|
Yage Dam
''Banisteriopsis caapi'', also known as ayahuasca, caapi, soul vine, or yagé (yage), is a South American liana of the family Malpighiaceae. It is one half of ayahuasca, a decoction with a long history of its entheogenic (connecting to spirit) use and its status as a "plant teacher" among the Indigenous peoples of the Amazon rainforest. According to ''The CRC World Dictionary of Plant Names'' by Umberto Quattrocchi, the naming of the genus '' Banisteriopsis'' was dedicated to John Banister, a 17th-century English clergyman and naturalist. An earlier name for the genus was ''Banisteria'' and the plant is sometimes referred to as ''Banisteria caapi''. Other names include ''Banisteria quitensis'', ''Banisteriopsis inebrians'', and ''Banisteriopsis quitensis''. Description Caapi is a giant vine with characteristic white or pale pink flowers which most commonly appear in January, but are known to bloom infrequently. It resembles ''Banisteriopsis membranifolia'' and '' Banisteriopsis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Spruce
Richard Spruce (10 September 1817 – 28 December 1893) was an English botanist specializing in bryology. One of the great Victorian botanical explorers, Spruce spent 15 years exploring the Amazon from the Andes to its mouth, and was one of the first Europeans to visit many of the places where he collected specimens. Spruce discovered and named a number of new plant species, and corresponded with some of the leading botanists of the nineteenth century. Early life and Career Richard Spruce was born near Ganthorpe, a small village near Castle Howard in Yorkshire. After training under his father, a local schoolmaster, Spruce began a career as a tutor and then as a mathematics master at St. Peter's School, York between 1839 and 1844. Spruce started his botanical collecting in Yorkshire about 1833. In 1834, at age 16, he drew up a neatly written list of all of the plants he had found on trips around Ganthorpe, focusing on bryophytes. Arranged alphabetically and containing 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmala Alkaloid
Several alkaloids that function as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are found in the seeds of ''Peganum harmala'' (also known as ''Harmal'' or ''Syrian Rue''), as well as tobacco leaves including harmine, harmaline, and harmalol, which are members of a group of substances with a similar chemical structure collectively known as ''harmala alkaloids''. These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. The harmala alkaloid harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring beta-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine ''Banisteriopsis caapi''. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in ''B. caapi'' and ''P. harmala''. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are both a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs). They can stimulate the central nervous system by inhibiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromodeoxyuridine
Bromodeoxyuridine (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU, BUdR, BrdUrd, broxuridine) is a synthetic nucleoside analogue with a chemical structure similar to thymidine. BrdU is commonly used to study cell proliferation in living tissues and has been studied as a radiosensitizer and diagnostic tool in people with cancer. During S phase of the cell cycle (when DNA replication occurs), BrdU can be incorporated in place of thymidine in newly synthesized DNA molecules of dividing cells. Cells that have recently performed DNA replication or DNA repair can be detected with antibodies specific for BrdU using techniques such as immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence. BrdU-labelled cells in humans can be detected up to two years after BrdU infusion. Because BrdU can replace thymidine during DNA replication, it can cause mutations, and its use is therefore potentially a health hazard. However, because it is neither radioactive nor myelotoxic at labeling concentrations, it is widely preferred f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentate Gyrus
The dentate gyrus (DG) is part of the hippocampal formation in the temporal lobe of the brain, which also includes the hippocampus and the subiculum. The dentate gyrus is part of the hippocampal trisynaptic circuit and is thought to contribute to the formation of new episodic memories, the spontaneous exploration of novel environments and other functions. It is notable as being one of a select few brain structures known to have significant rates of adult neurogenesis in many species of mammals, from rodents to primates. Other sites of adult neurogenesis include the subventricular zone, the striatum and the cerebellum. However, whether significant neurogenesis exists in the adult human dentate gyrus has been a matter of debate. 2019 evidence has shown that adult neurogenesis does take place in the subventricular zone and in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus. Structure The dentate gyrus, like the hippocampus, consists of three distinct layers: an outer molecular layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricants, to prevent oxidation, and to foods to prevent spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress. The only dietary antioxidants are vitamins A, C, and E, but the term ''antioxidant'' has also been applied to numerous other dietary compounds that only have antioxidant properties in vitro, with little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants have not been shown to maintain health or prevent disease in humans. History As part of their adaptation from marine life, terrestrial plants began producing non-marine antioxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procyanidin B2
Procyanidin B2 is a B type proanthocyanidin. Its structure is (−)-Epicatechin-(4β→8)-(−)-epicatechin. Procyanidin B2 can be found in '' Cinchona pubescens'' (Chinchona: in the rind, bark, and cortex), in ''Cinnamomum verum'' (Ceylon cinnamon: in the rind, bark, and cortex), in ''Crataegus monogyna'' (Common hawthorn: in the flower and blossom), in ''Uncaria guianensis'' (Cat's claw: in the root), in ''Vitis vinifera'' (Common grape vine: in the leaf), in ''Litchi chinensis'' (litchi: in the pericarp), in the apple, and in '' Ecdysanthera utilis''. Procyanidin B2 can be converted into procyanidin A2 by radical oxidation using 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals under neutral conditions. Procyanidin B2 has been shown to inhibit the formation of the advanced glycation end-products pentosidine, carboxymethyllysine (CML), and methylglyoxal (MGO). See also * Phenolic content in wine The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicatechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids. The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tannic juice or boiled extract of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu'' L.f). Chemistry Catechin possesses two benzene rings (called the A- and B-rings) and a dihydropyran heterocycle (the C-ring) with a hydroxyl group In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ... on carbon 3. The A-ring is similar to a resorcinol moiety while the B-ring is similar to a catechol moiety. There are two chirality (chemistry), chiral centers on the molecule on carbons 2 and 3. Therefore, it has four diastereoisomers. Two of the isomers are in trans configura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proanthocyanidins
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in many plants, such as cranberry, blueberry, and grape seeds. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More complex polyphenols, having the same polymeric building block, form the group of tannins. Proanthocyanidins were discovered in 1947 by Jacques Masquelier, who developed and patented techniques for the extraction of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from pine bark and grape seeds. Often associated with prevention of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by consuming cranberries, grape seeds or red wine, proanthocyanidins have not been conclusively shown as effective for preventing or treating UTIs. Distribution in plants Proanthocyanidins, including the lesser bioactive and bioavailable polymers (four or more catechins), represent a group of condensed flavan-3-ols, such as procyanidins, prodelphinidins and propelargonidins. They can be found in many plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychotria Viridis
''Psychotria viridis'', also known as ''chacruna'', ''chacrona'', or ''chaqruy'' in the Quechua languages, is a perennial, shrubby flowering plant in the coffee family Rubiaceae. It is a close relative of '' Psychotria carthagenensis'' (a.k.a. ''samiruka'' or ''amiruca'') of Ecuador. It is one half of ayahuasca, a decoction with a long history of its entheogenic (connecting to spirit) use and its status as a "plant teacher" among the Indigenous peoples of the Amazon rainforest. Description ''P. viridis'' is a perennial shrub that grows to a height of approximately . Its branches span a diameter of about Stems In the middle and lower parts of the stem, situated between the insertion points of the two opposite leaves there is a horizontal scar wide that extends between the leaves (or leaf scars) and sometimes also connects over the tops of these scars, and along the top side of this scar there is a dense, usually furry line of fine trichomes (i.e., plant hairs) usually long t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N,N-dimethyltryptamine
''N'',''N''-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT or ''N'',''N''-DMT, SPL026) is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including human beings, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. It is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen. DMT has a rapid onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the "business trip" during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as LSD or psilocybin mushrooms. DMT can be inhaled, ingested, or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last a short period of time: about five to 15 minutes. Effects can last three hours or more when orally ingested along with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
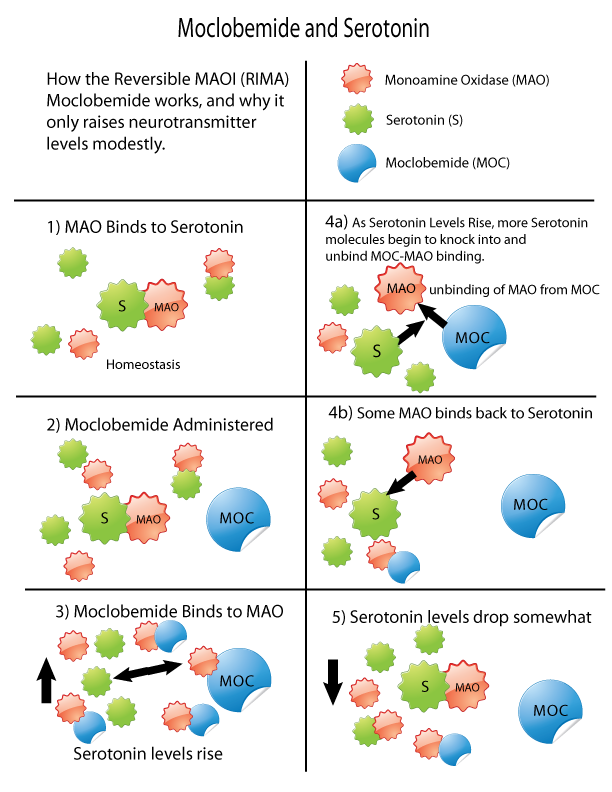
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-Carboline
β-Carboline (9''H''- pyrido ,4-''b'' ndole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline derivatives have recently been shown to have neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties. Pharmacology The pharmacological effects of specific β-carbolines are dependent on their substituents. For example, the natural β-carboline harmine has substituents on position 7 and 1. Thereby, it acts as a selective inhibitor of the DYRK1A protein kinase, a molecule necessary for neurodevelopment. It also exhibits various antidepressant-like effects in rats by interacting with serotonin receptor 2A. Furthermore, it increases levels of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in rat hippocampus. A decreased BDNF le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |