|
XF-103
The Republic XF-103 was an American project to develop a powerful missile-armed interceptor aircraft capable of destroying Soviet bombers while flying at speeds as high as Mach 3. Despite a prolonged development, it never progressed past the mockup stage. Development In 1949, the USAF issued a request for an advanced supersonic interceptor to equip the Air Defense Command. Known formally as Weapon System WS-201A, but better known informally as the 1954 interceptor, it called for a supersonic aircraft with all-weather capability, powerful airborne interception radar, and air-to-air missile armament. Republic was one of six companies to submit proposals. On 2 July 1951, three of the designs were selected for further development, Convair's scaled-up XF-92 that evolved into the F-102, a Lockheed design that led to the F-104, and Republic's AP-57. AP-57 was an advanced concept to be built almost entirely of titanium and capable of Mach 3 at altitudes of at least . A full-sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1954 Interceptor
WS-201A, informally known as the 1954 Interceptor, was a United States Air Force project to develop a dedicated interceptor aircraft that would enter service in 1954. Several aircraft were developed as part of the project, leading to the F-102 Delta Dagger, F-106 Delta Dart, Republic XF-103 and, indirectly, the F-101B Voodoo and F-104 Starfighter. The electronics and weapons developed for the program would become common on US designs, including the AIM-4 Falcon missile and a variety of Hughes Aircraft-supplied radar and fire control systems. The project also led, eventually, to the upgrading of the SAGE battle control computers to directly control the interceptors for much of their flight. Although greatly delayed, the resulting systems operated for approximately 20 years, into the 1980s. Background The "1954 interceptor" concept first appeared shortly after the creation of the Air Force from the former US Army Air Force in the post-World War II era. With the re-arrangement of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kartveli
Alexander Kartveli, born Aleksandre Kartvelishvili, ( ka, ალექსანდრე ქართველიშვილი) (September 9, 1896 – July 20, 1974) was a Georgian aeronautical engineer and an aviation pioneer in the United States. Kartveli achieved important breakthroughs in military aviation in the time of turbojet fighters. (June 30, 2002). Retrieved on October 17, 2011. Education and early career Alexander Kartvelishvili was born in Tbilisi, Georgia, which was part of Russian Empire at that time; into a noble Georgian family. (Georgians call themselves "kartvelebi", and his surname derives from "Kartveli", or Georgian). He graduated from the grammar school in Tbilisi in 1914. Later on, he decided to move to France, as one of several aviation engineer aspirants of Georgian origin, such as Michael Gregor. Kartvelishvili graduated in 1922 from the Institut supérieur de l'aéronautique et de l'espace in Paris.. He began working as a test pilot but was seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIM-47 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after its cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix. Development Development for XF-108 In the early 1950s, the United States Air Force developed requirements for a high speed, high performance interceptor aircraft, originally called the LRI-X. In 1957, Hughes won the contract to supply the weapons system for this aircraft. This system consisted of the GAR-X missile and the YX-1 radar and fire control system. The original missile design had a range of 15 to 25 miles (25 to 40 km), and could be equipped with a conventional warhead or a 0.25 kiloton version of the W42 nuclear warhead. When the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Aviation
The Republic Aviation Corporation was an American aircraft manufacturer based in Farmingdale, New York, on Long Island, New York, Long Island. Originally known as the Seversky Aircraft Company, the company was responsible for the design and production of many important military aircraft, including its most famous products: World War II's Republic P-47 Thunderbolt, P-47 Thunderbolt fighter, the Republic F-84 Thunderjet, F-84 Thunderjet and Republic F-105 Thunderchief, F-105 Thunderchief jet fighters, as well as the Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II, A-10 Thunderbolt II close-support aircraft. History Seversky Aircraft The Seversky Aircraft Company was founded in 1931 by Alexander de Seversky, a Russians, Russian expatriate and veteran World War I Aviator, pilot who had lost a leg in the war. In the beginning, many of Seversky Aircraft's designers were Russian and Georgians, Georgian engineers, including Michael Gregor (aircraft engineer), Michael Gregor and Alexander Kartveli, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Aviation Company
The Republic Aviation Corporation was an American aircraft manufacturer based in Farmingdale, New York, on Long Island. Originally known as the Seversky Aircraft Company, the company was responsible for the design and production of many important military aircraft, including its most famous products: World War II's P-47 Thunderbolt fighter, the F-84 Thunderjet and F-105 Thunderchief jet fighters, as well as the A-10 Thunderbolt II close-support aircraft. History Seversky Aircraft The Seversky Aircraft Company was founded in 1931 by Alexander de Seversky, a Russian expatriate and veteran World War I pilot who had lost a leg in the war. In the beginning, many of Seversky Aircraft's designers were Russian and Georgian engineers, including Michael Gregor and Alexander Kartveli, who would go on to design many of Republic's most famous aircraft. After several failed attempts, Seversky Aircraft finally won a design competition for a new United States Army Air Corps fighter, and was aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an assisted take-off like a rocket assist to accelerate it to a speed where it begins to produce thrust. Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around and can operate up to speeds of . Ramjets can be particularly useful in applications requiring a small and simple mechanism for high-speed use, such as missiles. The US, Canada, and UK had widespread ramjet powered missile defenses during the 1960s onward, such as the CIM-10 Bomarc and Bloodhound. Weapon designers are looking to use ramjet technology in artillery shells to give added range; a 120 mm mortar shell, if assisted by a ramjet, is thought to be able to attain a range of . They have also been used successfully, though not efficiently, as tip jets on the ends of helicopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American XF-108 Rapier
The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would have cruised at speeds around with an unrefueled combat radius over , and was equipped with radar and missiles offering engagement ranges up to against bomber-sized targets. To limit development costs, the program shared engine development with the North American XB-70 Valkyrie strategic bomber program, and used a number of elements of earlier interceptor projects. The program had progressed only as far as the construction of a single wooden mockup when it was cancelled in 1959, due to a shortage of funds and the Soviets' adoption of ballistic missiles as their primary means of nuclear attack. Had it flown, the F-108 would have been the heaviest fighter of its era. Prior to the project's cancellation, U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower noted that rais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright J65
The Wright J65 was an axial-flow turbojet engine produced by Curtiss-Wright under license from Armstrong Siddeley. A development of the Sapphire, the J65 powered a number of US designs. Design and development Curtiss-Wright purchased a license for the Sapphire in 1950, with plans to have the production lines running in 1951. However a series of delays due to design changes by Curtiss-Wright, such as substituting the Sapphire's machined midsection solid forged diffuser frame with a fabricated one of welded nodular iron, led to its service introduction slipping two years. The fabricated assembly, a more practicable production job with about one fifth the cost, was subsequently adopted for the Sapphire. Another change addressed the Sapphire's only major problem. The Sapphire was found to work well through the entire RPM range without the compressor stalling, which allowed it to dispense with inlet guide vanes or other solutions found on contemporary designs. However, in service it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
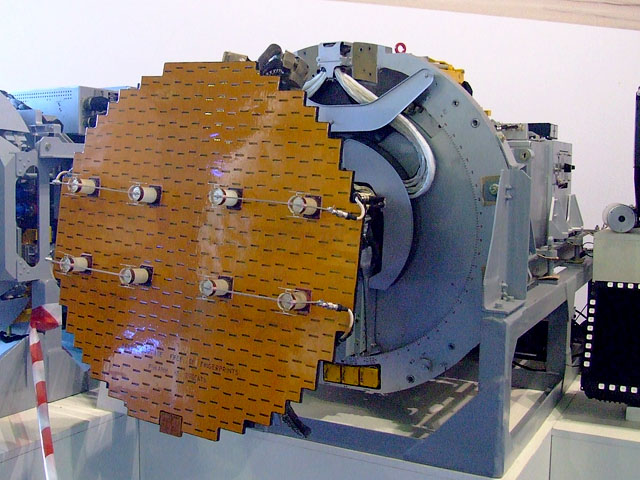
Hughes AN/ASG-18
The Hughes AN/ASG-18 Fire Control System was a prototype airborne fire control radar system for the planned North American XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft, and the Lockheed YF-12 for the United States Air Force. It was the US's first Pulse-Doppler radar, giving it look-down/shoot-down capability, and was also the first track while scan radar (could track one target at a time). This was paired with an infrared search and track (IRST) system. Range of the radar was estimated at between 200 and 300 miles (322 to 482 km), with reliable detection of bomber-sized targets at 100 miles. The installation itself was massive, weighing 2,100 lb (953 kg), and taking up most of the nose of the aircraft. The system was to be used with the Hughes AIM-47 Falcon missile, which also had a range of about 100 miles. While development work was done with the XF-108, the AN/ASG-18 and Falcon missiles were first tested on a highly modified Convair B-58 Hustler bomber. To fit the radar, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair B-58 Hustler
The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight. The B-58 was developed during the 1950s for the United States Air Force (USAF) Strategic Air Command (SAC). To achieve the high speeds desired, Convair chose a delta wing design used by contemporary fighters such as the Convair F-102. The bomber was powered by four General Electric J79 engines in underwing pods. It had no bomb bay: it carried a single nuclear weapon plus fuel in a combination bomb/fuel pod underneath the fuselage. Later, four external hardpoints were added, enabling it to carry up to five weapons. The B-58 entered service in March 1960, and flew for a decade with two SAC bomb wings: the 43rd Bombardment Wing and the 305th Bombardment Wing. It was considered difficult to fly, imposing a high workload upon its three-man crews. Designed to replace the subsonic Boeing B-47 Stratojet strategic bomber, the B-58 be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |