in Sivakasi employ over 2,50,000 people with an estimated turn over of . Sivakasi was established in the 15th century during the reign of the Pandya king Harikesari Parakkirama Pandian. The town was a part of Madurai empire and had been ruled at various times by the Pandyas, Later Pandyas, Vijayanagara Empire, Madurai Nayaks, Chanda Sahib, Nawab of the Carnatic, Carnatic kingdom and the British Raj, British. A Sivakasi riots of 1899, major riot during the British Raj took place in 1899. Sivakasi has dry weather, making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_by_Dharani_Prakash.jpg)






_e_(_Zonotrichia_Capensis_).jpg)

