|
Yang Fu
Yang Fu ( 210s–230s), courtesy name Yishan, was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He previously served as a regional official in Liang Province during the late Eastern Han dynasty. In the 210s, when the warlord Ma Chao rebelled against the Han central government, occupied Liang Province by force and murdered some of the provincial officials, Yang Fu and his colleagues pretended to submit to Ma Chao. Later, they plotted a revolt against him and succeeded in forcing him out of Liang Province. During the reign of the second Wei emperor Cao Rui, Yang Fu proposed to the emperor to scale down his extravagant construction projects but the emperor ignored him. Early life Yang Fu was from Ji County (冀縣; or Jicheng 冀城), Tianshui Commandery (), which is around present-day Gangu County, Gansu. He served as a minor official in the local commandery office in his youth. Once, when the military officers in his home commandery sought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Pi
Cao Pi () ( – 29 June 226), courtesy name Zihuan, was the first emperor of the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was the second son of Cao Cao, a warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty, but the eldest son among all the children born to Cao Cao by his concubine (later wife), Lady Bian. According to some historical records, he was often in the presence of court officials in order to gain their support. He was mostly in charge of defence at the start of his career. After the defeat of Cao Cao's rival Yuan Shao at the Battle of Guandu, he took Yuan Xi's widow, Lady Zhen, as a concubine, but in 221 Lady Zhen died and Guo Nüwang became empress. On 25 November 220, Cao Pi forced Emperor Xian, the last ruler of the Eastern Han dynasty, to abdicate in his favour, after which on 11 December 220 he proclaimed himself emperor and established the state of Cao Wei. Cao Pi continued the wars against the states of Shu Han and Eastern Wu, founded by his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
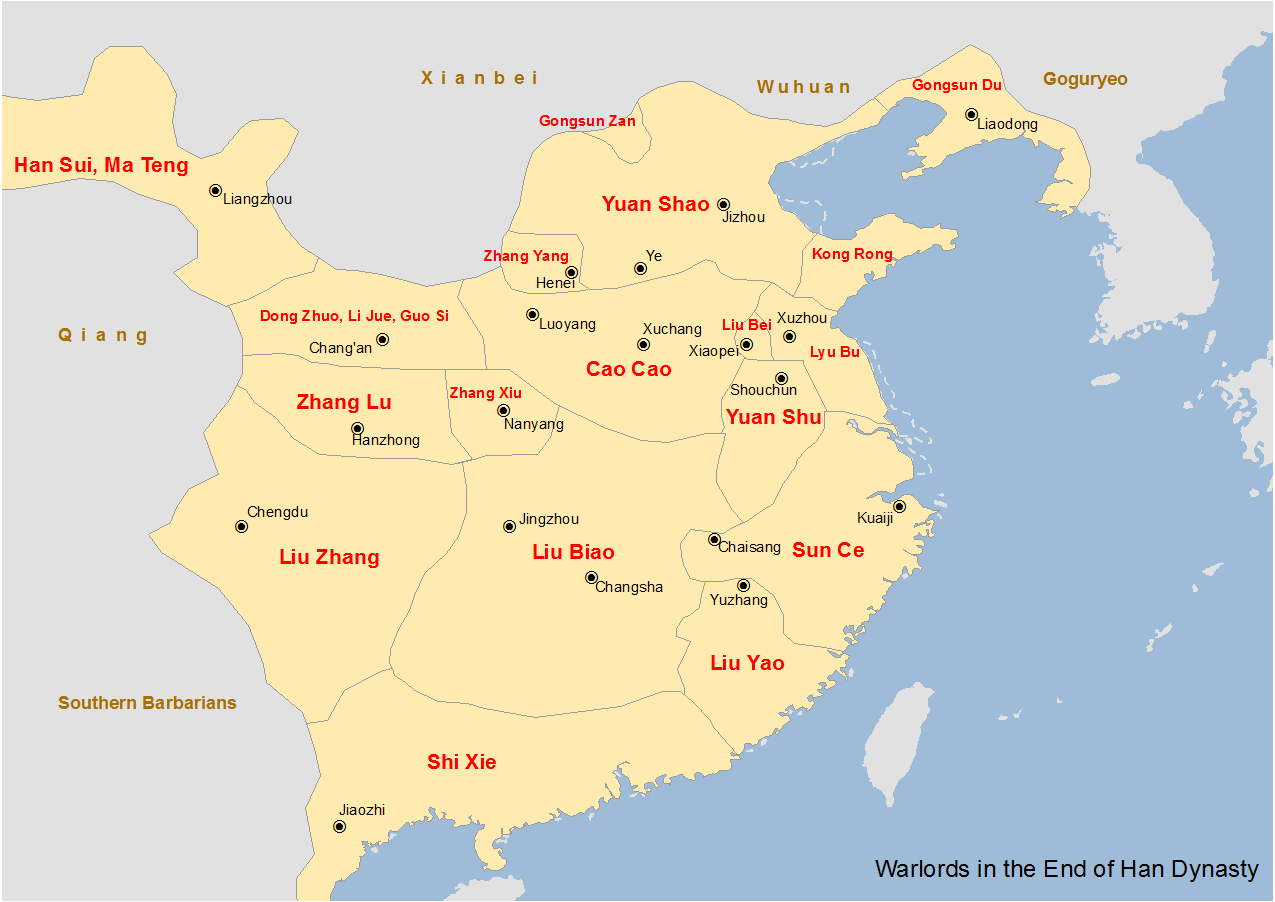
Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other. One of the most powerful warlords of his time, Yuan Shao spearheaded a coalition of warlords against Dong Zhuo, who held Emperor Xian hostage in the imperial capital, Luoyang, but failed due to internal disunity. In 200, he launched a campaign against his rival Cao Cao but was defeated at the Battle of Guandu. He died of illness two years later in Ye. His eventual failure despite his illustrious family background and geographical advantages was commonly blamed on his indecisiveness and inability to heed the advice of his advisors. Family background Yua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jicheng
The siege of Jicheng was a part of the campaign Ma Chao initiated in an attempt to retake Liang Province after the coalition of Guanxi (west of Hangu Pass) was defeated at the Battle of Tong Pass in the winter of 211 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. Background After the coalition melted down, Ma Chao took the remainder of his army towards Lantian, where he could prepare a stand against Cao Cao. Unexpectedly, Su Bo in Hejian rebelled, and Cao Cao decided to lead his main army to quell the uprising, sparing Ma Chao the time to recuperate. Thus, Ma Chao gradually regained his strength, and once again wielded great influence over local non-Han people. To resist Cao Cao, Ma Chao had recruited many Qiang and Hu soldiers, and received reinforcements from Zhang Lu of Hanzhong. He had planned to conquer all counties in Longxi (west of Long Ridges), and within a year, all cities except Jicheng (capital of Tianshui Commandery) in the area surrendered to the allied force. The siege I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west. The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as the king of the Hanzhong region after overthrowing the Qin dynasty. During the Chu-Han contention, Liu Bang shortened his title to the King of Han (), and later used it as the name of his imperial dynasty. In this way, Hanzhong was responsible for the naming of the Han dynasty, which was later hailed as the first golden age in imperial Chinese history and lends its name to the principal ethnic group in China. Hanzhong is located at the modern headwater of the Han River, the largest tributary of the Yangtze River. Hanzhong city covers and is centered around the Hantai District. The prefecture-level city consists of two urban district and nine rural counties. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,211,462, of whom 1,084,448 lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Lu (Han Dynasty)
Zhang Lu () (died 216), courtesy name Gongqi, was a Chinese politician, religious leader, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. He was the third generation Celestial Master, a Taoist religious order. He controlled a state in the Hanzhong region, which he had named Hanning () until 215, when he surrendered to Cao Cao, whom he would serve until his death one year later. Warlord of Hanzhong Upon the death of his father, Zhang Heng ( 张衡), Zhang Lu inherited control of the Celestial Masters religious group, and therefore became its third leader (the first was Zhang Lu's grandfather Zhang Daoling). The religion enjoyed its greatest popularity in Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing), but when Zhang Lu took control of the group, it was being challenged in the area by a shamanistic religion led by Zhang Xiu ( 張脩, no family relation to Zhang Lu). Against this background, both Zhang Lu and Zhang Xiu were abruptly ordered by Liu Yan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ruxu (213)
The Battle of Ruxu, also known as the Battle of Ruxukou, was fought between the warlords Cao Cao and Sun Quan in 213 during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. The battle consisted of multiple attacks led by Cao Cao, but all were eventually lifted after efforts by Sun Quan's forces. Background Before 213, Cao Cao was waging war with Ma Chao and Sun Quan following his defeat during the Battle of Red Cliffs. One of the moves that Cao Cao wanted to make in his war against Sun Quan was to intimidate Sun Quan by stationing one of his officers, Xie Qi (謝奇), at Wancheng (皖城; present-day Qianshan County, Anhui) and spread his forces to Qichun County in order to agitate Sun Quan. In order to stop Cao Cao's harassment, Sun Quan sent his general Lü Meng to demand Xie Qi surrender. Xie Qi refused, and Lü Meng attacked. Xie Qi went down easily and retreated. Two of Xie Qi's subordinates, Sun Zicai and Song Hao, surrendered to Lü Meng, boosting morale. Cao Cao then began to mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Quan
Sun Quan (, Chinese: 孫權) (183 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of the Eastern Wu dynasty, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime established by his elder brother, Sun Ce, in 200. He declared formal independence and ruled from 222 to 229 as the King of Wu and from 229 to 252 as the Emperor of Wu. Unlike his rivals Cao Cao and Liu Bei, Sun Quan was much younger than they were and governed his state mostly separate of politics and ideology. He is sometimes portrayed as neutral considering he adopted a flexible foreign policy between his two rivals with the goal of pursuing the greatest interests for the country. Sun Quan was born while his father Sun Jian served as the adjutant of Xiapi County. After Sun Jian's death in the early 190s, he and his family lived at various cities on the lower Yangtze River, until Sun Ce carved out a warlord regime in the Jiangdong region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hejian Commandery
Hejian Kingdom, also translated as Hejian Principality ( zh, 河閒國), was a kingdom in early Imperial China, located in present-day southern Hebei province. History In early Han dynasty, Hejian was part of the Zhao Kingdom. The kingdom was created in 178 BC when it was granted to Liu Piqiang (劉辟彊), son of Liu You, King You of Zhao (趙幽王) and brother of Liu Sui, King of Zhao. After Piqiang's death, the territory passed to his son Liu Fu (劉福). Fu died without an heir and the kingdom was dissolved. In 155 BC, Emperor Jing granted the title King of Hejian to Liu De (劉德), his third son. De's descendants held the title to the end of Western Han dynasty.''Book of Han'', Chapter 14. The kingdom was briefly restored under Emperor Guangwu's reign. In 90 AD, Emperor Zhang reestablished Hejian on the territories of Lecheng, Bohai and Zhuo commanderies. Liu Kai (劉開), the sixth son of the emperor, became the King of Hejian. Kai's lineage held Hejian until the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Xin
Han Xin (; 231/230–196 BC) was a Chinese military general and politician who served Liu Bang during the Chu–Han Contention and contributed greatly to the founding of the Han dynasty. Han Xin was named as one of the "Three Heroes of the early Han dynasty" ( zh, script=Hant, 漢初三傑), along with Zhang Liang and Xiao He. Han Xin is best remembered as a brilliant military leader for the strategies and tactics he employed in warfare, some of which became the origins of certain Chinese idioms, he was undefeated in battle and for his accomplishments he was considered the "God of War". In recognition of Han Xin's contributions, Liu Bang conferred the titles of " King of Qi" on him in 203 BC and "King of Chu" in the following year. However, Liu Bang feared Han Xin's growing influence and gradually reduced his authority, demoting him to "Marquis of Huaiyin" in late 202 BC. In 196 BC, Han Xin was accused of participating in a rebellion and lured into a trap and executed on Empre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ying Bu
Ying Bu (died 195 BC) was a warlord and vassal king who lived in the early Han dynasty. He was a native of Lu County (六縣; present-day Lu'an, Anhui). In his early life under the Qin dynasty, Ying Bu was convicted and sentenced to ''qing'' (黥; a form of punishment which involved branding a criminal by tattooing his face), so he was also called Qing Bu (). He was then sent to Mount Li to perform hard labour by constructing Qin Shi Huang's mausoleum. He later escaped with some men and became the leader of a bandit gang. Ying Bu participated in the insurrection against the Qin dynasty after the Dazexiang Uprising broke out in 209 BC. After the uprising failed, he became part of a rebel force led by Xiang Liang. He assisted Xiang Liang's nephew and successor Xiang Yu in overthrowing the Qin dynasty. After the fall of Qin, he initially fought on Xiang Yu's side in the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), a power struggle for supremacy over China between Xiang Yu and Liu Bang (Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anding Commandery
Anding Commandery ( zh, c=安定郡, l=Peaceful and Stable) was a historical commandery of China, located in what is now eastern Gansu and southern Ningxia. History Anding commandery was carved out of Beidi in 114 BC. Its capital was Gaoping (高平, modern Guyuan, Ningxia). In late Western Han period, the commandery administered 21 counties: Gaoping (高平), Fulei (復累), Anbi (安俾), Fuyi (撫夷), Chaona (朝那), Jingyang (涇陽), Linjing (臨涇), Lu (鹵), Wushi (烏氏), Yinmi (陰密), Anding (安定), Candu (參讀), Sanshui (三水), Yinpan (陰槃), Anwu (安武), Zuli (祖厲), Yuande (爰得), Xuanjuan (眴卷), Pengyang (彭陽), Chunyin (鶉陰) and Yuezhidao (月支道). The total population in 2 AD was 143,294 (42,725 households). The Eastern Han census in 140 AD, however, documented a popolation of only 29,060 (6,094 households), and the number of counties had reduced to 8. Due to attacks by the Qiang people, the commandery's administration was relocated to Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiang People
The Qiang people ( Qiangic: ''Rrmea''; ) are an ethnic group in China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised by the People's Republic of China, with a population of approximately 310,000 in 2000. They live mainly in a mountainous region in the northwestern part of Sichuan (Szechwan) on the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Names The modern Qiang refer to themselves as Rma ( or , , ''erma'' in Chinese or ''RRmea'' in Qiang orthography) or a dialect variant of this word. However, they did not define themselves with the Chinese term "Qiang ethnicity" ( zh, 羌族) until 1950, when they were officially designated ''Qiāngzú''. History People called " Qiang" have been mentioned in ancient Chinese texts since 3,000 years ago when they first appeared in oracle bone inscriptions. However, this term was applied to a variety of groups that might not be the same as the modern Qiang. Many of the people formerly designated as "Qiang" were gradually removed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
