|
Xinhuang Dong Autonomous County
Xinhuang Dong Autonomous County (; usually referred to as "Xinhuang County", commonly abbreviated as Xinhuang, ) is an autonomous county of Dong people and the westernmost county of Hunan Province, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Huaihua. On the map, Xinhuang County looks like the insertion of a wedge on the eastern margin of Guizhou Province. It is the westernmost county of the province, the county is surrounded by Guizhou to the north, west and south. it is bordered to the north by Wanshan District of Tongren, to the west by Yuping, Zhenyuan and Sansui Counties, to the north by Tianzhu County, to the east by Zhijiang County. The county covers , as of 2015, it has a census registered population of 258,246 and a permanent resident population of 249,100.the population of Xinhuang County in 2015, according to the oahmhxc.com/ref> The county has nine towns and two townships under its jurisdiction, the county seat is the town of Huangzhou () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Postal Codes In China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures or prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000–009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People's Republic of China. Mail to ROC is treated as international mail, and uses postal codes set forth by Chunghwa Post. Codes starting from 999 are the internal codes use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianzhu County, Guizhou
Tianzhu County () is a county in eastern Guizhou province, China, bordering Hunan province to the north, east, and southeast. It is under the administration of the Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture (; Hmu language: ''Qeef Dongb Naif Dol Hmub Dol Gud Zid Zid Zeb''; Kam language: ''Qeens Donc Nanc Nyenc Miiul Nyenc Gaeml Zil Zl Zous''), also known as Southeast Qian Autonomous Prefecture of Miao a .... Climate References County-level divisions of Guizhou Counties of Qiandongnan Prefecture {{Guizhou-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor () of the Qin dynasty from 221 to 210 BC. His self-invented title "emperor" ( ') would continue to be borne by Chinese rulers for the next two millennia. Historically, he was often portrayed as a tyrannical ruler and strict Legalist, in part from the Han dynasty's scathing assessments of him. Since the mid 20th-century, scholars have begun to question this evaluation, inciting considerable discussion on the actual nature of his policies and reforms. Regardless, according to sinologist Michael Loewe "few would contest the view that the achievements of his reign have exercised a paramount influence on the whole of China's subsequent history, marking the start of an epoch that closed in 1911". Born in the Zhao state capital Handan, as Ying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (state)
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the Spring and Autumn period. At the end of the Warring States period it was destroyed by the Qin in 223 BCE during the Qin's wars of unification. Also known as Jing () and Jingchu (), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai ( OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as Mi ( OC: /*meʔ/). They also bore the lineage name Yan ( OC: /*qlamʔ/, /*qʰɯːm/) which would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin's wars of unification, Qin wars of conquest that saw the annexation of all other contender states, which ultimately led to the Qin (state), Qin state's victory in 221 BC as the first unified History of China#Imperial China, Chinese empire, known as the Qin dynasty. Although different scholars point toward different dates ranging from 481 BC to 403 BC as the true beginning of the Warring States, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC is the most often cited. The Warring States era also overlaps with the second half of the Eastern Zhou Period, Eastern Zhou dynasty, though the Chinese sovereign, known as the king of Zhou, ruled merely as a figurehead and served as a backdrop against the machinations of the warring states. The "Warring St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by the royal house, surnamed Ji, lasted initially from 1046 until 771 BC for a period known as the Western Zhou, and the political sphere of influence it created continued well into the Eastern Zhou period for another 500 years. The establishment date of 1046 BC is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. During the Zhou dynasty, centralized power decreased throughout the Spring and Autumn period until the Warring States period in the last two centuries of the dynasty. In the latter period, the Zhou court had little control over its constituent states that were at war with each other until the Qin state consolidated power and forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
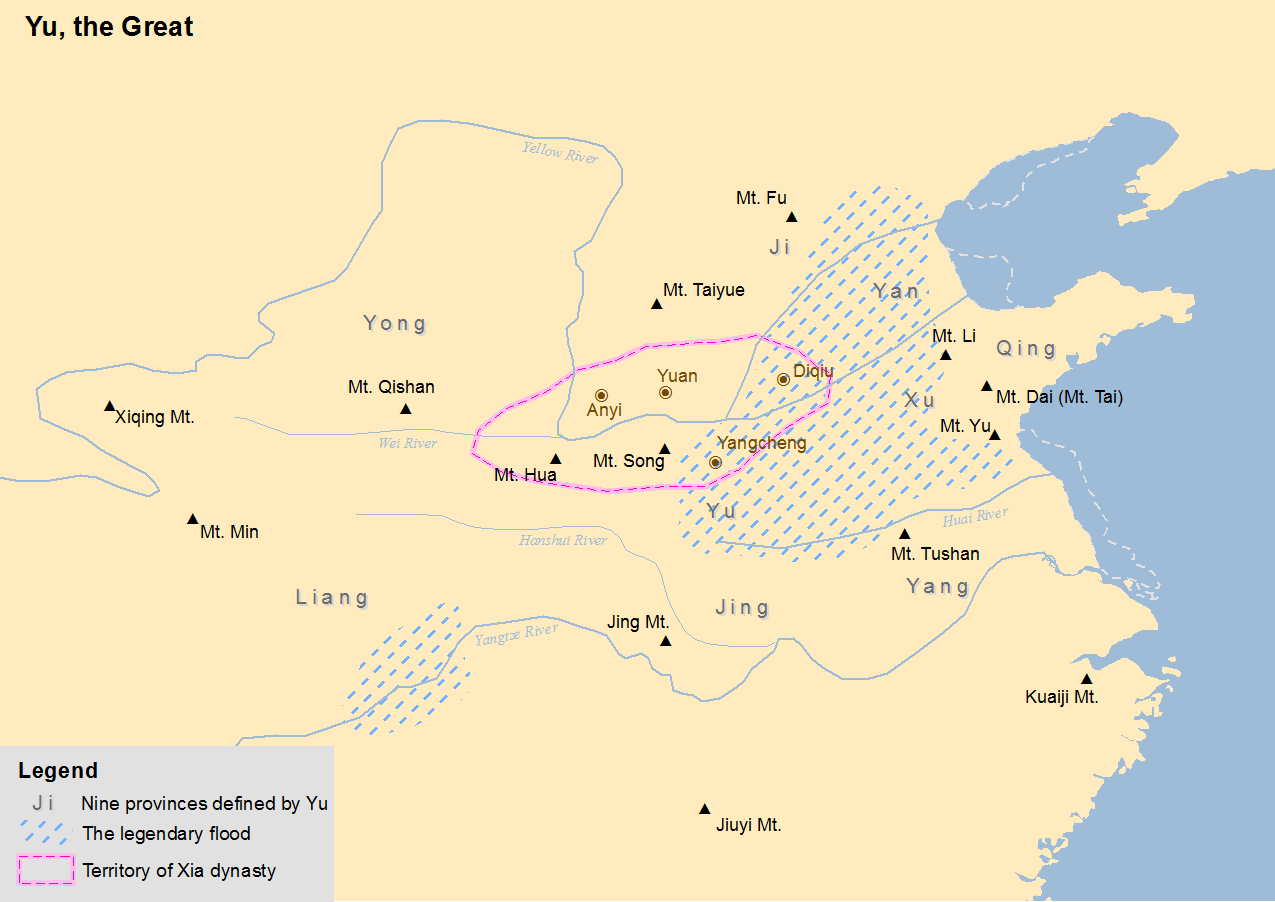
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by hominins, 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, 11,650 cal BP. The Paleolithic Age in Europe preceded the Mesolithic Age, although the date of the transition varies geographically by several thousand years. During the Paleolithic Age, hominins grouped together in small societies such as bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals. The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of knapped stone tools, although at the time humans also used wood and bone tools. Other organic commodities were adapted for use as tools, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |